Electric vehicles (EVs) rely on advanced battery technology to power their electric motors, and understanding the types of batteries used is crucial for optimizing performance and sustainability. The most common type of battery in EVs is the lithium-ion battery, which has become the industry standard due to its high energy density, lightweight design, and long cycle life. These batteries store electrical energy in the form of lithium ions that move between the anode and cathode during charging and discharging, allowing for efficient energy storage and release. However, the automotive industry is also exploring other battery technologies, such as solid-state batteries and nickel-metal hydride (NiMH) batteries, to enhance performance and address the challenges of lithium-ion batteries, including range anxiety and the need for faster charging.
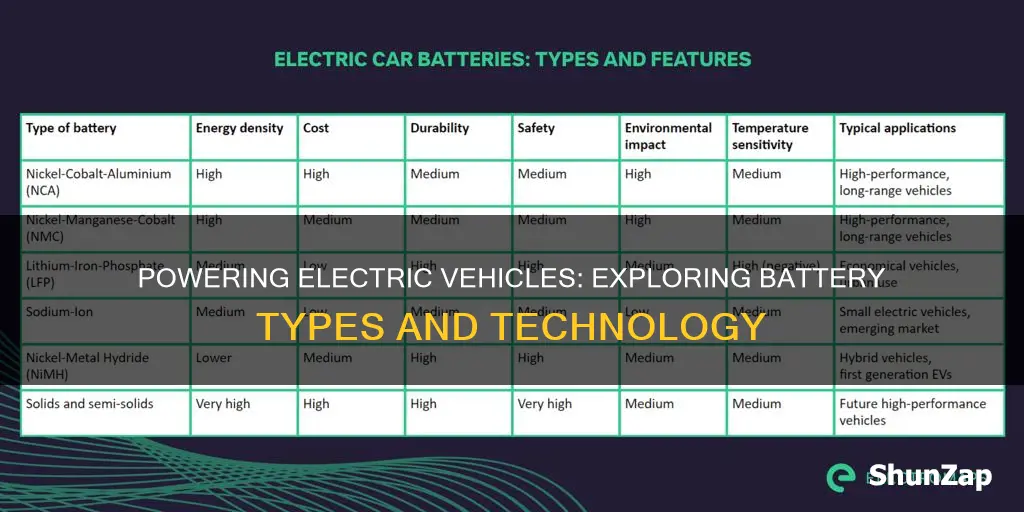
Battery Characteristics in Electric Vehicles
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Type | Lithium-ion (Li-ion) |
| Chemistry | Various, including lithium cobalt oxide (LCO), lithium nickel manganese cobalt (NMC), and lithium iron phosphate (LFP) |
| Energy Density | High, typically around 200-300 Wh/kg |
| Voltage | 3.7-4.2 V per cell (for Li-ion) |
| Capacity | Varies widely, typically 30-100 kWh for passenger cars, up to 100 kWh or more for larger EVs |
| Cycle Life | 1000-2000 cycles (80% DOD) or more, depending on usage and technology |
| Operating Temperature | Typically -20°C to 60°C (-4°F to 140°F) |
| Self-Discharge | Low, around 2-5% per month at room temperature |
| Safety | Designed with multiple safety mechanisms, including thermal runaway protection |
| Weight | Light, typically 100-300 kg per pack, depending on capacity and vehicle size |
| Size | Various, often compact and optimized for vehicle design |
| Charging Speed | Fast charging possible, with 0-80% in under an hour using DC fast charging |
| Cost | Decreasing, but still a significant factor in EV pricing |
| Environmental Impact | Generally lower than traditional internal combustion engine vehicles due to reduced emissions |
What You'll Learn
- Battery Chemistry: Lithium-ion dominance, with variations like nickel-cobalt-manganese
- Energy Density: High energy density for efficient range
- Charging Technology: Fast charging, wireless, and battery swapping methods
- Battery Management Systems: Monitoring and optimizing battery health and performance
- Recycling and Sustainability: Recycling processes and environmental impact of EV batteries

Battery Chemistry: Lithium-ion dominance, with variations like nickel-cobalt-manganese
The world of electric vehicles (EVs) relies heavily on advanced battery technology to power their operations. Among the various battery chemistries, lithium-ion batteries have emerged as the dominant choice for EVs, offering a combination of high energy density, long cycle life, and relatively low self-discharge rates. This dominance is primarily due to the unique properties of lithium, which allows for efficient energy storage and release.
