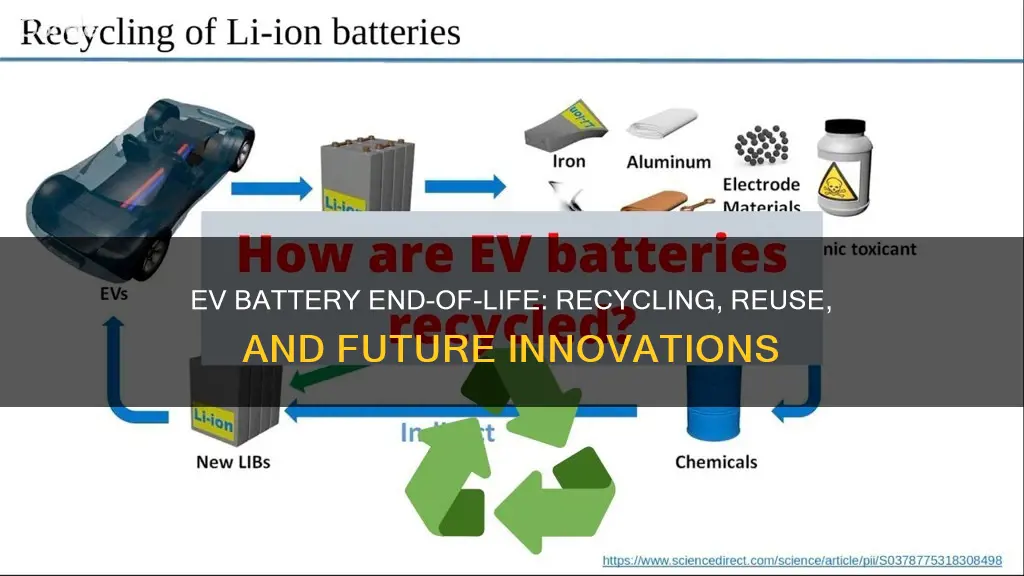
As the world shifts towards electric vehicles (EVs), it's crucial to consider the end-of-life management of their batteries. These powerful energy storage systems, typically lithium-ion, are designed to be long-lasting, but eventually, they will need to be replaced. Understanding the environmental and economic implications of battery disposal and recycling is essential for sustainable EV adoption. This paragraph will explore the various paths batteries take after their useful life, including recycling processes, potential environmental impacts, and the challenges and opportunities in managing these resources effectively.
What You'll Learn
- Battery Recycling: Reusing EV batteries to create new ones, reducing waste
- End-of-Life Management: Proper disposal methods for spent EV batteries
- Second-Life Applications: Finding new uses for retired EV batteries
- Environmental Impact: Assessing the ecological consequences of EV battery disposal
- Research and Innovation: Exploring new technologies for battery recycling and reuse

Battery Recycling: Reusing EV batteries to create new ones, reducing waste
The increasing popularity of electric vehicles (EVs) has led to a growing concern about the environmental impact of their batteries. As these vehicles age or become obsolete, the question of what happens to their batteries becomes crucial. Battery recycling is an essential process that aims to address this issue, ensuring that EV batteries are reused and their valuable materials are recovered, thereby reducing waste and promoting sustainability.
When an EV battery reaches the end of its life, it can still retain a significant amount of its original capacity. Instead of discarding these batteries, recycling processes can extract valuable metals and chemicals, which can then be used to manufacture new batteries or other products. This approach not only reduces the demand for raw materials but also minimizes the environmental impact associated with mining and extracting these resources.
The recycling process typically involves several stages. Firstly, the batteries are carefully disassembled to separate their various components. This includes removing the battery cells, which are often made of lithium-ion technology, and isolating other parts like the casing, terminals, and cooling systems. Each component is then processed differently to extract the most valuable materials. For instance, the lithium-ion cells can be shredded to recover metals like cobalt, nickel, and manganese, which are essential for new battery production.
After the initial separation, the shredded battery materials undergo further processing. This may involve chemical treatments to dissolve or separate specific compounds, allowing for the recovery of high-purity metals. These metals can then be used in the manufacturing of new EV batteries, ensuring a continuous supply of essential resources for the growing EV market. Additionally, the recycling process can also recover other valuable materials, such as copper and aluminum, which are commonly used in battery construction.
By implementing effective battery recycling practices, the EV industry can significantly reduce its environmental footprint. This approach not only minimizes the amount of waste sent to landfills but also decreases the need for environmentally damaging extraction processes. Furthermore, recycling EV batteries can contribute to a more sustainable and circular economy, where resources are reused and repurposed, creating a more efficient and environmentally friendly system. As the demand for EVs continues to rise, the importance of responsible battery disposal and recycling becomes increasingly vital for a greener future.
Electric Vehicles: Powering the Future, Yet Lacking Essential Features
You may want to see also

