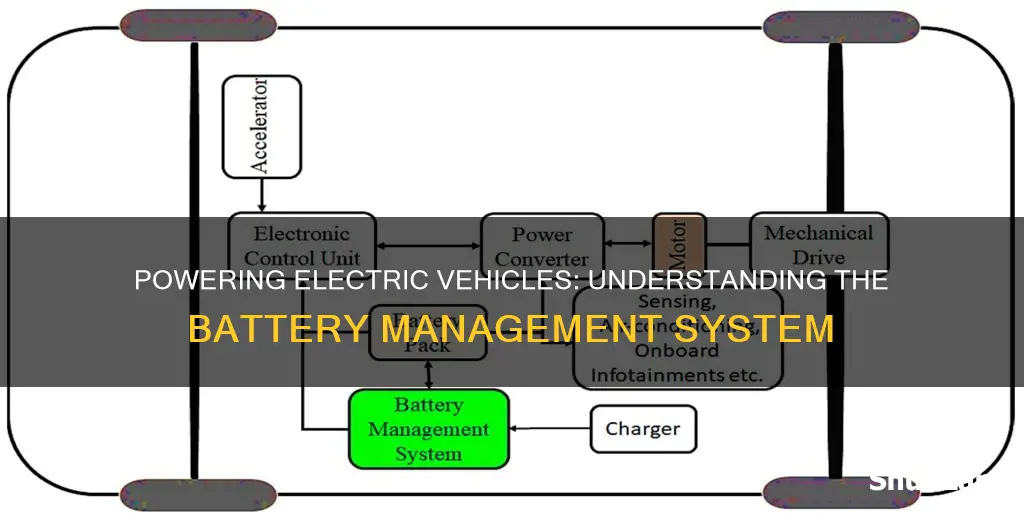
A battery management system (BMS) is a crucial component in electric vehicles (EVs), responsible for optimizing the performance, safety, and longevity of the vehicle's battery pack. It acts as the brain of the battery, monitoring and controlling various parameters to ensure efficient operation. The BMS manages the charging and discharging cycles, temperature control, state of charge (SOC) estimation, and cell balancing, all of which are essential for maximizing the battery's efficiency, extending its lifespan, and ensuring the overall safety of the EV. This system plays a vital role in enhancing the driving range, improving performance, and providing a reliable and safe driving experience for electric vehicle owners.
What You'll Learn
- Battery Monitoring: Real-time data on cell voltage, temperature, and state of charge
- Thermal Management: Regulating battery temperature for optimal performance and safety
- Charging Control: Optimizing charging rates and preventing overcharging/over-discharging
- Cell Balancing: Equalizing cell voltages to extend battery life and improve efficiency
- Safety Mechanisms: Protecting against short circuits, overcurrent, and thermal runaway

Battery Monitoring: Real-time data on cell voltage, temperature, and state of charge
Battery monitoring is a critical aspect of battery management systems (BMS) in electric vehicles (EVs), as it provides real-time data that is essential for optimizing performance, safety, and longevity of the battery pack. This monitoring system offers a comprehensive view of the battery's health and status, allowing for efficient management and decision-making. Here's a detailed look at the key parameters:
Cell Voltage: Each cell in a battery pack has a specific voltage range it operates within. Monitoring the voltage of individual cells is vital as it provides insights into the overall health and performance of the battery. Real-time voltage data helps identify cells that are underperforming or overcharged, which can lead to potential safety hazards. For instance, if a cell voltage drops significantly below the expected range, it might indicate a short circuit or internal damage. Conversely, a cell voltage that consistently exceeds the safe limit could result in overcharging and potential thermal runaway.
Temperature: Temperature monitoring is another critical aspect of battery management. The operating temperature of a battery directly impacts its performance and longevity. Real-time temperature data helps in identifying cells or modules that are overheating or operating outside the optimal temperature range. Excessive heat can accelerate battery degradation and, in extreme cases, lead to fire or explosion risks. On the other hand, extremely low temperatures can reduce battery capacity and performance. By monitoring temperature, the BMS can adjust charging and discharging rates to maintain the battery within safe operating limits.
State of Charge (SoC): The State of Charge is a measure of the battery's current level of charge relative to its full capacity. Real-time SoC monitoring is crucial for EV drivers and the BMS itself. It provides an accurate representation of the battery's remaining capacity, allowing for better trip planning and range estimation. Moreover, the BMS can use this data to optimize charging and discharging processes, ensuring the battery operates within safe and efficient limits. For example, during charging, the BMS can adjust the charging rate based on the current SoC to prevent overcharging, which can damage the battery.
In summary, battery monitoring in electric vehicles involves continuous tracking of cell voltage, temperature, and state of charge. This real-time data collection enables the BMS to make informed decisions, ensuring the battery operates within safe limits, maintains optimal performance, and extends its overall lifespan. By closely monitoring these parameters, the system can prevent potential issues, enhance efficiency, and provide a reliable and safe driving experience for EV owners.
Unraveling the Mystery: Why Some Animals Chew on Car Wires
You may want to see also

