Non-GamePass electric vehicles are a new breed of sustainable transportation, designed to offer an eco-friendly and cost-effective alternative to traditional cars. These vehicles are not tied to any subscription service or game-related features, focusing instead on providing an efficient and environmentally friendly driving experience. They are equipped with advanced electric powertrains, offering zero-emission performance and a smooth, quiet ride. Non-GamePass electric vehicles often feature innovative technologies, such as rapid charging capabilities and smart connectivity, ensuring a seamless and enjoyable driving experience for environmentally conscious consumers.
What You'll Learn
- Battery Technology: Focuses on advanced battery systems for electric vehicles
- Charging Infrastructure: Details the development of charging stations and networks
- Performance: Compares performance metrics of non-GamePass EVs to traditional cars
- Cost Analysis: Examines the economic benefits of non-GamePass electric vehicles
- Environmental Impact: Discusses the ecological advantages of non-GamePass electric cars

Battery Technology: Focuses on advanced battery systems for electric vehicles
Battery technology is a critical component in the development of electric vehicles (EVs), and advancements in battery systems have been a key focus for researchers and engineers in the automotive industry. The primary goal is to enhance the performance, efficiency, and longevity of batteries, ensuring that EVs can compete with traditional internal combustion engine vehicles in terms of range, speed, and overall driving experience.
One of the main areas of development is the creation of advanced battery systems that offer higher energy density. This is crucial for extending the driving range of electric vehicles, addressing a significant concern for potential EV buyers. By utilizing cutting-edge materials and innovative cell designs, engineers aim to pack more energy into a smaller volume, allowing for longer journeys on a single charge. For instance, lithium-ion batteries, currently the most common type in EVs, are being improved through the use of novel cathode and anode materials, such as lithium-nickel-manganese-cobalt (NMC) and silicon-based compounds, respectively. These advancements can lead to batteries with higher energy storage capacity and improved cycle life, making EVs more practical for daily use.
Another focus is on developing faster-charging batteries without compromising safety and longevity. The ability to quickly recharge an EV's battery is essential for convenience and can significantly impact the adoption of electric vehicles. Researchers are exploring various approaches, including solid-state batteries, which replace the liquid electrolyte with a solid conductive material, enabling faster charging and higher energy density. Additionally, improving the charging infrastructure and optimizing charging algorithms can further enhance the user experience.
Safety is a critical aspect of battery technology, especially with the increasing popularity of EVs. Advanced battery systems must be designed to prevent thermal runaway, a dangerous process where the battery overheats and releases its stored energy rapidly. This is achieved through sophisticated cooling systems, improved battery management systems (BMS), and the use of safer, more stable electrolytes. BMS plays a vital role in monitoring and controlling various parameters, such as temperature, voltage, and current, to ensure the battery operates within safe limits and extends its overall lifespan.
Furthermore, the environmental impact of battery production and disposal is a growing concern. Researchers are working on developing more sustainable battery technologies, such as flow batteries and redox flow batteries, which offer the advantage of scalability and longer lifespans. These technologies can also contribute to grid stability and energy storage solutions, making them valuable for the broader energy sector. As the demand for electric vehicles continues to rise, the focus on battery technology will remain a key driver of innovation, ensuring that EVs become more accessible, efficient, and environmentally friendly.
A Green Revolution: The Electric Vehicle Takeover
You may want to see also

Charging Infrastructure: Details the development of charging stations and networks
The development of charging infrastructure is a critical aspect of supporting the widespread adoption of electric vehicles (EVs). As the number of EVs on the road increases, so does the demand for convenient and efficient charging solutions. This has led to significant investments and innovations in charging technology and infrastructure.
Charging stations, also known as EVSE (Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment), are the physical locations where EVs can be recharged. These stations are typically equipped with charging connectors and power sources, allowing EV owners to plug in their vehicles and restore their battery charge. The design and placement of charging stations are crucial to ensuring accessibility and convenience for EV drivers. Public charging stations are often strategically located along highways, in urban areas, and in parking lots of shopping centers and office buildings, providing a network of charging points for EV users.
The evolution of charging networks has been rapid, with various types of charging stations being developed to cater to different needs. Slow, or 'trickle' charging, is a basic method using standard household outlets, but it is slow and not suitable for long-distance travel. Fast charging, typically using Level 2 chargers (240V), can significantly reduce charging times and is commonly found in public stations. Rapid charging, often utilizing DC (Direct Current) chargers, can provide an even faster charge and is ideal for quick top-ups during long journeys. Some stations even offer ultra-fast charging, which can recharge batteries to 80% capacity in as little as 20-30 minutes.
The key to successful charging infrastructure development lies in creating a comprehensive network. This involves strategic planning to ensure an even distribution of charging stations across regions, especially in areas with high EV ownership. Governments and energy companies are investing in large-scale charging networks, often deploying thousands of stations to support the growing EV market. These networks are designed to provide reliable and efficient charging, ensuring that EV owners have access to convenient charging options whenever needed.
Additionally, the integration of smart technologies is transforming charging infrastructure. Smart charging systems use advanced algorithms and communication protocols to optimize charging processes. These systems can dynamically adjust charging rates based on grid demand, vehicle availability, and energy prices, helping to balance the load on the electricity network. Smart charging also enables vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technology, where EVs can feed power back to the grid, further enhancing the efficiency and sustainability of the charging infrastructure.
In summary, the development of charging infrastructure is essential to support the electric vehicle revolution. It involves creating a network of charging stations, offering various charging speeds and technologies, and ensuring strategic placement to cater to the needs of EV drivers. With continued innovation and investment, charging networks will play a pivotal role in the widespread adoption of non-gamepass electric vehicles, contributing to a more sustainable and efficient transportation ecosystem.
Unveiling PEVs and BEVs: The Electric Vehicle Revolution
You may want to see also

