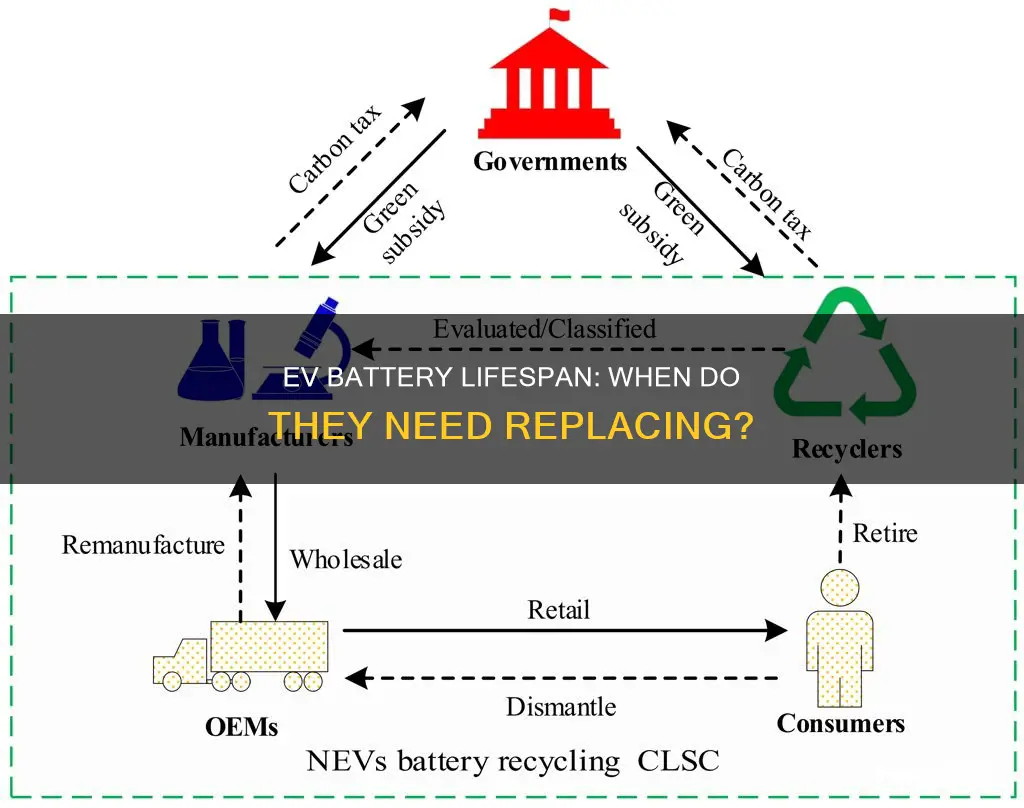
Electric vehicle batteries, a cornerstone of sustainable transportation, have a finite lifespan, and their end-of-life management is a critical aspect of the industry's sustainability. The retirement of these batteries, often referred to as end-of-life (EOL) batteries, is a complex process that involves assessing their remaining capacity, performance, and overall health. Typically, EV batteries are considered retired when they no longer meet the performance standards required for their intended use, often due to degradation from repeated charging and discharging cycles, physical damage, or reaching the end of their design lifespan. This retirement process is crucial for environmental and economic reasons, as it involves proper disposal or recycling to minimize the environmental impact and recover valuable materials.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Battery Life Expectancy | 8-10 years or 100,000-150,000 miles |
| Depends on Usage | More frequent charging and rapid charging can reduce battery lifespan |
| Climate Conditions | Extreme temperatures can impact battery performance and longevity |
| Battery Chemistry | Different chemistries (e.g., lithium-ion) have varying lifespans |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance and monitoring can extend battery life |
| Age | Batteries may degrade over time, even if not in use |
| State of Charge (SoC) | Keeping the battery at high SoC can accelerate degradation |
| Temperature Management | Efficient cooling systems can improve battery longevity |
| Charging Habits | Optimizing charging patterns can extend battery lifespan |
| Battery Capacity | Capacity loss is a natural process over time |
What You'll Learn
- Battery Degradation: When does battery capacity drop below acceptable levels
- Age and Mileage: How do age and usage impact battery lifespan
- Performance Decline: What causes a decline in battery performance over time
- End-of-Life Recycling: How are retired batteries recycled and what materials are recovered
- Second-Life Applications: Can retired batteries be used for other purposes after retirement

Battery Degradation: When does battery capacity drop below acceptable levels?
