Electric vehicles (EVs) have revolutionized the automotive industry, offering an eco-friendly and efficient alternative to traditional gasoline-powered cars. One of the key aspects that set EVs apart is their unique electrical systems, which operate on different voltage levels compared to conventional vehicles. Understanding the voltage requirements of electric cars is essential for their performance, charging infrastructure, and overall user experience. This paragraph will explore the various voltage specifications of electric vehicles, highlighting the importance of this technical detail in the rapidly growing EV market.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Battery Voltage | Typically 300-400 volts, but can vary depending on the vehicle and its battery pack. |
| Charging Voltage | Usually 240V or 480V for home charging, and up to 900V for fast charging stations. |
| Motor Voltage | Varies, but often around 300-400 volts for AC motors and higher for DC motors. |
| Power Electronics | Converters and inverters are used to regulate voltage and power flow, often operating at 400V or higher. |
| Voltage Regulation | Electric vehicles use sophisticated voltage regulation systems to maintain optimal performance and efficiency. |
| Range | Voltage directly impacts range, with higher voltage batteries generally providing longer ranges. |
| Efficiency | Voltage efficiency is crucial, with higher voltage systems often being more efficient in energy conversion. |
| Safety | Voltage levels are designed with safety in mind, with protective measures to prevent electrical hazards. |
| Charging Time | Voltage affects charging speed, with higher voltage allowing for faster charging times. |
| Vehicle Type | Different types of electric vehicles (EVs) may have varying voltage requirements, such as plug-in hybrids vs. fully electric cars. |
What You'll Learn
- Battery Voltage: EVs typically use 300-400 volts for their high-voltage batteries
- Charging Standards: Different charging standards may require specific voltage levels
- Motor Voltage: Electric motors operate at various voltages, often 200-400 volts
- Grid Interaction: Grid voltage can impact EV charging and power supply
- Safety Considerations: Voltage levels are designed to ensure safe operation and prevent hazards

Battery Voltage: EVs typically use 300-400 volts for their high-voltage batteries
Electric vehicles (EVs) have revolutionized the automotive industry, offering an eco-friendly and efficient mode of transportation. One of the critical aspects of these vehicles is their battery systems, which power the electric motors and drive the wheels. When it comes to the voltage of EV batteries, it is essential to understand the specifications to appreciate the technology behind these vehicles.
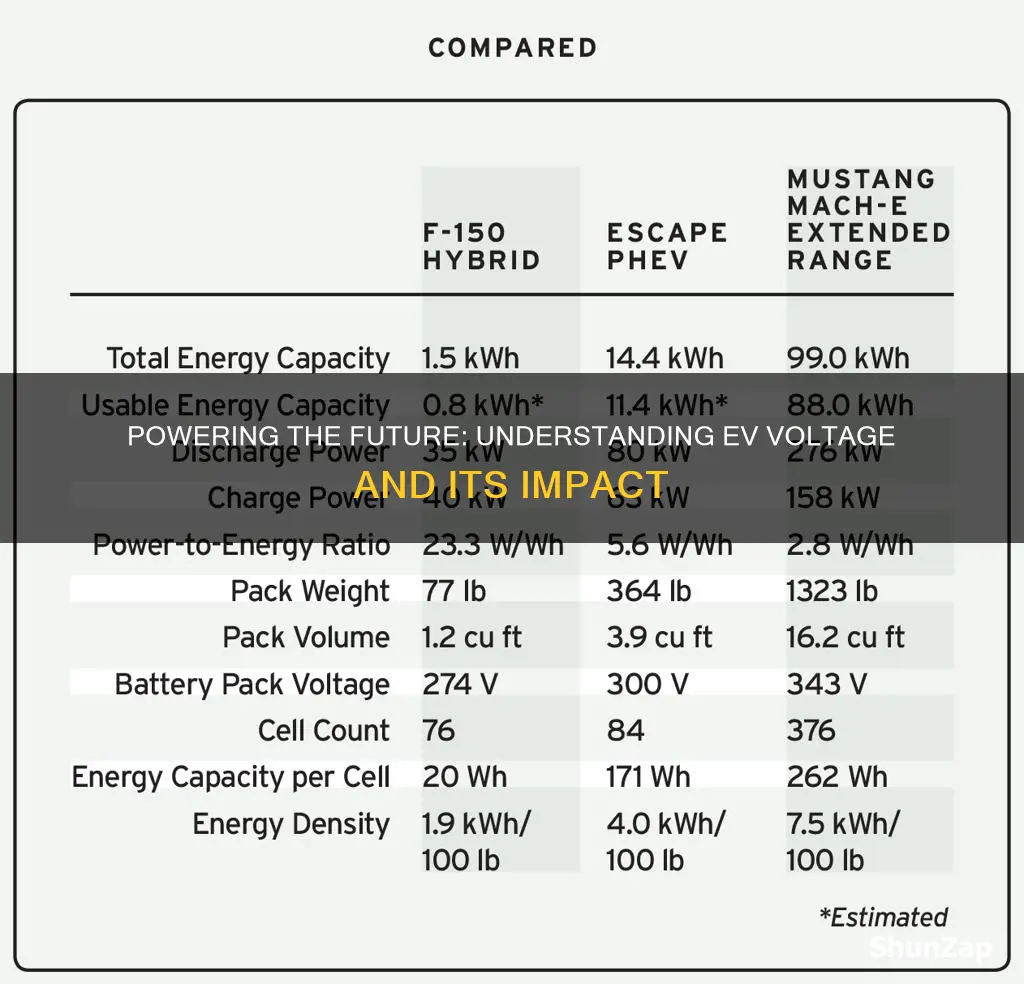
EVs are designed with high-voltage batteries, typically operating at a range of 300 to 400 volts. This voltage level is significantly higher than the standard 12 volts found in conventional internal combustion engine vehicles. The higher voltage is a key factor in the efficiency and performance of electric cars. By utilizing a more robust electrical system, EVs can deliver the necessary power to the motors while maintaining a longer driving range.
