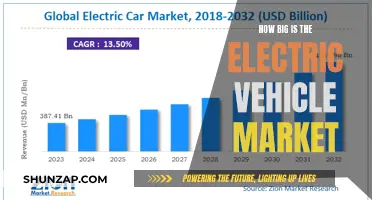
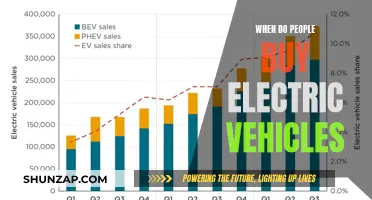
When a vehicle is in motion, it relies on a complex system to generate the electricity needed to power various components. This essential process is facilitated by the alternator, a crucial component that plays a vital role in keeping the vehicle's electrical system operational. The alternator is responsible for converting mechanical energy into electrical energy, ensuring that the vehicle's battery remains charged and ready to provide the necessary power for essential functions while the engine is running. Understanding the role of the alternator is key to comprehending how vehicles maintain their electrical systems during operation.
What You'll Learn
- Engine: Internal combustion engine generates power to produce electricity
- Alternator: Converts mechanical energy into electrical energy for the vehicle
- Battery: Stores electrical energy and provides power when the engine is off
- Generator: Similar to an alternator, it produces electricity through mechanical motion
- Solar Panel: Converts sunlight into electricity, often used in electric vehicles

Engine: Internal combustion engine generates power to produce electricity
The internal combustion engine is a crucial component in vehicles, and its primary function is to generate the power required to keep the vehicle running. This engine operates on the principle of burning fuel, typically gasoline or diesel, to produce energy. When the vehicle is in motion, the engine's role is to convert this chemical energy into mechanical energy, which is then used to turn the wheels and propel the car forward.
However, the internal combustion engine also plays a vital role in providing electricity to the vehicle's electrical systems. As the engine runs, it generates electricity through a process called alternation. The alternator is an essential component that works in conjunction with the engine to produce electrical power. When the engine is operational, it drives the alternator, which then converts the mechanical energy into electrical energy. This electrical energy is crucial for powering various vehicle systems, including the lights, dashboard instruments, and other electronic components.
The process of generating electricity while the vehicle is running is a complex one. It involves the coordination of multiple components, including the engine, alternator, and electrical system. The engine's power output is regulated by the engine control unit (ECU), which ensures that the electrical load is met without overloading the system. The alternator, driven by the engine, then supplies the required electricity to the vehicle's battery and other electrical components.
In modern vehicles, the efficiency of electricity generation is a critical factor. Engineers have designed engines with advanced technologies to optimize power output and minimize fuel consumption. For instance, some engines use variable valve timing and direct fuel injection to improve performance and fuel efficiency. These advancements contribute to the overall efficiency of the vehicle, ensuring that the engine can generate sufficient electricity while consuming less fuel.
Additionally, the design of the electrical system plays a significant role in managing the electricity generated by the engine. The system includes a battery, which stores excess electrical energy when the engine is running and provides power during periods of low engine speed or when the vehicle is stationary. This ensures that the vehicle's electrical needs are met even when the engine is not generating maximum power. The electrical system also includes various sensors and actuators that monitor and control the vehicle's performance, further emphasizing the importance of efficient electricity generation.
A Green Revolution: The Electric Vehicle Takeover
You may want to see also

Alternator: Converts mechanical energy into electrical energy for the vehicle
The alternator is a crucial component in a vehicle's electrical system, playing a vital role in ensuring a steady supply of electricity while the car is in motion. It is an essential device that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy, which powers various electrical components and accessories in the vehicle. This process is fundamental to keeping the car's engine running and the electrical systems functioning optimally.
Mechanically, the alternator is driven by the engine's crankshaft via a pulley belt or a dedicated drive shaft. As the engine operates, the alternator rotates, generating electrical current through the use of electromagnetic fields and coils of wire. This current is then directed to the battery, which stores the electrical energy for later use, and also powers the vehicle's electrical systems directly. The alternator's efficiency is critical, as it needs to provide enough power to meet the demands of the car's electrical components while also recharging the battery.
The design of an alternator typically includes a rotor and a stator. The rotor, often made of a durable metal alloy, is the rotating part that spins within the stator's stationary coils of wire. When the rotor rotates, it induces an electrical current in the stator windings due to the changing magnetic field, thus generating electricity. This process is a fundamental principle of electromagnetic induction, where mechanical motion is converted into electrical energy.
Alternators can vary in design and output capacity depending on the vehicle's make and model, as well as its intended use. For instance, high-performance vehicles or those with advanced electrical systems may require alternators with higher output ratings to meet the increased power demands. Modern alternators often incorporate advanced features such as voltage regulation to ensure a stable electrical supply, even under varying load conditions.
In summary, the alternator is a critical component that enables vehicles to generate and manage their electrical power needs while in operation. Its role in converting mechanical energy into electrical energy is essential for the functionality of modern automobiles, ensuring that various electrical systems can operate efficiently and reliably. Understanding the alternator's function provides valuable insight into the intricate relationship between a vehicle's mechanical and electrical systems.
Exploring the World of All-Electric Vehicles: Powering a Sustainable Future
You may want to see also

