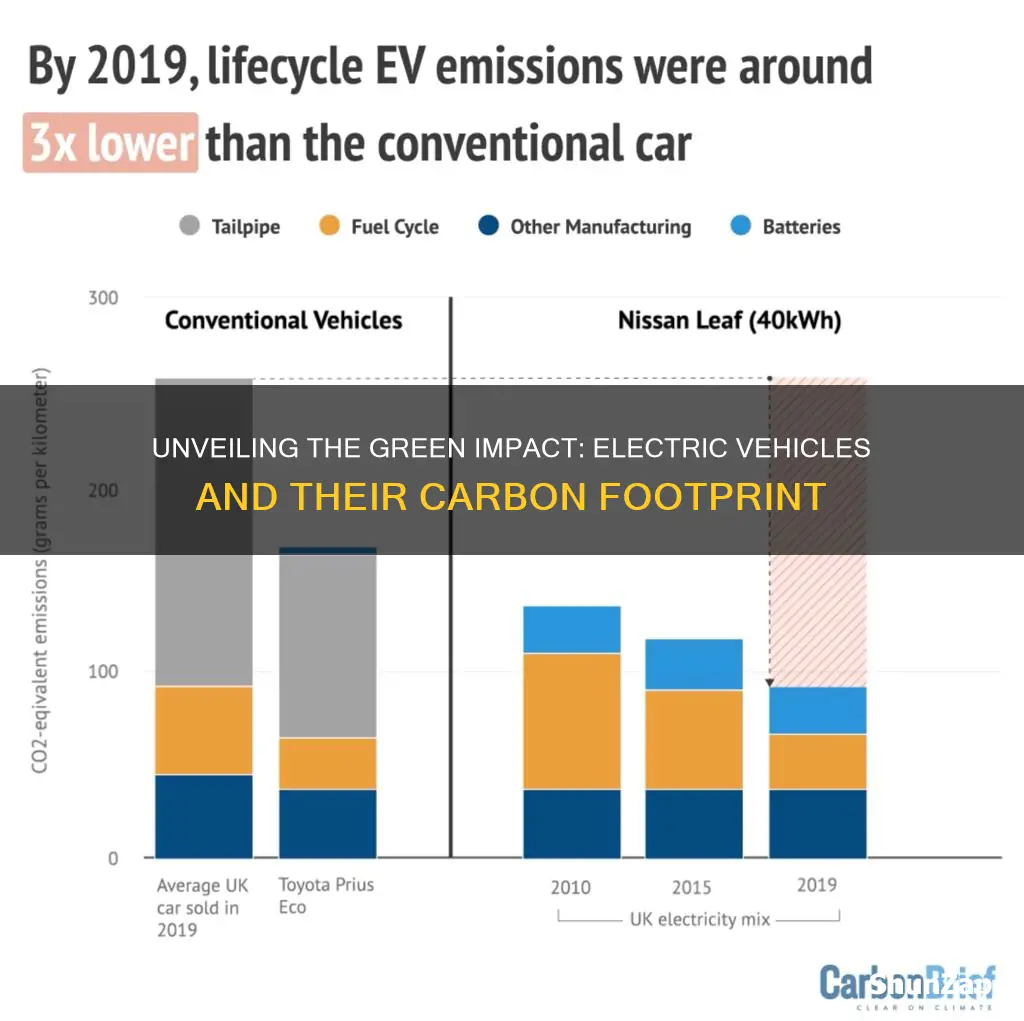
The carbon footprint of an electric vehicle (EV) is a crucial aspect to consider when evaluating its environmental impact. Unlike traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles, EVs produce zero tailpipe emissions, which significantly reduces their direct contribution to air pollution. However, the carbon footprint of an EV extends beyond the vehicle itself and includes the entire lifecycle of the car, from manufacturing to disposal. This includes the energy used to produce the vehicle, the electricity used to power it, and the materials and resources required for its construction. Understanding the carbon footprint of EVs is essential for consumers and policymakers alike, as it helps in making informed decisions about the sustainability of electric transportation and its role in combating climate change.