The 300-400 volt range is chosen for its ability to provide a balance between power and energy efficiency. Higher voltage batteries allow for more efficient energy transfer, ensuring that the vehicle can accelerate quickly and maintain higher speeds. This voltage also enables the use of powerful electric motors, which are essential for the smooth and responsive driving experience that EVs are known for.
Furthermore, the high voltage in EV batteries is crucial for the overall safety of the vehicle. It allows for the implementation of advanced safety features, such as sophisticated battery management systems. These systems monitor and control the battery's performance, ensuring optimal operation and protecting against potential hazards like overcharging or overheating.
In summary, the battery voltage in electric vehicles is a critical component that defines their performance and capabilities. The 300-400 volt range provides the necessary power for efficient acceleration and a longer driving range. Additionally, this voltage level contributes to the safety and reliability of EV battery systems, making them a popular choice for environmentally conscious consumers. Understanding these technical details highlights the innovation and engineering prowess behind modern electric vehicles.
Toyota's Electric Evolution: A Green Revolution in the Works?
You may want to see also

Charging Standards: Different charging standards may require specific voltage levels
The world of electric vehicles (EVs) is rapidly expanding, and with it comes the need for standardized charging solutions to ensure compatibility and efficiency. When it comes to charging EVs, voltage plays a critical role in determining the charging speed and overall performance. Different charging standards have been developed to accommodate various EV models and charging infrastructure, each with its own specific voltage requirements. Understanding these charging standards and their respective voltage levels is essential for EV owners and charging station operators alike.
One of the most widely recognized charging standards is the Combined Charging System (CCS), which is used in many countries, including the United States, Europe, and Japan. CCS employs a single connector that supports multiple charging modes, including direct current (DC) fast charging and alternating current (AC) slow charging. For DC fast charging, the CCS standard typically requires a voltage of around 400 volts, which enables rapid charging of EV batteries. This high voltage allows for efficient power transfer, reducing charging times significantly. On the other hand, AC slow charging, often used for overnight charging at home, operates at a lower voltage, typically around 240 volts, which is standard for household electrical outlets.
Another widely adopted charging standard is the CHAdeMO, primarily used in Japan and some other Asian markets. CHAdeMO charging stations provide DC fast charging, and the recommended voltage level is 400 volts as well. This standard has been instrumental in promoting the widespread adoption of fast-charging infrastructure in Japan. It's important to note that while both CCS and CHAdeMO support high-voltage DC charging, they have different connector types and communication protocols, requiring EV manufacturers to design specific models to accommodate these standards.