Battery degradation is a natural process that occurs over time in all rechargeable batteries, including those used in electric vehicles (EVs). This phenomenon is primarily driven by the chemical changes that take place within the battery cells during their operational life. As an EV battery ages, its capacity to store and release electrical energy efficiently decreases, leading to a reduction in overall performance. The question of when an EV battery's capacity drops below an acceptable level is crucial for determining when it needs to be retired or replaced.
The acceptable level of battery capacity can vary depending on the manufacturer's specifications and the intended use of the vehicle. For most EVs, a battery's capacity is considered degraded when it can no longer hold a charge at the same rate as when it was new. This is often measured in terms of percentage of the original capacity, with a common threshold being around 80% of the initial capacity. Below this threshold, the battery's performance may become noticeable to the driver, resulting in reduced range and potentially impacting the overall driving experience.
Several factors contribute to battery degradation. One significant factor is the number of charge-discharge cycles the battery undergoes. Each time the battery is fully charged and then discharged, the chemical reactions within the cells cause some irreversible changes, leading to capacity loss. Additionally, the frequency of charging and the charging habits can also play a role. For instance, frequently charging the battery to very high levels or leaving it in a fully discharged state for extended periods can accelerate degradation.
Environmental conditions also have a substantial impact on battery health. Extreme temperatures, both hot and cold, can accelerate degradation. High temperatures can cause increased internal resistance and faster chemical breakdown, while cold temperatures can reduce the battery's ability to deliver current efficiently. Furthermore, exposure to direct sunlight and extreme humidity can also negatively affect battery performance over time.
Understanding the signs of battery degradation is essential for EV owners. As the battery ages, you may notice a decrease in the vehicle's range, with the car needing to be recharged more frequently. The time required for a full charge may also increase, and the battery may not reach the same level of charge as it once did. Regular monitoring of these changes can help drivers make informed decisions about battery maintenance and replacement, ensuring they get the most out of their electric vehicles.
Electric Vehicle Tax Credit: Annual or One-Time?
You may want to see also

Age and Mileage: How do age and usage impact battery lifespan?
The lifespan of an electric vehicle (EV) battery is influenced by various factors, with age and mileage being two of the most critical. As with any component, batteries degrade over time, and this degradation is accelerated by frequent use and exposure to environmental conditions. Understanding how these factors impact battery health is essential for EV owners and enthusiasts.
Age is a significant determinant of battery performance. Over time, the chemical reactions within the battery cells lead to a gradual loss of capacity. This means that as the battery ages, it can store less energy, resulting in reduced range. On average, EV batteries retain about 70-80% of their original capacity after 10 years of use. While this may still provide sufficient range for daily commutes, it highlights the importance of considering battery age when planning long-distance trips.
Mileage, or the number of miles driven, also plays a crucial role in battery lifespan. Higher mileage generally correlates with increased wear and tear on the battery. Frequent charging and discharging cycles, especially in extreme temperatures, can accelerate battery degradation. For instance, rapid charging, while convenient, can put additional strain on the battery, potentially reducing its overall lifespan. Similarly, driving in harsh weather conditions, such as extremely hot or cold climates, can impact battery performance and longevity.
The relationship between age and mileage is interdependent. As a battery ages, its ability to handle frequent charging and discharging cycles diminishes, making it more susceptible to mileage-related degradation. Conversely, high mileage can accelerate the aging process, leading to faster capacity loss. This interplay highlights the need for EV owners to strike a balance between regular use and proper maintenance to optimize battery health.
To maximize battery lifespan, EV owners should consider implementing certain practices. Regularly monitoring battery health and keeping it within an optimal temperature range can help. Avoiding rapid charging whenever possible and using slower charging methods can also contribute to longer battery life. Additionally, maintaining a consistent driving pattern and avoiding excessive speeding or aggressive driving can reduce the strain on the battery. By understanding the impact of age and mileage, EV owners can take proactive measures to ensure their batteries remain efficient and reliable over time.
