Electric vehicles (EVs) are becoming increasingly popular, but what percentage of the total vehicle population on the road are electric? This question is crucial for understanding the current state of the automotive industry and predicting future trends. The adoption of electric cars has been growing rapidly, but the exact proportion of EVs on the road varies significantly by region and country. This paragraph aims to explore these variations and provide insights into the global shift towards electric mobility.
What You'll Learn
- Market Share: What percentage of new car sales are electric vehicles (EVs)
- Geographical Distribution: How do EV adoption rates vary by region
- Timeframe Analysis: What is the historical trend in EV market penetration
- Fuel Type Comparison: How do EVs compare to gasoline/diesel in terms of market share
- Consumer Preferences: What factors influence consumers' choice to buy electric cars

Market Share: What percentage of new car sales are electric vehicles (EVs)?
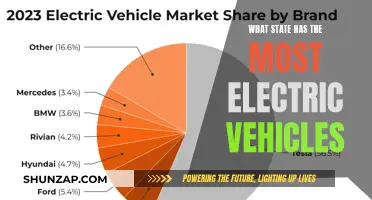
The market share of electric vehicles (EVs) in the automotive industry has been steadily rising, reflecting a global shift towards more sustainable transportation options. As of 2023, the percentage of new car sales that are electric vehicles varies significantly across different regions and markets. In some countries, EVs have gained substantial traction, while in others, they are still emerging.
In regions like Norway, the market share of EVs in new car sales has been impressive. According to the Norwegian Electric Vehicle Association, in 2022, over 80% of new car registrations were electric, making Norway a global leader in EV adoption. This rapid growth can be attributed to government incentives, such as tax benefits and subsidies, which have encouraged consumers to make the switch. Similarly, in the United States, the market share of EVs has been increasing, with a notable rise in sales of electric cars from major manufacturers. The introduction of popular models like the Tesla Model 3 and the recent push for stricter emissions standards have contributed to this trend.
However, the global picture is more nuanced. In many European countries, the market share of EVs is still relatively low but growing. For instance, in Germany, despite a significant increase in EV sales, they accounted for only around 10% of new car sales in 2022. This disparity in market share can be attributed to various factors, including consumer preferences, infrastructure development, and the availability of suitable EV models.
The rise in EV sales is closely tied to the increasing consumer demand for environmentally friendly vehicles. As environmental concerns grow and governments introduce stricter regulations, the automotive industry is responding with more electric options. This shift is also driven by technological advancements, making EVs more affordable, efficient, and appealing to a broader audience.
In summary, the market share of electric vehicles in new car sales is a dynamic and evolving statistic. While some regions have achieved impressive adoption rates, others are still in the early stages of the transition. Understanding these market shares is crucial for investors, policymakers, and consumers alike, as it provides insights into the pace of change and the potential for future growth in the EV market.
Sustainable Solutions: Navigating EV Battery Disposal and Recycling
You may want to see also

Geographical Distribution: How do EV adoption rates vary by region?
The adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) varies significantly across different regions, influenced by a multitude of factors including government policies, infrastructure development, cultural attitudes, and economic conditions. This geographical distribution provides valuable insights into the global transition towards sustainable transportation.
In North America, particularly the United States, EV adoption has been relatively slower compared to other developed nations. Despite the presence of major EV manufacturers like Tesla, the market share of electric cars remains modest. This can be attributed to several factors. Firstly, the vast distances and less dense population in the US make charging infrastructure less economically viable, especially in rural areas. Additionally, the strong influence of the automotive industry, which has traditionally focused on gasoline-powered vehicles, has slowed the transition to EVs. However, recent years have seen a surge in EV sales, with incentives and subsidies from state governments playing a crucial role in boosting adoption.
European countries, on the other hand, have embraced EVs more enthusiastically. Norway, for instance, leads the way in global EV adoption, with over 50% of new car sales being electric in 2021. This success can be attributed to a combination of factors. Firstly, the Norwegian government has implemented aggressive incentives, including a zero-emission car quota for new car sales, tax benefits, and free access to toll roads and ferry services for EVs. Secondly, the country's robust charging infrastructure, with a high density of charging stations, ensures convenience for EV owners. Other European nations, such as the Netherlands, Germany, and Sweden, have also made significant strides in EV adoption, driven by similar incentives and a growing awareness of environmental issues.
In Asia, the story is more diverse. China, being the world's largest auto market, has witnessed a rapid increase in EV sales, with local brands like BYD and NIO gaining significant market share. The Chinese government's support, including subsidies and tax incentives, has been instrumental in this growth. However, in other Asian countries, such as India and Southeast Asian nations, the adoption of EVs is still in its infancy. Factors like lower disposable incomes, less developed charging infrastructure, and a preference for two-wheelers over four-wheelers contribute to this disparity.
The Middle East and Africa present unique challenges and opportunities for EV adoption. In regions like the United Arab Emirates, where extreme temperatures are common, the efficiency and range of EVs are critical considerations. Governments in these regions are investing in charging infrastructure and offering incentives to encourage EV sales. Meanwhile, in sub-Saharan Africa, the focus is on affordable mobility solutions, and the adoption of EVs is primarily driven by the need for cost-effective transportation rather than environmental concerns.
In conclusion, the geographical distribution of EV adoption rates is shaped by a complex interplay of economic, political, and cultural factors. While some regions have embraced EVs with enthusiasm, others face unique challenges that hinder their transition to sustainable transportation. Understanding these variations is crucial for policymakers, businesses, and environmental advocates to tailor strategies and accelerate the global shift towards a greener automotive future.
Green Machines: Uncovering the Environmental Trade-offs of Electric Vehicles
You may want to see also