In Europe, the IEC 62196-2 standard, also known as the Type 2 connector, is prevalent for AC charging. This standard specifies a voltage of 240 volts for slow charging, making it suitable for residential and public charging stations. The Type 2 connector is widely used in Europe and has become a de facto standard for AC charging infrastructure. Additionally, some countries have their own charging standards, such as the GB/T 20234-2015 standard in China, which defines different voltage levels for various charging modes.
Understanding these charging standards and their respective voltage requirements is crucial for EV owners to ensure they have the right charging equipment and adapters. It also enables charging station operators to provide compatible and efficient charging solutions. As the EV market continues to grow, standardization of charging protocols and voltage levels will play a vital role in fostering a seamless and accessible charging experience for all EV drivers.
Is Toyota CH-R an Electric Vehicle? Unveiling the Truth
You may want to see also

Motor Voltage: Electric motors operate at various voltages, often 200-400 volts
Electric vehicles (EVs) have revolutionized the automotive industry, and at the heart of their operation are electric motors, which are a critical component in converting electrical energy into mechanical motion. The voltage at which these motors operate is a crucial factor in their performance and efficiency.
Electric motors in EVs typically run at a range of voltages, with 200 to 400 volts being the most common. This voltage range is chosen for its balance between power and efficiency. Higher voltages can provide more torque and faster acceleration, which are desirable traits for electric cars. For instance, a 400-volt motor can deliver a significant amount of power, enabling quick bursts of speed and efficient performance. This voltage is often used in high-performance electric vehicles, where rapid acceleration and responsive handling are essential.
The choice of voltage also depends on the specific design and requirements of the vehicle. For example, some electric cars might use a lower voltage to ensure a more efficient and cost-effective system, especially in longer-range vehicles where energy conservation is key. In contrast, sports cars or vehicles designed for performance might opt for higher voltages to maximize power output.
Motor voltage is a critical consideration in the design and manufacturing processes of electric vehicles. It influences the motor's size, weight, and overall cost. Higher voltages can lead to more compact and lightweight designs, which are advantageous for improving the vehicle's overall performance and handling. Additionally, the voltage rating affects the motor's efficiency, with higher voltages generally providing better energy conversion and utilization.
Understanding the voltage requirements of electric motors is essential for engineers and manufacturers to optimize the performance and efficiency of electric vehicles. It allows for the creation of powerful yet efficient transportation systems, contributing to the widespread adoption of electric mobility.
Unveiling the Power of EV: Electric Vehicles Explained
You may want to see also

Grid Interaction: Grid voltage can impact EV charging and power supply
The interaction between electric vehicles (EVs) and the power grid is a critical aspect of the widespread adoption of EVs. One of the key factors influencing this interaction is grid voltage, which can significantly impact EV charging and power supply. Understanding these impacts is essential for optimizing the efficiency and reliability of EV charging infrastructure.
Grid voltage refers to the electrical potential difference between two points in the power grid. In the context of EVs, this voltage is crucial because it determines the rate at which EVs can charge. When an EV is connected to a charging station, the grid voltage influences the charging speed and efficiency. Higher grid voltage generally allows for faster charging, as it provides a greater potential difference, enabling more rapid transfer of energy from the grid to the vehicle's battery. For example, a 240-volt charging station can typically charge an EV much faster than a 120-volt outlet, assuming the EV's on-board charger can handle the higher voltage.
However, the impact of grid voltage on EV charging goes beyond just charging speed. It also affects the overall power supply and stability of the grid. During peak charging times, when multiple EVs are connected to the grid, the demand for power can surge. If the grid voltage is not stable or is too low, it may struggle to meet this increased demand, potentially leading to voltage drops. These drops can result in slower charging rates and even temporary disruptions in the charging process. In extreme cases, a low grid voltage can cause the charging circuit to trip, protecting the EV and the grid from potential damage.
To ensure efficient and safe EV charging, grid operators and vehicle manufacturers often work together to optimize charging infrastructure. This includes designing charging stations with appropriate voltage levels and implementing smart charging systems that can adjust charging rates based on grid conditions. Smart charging algorithms can help balance the load on the grid by scheduling charging during off-peak hours when voltage levels are more stable. Additionally, some EVs are equipped with voltage-sensitive charging systems, allowing them to adapt to varying grid conditions and ensure a consistent charging experience.