Performance: Compares performance metrics of non-GamePass EVs to traditional cars
The term "non-GamePass" is not a standard automotive or electric vehicle (EV) terminology, and it's unclear what specific aspect or feature you're referring to when you mention "non-GamePass EVs." However, I can provide a comparison of performance metrics between traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) cars and non-GamePass EVs, assuming you're referring to electric vehicles that are not part of a specific subscription or access service like GamePass.
Acceleration and Speed:
Non-GamePass EVs often offer impressive acceleration, thanks to their instant torque delivery. Electric motors provide a powerful surge of torque from a standstill, resulting in quick acceleration. For example, high-performance electric cars like the Tesla Model S Plaid can accelerate from 0 to 60 mph in under 2 seconds. In contrast, traditional ICE cars typically have a more gradual acceleration response, with performance varying widely depending on the engine size and vehicle weight. Sports cars with powerful engines can still match or exceed some EVs in acceleration, but the overall trend shows that EVs are gaining ground in this area.
Top Speed:
While EVs have made significant strides in acceleration, they generally have a lower top speed compared to traditional cars. This is primarily due to the physical limitations of electric motors and the need for efficient energy management. Most EVs have a top speed of around 150-160 mph, while high-performance ICE cars can reach speeds over 200 mph. However, it's worth noting that for everyday driving, the top speed is often not a limiting factor, and EVs provide a smooth and responsive driving experience at various speeds.
Power and Torque:
Electric vehicles are renowned for their high torque output, which translates to excellent low-end performance. This is particularly beneficial for quick starts and passing maneuvers. Non-GamePass EVs can offer torque figures that rival or even surpass those of high-performance ICE cars. For instance, the Lucid Air Dream Edition has a massive 1,050 lb-ft of torque, providing exceptional acceleration. Traditional cars, especially those with smaller engines, may not match the torque of some EVs, but larger, more powerful ICE engines can still deliver impressive performance.
Handling and Dynamics:
The lightweight nature of many EVs contributes to better handling and overall driving dynamics. The absence of a traditional transmission and the low center of gravity due to the battery placement can result in a more agile and responsive ride. Non-GamePass EVs often provide a smooth and comfortable driving experience, with precise steering and excellent road feedback. Traditional cars, especially those with larger engines and heavier bodies, may offer a more robust and stable ride, but the overall driving experience is evolving with the rise of electric vehicles.
In summary, non-GamePass EVs, when compared to traditional cars, offer superior acceleration, impressive torque, and excellent handling characteristics. While top speed may be a slightly weaker suit for EVs, the overall performance and driving experience are becoming increasingly competitive, making electric vehicles an attractive choice for performance-oriented drivers.
Electric Vehicles: Unlocking Value Beyond the Price Tag
You may want to see also