Thermal Management: Regulating battery temperature for optimal performance and safety
The thermal management system is a critical component of an electric vehicle's battery management system (BMS), designed to maintain the battery's temperature within an optimal range for both performance and safety. Effective thermal management is essential to ensure the longevity and efficiency of the battery pack, as well as to prevent potential hazards such as thermal runaway.
Battery packs in electric vehicles generate heat during operation due to the chemical reactions occurring within the cells. This heat can cause a rise in temperature, which, if left unchecked, can lead to several issues. Firstly, high temperatures can accelerate the degradation of the battery's components, reducing its overall lifespan. Secondly, excessive heat can impact the battery's performance, leading to decreased energy output and efficiency. For instance, at elevated temperatures, the internal resistance of the battery increases, resulting in reduced power delivery to the vehicle's drive system.
To address these challenges, thermal management systems employ various strategies. One common approach is the use of cooling fluids or air circulation systems. These mechanisms absorb heat from the battery pack and transfer it to a cooler area, typically outside the vehicle, where it can be dissipated into the environment. Liquid cooling, often used in high-performance electric vehicles, is highly effective as it provides rapid heat dissipation and can maintain lower temperatures compared to air cooling.
Another critical aspect of thermal management is temperature monitoring and control. Sensors are strategically placed throughout the battery pack to measure temperature at different points. This data is then used to adjust the cooling system's operation, ensuring that no single cell or module becomes excessively hot. Advanced BMS systems can also implement temperature-based control algorithms, such as pre-conditioning, where the battery is heated or cooled before use to optimize performance and extend its lifespan.
In summary, thermal management is a vital function within the battery management system of electric vehicles. By regulating temperature, it ensures the battery operates within its optimal performance window, enhances safety by preventing overheating, and contributes to the overall reliability and efficiency of the vehicle's power source. Effective thermal management is a key enabler for the widespread adoption of electric vehicles, addressing concerns related to range, performance, and longevity.
America's Electric Vehicle Revolution: Top Models and Trends
You may want to see also

Charging Control: Optimizing charging rates and preventing overcharging/over-discharging
The battery management system (BMS) plays a critical role in ensuring the safe and efficient operation of electric vehicles (EVs) by implementing precise charging control mechanisms. This control is essential to prevent overcharging and over-discharging, which can significantly impact battery health and performance.
One of the primary functions of charging control is to optimize the charging rate. The BMS monitors the battery's state of charge (SOC) and adjusts the charging current accordingly. During the initial stages of charging, the BMS may start with a higher current to quickly reach a moderate SOC level. As the battery approaches a higher SOC, the charging rate is reduced to a safer, slower pace to avoid overcharging. This dynamic approach ensures that the battery is charged efficiently without compromising its longevity.
Overcharging can lead to several issues, including reduced battery life, increased stress on the battery cells, and potential safety hazards. To prevent overcharging, the BMS employs various strategies. It may limit the maximum charging current or voltage to ensure the battery doesn't exceed its safe operating range. Additionally, the BMS can monitor the battery's temperature and adjust the charging rate accordingly. If the temperature is too high, the charging process might be paused or reduced to prevent further overheating.
Another aspect of charging control is the prevention of over-discharging, which can also damage the battery. The BMS tracks the battery's SOC and triggers a warning or intervention if the charge drops below a predefined threshold. This action might include disconnecting the load or reducing the power draw to maintain a minimum charge level. By preventing over-discharging, the BMS helps maintain the battery's health and ensures it remains within safe operating limits.
In summary, charging control is a vital component of the BMS, enabling the optimization of charging rates and the prevention of overcharging and over-discharging. Through intelligent monitoring and adjustment of charging parameters, the BMS ensures that EV batteries are charged efficiently, safely, and with extended longevity. This technology is key to enhancing the overall performance and reliability of electric vehicles.
Electric Vehicle Fuse Safety: Fast-Blow or Slow-Blow?
You may want to see also