End-of-Life Management: Proper disposal methods for spent EV batteries
The end-of-life management of spent electric vehicle (EV) batteries is a critical aspect of sustainable EV ownership and environmental responsibility. As the demand for EVs rises, so does the need for proper disposal methods to handle their batteries at the end of their useful life. Spent EV batteries contain valuable materials and potential environmental hazards, making their responsible disposal essential.
When an EV battery reaches the end of its life, it should not be discarded with regular household waste. The most common method of disposal for spent EV batteries is recycling. Recycling centers can safely extract valuable materials like lithium, cobalt, and nickel, which can then be reused in new batteries or other products. This process helps reduce the need for mining new raw materials and minimizes the environmental impact of battery production. Many automotive manufacturers and battery producers have established recycling programs to ensure the proper handling of end-of-life batteries.
Proper disposal methods are crucial to prevent potential environmental and health risks. Spent EV batteries can contain hazardous substances, including heavy metals and toxic chemicals. If not managed correctly, these materials can leach into the environment, causing soil and water contamination. Incineration, a common method for waste disposal, can release toxic fumes if not conducted under controlled conditions. Therefore, it is essential to follow specialized recycling processes that are designed to handle the unique composition of EV batteries.
To ensure proper end-of-life management, EV owners should contact their vehicle manufacturers or authorized service centers to inquire about battery recycling options. Many manufacturers offer take-back programs, where they collect and recycle the batteries, ensuring they are handled according to industry standards. Some regions also have specialized recycling facilities that can accommodate the specific requirements of EV batteries. By utilizing these services, individuals can contribute to a more sustainable approach to EV ownership.
In summary, the responsible disposal of spent EV batteries is vital for environmental protection and resource conservation. Recycling is the preferred method, allowing for the recovery of valuable materials and the prevention of hazardous waste. EV owners play a crucial role in this process by seeking out specialized recycling programs and ensuring that their batteries are disposed of correctly. With proper end-of-life management, the EV industry can continue to grow while minimizing its environmental footprint.
Green Revolution: Unlocking Nature's Power with Electric Vehicles
You may want to see also

Second-Life Applications: Finding new uses for retired EV batteries
The increasing adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) has led to a growing number of retired batteries, prompting the need to explore innovative second-life applications. These applications aim to extend the usefulness of these batteries beyond their initial purpose in EVs, addressing environmental concerns and maximizing resource efficiency. One promising avenue is the development of energy storage systems for renewable energy integration. As the world shifts towards cleaner energy sources, retired EV batteries can be repurposed to store excess energy generated from solar panels and wind turbines. This stored energy can then be utilized during periods of low generation, ensuring a stable and reliable power supply. By integrating these batteries into renewable energy systems, we can enhance grid stability and reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
Another potential second-life application lies in the field of grid-scale energy storage. The large-scale deployment of renewable energy sources often requires efficient storage solutions to manage intermittent power generation. Retired EV batteries, with their proven reliability and scalability, can be utilized to create robust energy storage systems for power grids. These systems can help balance supply and demand, provide backup power during outages, and support voltage regulation. By leveraging the existing infrastructure and technology of EVs, the transition to a more sustainable energy grid becomes more feasible and cost-effective.
Furthermore, the unique characteristics of EV batteries make them suitable for residential energy storage. Homeowners can install battery systems to store excess electricity generated from rooftop solar panels or purchased from the grid. This stored energy can be used during peak demand periods or power outages, reducing electricity bills and increasing energy independence. With the growing popularity of home energy management systems, retired EV batteries can play a crucial role in empowering individuals to take control of their energy consumption and contribute to a more decentralized power grid.
In addition to energy storage, retired EV batteries can find new life in other innovative applications. Researchers are exploring the use of these batteries in microgrids, which are localized power grids that can operate independently or in conjunction with the main grid. Microgrids enhance community resilience and reliability, especially in remote or disaster-prone areas. Furthermore, the thermal management systems of EV batteries can be utilized for heating or cooling purposes, providing an eco-friendly alternative to traditional HVAC systems.
The second-life applications of retired EV batteries present a sustainable approach to managing the growing e-waste problem associated with these vehicles. By extending the lifespan of batteries and finding new uses, we can reduce the environmental impact of EV disposal and contribute to a circular economy. As the EV market continues to expand, investing in research and development for these second-life applications will be crucial to ensure a greener and more resilient future for energy storage and distribution.
Revolutionizing Design: A Guide to Crafting the Future of Electric Vehicles
You may want to see also

