The production of electric vehicles (EVs) is a rapidly growing industry, and understanding the average costs associated with manufacturing these vehicles is crucial for investors, policymakers, and consumers alike. The industry average to produce an electric vehicle encompasses various factors, including research and development, component sourcing, assembly, and regulatory compliance. This analysis aims to explore the financial and operational aspects that contribute to the overall cost structure of EV production, shedding light on the factors that influence the industry's average production expenses. By examining these elements, we can gain insights into the economic landscape of the EV market and its potential for future growth and innovation.
What You'll Learn
- Battery Technology: Cost, efficiency, and performance of battery packs
- Manufacturing Processes: Assembly, automation, and labor costs
- Raw Materials: Availability and pricing of key materials like lithium
- Infrastructure: Charging stations, battery recycling, and supply chain logistics
- Market Dynamics: Sales, pricing, and consumer adoption trends

Battery Technology: Cost, efficiency, and performance of battery packs
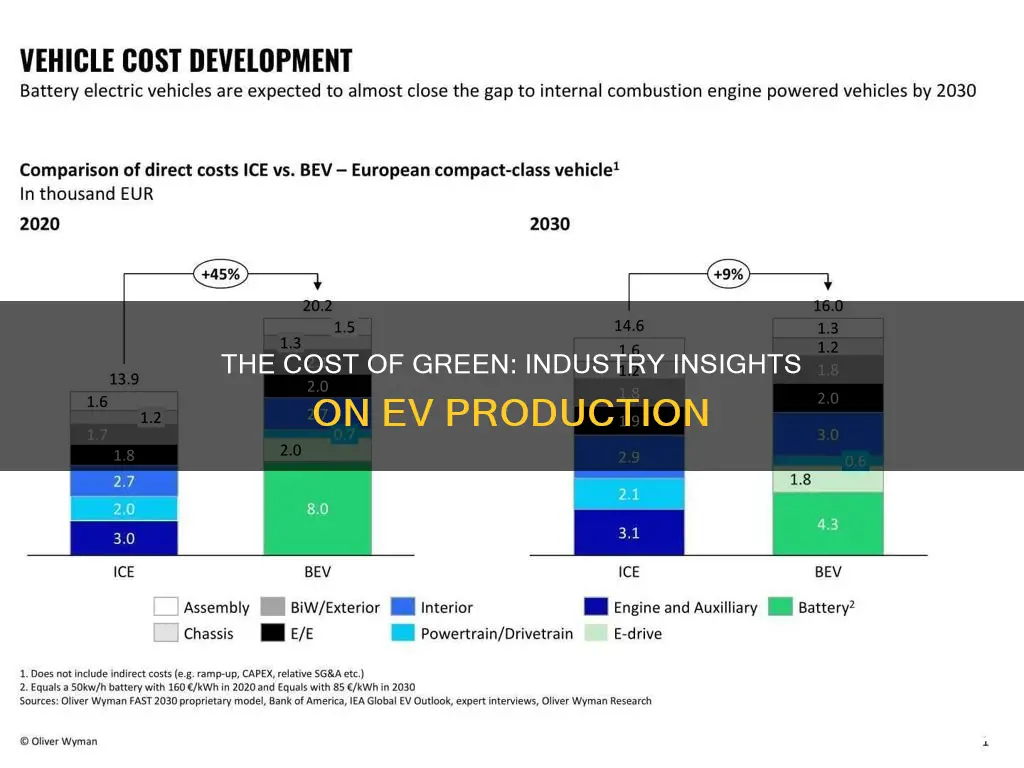
The cost, efficiency, and performance of battery packs are critical factors in the production of electric vehicles (EVs), as they directly impact the overall cost, range, and performance of the vehicle. The industry average for battery production costs has been steadily decreasing over the years due to technological advancements and economies of scale. As of 2023, the average cost of a lithium-ion battery pack for an EV is estimated to be around $150-200 per kWh, with some high-end models reaching over $300 per kWh. This cost includes the battery cells, BMS (Battery Management System), and other supporting components.
Efficiency is another crucial aspect, as it determines how much energy the battery can store and deliver. The industry standard for battery efficiency is typically around 90-95%, with some advanced packs achieving over 98% efficiency. This means that 90-95% of the energy stored in the battery is actually usable, with the remaining 5-10% lost as heat during charging and discharging processes. Higher efficiency batteries not only improve the range of the EV but also reduce the time required for charging.