Cell Balancing: Equalizing cell voltages to extend battery life and improve efficiency
Battery management systems (BMS) play a crucial role in optimizing the performance and longevity of electric vehicle (EV) batteries. One of the key functions of a BMS is cell balancing, which is an essential process to ensure the overall health and efficiency of the battery pack. Cell balancing refers to the technique of adjusting and equalizing the voltage levels across individual cells within the battery pack to maintain optimal performance and extend the battery's lifespan.
In an EV battery pack, multiple cells are connected in series and parallel to achieve the desired voltage and capacity. However, due to variations in manufacturing processes, age, and usage, these cells can experience different rates of charge and discharge, leading to voltage discrepancies. Over time, these imbalances can result in reduced battery capacity, decreased efficiency, and even premature cell failure. Cell balancing aims to mitigate these issues by ensuring that all cells operate within a similar voltage range.
The process of cell balancing involves monitoring the voltage of each cell and making precise adjustments to equalize them. This is typically achieved through a network of electronic components, such as switches, resistors, and capacitors, which are strategically placed within the battery pack. When a voltage difference is detected between cells, the BMS activates specific balancing algorithms to redistribute energy and bring the voltages back into equilibrium. This equalization process ensures that no single cell is overcharged or over-discharged, promoting a more uniform and efficient battery operation.
By implementing cell balancing, the BMS can significantly improve the overall efficiency of the EV battery. It helps to reduce energy losses associated with voltage differences, allowing for better utilization of the available energy. Additionally, cell balancing contributes to longer battery life by preventing excessive stress on individual cells, which can lead to degradation and reduced capacity over time. This is particularly important for EV owners, as it ensures their vehicles maintain optimal performance and range, providing a more reliable and cost-effective driving experience.
In summary, cell balancing is a critical aspect of battery management systems in electric vehicles. It involves equalizing cell voltages to maintain optimal performance and extend the battery's lifespan. Through precise voltage monitoring and adjustments, the BMS ensures that all cells operate harmoniously, reducing energy losses and promoting efficient energy utilization. This process ultimately contributes to the overall reliability and longevity of EV batteries, making it an essential component in the advancement of sustainable transportation.
Unlocking EV Savings: A Guide to Claiming Your Subsidy
You may want to see also

Safety Mechanisms: Protecting against short circuits, overcurrent, and thermal runaway
A battery management system (BMS) is a critical component in electric vehicles (EVs) that ensures the safe and efficient operation of the battery pack. One of its primary functions is to implement robust safety mechanisms to protect against various electrical hazards, including short circuits, overcurrent, and thermal runaway. These mechanisms are essential to prevent damage to the battery, ensure the vehicle's safety, and maintain the overall performance of the EV.
Short Circuit Protection:
Short circuits can occur when there is an unintended connection between two points in the circuit, leading to a sudden and excessive current flow. To mitigate this risk, the BMS incorporates several protective measures. Firstly, it employs current sensors to continuously monitor the flow of electricity within the battery pack. If a short circuit is detected, the BMS can quickly isolate the affected cell or module by disconnecting it from the power source. This isolation prevents the potential damage caused by the high current surge. Additionally, some advanced BMS designs use a technique called 'cell balancing,' which ensures that all cells in the pack are charged and discharged at similar levels, reducing the likelihood of a short circuit due to cell imbalance.
Overcurrent Protection:
Overcurrent situations arise when the current flowing through a circuit exceeds its safe limit, often due to excessive charging or discharging rates. To address this, the BMS includes current-limiting devices such as fuses or circuit breakers. These devices are designed to trip or open when the current exceeds a predetermined threshold, effectively interrupting the circuit and preventing potential damage. The BMS also monitors the battery's temperature and voltage, as these parameters can provide early indicators of overcurrent conditions. By analyzing these data points, the system can take appropriate action, such as reducing the charging rate or activating cooling systems to mitigate the risk.
Thermal Runaway Prevention:
Thermal runaway is a dangerous condition where a battery cell's temperature rises uncontrollably, leading to potential fire hazards. BMS plays a vital role in preventing this by implementing several strategies. One approach is to monitor the temperature of each cell individually and take corrective actions if a cell exceeds its safe operating temperature. This may involve reducing the charging current, activating cooling fans, or even disconnecting the affected cell to prevent further heat generation. Additionally, the BMS can analyze the battery's overall temperature distribution and make adjustments to ensure optimal thermal management. This includes controlling the charging and discharging rates to maintain a balanced and safe operating temperature across all cells.
In summary, the safety mechanisms within a BMS are designed to safeguard the electric vehicle's battery pack from various electrical and thermal hazards. By employing short circuit detection, overcurrent protection, and thermal management strategies, the BMS ensures the longevity and reliability of the battery while prioritizing the overall safety of the EV. These protective measures are essential to address the unique challenges associated with high-energy density battery systems in modern electric vehicles.
Revolutionizing the Road: The Karma Electric Vehicle's Impact
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
A Battery Management System is an essential component in electric vehicles, acting as the brain that monitors and controls the battery pack's performance. It ensures the safe and efficient operation of the battery by managing various parameters such as voltage, current, temperature, and state of charge. BMS is crucial as it optimizes battery performance, extends its lifespan, and enhances overall safety by preventing overcharging, over-discharging, and overheating.
The BMS continuously monitors the battery's health and status through a network of sensors. It measures the voltage of each cell, the overall current flow, and the temperature to ensure the battery operates within safe limits. It also calculates the state of charge, which represents the battery's current level of power. BMS uses this data to make decisions, such as controlling the charging and discharging rates, balancing cell voltages, and providing diagnostic information to the vehicle's control system.
Absolutely! A sophisticated BMS offers several advantages. It improves battery efficiency by optimizing charging and discharging processes, resulting in longer driving ranges. It enhances safety by implementing protective measures against short circuits, overcurrent, and thermal runaway. BMS also contributes to battery longevity by preventing excessive cycling and maintaining optimal operating conditions. Additionally, it provides valuable data for diagnostics, helping EV manufacturers and owners understand battery behavior and performance over time.