Lithium-ion batteries consist of several key components, including an anode, a cathode, a separator, and an electrolyte. The anode is typically made of carbon, which can store lithium ions during charging. The cathode, on the other hand, is where the chemical reactions occur, and it is often composed of a blend of materials, such as nickel, cobalt, and manganese (NMC). These materials are chosen for their ability to facilitate the movement of lithium ions and electrons, enabling the battery to store and release energy efficiently.
The NMC chemistry is a popular variation in EV batteries. It offers a balance of performance and cost-effectiveness. Nickel, cobalt, and manganese are combined in specific ratios to create different NMC blends, each with its own set of advantages. For instance, a higher nickel content can enhance energy density, making the battery more compact and lightweight. However, it may also increase the cost and reduce the battery's thermal stability. Cobalt, known for its high melting point and excellent conductivity, contributes to the overall stability and safety of the battery. Manganese, with its low cost and high specific heat capacity, helps in maintaining the battery's performance over a wide temperature range.
The choice of NMC blend can significantly impact an EV's range, charging speed, and overall performance. Manufacturers often select specific NMC compositions to meet the requirements of their vehicles. For example, a high-nickel NMC blend might be used in high-performance EVs that demand rapid charging and extended range. In contrast, a more cost-effective blend with a higher cobalt content could be employed in mass-market EVs, providing a good balance between performance and affordability.
In summary, lithium-ion batteries, particularly those with nickel-cobalt-manganese chemistries, are the cornerstone of electric vehicle technology. The careful selection of materials and their ratios allows manufacturers to tailor battery performance to the specific needs of different EV models. As research and development in battery chemistry continue, we can expect further improvements in energy density, charging efficiency, and safety, solidifying the dominance of lithium-ion technology in the EV market.
The Electric Revolution: Exploring the Current EV Landscape
You may want to see also

Energy Density: High energy density for efficient range
The energy density of a battery is a critical factor in determining the range and performance of electric vehicles (EVs). High energy density means that a battery can store a significant amount of energy in a relatively small and lightweight package, allowing EVs to travel longer distances on a single charge. This is a key differentiator for electric vehicles compared to traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) cars, as it addresses one of the primary concerns of potential EV buyers: range anxiety.
Energy density is typically measured in watt-hours per liter (Wh/L) or watt-hours per kilogram (Wh/kg). The higher the energy density, the more energy the battery can store, and the longer the vehicle can travel without needing to recharge. For example, lithium-ion batteries, which are commonly used in EVs, have an energy density of around 150-250 Wh/kg, while some advanced lithium-ion chemistries can achieve densities of over 300 Wh/kg. This higher energy density translates to a longer driving range, making it possible for EVs to compete with conventional vehicles in terms of usability.
The concept of energy density is closely tied to the physical size and weight of the battery. A battery with high energy density can be designed to be smaller and lighter, which is essential for optimizing the overall weight distribution in an EV. This is particularly important in high-performance electric vehicles, where the weight of the battery pack can significantly impact acceleration, handling, and overall driving dynamics. By maximizing energy density, engineers can fit larger battery packs into smaller spaces, allowing for more efficient use of the vehicle's interior and exterior dimensions.
Furthermore, high energy density batteries enable the development of fast-charging technologies. When a battery has a higher energy density, it can store more energy in a shorter period, reducing the time required to recharge. This is a significant advantage for EV owners, as it provides more flexibility and convenience in their daily driving routines. Fast-charging stations are becoming increasingly common, and with high energy density batteries, the time spent charging can be significantly reduced, making the EV experience more comparable to that of a conventional car.
In summary, high energy density is a crucial aspect of battery technology in electric vehicles, enabling longer ranges, improved performance, and faster charging times. As battery technology continues to advance, we can expect to see even more impressive energy densities, further enhancing the appeal and practicality of electric vehicles in the automotive market. This development is essential to address the range limitations of early EVs and to make electric mobility a more viable and attractive option for the general public.