Performance-wise, battery packs are evaluated based on their power output, cycle life, and temperature performance. Power output is measured in kW and determines how quickly the battery can deliver energy to the vehicle's motor. Higher power output batteries are desirable for sports cars and high-performance EVs. Cycle life refers to the number of times a battery can be charged and discharged before its capacity significantly degrades. Modern lithium-ion batteries can typically withstand around 1,000-3,000 cycles, with some advanced packs designed for over 5,000 cycles. Temperature performance is crucial, as batteries operate optimally within a specific temperature range. Overheating can reduce efficiency and performance, while extreme cold can limit the battery's ability to deliver power.
The development of battery technology is an ongoing process, with manufacturers constantly striving to improve cost, efficiency, and performance. Solid-state batteries, for example, are being researched as a potential replacement for lithium-ion, offering higher energy density and improved safety. Additionally, advancements in battery chemistry, such as lithium-sulfur and lithium-air batteries, could significantly reduce costs and increase range in the future.
In summary, the industry average for battery production in EVs is focused on achieving a balance between cost, efficiency, and performance. While costs have been decreasing, efficiency and performance continue to be key areas of innovation. As battery technology advances, we can expect to see more affordable, efficient, and high-performing EV batteries, contributing to the widespread adoption of electric vehicles.
Electric Vehicles: Powering Progress Without Neet
You may want to see also

Manufacturing Processes: Assembly, automation, and labor costs
The production of electric vehicles (EVs) involves a complex assembly process that requires a combination of manual labor, automated machinery, and strategic planning to achieve efficiency and cost-effectiveness. The industry average to produce an EV can vary significantly depending on the manufacturer, the specific model, and the production volume. However, understanding the key manufacturing processes and their associated costs is essential to grasp the overall economics of EV production.
Assembly is a critical phase in EV manufacturing, where individual components are brought together to create the final product. This process typically involves a highly organized and specialized workforce. Skilled technicians and engineers play a vital role in ensuring that each vehicle is assembled according to precise specifications. The assembly line is designed to handle various tasks, including the installation of the battery pack, electric motor, wiring harnesses, and other electronic components. Manual labor is often required for intricate tasks, such as soldering and fine-tuning, which demand a high level of precision.
Automation has become increasingly prevalent in EV assembly to improve efficiency and reduce labor costs. Robotic arms and automated machinery are utilized for repetitive tasks, such as welding, painting, and the assembly of certain components. Automation can significantly speed up the production process, reduce human error, and improve overall quality control. However, the initial investment in automated equipment can be substantial, and regular maintenance is necessary to ensure optimal performance. The industry trend is towards a hybrid approach, where automation handles repetitive tasks, and skilled labor focuses on more complex, value-added activities.
Labor costs are a significant factor in EV production, and the industry average can vary based on regional labor markets and manufacturing strategies. In regions with a high cost of living and skilled labor, production costs tend to be higher. Conversely, areas with lower labor costs may offer advantages in terms of production expenses. The labor force in EV manufacturing includes not only assembly line workers but also engineers, quality control specialists, and researchers. The industry is increasingly focusing on upskilling and reskilling the workforce to adapt to the evolving nature of EV production, which demands a blend of technical and specialized skills.
Optimizing assembly processes and labor allocation is crucial for achieving industry-average production costs. This involves careful planning, including the design of efficient assembly lines, the implementation of just-in-time inventory management, and the strategic placement of labor resources. Manufacturers are also exploring modular assembly techniques, where different vehicle configurations can be produced on the same production line, further enhancing efficiency. Additionally, the use of advanced software and data analytics can help identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies, allowing for continuous improvement in manufacturing processes.
Deadhead Miles: The Hidden Cost of Electric Vehicle Ownership
You may want to see also

Raw Materials: Availability and pricing of key materials like lithium
The production of electric vehicles (EVs) relies heavily on specific raw materials, with lithium being one of the most critical. Its demand has surged due to the growing popularity of EVs, and its availability and pricing are key factors influencing the overall cost and competitiveness of EV manufacturing.