Electric Vehicle Sales: The Top-Purchasing State Revealed
You may want to see also

Performance Decline: What causes a decline in battery performance over time?
The performance of electric vehicle (EV) batteries naturally degrades over time, and understanding the causes of this decline is crucial for managing EV battery health and longevity. Several factors contribute to the gradual reduction in battery capacity and overall performance.
One primary cause of performance decline is the chemical reactions within the battery itself. Over time, the electrochemical processes that facilitate the storage and release of energy can lead to the degradation of the battery's active materials. This degradation is often associated with the formation of solid-electrolyte interface (SEI) layers, which can hinder the movement of ions and electrons, thereby reducing the battery's efficiency. Additionally, the repeated charging and discharging cycles put stress on the battery's components, leading to structural changes and potential damage to the electrodes and electrolyte.
Environmental factors also play a significant role in battery performance decline. Extreme temperatures, both hot and cold, can accelerate degradation. High temperatures can cause increased internal resistance and thermal runaway, while cold temperatures can slow down the chemical reactions, reducing the battery's ability to deliver power efficiently. Moreover, exposure to moisture and humidity can lead to corrosion and the degradation of the battery's components, especially in the case of lithium-ion batteries.
The number of charge-discharge cycles is another critical factor. Each cycle causes a small amount of capacity loss, and over time, this cumulative effect can significantly reduce the battery's performance. The rate of capacity loss is often higher in the initial stages of a battery's life, and it gradually slows down as the battery ages. This phenomenon is known as 'calendar aging' and is a natural process that occurs regardless of the battery's usage.
Additionally, the way EV batteries are managed and operated can impact their performance. Over-charging and over-discharging can put unnecessary strain on the battery, leading to faster degradation. Maintaining the battery at a high state of charge for extended periods or allowing it to drop too low can also contribute to performance decline. Proper battery management systems and user practices, such as avoiding extreme charging habits, can help mitigate these issues.
In summary, the decline in EV battery performance is a multifaceted issue influenced by chemical reactions, environmental factors, the number of charge-discharge cycles, and operational practices. Understanding these causes is essential for developing strategies to optimize battery health, extend their lifespan, and ensure reliable performance throughout the EV's lifetime.
The Future is Electric: Is Now the Time to Buy?
You may want to see also

End-of-Life Recycling: How are retired batteries recycled and what materials are recovered?
The retirement of electric vehicle (EV) batteries is a critical aspect of the EV lifecycle, ensuring that these valuable resources are managed sustainably and efficiently. When EV batteries reach the end of their useful life, they are considered retired and are subject to a specialized recycling process. This process is designed to recover valuable materials and minimize environmental impact.
The recycling process for retired EV batteries typically begins with the safe transportation of the batteries to a specialized recycling facility. These facilities are equipped to handle the unique challenges posed by EV batteries, including their size, weight, and potential chemical hazards. Upon arrival, the batteries undergo a series of meticulous steps to extract valuable materials.
One of the primary methods used in EV battery recycling is hydrometallurgy. This process involves dissolving the battery's components in a chemical solution to separate and recover metals. For instance, the lithium-ion batteries commonly used in EVs can be processed to extract lithium, cobalt, nickel, and manganese. These metals are then refined and purified to meet the standards required for reuse in various industries. For example, lithium can be recycled and used in new batteries or other applications, such as glass production. Cobalt, a critical component in the cathode material, can be recovered and utilized in the manufacturing of new batteries or other high-tech products.
Mechanical processing is another crucial technique in EV battery recycling. This method involves physically breaking down the batteries into their constituent parts. The process starts with shredding the batteries to reduce their size and facilitate further processing. The shredded material is then sorted using advanced separation techniques, such as eddy current separators and magnetic separators, to separate different types of metals and plastics. This mechanical separation ensures that valuable materials are recovered while minimizing the environmental impact of the recycling process.