Exploring the World of Non-GamePass Electric Vehicles: A Comprehensive Guide
You may want to see also

Charging Technology: Fast charging, wireless, and battery swapping methods
The evolution of electric vehicle (EV) technology has led to significant advancements in charging methods, offering faster, more convenient, and innovative ways to power up these vehicles. This is crucial as the demand for EVs continues to rise, and efficient charging infrastructure becomes essential to support their widespread adoption. Here's an overview of the various charging technologies:
Fast Charging: One of the most significant improvements in EV charging is the development of fast-charging stations. These stations utilize advanced power electronics and high-voltage direct current (DC) to rapidly replenish the battery. Fast chargers can provide a substantial charge in a short time, often reducing charging times from hours to just minutes. The technology behind fast charging involves high-power AC (alternating current) or DC power sources, which can deliver up to 350 kW or more. This rapid charging capability is made possible by the use of specialized connectors and cables that can handle the high currents. Fast-charging stations are typically found along highways and in urban areas, providing a quick boost of power for long-distance travel or when time is limited.
Wireless Charging: Wireless charging technology, also known as inductive charging, is an emerging trend in EV charging. This method eliminates the need for physical cables and connectors, offering a convenient and potentially faster charging experience. Wireless charging stations use electromagnetic fields to transfer energy between a charging pad or station and a receiver installed in the vehicle. The process involves placing the vehicle over the charging pad, which then induces an electric current in the vehicle's battery. While wireless charging is still in its development phase, it has the potential to revolutionize the way EVs are charged, making the process more user-friendly and efficient.
Battery Swapping: Battery swapping is a unique and innovative approach to charging, where depleted batteries are exchanged for fully charged ones at specialized stations. This method is particularly useful for commercial fleets and ride-sharing services, ensuring that vehicles are always ready for use. Battery-swapping stations are equipped with robotic arms that automatically remove the depleted battery and insert a fully charged one. This technology reduces downtime significantly, as the process can be completed within minutes. Battery swapping is an efficient solution for managing battery life and availability, especially in scenarios where vehicles need to be constantly operational.
These charging technologies are designed to address the challenges of EV ownership, such as range anxiety and long charging times. Fast charging stations provide a quick solution for long-distance travel, while wireless charging and battery swapping aim to make the charging process more accessible and user-friendly. As EV technology advances, the integration of these charging methods will play a vital role in shaping the future of sustainable transportation.
Honda's Electric Revolution: Unveiling the Quiet Power
You may want to see also

Battery Management Systems: Monitoring and optimizing battery health and performance
Battery Management Systems (BMS) are integral to the efficient and safe operation of electric vehicles (EVs). These systems play a critical role in monitoring and optimizing the performance and health of the batteries that power EVs. The primary function of a BMS is to ensure that the battery pack operates within safe and optimal parameters, maximizing its lifespan and efficiency.
At its core, a BMS is a sophisticated electronic control unit designed to manage the complex interplay of various battery cells. It does this by continuously monitoring and controlling several key aspects. Firstly, it measures the state of charge (SOC) and state of health (SOH) of each cell, providing an accurate representation of the battery's current condition. This data is crucial for determining the battery's remaining capacity, performance, and overall health. By tracking these parameters, the BMS can predict potential issues and optimize charging and discharging cycles.
One of the critical tasks of a BMS is to prevent over-charging and over-discharging, which can significantly damage the battery. It achieves this by implementing precise control algorithms that regulate the charging and discharging rates. For instance, during charging, the BMS ensures that the battery is not overcharged by monitoring the voltage and current levels. Similarly, when discharging, it prevents deep discharge by controlling the voltage and current to maintain the battery within safe operating limits. This optimization process helps extend the battery's lifespan and ensures consistent performance.
In addition to monitoring and controlling charging and discharging, BMS also plays a vital role in temperature management. Battery performance and longevity are significantly influenced by temperature. Therefore, BMS continuously monitors the temperature of each cell and the overall battery pack. If the temperature deviates from the optimal range, the system can activate cooling or heating mechanisms to maintain the ideal operating temperature. This temperature control is essential for optimizing performance and safety, especially in extreme weather conditions.
Furthermore, BMS provides valuable data and insights to EV manufacturers and users. It records and analyzes various parameters, including current, voltage, temperature, and time. This data can be used to identify patterns, predict battery behavior, and optimize the overall EV system. For instance, manufacturers can use this information to design more efficient charging infrastructure or to develop strategies for battery replacement and recycling. For EV owners, the BMS provides real-time feedback on battery health, allowing them to make informed decisions about their vehicle's maintenance and usage.