Lithium is a crucial component in the production of lithium-ion batteries, which power most electric vehicles. These batteries store energy and provide the necessary range and performance for EVs. The availability of lithium is a significant concern, as it is a finite resource, and its extraction and processing can be environmentally challenging. The primary sources of lithium include hard-rock mining and brine extraction from natural deposits. While hard-rock mining has been the traditional method, brine extraction, often associated with solar evaporation ponds, is gaining traction due to its lower environmental impact and higher efficiency.
The pricing of lithium is volatile and subject to market dynamics. The cost of lithium has been on a steady rise due to increasing demand and limited supply. This trend is expected to continue as the EV market expands. The pricing volatility can be attributed to various factors, including the complexity of lithium extraction processes, the geographical distribution of reserves, and the varying costs associated with different extraction methods. For instance, lithium hydroxide, a common form used in battery production, has seen significant price fluctuations, impacting the overall production costs of EVs.
To ensure a stable supply of lithium, manufacturers and governments are exploring strategies such as recycling lithium-ion batteries and developing new, more efficient extraction methods. Recycling programs can help recover lithium from end-of-life batteries, reducing the need for primary extraction. Additionally, research and development efforts are focused on improving the efficiency of lithium extraction processes, which could lead to more cost-effective production.
In summary, the availability and pricing of lithium are critical aspects of the EV production industry. The finite nature of lithium and the increasing demand from the EV market have led to a focus on sustainable extraction methods and recycling. As the industry continues to evolve, addressing these raw material challenges will be essential to maintaining the competitiveness and sustainability of electric vehicle manufacturing.
Unraveling the Mystery: Hyundai's Electric Vehicle Credit
You may want to see also

Infrastructure: Charging stations, battery recycling, and supply chain logistics
The production of electric vehicles (EVs) is a complex process that relies heavily on robust infrastructure to support the entire lifecycle of these vehicles, from manufacturing to disposal. Three critical components of this infrastructure are charging stations, battery recycling, and supply chain logistics.
Charging Stations:
The widespread adoption of EVs is closely tied to the availability of convenient and efficient charging infrastructure. Charging stations play a pivotal role in this regard. The industry standard for charging stations varies depending on the region and the specific EV model. However, a common goal is to provide fast and efficient charging options to reduce the time required to recharge an EV battery. Rapid charging stations, capable of replenishing a battery's charge in under an hour, are becoming increasingly common, especially along major highways and in urban areas. These stations often utilize advanced technologies like direct current (DC) fast charging, which can significantly reduce charging times compared to alternating current (AC) charging.
The placement of charging stations is strategic, aiming to cover long distances and provide multiple options for EV owners. This includes installing stations at rest stops, shopping malls, parking lots, and even residential areas. The industry is also exploring innovative solutions, such as wireless charging technology, which eliminates the need for physical cables and connectors, making the charging process more convenient and user-friendly.
Battery Recycling:
As the demand for EVs grows, so does the importance of sustainable battery recycling practices. Electric vehicle batteries, typically lithium-ion, contain valuable materials that can be recycled and reused. The recycling process involves several stages, including collecting used batteries, disassembling them, and separating the various components. The industry standard for battery recycling aims to minimize environmental impact and maximize resource recovery.
One key aspect of battery recycling is the development of efficient and environmentally friendly processes to recover materials like lithium, cobalt, nickel, and manganese. These materials can be reused in new batteries or other products, reducing the need for mining and minimizing the environmental footprint of the EV industry. Additionally, proper recycling ensures that hazardous materials are handled safely, preventing potential environmental and health risks.
Supply Chain Logistics:
The supply chain logistics for EV production involve a complex network of suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors. Efficient logistics are crucial to ensure timely delivery of raw materials, components, and finished vehicles. The industry average for supply chain efficiency is continually improving, with a focus on reducing lead times and optimizing transportation routes.
Advanced supply chain management techniques, such as just-in-time inventory and lean manufacturing principles, are employed to minimize waste and maximize productivity. This includes streamlining the flow of materials and components, ensuring that they arrive at manufacturing facilities when needed, and reducing storage costs. Additionally, the industry is exploring the use of electric and sustainable transportation methods to further reduce the environmental impact of the supply chain.
In summary, the production of electric vehicles requires a robust infrastructure that includes charging stations, battery recycling facilities, and efficient supply chain logistics. These components work together to support the widespread adoption of EVs, ensuring convenience, sustainability, and reliability throughout the vehicle's lifecycle.