Battery: Stores electrical energy and provides power when the engine is off
The battery is a crucial component in a vehicle's electrical system, serving as the primary source of power when the engine is not running. It is a storage device that holds electrical energy, which is then utilized to start the engine and power various electrical components in the car. This function is essential, especially during the vehicle's initial startup phase, where the battery provides the necessary current to turn the engine over.
In a typical vehicle, the battery is a lead-acid type, consisting of several cells connected in series. Each cell contains lead plates immersed in sulfuric acid, creating a chemical reaction that generates electrical energy. The battery's capacity is measured in ampere-hours (Ah) or watt-hours (Wh), indicating the amount of energy it can store and provide. A higher capacity battery means it can store more energy, ensuring the vehicle has sufficient power for extended periods without the engine running.
When the engine is running, it charges the battery through the alternator, which converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. This process replenishes the battery's charge, ensuring it remains ready to provide power when needed. The alternator is connected to the engine's crankshaft, and as the engine rotates, it drives the alternator's rotor, generating an alternating current (AC) that is then converted to direct current (DC) to charge the battery.
During periods of high electrical demand, such as when the air conditioning or headlights are used, the battery's role becomes even more critical. It acts as a reserve power source, supplying additional energy to meet the increased demand without draining the main power supply. This ensures that the vehicle's electrical systems remain functional, even under heavy load conditions.
In summary, the battery is a vital component that stores electrical energy and provides power when the engine is off, ensuring the vehicle's electrical systems remain operational. Its capacity and efficiency are essential considerations in vehicle design, as they directly impact the reliability and performance of the entire electrical system. Regular maintenance and monitoring of the battery's health are recommended to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Troubleshooting Electrical Issues: A Comprehensive Guide to Diagnosing Vehicle Problems
You may want to see also

Generator: Similar to an alternator, it produces electricity through mechanical motion
A generator is a crucial component in vehicles, responsible for converting mechanical energy into electrical power while the engine is in operation. It operates on a principle similar to that of an alternator, which is to generate electricity through the mechanical motion of the engine. This process is essential for keeping the vehicle's electrical systems powered, ensuring that various functions like lights, radio, air conditioning, and even the ignition system work seamlessly.
The generator's design typically involves a rotating armature, which is a coil of wire that rotates within a magnetic field. This rotation is directly linked to the engine's crankshaft, meaning that as the engine turns, the generator spins as well. The magnetic field is created by permanent magnets or an electromagnet, and the interaction between the magnetic field and the rotating armature induces an electric current. This current is then harnessed and distributed to power the vehicle's electrical components.
One of the key advantages of using a generator is its ability to provide a consistent and stable source of electricity. Unlike some other methods of generating power, generators can deliver a steady output, ensuring that the vehicle's electrical systems receive a reliable power supply. This is particularly important in vehicles, where sudden voltage fluctuations can lead to issues with sensitive electronics.
In terms of maintenance, generators require regular checks to ensure they are functioning optimally. This includes inspecting the brushes that make contact with the armature, as well as checking the generator's voltage output. Proper maintenance ensures that the generator can efficiently convert mechanical energy into electricity, contributing to the overall reliability and performance of the vehicle.
In summary, the generator is a vital component in vehicles, playing a similar role to an alternator by generating electricity through mechanical motion. Its design and operation are tailored to provide a consistent and reliable power source, ensuring that the vehicle's electrical systems function without interruption. Regular maintenance is essential to keep the generator in good working order, thus maintaining the overall efficiency and dependability of the vehicle's electrical power supply.
Amazon's Electric Vehicle Acquisition: A Green Revolution
You may want to see also

Solar Panel: Converts sunlight into electricity, often used in electric vehicles
Solar panels are an innovative and sustainable solution for powering electric vehicles (EVs), offering a clean and renewable energy source. These panels are designed to harness the sun's energy and transform it into electricity, which can then be utilized to charge the vehicle's battery. This technology is particularly appealing for EVs as it provides a means to generate electricity while the vehicle is in motion, reducing the reliance on external power sources and promoting environmental sustainability.
The process begins with the solar panel's ability to absorb sunlight through its photovoltaic cells, typically made of semiconductor materials like silicon. When sunlight hits these cells, it excites the electrons, creating a flow of direct current (DC) electricity. This DC electricity is then converted into alternating current (AC) electricity through an inverter, making it compatible with the vehicle's electrical system. The AC electricity is then directed to the vehicle's battery, where it charges and stores the energy for later use.
One of the key advantages of using solar panels in EVs is their ability to generate electricity even while the vehicle is stationary. This is especially useful for charging the battery when the vehicle is parked, eliminating the need for traditional charging stations. Additionally, solar panels can be integrated into the vehicle's design, such as on the roof or hood, allowing for efficient energy capture without compromising the vehicle's aesthetics.
The efficiency of solar panels in EVs can vary depending on several factors, including the quality of the panels, the amount of sunlight available, and the vehicle's design. Modern solar panels can achieve conversion efficiencies of around 15-20%, meaning they can convert up to 20% of the sunlight they receive into usable electricity. This efficiency, combined with advancements in battery technology, allows EVs with solar panels to travel longer distances on a single charge.
Incorporating solar panels into electric vehicles has the potential to revolutionize the automotive industry and contribute to a more sustainable future. It offers a unique opportunity to reduce the carbon footprint of transportation and provide a more reliable and cost-effective energy source for EVs. As technology advances, we can expect to see more widespread adoption of solar-powered EVs, making them an increasingly viable and environmentally friendly choice for drivers worldwide.
The Future of Driving: Understanding Autonomous Electric Vehicles
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The primary source of electricity in a running vehicle is the alternator, which is driven by the engine's crankshaft. It converts mechanical energy into electrical energy, providing power to the vehicle's electrical systems.
The alternator maintains a steady power output by regulating the voltage and current. It monitors the electrical load and adjusts its speed accordingly to meet the demand. This ensures that the vehicle's electrical components receive a consistent and reliable power supply while the engine is running.
The battery serves as a temporary energy storage system. When the engine is off, the battery provides power to the vehicle's electrical systems. While the engine is running, the alternator charges the battery, keeping it fully charged and ready to supply power when needed, especially during engine restarts and when the electrical demand exceeds the alternator's output.