Environmental Impact: Assessing the ecological consequences of EV battery disposal
The environmental implications of electric vehicle (EV) battery disposal are a critical aspect of the broader sustainability debate surrounding the rise of EVs. As the world shifts towards cleaner transportation, understanding the ecological consequences of managing these batteries is essential to ensure a truly green future. The disposal of EV batteries is a complex process that involves various stages, each presenting unique challenges and potential environmental risks.
One of the primary concerns is the chemical composition of these batteries. Modern EVs typically use lithium-ion batteries, which contain valuable metals like lithium, cobalt, nickel, and manganese. While these materials are essential for the battery's performance, they also pose significant environmental challenges when not managed properly. For instance, lithium, when released into the environment, can contaminate soil and water sources, leading to ecological imbalances and potential harm to wildlife. Similarly, cobalt, a metal often associated with ethical concerns in mining, can have detrimental effects on ecosystems if not disposed of or recycled appropriately.
The process of battery disposal often begins with the collection and transportation of used batteries from various EV models. This stage is crucial as improper handling can lead to accidents and spills, releasing hazardous substances into the environment. Specialized facilities are required to safely store and process these batteries, ensuring that they are not damaged during transit. Once at the facility, batteries undergo a series of tests to assess their condition, which determines the most suitable disposal or recycling method.
Recycling is a key strategy to mitigate the environmental impact of EV batteries. It involves extracting valuable materials from the batteries and reusing them in new products. However, the recycling process itself can be energy-intensive and may generate emissions. For instance, the process of recovering lithium from batteries requires significant energy, and the release of certain chemicals during recycling can have ecological consequences if not managed properly. Despite these challenges, recycling offers a more sustainable alternative to disposal, reducing the demand for raw materials and minimizing the environmental footprint of EV production.
In summary, the environmental impact of EV battery disposal is a multifaceted issue. It requires a comprehensive approach that includes responsible collection, specialized storage, and efficient recycling processes. By addressing these aspects, we can work towards minimizing the ecological consequences of EV battery management, ensuring that the benefits of electric transportation are not offset by environmental degradation. This includes investing in research to improve recycling technologies, developing more sustainable battery designs, and educating the public about the importance of proper disposal methods.
Chevy Volt: Unveiling Its True Electric Nature
You may want to see also

Research and Innovation: Exploring new technologies for battery recycling and reuse
The growing adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) has sparked a critical need for innovative solutions in battery recycling and reuse. As the demand for sustainable transportation increases, understanding the end-of-life management of EV batteries becomes essential. Research and development in this field aim to address the environmental and economic challenges associated with battery disposal while exploring opportunities for resource recovery.
One of the primary focuses of current research is developing efficient recycling processes for lithium-ion batteries, which are commonly used in EVs. These batteries contain valuable materials like lithium, cobalt, and nickel, which can be recovered and reused. Scientists and engineers are working on advanced separation techniques to extract these metals from the battery cells, aiming to minimize waste and maximize resource recovery. For instance, researchers are exploring the use of hydrometallurgical processes, which involve dissolving the battery materials in a liquid solution to separate and recover the desired metals. This approach can be more environmentally friendly compared to traditional pyrometallurgical methods, which involve high-temperature incineration.
In addition to recycling, there is a growing interest in finding ways to reuse EV batteries. Instead of completely disassembling and recycling the batteries, researchers are investigating methods to repurpose them for other applications. One potential use is in energy storage systems for renewable energy sources like solar and wind power. By integrating EV batteries into these systems, it becomes possible to store excess energy during periods of high generation and discharge it when needed, thus improving grid stability and efficiency. Another idea is to utilize the batteries in stationary energy storage applications, such as providing backup power for data centers or remote locations.
Furthermore, the development of novel battery designs and chemistries is an active area of research. Scientists are exploring alternative materials and structures that could improve the performance, longevity, and recyclability of EV batteries. For example, solid-state batteries, which replace the liquid electrolyte with a solid conductive material, offer potential advantages in terms of energy density and safety. Researchers are also investigating lithium-sulfur and lithium-air batteries, which could provide higher energy storage capacities and lower environmental impacts.
International collaboration and knowledge-sharing are vital to driving innovation in battery recycling and reuse. Governments, industries, and research institutions are forming partnerships to exchange ideas, resources, and best practices. These collaborations facilitate the development of standardized recycling processes, ensuring that EV batteries are managed consistently and sustainably across different regions. Additionally, the sharing of research findings accelerates the progress of new technologies, as scientists can build upon each other's work and avoid duplicating efforts.
Electric Vehicle Owners: Taxed for a Greener Future?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
When the batteries in electric vehicles reach the end of their useful life, they can be recycled or repurposed. Many manufacturers and recycling companies have established processes to handle these batteries safely and sustainably. The recycling process involves extracting valuable materials like lithium, cobalt, and nickel, which can then be used to produce new batteries or other products. Some companies also explore second-life applications, where the batteries are refurbished and used for energy storage systems or in less demanding applications.
Proper disposal and recycling of EV batteries is crucial to minimize environmental impact. While these batteries contain valuable and potentially hazardous materials, they can be safely managed through specialized recycling processes. It's important to note that improper disposal, such as dumping in landfills, can lead to soil and water contamination due to the release of heavy metals and chemicals. Many countries and regions have strict regulations and incentives to encourage the proper recycling of EV batteries, ensuring a more sustainable approach to managing these used batteries.
The lifespan of EV batteries varies depending on several factors, including the type of battery, usage patterns, climate conditions, and maintenance. On average, EV batteries can retain around 70-80% of their original capacity after 10 years of use. However, this doesn't mean they are unusable; they can still power the vehicle for many miles. Factors like temperature extremes, frequent rapid charging, and aggressive driving can accelerate battery degradation. Regular maintenance, such as software updates and monitoring battery health, can help optimize performance and extend the battery's lifespan.