What You'll Learn
- Energy Consumption: EV efficiency compared to traditional cars
- Battery Production: Environmental impact of battery manufacturing
- Charging Infrastructure: Carbon emissions from electricity generation
- Recycling Potential: Benefits of recycling EV batteries
- Lifetime Emissions: Total emissions over an EV's lifespan

Energy Consumption: EV efficiency compared to traditional cars
The energy consumption and efficiency of electric vehicles (EVs) compared to traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) cars is a crucial aspect when evaluating their environmental impact and overall sustainability. EVs have gained significant attention as a cleaner and more eco-friendly transportation alternative, but their energy efficiency and consumption patterns are often misunderstood.
In terms of energy efficiency, EVs offer a substantial advantage over traditional cars. When an ICE vehicle burns gasoline, a significant portion of the energy is wasted as heat, which is why you might feel the engine's heat when the car is idling. In contrast, EVs convert a much higher percentage of the electrical energy stored in their batteries into actual vehicle movement. This efficiency is primarily due to the absence of the need for a complex internal combustion process, which results in fewer moving parts and less energy loss. As a result, EVs can achieve higher energy efficiency, often ranging from 70% to 80%, compared to the 20-30% efficiency of ICE vehicles.
The energy consumption of EVs is also influenced by their design and engineering. Modern EVs are built with lightweight materials, aerodynamic bodies, and efficient power trains, all of which contribute to reduced energy usage. For instance, the use of regenerative braking in EVs allows for energy recovery during deceleration, further improving overall efficiency. This technology captures the kinetic energy that would otherwise be lost as heat and converts it back into electrical energy to recharge the battery.
When comparing the energy consumption of EVs to traditional cars, it's essential to consider the entire lifecycle, including the production and end-of-life stages. While the manufacturing of EVs may require more energy and resources, the overall energy consumption over the vehicle's lifetime is significantly lower for EVs. This is because EVs have fewer mechanical components that require frequent maintenance and replacements, which are energy-intensive processes in ICE vehicles.
In summary, electric vehicles demonstrate superior energy efficiency and lower energy consumption compared to traditional cars. Their design, technology, and the way they utilize energy make them a more environmentally friendly choice. As the world shifts towards sustainable transportation, understanding and appreciating the energy efficiency of EVs is crucial in promoting their adoption and reducing the carbon footprint of the transportation sector.
Unlocking California's EV Future: Exploring Tax Credits and Incentives
You may want to see also

Battery Production: Environmental impact of battery manufacturing
The environmental impact of battery manufacturing is a critical aspect of understanding the carbon footprint of electric vehicles (EVs). The production of batteries, particularly lithium-ion batteries, involves several stages that contribute to greenhouse gas emissions and resource depletion. Here's an overview of the key considerations:
Battery manufacturing requires a substantial amount of raw materials, including lithium, cobalt, nickel, and graphite. The extraction and processing of these materials often have significant environmental consequences. For instance, lithium mining can lead to water pollution and habitat destruction, especially when improper practices are employed. Similarly, the extraction of cobalt, a critical component in some battery chemistries, has been associated with environmental degradation and human rights issues in mining regions. The energy-intensive nature of refining and processing these materials further adds to the carbon footprint.
The manufacturing process itself is energy-intensive, typically requiring large amounts of electricity, often sourced from fossil fuels in many regions. This stage contributes significantly to the overall carbon emissions associated with battery production. The use of heavy machinery and complex assembly lines also results in higher energy consumption and potential emissions. Additionally, the production of battery cells and packs involves various chemical processes, some of which may have environmental implications if not managed sustainably.
Another critical aspect is the disposal and recycling of batteries. As the demand for EVs increases, so does the need for efficient and environmentally friendly battery recycling processes. Improper disposal of batteries can lead to soil and water contamination due to the release of heavy metals and toxic chemicals. Implementing effective recycling methods is essential to minimize the environmental impact and ensure a sustainable supply of raw materials for battery production.
Despite the challenges, efforts are being made to improve the sustainability of battery manufacturing. Researchers and industries are exploring ways to reduce the environmental footprint, such as developing more efficient and eco-friendly extraction processes, adopting renewable energy sources for manufacturing, and designing batteries with recyclable materials. These initiatives aim to address the concerns related to resource depletion and carbon emissions, making electric vehicle batteries more environmentally friendly over their lifecycle.