In summary, Battery Management Systems are essential components of electric vehicles, ensuring the safe and efficient operation of battery packs. Through continuous monitoring and optimization, BMS enhances battery health, performance, and longevity. Its ability to manage charging, discharging, and temperature control, while also providing valuable data, contributes to the overall reliability and sustainability of EVs. As technology advances, BMS will continue to play a pivotal role in the widespread adoption and success of electric vehicles.
Unveiling the Green Myth: Is the Toyota Prius an Electric Car?
You may want to see also

Recycling and Sustainability: Recycling processes and environmental impact of EV batteries
The recycling and sustainability of electric vehicle (EV) batteries is a critical aspect of the EV industry's long-term viability and environmental impact. As the demand for EVs grows, so does the need for efficient and eco-friendly methods to handle their batteries at the end of their lifespan. The types of batteries used in EVs vary, but the most common are lithium-ion batteries, which are known for their high energy density and efficiency. These batteries are a key component in the success of EVs, but their disposal and recycling present unique challenges.
Recycling processes for EV batteries are designed to recover valuable materials and minimize environmental harm. The process typically begins with the safe disassembly of the battery pack, ensuring that any hazardous materials are contained and managed appropriately. Lithium-ion batteries contain various metals, including lithium, cobalt, nickel, and manganese, which can be recycled and reused. The recycling process often involves several stages: first, the battery cells are shredded to release the internal components, then the shredded material is processed to separate the different metals. This separation is crucial as it allows for the recovery of high-purity metals, which can be used in the production of new batteries or other products.
One of the key environmental benefits of recycling EV batteries is the reduction of waste. Many traditional batteries contain heavy metals and toxic chemicals, which, if not properly managed, can leach into the environment, causing soil and water contamination. By recycling, these hazardous materials can be safely contained and reused, significantly reducing the environmental footprint of the EV industry. Additionally, recycling helps conserve natural resources by providing an alternative source of metals, reducing the need for mining and the associated environmental degradation.
The sustainability of EV batteries also extends to the development of closed-loop recycling systems. This approach aims to create a continuous cycle where used batteries are collected, recycled, and transformed into new battery components. Such a system would minimize the reliance on virgin materials and ensure a steady supply of recycled materials for battery manufacturing. Several companies are already investing in and developing these closed-loop systems, which could revolutionize the way EV batteries are managed and recycled.
In conclusion, the recycling and sustainability of EV batteries are essential for the long-term success and environmental benefits of electric vehicles. The recycling process, while complex, is designed to recover valuable materials and minimize waste, ensuring that the EV industry can continue to grow while reducing its environmental impact. As the technology advances, the focus on sustainable practices will likely drive further innovations in battery recycling, making EVs an even greener and more sustainable transportation option.
The Evolution of the Milkman's Electric Vehicle: A Historical Perspective
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Electric vehicles primarily use lithium-ion batteries, which are known for their high energy density, lightweight design, and ability to provide high power output. These batteries have revolutionized the automotive industry and are a key component in making EVs a viable and popular transportation option.
Lithium-ion batteries store electrical energy through a chemical reaction between lithium ions and a host material, typically a transition metal oxide. When the vehicle is in use, these batteries release the stored energy as electricity, powering the electric motor and other components. The process involves the movement of lithium ions between the anode and cathode, facilitating the flow of current.
Lithium-ion batteries offer several benefits for electric vehicles. They provide a high energy-to-weight ratio, allowing for efficient power delivery. These batteries also have a low self-discharge rate, meaning they can retain their charge for extended periods when not in use. Additionally, lithium-ion technology has improved safety features, making it a reliable choice for powering EVs.
Yes, there are various types of lithium-ion chemistries used, such as NMC (Nickel-Manganese-Cobalt) and LFP (Lithium Iron Phosphate). NMC batteries offer a good balance of energy density and temperature stability, while LFP batteries are known for their safety and long cycle life. Each type has its own advantages and is chosen based on specific vehicle requirements.
The lifespan of EV batteries varies depending on several factors, including usage patterns, climate conditions, and maintenance. On average, a well-maintained lithium-ion battery pack can last between 8 to 15 years. Some manufacturers offer warranties that cover battery degradation, ensuring peace of mind for EV owners. Regular charging practices and avoiding extreme temperatures can contribute to prolonging the battery's lifespan.