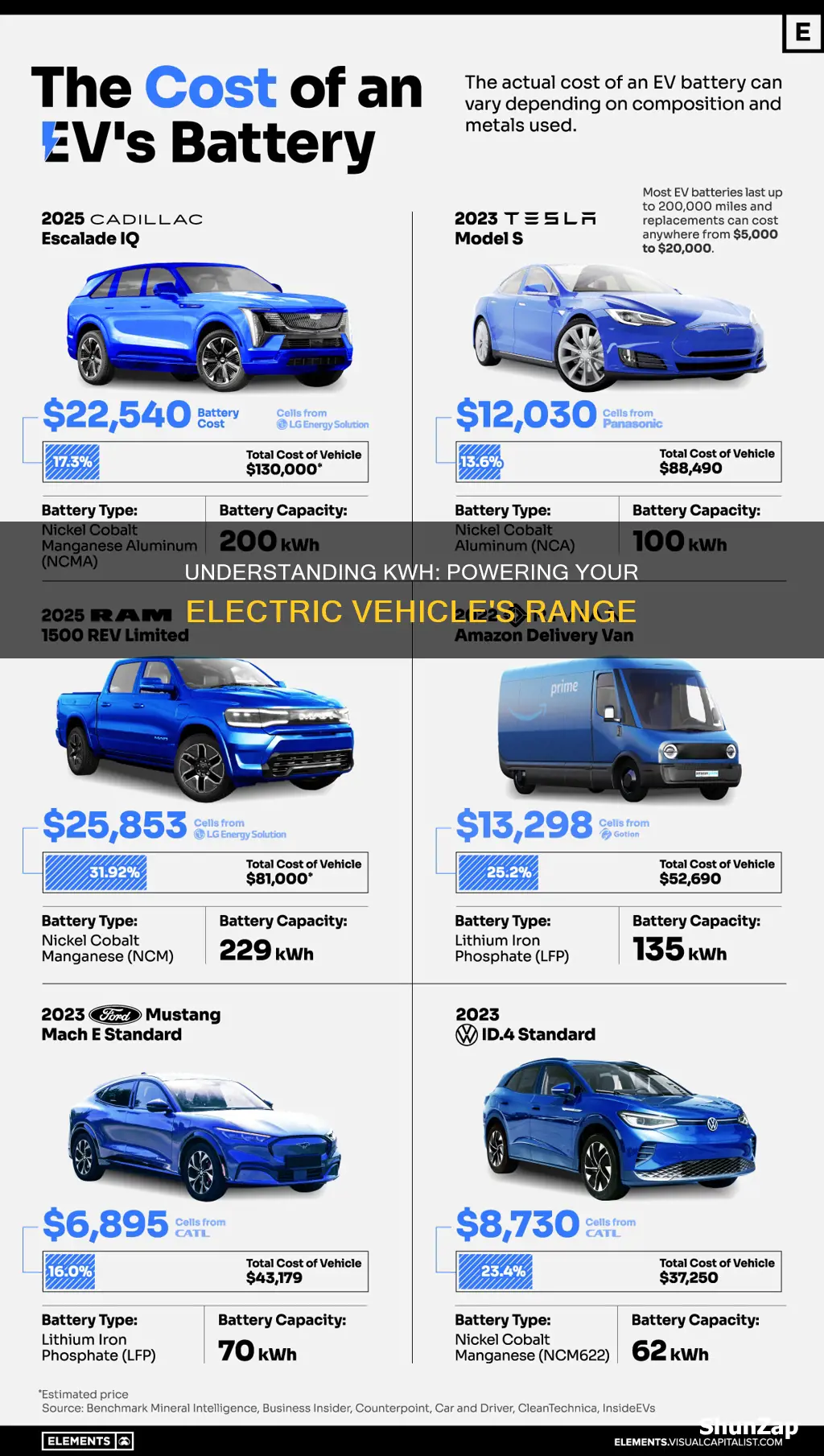
The kilowatt-hour (kWh) rating is a crucial metric for electric vehicles (EVs), indicating the battery's energy storage capacity. This measurement directly impacts an EV's range, with higher kWh values generally translating to longer driving distances on a single charge. Understanding kWh ratings is essential for EV buyers, as it influences the vehicle's performance, charging times, and overall efficiency, making it a key consideration when choosing an electric car.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Definition | The kWh (kilowatt-hour) rating is a measure of an electric vehicle's battery capacity, indicating the amount of energy the battery can store and supply to the vehicle's electric motor. |
| Unit of Measurement | Kilowatt-hours (kWh) |
| Purpose | To provide an estimate of the vehicle's range and performance, allowing consumers to compare different electric car models. |
| Range Estimation | A higher kWh rating generally means a larger battery capacity, which can result in a longer driving range before needing a recharge. |
| Efficiency | kWh rating alone doesn't determine efficiency; it's a factor alongside other specifications like motor power and vehicle weight. |
| Charging Time | Higher kWh batteries may take longer to charge fully, but this can vary based on charging infrastructure and power availability. |
| Cost | Larger kWh batteries can increase the overall cost of the vehicle, but this is offset by potential long-term savings on fuel and maintenance. |
| Real-World Performance | Actual range achieved by an EV can vary due to factors like driving habits, weather conditions, and terrain. |
| Industry Standard | kWh ratings have become a standard metric for EV manufacturers to communicate their vehicles' battery capabilities. |
| Consumer Considerations | Buyers should consider kWh rating alongside other specifications, driving needs, and local charging infrastructure. |
What You'll Learn
- Energy Consumption: kWh rating indicates the electricity used per mile, helping drivers understand efficiency
- Range Estimation: It provides a basis for estimating the vehicle's range on a full charge
- Charging Time: Higher kWh allows for faster charging, reducing wait times
- Battery Size: The rating reflects the battery capacity, impacting overall range and performance
- Performance Impact: kWh affects acceleration and overall driving experience

Energy Consumption: kWh rating indicates the electricity used per mile, helping drivers understand efficiency
The kWh (kilowatt-hour) rating is a crucial metric for electric vehicles (EVs) as it provides valuable insight into their energy efficiency. This rating represents the amount of electricity an EV consumes per mile, offering drivers a clear understanding of how efficiently their vehicle utilizes power. By measuring energy consumption in kWh per mile, manufacturers and drivers can make informed decisions about the vehicle's performance and its environmental impact.