After the initial separation, the recovered materials undergo further processing to extract the highest quality resources. For instance, the separated metals are sent to specialized smelters where they are melted and refined to produce high-purity metals. These metals can then be reused in various industries, including the production of new batteries, steel manufacturing, and electronics. The plastics and other non-metallic materials are also recycled and repurposed, ensuring that as much of the battery as possible is utilized.
In summary, the end-of-life recycling of EV batteries is a complex but essential process. It involves a combination of hydrometallurgy and mechanical processing to recover valuable materials such as lithium, cobalt, nickel, and manganese. These recovered resources can be reused in various industries, contributing to a circular economy and reducing the environmental impact of EV battery production. As the demand for EVs continues to grow, efficient and sustainable recycling methods will play a pivotal role in ensuring a steady supply of raw materials for the manufacturing of new batteries and other products.
Government Incentives: Accelerating the Shift to Electric Vehicles
You may want to see also

Second-Life Applications: Can retired batteries be used for other purposes after retirement?
The concept of "second-life applications" for retired electric vehicle (EV) batteries is an innovative approach to sustainability and resource management. As the demand for electric mobility grows, so does the need to address the end-of-life management of EV batteries. These batteries, once they can no longer power vehicles due to performance degradation, can still retain a significant amount of their original capacity and can be utilized for other purposes, extending their useful life.
One of the primary second-life applications for retired EV batteries is energy storage systems. These batteries can be integrated into larger energy storage units, providing a reliable and efficient way to store excess energy generated from renewable sources like solar and wind power. During periods of high energy production, the batteries can absorb and store this excess energy, and then discharge it when demand is high or when renewable sources are less productive. This application is particularly valuable for grid stabilization and supporting the integration of intermittent renewable energy sources into the power grid.
Another potential use for retired EV batteries is in the field of stationary energy storage. These batteries can be deployed in data centers, commercial buildings, or even residential settings to provide backup power during outages or to support energy-intensive operations. By utilizing retired EV batteries, businesses and homeowners can ensure a more sustainable and cost-effective power supply, reducing their reliance on traditional grid electricity.
Furthermore, retired EV batteries can be employed in off-grid applications, especially in remote areas or developing regions. These batteries can power remote monitoring systems, telecommunications infrastructure, or even small communities, providing a reliable and environmentally friendly energy source. This application promotes energy independence and can be particularly beneficial for disaster-prone areas or regions with limited access to the main power grid.
In addition to energy storage, retired EV batteries can also be considered for other innovative uses. Researchers are exploring the possibility of using these batteries in heating and cooling systems, where the stored thermal energy can be utilized for space heating or water heating. Additionally, the batteries' structural design and materials can be studied for potential reuse in construction or manufacturing, contributing to a circular economy.
In summary, the concept of second-life applications for retired EV batteries offers a promising solution to the growing environmental and resource management challenges associated with EV battery disposal. By repurposing these batteries for energy storage, stationary power, off-grid solutions, and potentially other innovative uses, we can extend their lifespan, reduce waste, and contribute to a more sustainable and resilient energy infrastructure. As the EV market continues to expand, exploring and implementing these second-life applications will be crucial in maximizing the benefits of electric mobility while minimizing its environmental impact.
Unlock Savings: Florida's EV Tax Credit Explained
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Electric vehicle batteries typically have a lifespan of around 8 to 10 years, depending on various factors such as usage, environmental conditions, and maintenance. Over time, the battery's capacity to store and deliver energy decreases, and it may no longer meet the performance and range requirements of the vehicle. This is when the battery is considered retired or end-of-life.
Several factors contribute to the retirement of an electric vehicle battery. These include the number of charge-discharge cycles, which is the total number of times the battery has been fully charged and discharged. Extreme temperatures, both hot and cold, can also impact battery health. Additionally, the overall condition of the battery, including any physical damage or internal degradation, plays a significant role in determining its retirement.
Proper disposal and recycling of retired electric vehicle batteries is crucial for environmental sustainability. When a battery is no longer usable, it should be sent to specialized recycling facilities. These facilities use advanced processes to recover valuable materials like lithium, cobalt, and nickel, which can be reused in new batteries or other products. Recycling helps reduce the environmental impact of battery disposal and ensures that valuable resources are conserved for future use.