In summary, grid voltage plays a pivotal role in the interaction between EVs and the power grid. It influences charging speed, efficiency, and overall grid stability. By understanding and managing these voltage-related impacts, the EV industry can work towards a more seamless and reliable charging infrastructure, fostering the widespread adoption of electric vehicles while maintaining a balanced and efficient power grid.
Strategies for Accelerating the Shift to Electric Vehicles
You may want to see also

Safety Considerations: Voltage levels are designed to ensure safe operation and prevent hazards
The voltage in electric vehicles (EVs) is a critical aspect of their design and operation, and it is carefully chosen to ensure the safety and efficiency of the vehicle. The voltage levels in EVs are typically much higher than those found in conventional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles, often ranging from 200 to 400 volts or more. This higher voltage is a key factor in the vehicle's performance and energy efficiency, allowing for more powerful electric motors and efficient power transmission.
Safety is a primary concern when dealing with high-voltage systems, and EV manufacturers have implemented various measures to mitigate potential hazards. One of the primary safety considerations is the use of high-voltage insulation and protective barriers. These materials are designed to withstand the electrical stress of the high voltage and prevent electrical discharge, ensuring that the high voltage remains contained within the vehicle's electrical system. Insulation materials, such as specialized rubber or ceramic compounds, are used to cover wires, cables, and components, providing a protective barrier against electrical arcing and short circuits.
Additionally, EVs employ sophisticated safety mechanisms to protect against electrical faults and prevent accidents. These include circuit breakers, fuses, and overcurrent protection devices that can automatically shut down the high-voltage system in the event of an overload or short circuit. These safety features are designed to rapidly isolate the fault, minimizing the risk of electrical fires, explosions, or other hazardous situations. The rapid response time of these safety systems is crucial in preventing potential accidents and ensuring the well-being of both the vehicle occupants and those around it.
Another important safety aspect is the design of the vehicle's high-voltage architecture. EVs often feature a modular design, with high-voltage components grouped together in specific areas. This arrangement allows for better control and monitoring of the electrical system, making it easier to identify and isolate potential issues. The placement of high-voltage components is also carefully planned to minimize the risk of damage from external factors, such as water intrusion or physical impact.
Furthermore, the charging infrastructure for EVs is designed with safety in mind. Charging stations use specialized equipment that communicates with the vehicle to ensure a safe and controlled charging process. This includes monitoring the vehicle's battery voltage and current levels, as well as implementing safety protocols to prevent overcharging or other charging-related hazards. The charging process is typically supervised by the vehicle's onboard computer, which communicates with the charging station to ensure a safe and efficient transfer of energy.
In summary, the voltage levels in electric vehicles are carefully selected and managed to ensure safe operation and prevent potential hazards. Through the use of advanced insulation materials, sophisticated safety mechanisms, and well-designed high-voltage architectures, EV manufacturers aim to minimize the risks associated with high-voltage systems. These safety considerations are vital in promoting the widespread adoption of electric vehicles and ensuring the well-being of both drivers and pedestrians.
Ford's Electric Future: Rumors of a Shift Unveiled
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Electric vehicles commonly operate on a high-voltage direct current (DC) system, usually ranging from 150 volts to 450 volts. This voltage is significantly higher than the standard 12-volt automotive battery found in conventional cars, which allows for more efficient power delivery and enables the high-performance capabilities of electric vehicles.
High voltage in electric vehicles is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, it enables the use of powerful electric motors that can deliver high torque and accelerate quickly. Secondly, the higher voltage allows for more efficient energy transfer and reduces energy losses during power conversion. This results in improved overall efficiency and longer driving ranges. Additionally, high voltage systems can support faster charging, making it more convenient for EV owners.
The voltage in electric vehicles plays a significant role in the charging process. Most electric vehicle charging stations use alternating current (AC) with a voltage of 230-400 volts. When an EV is plugged into a charging station, the high-voltage DC from the vehicle's battery is converted to AC at the appropriate voltage for charging. This process ensures that the charging infrastructure can supply the necessary power efficiently, and it also allows for the use of standard household outlets or dedicated charging stations with different power levels.