In simpler terms, the kWh rating tells you how much electricity is required to travel one mile. For instance, if an EV has a kWh rating of 0.25, it means that for every mile driven, the vehicle consumes 0.25 kWh of electricity. This metric is essential because it allows drivers to compare the efficiency of different EVs, helping them choose the most cost-effective and environmentally friendly option. A lower kWh rating indicates better efficiency, meaning the vehicle can travel more miles with the same amount of electricity.
This rating is particularly useful for EV owners as it provides a practical way to estimate running costs. By knowing the kWh rating, drivers can calculate the cost of charging their vehicle for a specific distance. For example, if a driver wants to travel 100 miles, they can multiply the kWh rating by 100 to get the approximate electricity consumption in kWh, and then multiply it by the local electricity rate to determine the cost. This calculation empowers drivers to make informed choices about their daily commutes and long-distance travel.
Furthermore, the kWh rating is an essential factor in understanding the overall environmental impact of an EV. Lower kWh ratings contribute to reduced carbon emissions, as EVs with higher efficiency require less electricity to operate. This is especially important in regions with varying electricity sources, as some may have a higher carbon footprint. By considering the kWh rating, drivers can select vehicles that align with their sustainability goals.
In summary, the kWh rating is a vital specification for electric vehicles, offering drivers a comprehensive view of energy efficiency. It enables them to make informed decisions about vehicle choice, running costs, and environmental impact. With this rating, drivers can navigate the EV market with confidence, ensuring they select the most suitable vehicle for their needs while contributing to a more sustainable future.
Electric Vehicle Mileage Tax: Fair or Unfair for Drivers?
You may want to see also

Range Estimation: It provides a basis for estimating the vehicle's range on a full charge
The kWh (kilowatt-hour) rating is a crucial metric for electric vehicles (EVs) as it directly impacts their range and performance. This rating indicates the amount of energy an EV's battery can store, measured in kilowatt-hours. Understanding this rating is essential for drivers as it provides a basis for estimating the vehicle's range on a full charge.
When you see a kWh rating on an EV, it represents the battery's capacity. For example, a 100 kWh battery can store more energy than a 50 kWh battery. This higher capacity allows for a greater range, as the vehicle can travel further on a single charge. The kWh rating is like a fuel tank's capacity in traditional cars, but for EVs, it determines how far you can go before needing to recharge.