In summary, the environmental impact of battery manufacturing is a complex issue, with significant emissions and resource utilization during production, extraction, and recycling. However, with ongoing advancements and a focus on sustainability, the carbon footprint of electric vehicle batteries can be reduced, contributing to the overall goal of minimizing the environmental impact of transportation.
Unveiling the Power of EV: Electric Vehicles Explained
You may want to see also

Charging Infrastructure: Carbon emissions from electricity generation
The carbon footprint of an electric vehicle (EV) is a topic of growing interest as the world shifts towards more sustainable transportation options. One crucial aspect often overlooked is the carbon emissions associated with the charging infrastructure that powers these vehicles. The process of generating electricity to charge EVs can vary significantly depending on the energy mix used in a particular region.
Electricity generation from fossil fuels, such as coal, oil, and natural gas, is a major contributor to greenhouse gas emissions. When EVs are charged using electricity produced from these sources, the carbon footprint of the vehicle can increase. For instance, in regions heavily reliant on coal-fired power plants, the carbon emissions from charging an EV can be substantial. This is because burning coal releases a significant amount of carbon dioxide, a potent greenhouse gas, into the atmosphere.
The impact of charging infrastructure on carbon emissions is particularly relevant when considering the widespread adoption of EVs. As more vehicles are added to the road, the demand for electricity to charge them increases. If the electricity grid relies heavily on fossil fuel-based power plants, the overall carbon footprint of the EV fleet could be considerable. This is especially true in areas where renewable energy sources like solar or wind power are not yet prevalent.
To address this issue, many countries and regions are focusing on transitioning their electricity generation to cleaner sources. This includes investing in renewable energy infrastructure, such as solar farms, wind turbines, and hydroelectric power plants. By diversifying the energy mix and reducing the reliance on fossil fuels, the carbon emissions from charging EVs can be significantly lowered. Governments and energy providers are also implementing policies and incentives to encourage the use of renewable energy for EV charging, further reducing the environmental impact.
In summary, the carbon emissions from charging infrastructure play a significant role in determining the overall carbon footprint of an electric vehicle. By understanding and addressing these emissions, we can work towards creating a more sustainable transportation system. This involves promoting renewable energy sources for electricity generation and implementing strategies to minimize the environmental impact of EV charging on a global scale.
Boosting EV Speed: Tips for Faster, More Efficient Driving
You may want to see also

Recycling Potential: Benefits of recycling EV batteries
The recycling potential of electric vehicle (EV) batteries is a crucial aspect of the broader environmental impact of EVs. As the demand for electric cars continues to rise, so does the need to address the end-of-life management of these batteries. Recycling EV batteries offers numerous benefits, both environmentally and economically, contributing to a more sustainable future.
One of the primary advantages of recycling EV batteries is the significant reduction in environmental impact compared to conventional disposal methods. Electric vehicle batteries contain valuable materials such as lithium, cobalt, nickel, and manganese, which can be recovered and reused. When these batteries are recycled, the extraction of raw materials from the earth is minimized, leading to a substantial decrease in the carbon footprint associated with battery production. This process helps conserve natural resources and reduces the energy-intensive mining processes that often come with extracting these materials.
The recycling process itself is an energy-efficient and environmentally friendly endeavor. Specialized recycling facilities can efficiently recover materials from used EV batteries, ensuring that valuable resources are not wasted. This recycling process often involves mechanical and chemical methods to separate the various components of the battery, making it a precise and controlled procedure. By optimizing the recycling techniques, the industry can minimize the energy consumption and environmental impact of the recycling process, further enhancing its sustainability.
Moreover, recycling EV batteries can contribute to a circular economy, where resources are reused and recycled, reducing the strain on finite resources. This approach encourages the development of a robust recycling infrastructure, creating jobs and fostering innovation in the recycling sector. As the demand for EVs grows, a well-established recycling industry can ensure that the necessary materials are readily available for new battery production, reducing the reliance on virgin resources.
In addition to environmental and economic benefits, recycling EV batteries can also have a positive impact on the second-life applications of the recovered materials. Some used EV batteries may not be suitable for high-performance vehicles but can still find value in other sectors. For instance, they can be utilized in energy storage systems for renewable energy integration or in less demanding applications like electric scooters or backup power systems. This extends the lifespan of the batteries and reduces the need for constant production of new ones, further lowering the overall carbon footprint.