Understanding Drive Cycles: The Key to Electric Vehicle Efficiency
You may want to see also

Market Dynamics: Sales, pricing, and consumer adoption trends
The electric vehicle (EV) market has experienced significant growth and transformation in recent years, driven by technological advancements, environmental concerns, and supportive government policies. This shift in the automotive industry has led to a dynamic landscape where sales, pricing, and consumer adoption trends are evolving rapidly.
Sales and Market Growth:
The sales of electric vehicles have witnessed a remarkable surge globally. According to industry reports, the EV market has been expanding at an impressive rate, with sales volumes increasing year over year. This growth is attributed to several factors. Firstly, the rising demand for sustainable transportation options has made EVs more appealing to consumers. Governments and environmental organizations worldwide have promoted the adoption of electric cars through incentives, subsidies, and awareness campaigns, encouraging consumers to make the switch. Secondly, the continuous improvement in battery technology has addressed range anxiety, a significant concern for potential EV buyers. Modern electric vehicles now offer competitive driving ranges, making them a viable alternative to traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) cars. As a result, major automotive manufacturers have increased their EV production and sales, leading to a diverse range of models available in the market.
Pricing and Cost Considerations:
Pricing is a critical aspect of the EV market dynamics. Historically, electric vehicles have been positioned as premium products due to higher production costs and lower sales volumes. However, as the market matures and production scales up, economies of scale are driving down prices. The industry average production cost for electric vehicles has been steadily decreasing, making EVs more affordable for consumers. This trend is particularly evident in the mass-market segment, where several automotive brands now offer competitive electric car models at price points similar to their ICE counterparts. As a result, consumers are increasingly considering EVs as a practical and cost-effective choice, especially with the potential for long-term savings on fuel and maintenance.
Consumer Adoption Trends:
Consumer adoption of electric vehicles is being influenced by various factors, shaping the market's future. Firstly, the shift towards sustainability and environmental consciousness is a significant driver. Many consumers are actively seeking eco-friendly alternatives, and EVs align with this growing trend. Secondly, the availability of charging infrastructure is becoming a crucial consideration. Consumers are more inclined to adopt EVs when they have access to convenient charging stations, either at home or through public networks. Governments and private entities are investing in expanding charging infrastructure, addressing range-related concerns and making EVs more accessible. Lastly, the overall consumer experience and brand reputation play a vital role. Automotive manufacturers are focusing on delivering high-quality, reliable electric vehicles with advanced features, ensuring customer satisfaction and loyalty.
In summary, the electric vehicle industry is experiencing a rapid transformation, with sales volumes increasing, pricing becoming more competitive, and consumer adoption trends shifting towards sustainability and convenience. As the market continues to evolve, it is essential for manufacturers and policymakers to stay attuned to these dynamics to meet the growing demand for electric transportation solutions.
Electric Vehicles: The Missing Piece in Sustainable Transportation
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The industry average cost to produce an electric vehicle can vary significantly depending on several factors, including the vehicle's size, range, technology, and production volume. As of 2023, the estimated global average production cost for EVs ranges from $10,000 to $30,000 per vehicle. However, this range can be narrower for specific models. For instance, compact EVs with shorter ranges might have production costs closer to the lower end of this spectrum, while high-end luxury EVs with advanced features and longer ranges could fall towards the higher end.
The cost of producing electric vehicles has been steadily decreasing over the past decade due to technological advancements, economies of scale, and increased production volumes. In the early 2010s, the production cost of EVs was significantly higher, often exceeding $50,000. This was primarily due to the high cost of batteries and the relatively low production volumes. However, with the rise of mass-market EV models and the expansion of battery manufacturing, the costs have come down dramatically. Many EV manufacturers now aim to reach a breakeven point or even achieve profitability, especially with the growing demand for sustainable transportation.
Several factors can impact the production cost of an electric vehicle. Firstly, the type and size of the battery play a crucial role, as larger batteries with higher energy density are more expensive. Secondly, the complexity of the vehicle's design and the number of advanced features can influence production costs. For example, adding advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) or a more sophisticated infotainment system will increase the overall cost. Additionally, production volume and efficiency have a significant effect; higher production volumes and improved manufacturing processes can lead to lower per-unit costs.