Range estimation is a critical aspect of EV ownership. It helps drivers plan their journeys and understand the limitations of their vehicle's battery. With the kWh rating, you can calculate an estimated range by considering various factors. These factors include the efficiency of the EV's motor, the driving conditions (such as speed and terrain), and the use of accessories like air conditioning or heating. By multiplying the kWh rating by the vehicle's efficiency, you can get an approximate range, giving drivers a realistic idea of how far they can travel.
For instance, if an EV has a 100 kWh battery and an efficiency of 0.85 kWh per mile, you can estimate its range. Multiplying 100 kWh by 0.85 kWh/mile gives you approximately 85 miles. This calculation provides a useful estimate, but it's important to remember that real-world driving conditions may vary, and factors like frequent acceleration or heavy cargo can impact the actual range.
In summary, the kWh rating is a fundamental specification for electric vehicles, offering a clear indication of their energy storage capacity. It empowers drivers to estimate their vehicle's range, enabling better trip planning and a more efficient use of the EV's battery. Understanding this rating is key to making informed decisions when choosing and using an electric vehicle.
GM's Electric Future: Unveiling Plans for a Green Revolution
You may want to see also

Charging Time: Higher kWh allows for faster charging, reducing wait times
The kWh (kilowatt-hour) rating is a crucial specification for electric vehicles (EVs) as it directly impacts charging efficiency and overall performance. When it comes to charging time, a higher kWh rating is a game-changer. This rating indicates the power output of the EV's battery, and a higher kWh value means the battery can store more energy. As a result, the vehicle can charge more quickly, making it an essential factor for those seeking to minimize their waiting time at charging stations.
In practical terms, a higher kWh-rated EV battery can accept a larger amount of energy during a charging session. This is particularly beneficial for fast-charging stations, where the goal is to replenish the battery's charge rapidly. With a higher kWh rating, the EV can take advantage of these fast-charging opportunities, reducing the time required to reach a full charge. For instance, a vehicle with a 100 kWh battery might charge to 80% in just over an hour at a high-power charging station, whereas a lower kWh-rated vehicle could take significantly longer to achieve the same level of charge.
The impact of kWh on charging speed is especially noticeable during rapid charging. When an EV's battery is nearly empty, a higher kWh rating ensures that the charging process accelerates quickly. This is because the battery can absorb a substantial amount of energy in a short time, as long as the charging infrastructure supports it. As a result, drivers can quickly top up their batteries during brief stops, ensuring they have sufficient range for their daily commutes or longer journeys.
It's important to note that while a higher kWh rating is advantageous for charging time, it also influences the overall driving range of an EV. A larger battery capacity means more stored energy, which translates to a longer driving range. However, this increased range might come at the cost of a slightly longer charging time, especially when using lower-power charging stations. Therefore, EV manufacturers often strike a balance between kWh rating, charging speed, and driving range to cater to various consumer needs.
In summary, the kWh rating is a critical consideration for electric vehicle owners, especially when it comes to charging time. A higher kWh value enables faster charging, reducing the wait times associated with topping up the battery. This feature is particularly valuable for those who frequently rely on their EVs for daily transportation or long-distance travel, ensuring they can quickly and efficiently charge their vehicles whenever needed. Understanding the kWh rating's impact on charging speed can help EV owners make informed decisions when choosing their next electric vehicle.
Affordable Electric Cars: Top Choices for Eco-Friendly Driving
You may want to see also

Battery Size: The rating reflects the battery capacity, impacting overall range and performance
The kWh (kilowatt-hour) rating is a crucial specification for electric vehicles (EVs), providing valuable insights into the battery's capacity and, consequently, the vehicle's performance. This rating directly correlates to the battery's energy storage capability, which is essential for determining the range an EV can achieve on a single charge. A higher kWh rating generally indicates a larger battery, allowing for increased energy storage and, subsequently, a longer driving range.
When considering EV models, the kWh rating is a key factor for potential buyers. It represents the amount of energy the battery can hold, measured in kilowatt-hours. For instance, a 100 kWh battery can store more energy than a 50 kWh one, enabling the vehicle to travel farther without the need for frequent recharging. This is particularly important for long-distance travel or for those who require a vehicle with extended range for their daily commute.