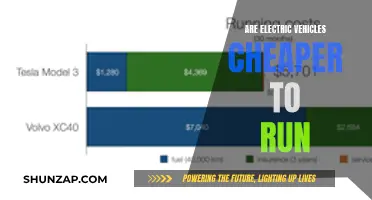
Cost Analysis: Examines the economic benefits of non-GamePass electric vehicles
The concept of non-GamePass electric vehicles refers to electric cars that are not part of a subscription-based service like GamePass, which is a popular gaming service offering access to various games. Instead, these vehicles are typically purchased or leased, and their ownership and usage are independent of any subscription model. This analysis aims to explore the economic advantages of owning and operating non-GamePass electric vehicles, focusing on long-term cost savings and potential financial benefits.
One of the most significant economic benefits of non-GamePass electric vehicles is the potential for substantial savings on fuel and maintenance costs. Electric cars are renowned for their efficiency, and compared to traditional gasoline or diesel vehicles, they offer lower running costs. Over time, the savings on fuel can be substantial, especially in regions where electricity prices are lower than gasoline prices. For instance, an electric vehicle (EV) with a range of 300 miles can travel for approximately 10 cents per mile, whereas a gasoline car might cost around 20-30 cents per mile. This translates to significant savings for EV owners, especially during long-distance travel or daily commutes.
In addition to fuel savings, electric vehicles often have lower maintenance expenses. Traditional cars require regular services, oil changes, and part replacements, which can be costly. However, electric cars have fewer moving parts, and their electric motors are generally more reliable and require less frequent maintenance. This reduced maintenance requirement can save vehicle owners a considerable amount of money over the vehicle's lifetime. Moreover, the absence of a complex internal combustion engine means that EV owners may avoid costly repairs associated with engine-related issues.
The initial purchase or lease price of non-GamePass electric vehicles might be higher compared to conventional cars, but this can be offset by the long-term cost advantages. Government incentives and subsidies for EV adoption can also contribute to making them more affordable upfront. Many countries offer tax credits, rebates, or grants to encourage the purchase of electric vehicles, which can significantly reduce the overall cost of ownership. These incentives can make non-GamePass electric vehicles more accessible and financially attractive to consumers.
Furthermore, the resale value of electric vehicles has been improving, with some studies indicating that EVs retain their value better over time. This is partly due to the increasing demand for electric cars and the potential for reduced depreciation rates. As the market for non-GamePass electric vehicles expands, more buyers and sellers will emerge, creating a more competitive environment and potentially benefiting consumers through better resale prices.
In summary, non-GamePass electric vehicles offer a compelling cost analysis for potential buyers. The combination of lower fuel and maintenance costs, along with potential government incentives, can result in significant long-term savings. While the initial investment may be higher, the economic benefits of owning an electric vehicle can be substantial, making it an attractive choice for environmentally conscious consumers and those seeking cost-effective transportation solutions.
EV Revolution: Will Prices Drop in 5 Years?
You may want to see also

Environmental Impact: Discusses the ecological advantages of non-GamePass electric cars
The term "non-GamePass" is not a widely recognized term in the automotive industry, and it's unclear what it specifically refers to. However, I can provide information about the environmental impact of electric vehicles (EVs) in general, which can be considered a step towards understanding the ecological advantages of non-GamePass electric cars.
Electric vehicles have gained significant attention as a potential solution to reduce the environmental impact of the transportation sector. One of the key environmental advantages of EVs is their zero-emission nature. Unlike traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles, electric cars produce no direct exhaust emissions, which means they do not release harmful pollutants such as nitrogen oxides (NOx), carbon monoxide (CO), and particulate matter (PM) into the atmosphere. This reduction in air pollution can lead to improved air quality, especially in urban areas, and contribute to better public health.
The environmental benefits of electric cars extend beyond tailpipe emissions. Firstly, EVs have a lower carbon footprint throughout their lifecycle. The production of electric vehicles has become more efficient, and the use of renewable energy sources for electricity generation further reduces their carbon emissions. Additionally, electric cars are more energy-efficient compared to ICE vehicles, converting a higher percentage of energy from the battery to power the vehicle, resulting in less energy waste.
Another ecological advantage is the potential for reduced water pollution. Traditional vehicles often release fluids containing heavy metals and other toxic substances, which can contaminate water sources. Electric vehicles, on the other hand, do not require these fluids, minimizing the risk of water pollution. Furthermore, the absence of exhaust emissions means that electric cars do not contribute to the formation of acid rain, which is caused by the release of sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides.
The widespread adoption of electric vehicles can also contribute to a more sustainable transportation system. As the electricity grid becomes greener with increased renewable energy integration, the environmental impact of EVs will further decrease. This shift towards electric mobility can help reduce our reliance on finite fossil fuels and mitigate the environmental consequences of the transportation sector.
In summary, electric vehicles, regardless of any specific term like "non-GamePass," offer significant ecological advantages. These include reduced air and water pollution, lower carbon emissions throughout their lifecycle, and the potential for a more sustainable transportation system. As the world aims to combat climate change and improve environmental sustainability, the adoption of electric cars plays a crucial role in achieving these goals.
Powering Up: A Beginner's Guide to Electric Vehicle Ownership
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
A non-GamePass electric vehicle refers to an electric car or vehicle that is not part of a subscription-based service like GamePass. These vehicles are typically purchased or leased by individuals and do not require a monthly or annual subscription to access their electric features or services. Non-GamePass electric vehicles often offer various benefits, such as tax incentives, reduced fuel costs, and access to car-sharing platforms, making them an attractive option for environmentally conscious consumers.
The primary difference lies in the ownership and access model. GamePass-subscribed electric vehicles are often part of a shared mobility service, where users pay a subscription fee to access and use the vehicle on-demand. Non-GamePass electric vehicles, on the other hand, are privately owned and can be used by the vehicle owner or shared with others through car-sharing or rental services. GamePass subscriptions typically provide access to a range of electric vehicles, while non-GamePass options offer more flexibility in terms of ownership and usage.
There are several advantages to owning a non-GamePass electric vehicle. Firstly, it provides ownership and control over the vehicle, allowing users to customize and personalize their driving experience. Non-GamePass electric vehicles often come with various features and technologies, such as advanced driver-assistance systems, autonomous driving capabilities, and efficient energy management. Additionally, owning an electric vehicle can lead to long-term cost savings due to reduced fuel and maintenance expenses compared to traditional gasoline-powered cars.