In summary, the recycling potential of EV batteries is a key component in maximizing the environmental and economic benefits of electric vehicles. It allows for the efficient recovery of valuable materials, reduces the carbon footprint associated with battery production, and promotes a circular economy. As the EV market expands, investing in and optimizing recycling processes will be essential to ensure a sustainable and responsible approach to managing the growing number of EV batteries.
Unveiling the Secrets of Electric Vehicles: A Beginner's Guide
You may want to see also

Lifetime Emissions: Total emissions over an EV's lifespan
The concept of lifetime emissions is crucial when evaluating the environmental impact of electric vehicles (EVs). It refers to the total greenhouse gas emissions generated throughout the entire lifecycle of an EV, from its production to disposal or recycling. This comprehensive view is essential to understanding the true environmental benefits of EVs compared to traditional internal combustion engine vehicles.
The production phase of an EV contributes significantly to its carbon footprint. Manufacturing processes, including the extraction of raw materials, battery cell production, and assembly, require substantial energy and often rely on fossil fuels. For instance, the production of lithium-ion batteries, a common type used in EVs, involves energy-intensive processes that can result in higher emissions. However, it's important to note that as the demand for EVs increases, manufacturers are investing in more sustainable production methods, and the overall emissions from manufacturing can decrease over time.
The operation of an EV is where it truly shines in terms of reducing lifetime emissions. Unlike conventional vehicles, EVs produce zero tailpipe emissions during driving, which means no direct release of harmful pollutants or greenhouse gases. This is a significant advantage, especially in urban areas where air quality is a concern. The electricity used to power EVs can also come from renewable sources, further reducing their environmental impact. As the grid becomes cleaner over time, the carbon footprint of driving an EV decreases, making it an increasingly attractive option for environmentally conscious consumers.
The end-of-life stage of an EV's lifecycle is another critical aspect to consider. Proper disposal and recycling of EV batteries are essential to minimize environmental harm. While the recycling process can be energy-intensive, it is still more environmentally friendly than disposing of batteries in landfills. Many countries and manufacturers are implementing recycling programs to ensure that EV batteries are handled responsibly, extracting valuable materials and reducing the need for new resource extraction.
In summary, the lifetime emissions of an electric vehicle encompass various stages, from production to end-of-life. While the manufacturing process may initially contribute to higher emissions, the operational phase of an EV offers significant environmental benefits. With the potential for cleaner energy sources and efficient recycling practices, the overall carbon footprint of EVs is expected to decrease, making them a more sustainable transportation option in the long term. Understanding these lifetime emissions is vital for consumers and policymakers to make informed decisions and further promote the adoption of electric mobility.
Navigating California's EV Battery Warranty: A Step-by-Step Guide to Filing a Complaint
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The carbon footprint of an EV refers to the total greenhouse gas emissions, primarily carbon dioxide (CO2), associated with its entire lifecycle, from production to disposal. EVs are considered more environmentally friendly than traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles because they produce zero tailpipe emissions during operation. However, the carbon footprint of an EV can vary depending on the source of electricity used to charge it.
Manufacturing EVs, especially those with lithium-ion batteries, requires significant energy and resources, which can result in higher emissions. The production process involves mining for raw materials, manufacturing components, and assembling the vehicle. While the exact emissions vary by model and region, studies suggest that the production of an EV can contribute to a larger carbon footprint compared to a conventional car, but this impact is often offset by the reduced emissions over the vehicle's lifetime.
Absolutely. The carbon footprint of an EV is highly dependent on the electricity grid used for charging. Regions with a higher proportion of renewable energy sources, such as wind, solar, or hydropower, have a lower carbon footprint for EV charging. In contrast, areas reliant on coal or natural gas for electricity generation will result in higher emissions. It's essential for EV owners to consider the environmental benefits of their vehicle when charged with clean energy.
Yes, driving an EV can significantly reduce your carbon footprint compared to a conventional vehicle. EVs produce zero tailpipe emissions, which means no direct release of harmful pollutants or greenhouse gases during operation. Over the vehicle's lifetime, the reduced emissions from manufacturing and the lower carbon intensity of electricity can lead to substantial environmental benefits. However, the overall impact depends on various factors, including the vehicle's efficiency, battery production, and the local energy mix.