The impact of battery size on performance is significant. A larger battery, indicated by a higher kWh rating, contributes to improved acceleration and overall vehicle responsiveness. This is because a more substantial battery can deliver more power to the electric motor, resulting in quicker acceleration from a standstill and better performance when driving uphill or against strong headwinds. Additionally, a larger battery can provide a more consistent power output, ensuring that the vehicle maintains its performance over a longer period.
However, it's essential to note that the kWh rating is just one aspect of battery performance. Other factors, such as battery chemistry, charging speed, and overall efficiency, also play a role in determining the real-world driving experience. For instance, a battery with a high kWh rating but poor charging efficiency may not provide the expected range, while a smaller battery with advanced chemistry could offer impressive performance.
In summary, the kWh rating is a critical specification for EV buyers, as it directly influences the battery's capacity and, consequently, the vehicle's range and performance. A higher kWh rating generally translates to a longer driving range and improved acceleration, making it an essential consideration when choosing an electric vehicle. Understanding this rating and its implications empowers consumers to make informed decisions based on their specific needs and driving requirements.
Powering Your Ride: Understanding Vehicle Electrical Connectors
You may want to see also

Performance Impact: kWh affects acceleration and overall driving experience
The kWh (kilowatt-hour) rating is a crucial metric for electric vehicles (EVs) as it directly influences their performance and driving characteristics. This rating provides an indication of the vehicle's energy capacity and efficiency, which in turn impacts its acceleration, range, and overall driving experience.
A higher kWh rating generally means the EV has a larger battery pack, which can store more energy. This increased energy storage capacity translates to a more powerful and responsive driving experience. When an EV has a higher kWh rating, it can deliver a more substantial amount of energy to the electric motor, resulting in quicker acceleration. During acceleration, the vehicle's motor requires a rapid influx of energy to generate the necessary torque and power. A higher kWh rating ensures that the battery can supply this energy demand, allowing for faster and more dynamic performance.
In terms of overall driving experience, kWh plays a role in the vehicle's range and efficiency. A higher kWh rating often contributes to a longer driving range, as the larger battery pack can store more energy for the motor. This is particularly beneficial for long-distance travel, as it reduces the need for frequent charging stops. Additionally, a higher kWh rating can lead to improved efficiency, as the vehicle's motor can operate more optimally within its energy capacity. This efficiency can result in a smoother and more comfortable driving experience, especially during highway cruising or city driving.
However, it's important to note that kWh alone does not determine the performance of an EV. Other factors, such as motor power, drivetrain efficiency, and vehicle weight, also play significant roles. A higher kWh rating in conjunction with a powerful motor and efficient drivetrain can create a well-rounded and impressive driving experience. For instance, a high-kWh EV with a responsive motor can offer a thrilling acceleration experience while still maintaining a reasonable range.
In summary, the kWh rating is a critical aspect of EV performance, impacting acceleration and overall driving dynamics. A higher kWh rating generally contributes to quicker acceleration and a longer driving range, enhancing the overall driving experience. When considering an EV, understanding the kWh rating in conjunction with other performance factors will help drivers make informed decisions about their ideal vehicle for specific driving needs.
Electric Vehicles: Unlocking the Hidden Demand
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
kWh is a unit of energy used to measure the amount of electricity consumed by an appliance or vehicle. For electric vehicles, the kWh rating indicates the battery capacity, which directly affects the vehicle's range. A higher kWh rating means the battery can store more energy, allowing the car to travel further on a single charge.
The kWh rating is a crucial factor in determining the performance and efficiency of an electric vehicle. It influences the car's acceleration, top speed, and overall driving experience. A higher kWh battery can provide more power, resulting in quicker acceleration and potentially higher top speeds. However, it's essential to note that other factors, such as motor power and vehicle weight, also play a significant role in performance.
While a higher kWh rating generally contributes to increased driving range, it is not the sole determinant. The efficiency of the vehicle's motor, aerodynamics, tire resistance, and driving habits all impact the actual range. For instance, a 100 kWh battery in a lightweight, aerodynamic car might offer an impressive range, while a lower kWh battery in a heavier vehicle could still provide sufficient range due to other efficiency factors.
Estimating driving range involves considering various factors. You can use the kWh rating as a starting point and adjust based on real-world driving conditions. For example, if your vehicle has a 60 kWh battery and you know your daily commute is 50 miles, you can estimate that a full charge will cover your daily needs. However, factors like temperature, driving style, and terrain can affect range, so it's beneficial to monitor your vehicle's actual performance and adjust your expectations accordingly.