Timeframe Analysis: What is the historical trend in EV market penetration?
The electric vehicle (EV) market has been steadily growing over the past few decades, but the rate of market penetration has not been uniform across different time periods. To understand the historical trend in EV market penetration, we need to analyze the data over specific timeframes.
Early Adoption (1990s-2000s): The early 1990s saw the introduction of the first-generation electric cars, primarily in the United States and Europe. These vehicles were often niche products, with limited production and high prices, making them accessible only to a small segment of the population. During this period, the market penetration of EVs was extremely low, with less than 0.1% of vehicles on the road being electric. The lack of charging infrastructure and the high cost of battery technology were significant barriers to widespread adoption.
Growing Interest and Government Incentives (2010s): The 2010s witnessed a significant shift in the EV market. With increasing environmental concerns and the need to reduce carbon emissions, many governments introduced incentives and subsidies to promote EV sales. This period saw the launch of several affordable and practical electric cars, such as the Nissan Leaf and the Chevrolet Volt. As a result, the market penetration of EVs started to show a steady increase, reaching around 1-2% of the total vehicle population in many countries. The growing interest in sustainable transportation and the availability of more affordable EV options contributed to this trend.
Rapid Expansion (2020s): The current decade has seen an unprecedented surge in EV sales and market penetration. Several factors have driven this growth. Firstly, the development of more advanced battery technologies has led to improved range and reduced charging times, addressing some of the earlier concerns. Secondly, the increasing availability of charging stations and the integration of EVs into the energy grid have made them more convenient and accessible. Additionally, the global push towards decarbonization and the implementation of stricter emission regulations have further accelerated the adoption of electric vehicles. As a result, the market share of EVs has skyrocketed, with estimates suggesting that in some regions, over 10% of vehicles on the road are now electric.
Regional Variations: It is essential to note that the historical trend in EV market penetration varies across different regions. In countries with strong government support and well-established charging infrastructure, the growth has been more rapid. For example, Norway, which has some of the highest EV ownership rates globally, has seen a remarkable increase in market penetration, with over 80% of new car sales being electric in 2021. In contrast, regions with less supportive policies and infrastructure may have experienced slower growth, but the overall trajectory is still upward.
Future Outlook: The historical trend indicates that the EV market is likely to continue its upward trajectory. As more countries adopt ambitious decarbonization targets and invest in charging infrastructure, the market penetration of EVs is expected to accelerate further. However, challenges such as battery recycling, grid stability, and the need for a more comprehensive charging network remain. Despite these obstacles, the long-term outlook for the EV market appears promising, with the potential to significantly reduce the carbon footprint of the transportation sector.
Unraveling the Qualified EV Credit: A Comprehensive Guide
You may want to see also

Fuel Type Comparison: How do EVs compare to gasoline/diesel in terms of market share?
The global automotive landscape is undergoing a significant transformation, with electric vehicles (EVs) increasingly taking center stage. As of 2023, the percentage of electric vehicles on the road is still relatively small compared to traditional gasoline and diesel-powered cars. According to various sources, including data from the International Energy Agency (IEA) and the International Organization of Motor Vehicle Manufacturers (OICA), the global market share of electric vehicles is estimated to be around 3-4% of total passenger car sales. This translates to approximately 1-2% of the total vehicles on the road being fully electric.
However, this number is growing rapidly. The rise in popularity of EVs can be attributed to several factors, including technological advancements, environmental concerns, and government incentives. Many countries are setting ambitious targets to phase out internal combustion engines, which is driving the demand for electric alternatives. For instance, the European Union aims to ban the sale of new fossil fuel cars by 2035, while China has already surpassed the 5% market share for EVs.
In contrast, gasoline and diesel vehicles still dominate the market. As of 2022, gasoline-powered cars accounted for approximately 95% of the global vehicle market, while diesel vehicles held around 10% of the market share. This dominance is primarily due to the established infrastructure and the lower cost of refueling compared to the charging of electric vehicles. Despite the growing interest in EVs, the transition to a fully electric fleet is expected to take several decades, given the existing infrastructure and the time required to phase out the current vehicle fleet.
The comparison between EVs and traditional fuel types also extends to their respective market shares in different regions. In North America and some Asian markets, gasoline vehicles still dominate, but the trend is shifting. For example, in Norway, a leading market for EVs, the percentage of electric vehicles on the road has reached over 8% as of 2022. This rapid growth is also evident in countries like the Netherlands, Sweden, and France, where government incentives and infrastructure investments have significantly boosted EV adoption.
In summary, while electric vehicles are gaining traction and their market share is increasing, they still represent a relatively small portion of the overall vehicle population. Gasoline and diesel engines remain the dominant fuel types, but the automotive industry is witnessing a gradual shift towards electrification. As the world moves towards more sustainable transportation, the market share of EVs is expected to grow exponentially, potentially reaching a majority within the next few decades.
Troubleshooting: Removing a Stuck Electrical Plug from Your Vehicle
You may want to see also

Consumer Preferences: What factors influence consumers' choice to buy electric cars?
The growing popularity of electric vehicles (EVs) is a trend that has been gaining momentum, and understanding the factors that influence consumer preferences is crucial to further accelerating this shift. When considering the purchase of an electric car, several key elements come into play that can either encourage or deter potential buyers.
One significant factor is the environmental impact. Many consumers are increasingly conscious of their carbon footprint and are actively seeking ways to reduce it. Electric cars, being emission-free, offer an attractive solution to those looking to minimize their environmental impact. The appeal of driving a vehicle that contributes to a cleaner, greener future is a powerful motivator for many. Additionally, government incentives and subsidies play a vital role in promoting EV adoption. Financial benefits such as tax credits, rebates, and reduced registration fees can significantly lower the overall cost of ownership, making electric cars more accessible and appealing to a broader audience.
Another critical aspect is the performance and technology associated with electric vehicles. Modern EVs are known for their instant torque, resulting in impressive acceleration and a smooth driving experience. The advanced technology within these vehicles, including efficient battery management systems and sophisticated driver-assistance features, also adds to their appeal. Many consumers are drawn to the cutting-edge nature of EVs, which often comes with a host of smart connectivity options and over-the-air software updates, ensuring their vehicles remain up-to-date and technologically advanced.
Range anxiety, a common concern among potential EV buyers, has been significantly alleviated by recent advancements. Modern electric cars offer improved range capabilities, addressing the fear of running out of power during a journey. This, coupled with the expanding network of charging stations, makes long-distance travel in an electric vehicle more feasible and less stressful. Furthermore, the convenience of home charging and the availability of fast-charging stations at various locations are increasingly attractive features for consumers.
Lastly, the overall cost of ownership is a significant consideration. While the initial purchase price of electric cars may be higher, the long-term savings on fuel and maintenance can be substantial. As the technology matures and production scales up, the cost of EVs is expected to decrease, making them even more competitive against traditional internal combustion engine vehicles. This, combined with the potential for increased resale value due to the growing demand for electric cars, is a compelling argument for consumers.
In summary, the choice to buy an electric car is influenced by a combination of environmental consciousness, financial incentives, performance and technology, range and charging infrastructure, and the overall cost of ownership. As the market continues to evolve, addressing these factors will be essential in driving consumer preference towards electric vehicles.
Unveiling the Power of Plug-In Electric Vehicles: A Comprehensive Guide
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
As of 2023, it is estimated that around 1% of the global vehicle fleet is fully electric, with a significant portion of these being in countries like Norway, the Netherlands, and China, which have strong incentives and infrastructure for EV adoption.
The number of EVs on the road has been increasing steadily, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 40% from 2015 to 2020. This growth is expected to continue, with many countries and automakers setting ambitious targets to phase out internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles and accelerate the transition to electric mobility.
Several factors contribute to the adoption rate of EVs, including government policies and incentives, the availability of charging infrastructure, consumer awareness and preferences, and the performance and range of electric vehicles. For example, regions with well-developed charging networks and favorable policies often see a higher percentage of electric cars on the road.