As the incentives for electric vehicles (EVs) in California gradually phase out, the state faces a critical juncture in its transition to a more sustainable transportation system. This shift will significantly impact the EV market, potentially affecting consumer behavior and the broader automotive industry. Understanding the implications of this transition is crucial for policymakers, industry stakeholders, and consumers alike, as they navigate the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead in the evolving landscape of electric mobility.
What You'll Learn
- Economic Impact: How the end of incentives affects California's EV market and economy
- Consumer Behavior: Changes in consumer choices and purchasing patterns post-incentive phase-out
- Infrastructure Challenges: The strain on charging networks and grid capacity as incentives fade
- Environmental Outcomes: Potential environmental benefits and drawbacks of reduced EV incentives
- Policy Adjustments: Strategies California might adopt to sustain EV adoption without incentives

Economic Impact: How the end of incentives affects California's EV market and economy
The phase-out of incentives for electric vehicles (EVs) in California has sparked significant interest and concern among industry stakeholders and policymakers. This strategic move, aimed at fostering a sustainable transportation ecosystem, has far-reaching implications for the state's economy and the EV market. As the incentives gradually diminish, a nuanced understanding of their economic impact becomes essential.
The initial success of California's EV incentive programs is undeniable. These initiatives have played a pivotal role in accelerating the adoption of electric vehicles, reducing greenhouse gas emissions, and promoting a cleaner environment. However, the long-term sustainability of these incentives is a subject of debate. The end of subsidies could potentially impact the state's economy in several ways. Firstly, it may lead to a temporary slowdown in the EV market. As incentives diminish, consumers might delay their purchases, expecting further reductions in the future. This behavior could result in a short-term dip in sales, affecting the revenue streams of EV manufacturers and related industries.
Despite the potential short-term setback, the overall economic impact is likely to be positive in the long run. The reduction in incentives will encourage a more mature and self-sustaining EV market. This shift will foster innovation, drive down costs, and enhance the overall competitiveness of electric vehicles. As the market matures, it will attract more diverse players, including startups and established automakers, leading to increased competition and improved product offerings. This competitive environment will stimulate economic growth, create new job opportunities, and contribute to the state's technological advancement.
The end of incentives also presents an opportunity for California to diversify its economy. With the EV market maturing, the state can focus on developing complementary industries, such as battery technology, charging infrastructure, and sustainable transportation services. These sectors have the potential to generate significant economic activity, attract investments, and create high-value jobs. By fostering a comprehensive ecosystem, California can position itself as a global leader in sustainable transportation and clean energy solutions.
In summary, the phase-out of EV incentives in California is a strategic move with a positive long-term economic outlook. While there may be a temporary impact on the market, the overall benefits include a more robust and competitive EV industry, technological advancements, and the creation of new economic opportunities. This transition will contribute to California's goal of achieving a sustainable and prosperous future, ensuring its leadership in the global shift towards electric mobility.
Unleash the Power: Understanding Gasoline-Electric Hybrid Vehicles
You may want to see also

Consumer Behavior: Changes in consumer choices and purchasing patterns post-incentive phase-out
The phase-out of incentives for electric vehicles (EVs) in California has sparked significant interest in understanding how consumer behavior might evolve in the post-incentive era. This shift in policy could potentially impact the market dynamics and consumer preferences, especially as the state aims to transition towards a more sustainable transportation system. Here's an analysis of the potential changes in consumer choices and purchasing patterns:
Shift in Purchase Decisions: With the removal of incentives, one of the most immediate effects is likely to be a change in consumer purchasing behavior. Historically, financial incentives have played a crucial role in attracting buyers to EVs, often making them more affordable and competitive against traditional gasoline vehicles. As these incentives disappear, consumers might reconsider their budgets and priorities. Some may opt for conventional vehicles, especially if the price difference becomes more pronounced. Others might delay their purchase decisions, waiting for potential future incentives or until the technology matures further.
Long-term Ownership Considerations: Post-incentive phase-out, consumers might start evaluating the long-term benefits of owning an EV. The reduced cost of ownership, including lower fuel and maintenance expenses, has been a significant selling point. Without incentives, buyers may focus more on the inherent advantages of EVs, such as reduced environmental impact, lower running costs, and the potential for increased vehicle value over time. This shift in perspective could encourage more consumers to view EVs as a long-term investment, despite the initial higher purchase price.
Market Segmentation and Targeted Marketing: As consumer behavior changes, marketers and automotive brands might need to adapt their strategies. The market could witness a segmentation of consumers based on their reasons for buying EVs. Some buyers might prioritize environmental concerns, while others may focus on cost savings. This segmentation could lead to targeted marketing campaigns, where brands emphasize different aspects of EV ownership to appeal to specific consumer groups. For instance, eco-conscious buyers might be drawn to the sustainability angle, while cost-sensitive consumers could be enticed by the long-term financial benefits.
Impact on Second-hand Market: The post-incentive phase-out period might also influence the second-hand EV market. As new buyers hold off on purchases, there could be a temporary surplus of used EVs in the market. This could potentially drive down prices, making EVs more affordable for those who were previously priced out of the new car market. Additionally, the used EV market might attract buyers who are still keen on owning an electric vehicle but are more price-conscious.
Consumer Education and Awareness: The absence of incentives could prompt a renewed focus on educating consumers about the benefits of EVs. Manufacturers and environmental advocacy groups might collaborate to highlight the long-term advantages, such as reduced carbon emissions and improved air quality. This educational approach could help maintain consumer interest and potentially drive future purchases, especially as the technology becomes more widely accepted and accessible.
Uncover the Tax Benefits: Electric Vehicles and You
You may want to see also

Infrastructure Challenges: The strain on charging networks and grid capacity as incentives fade
As the incentives for electric vehicle (EV) adoption in California begin to phase out, a critical challenge emerges: the strain on the state's charging infrastructure and power grid. This transition period poses significant questions about the sustainability of EV ownership and the readiness of the necessary supporting systems.
The initial boom in EV sales was largely fueled by substantial incentives, including rebates and tax credits, which made electric cars more affordable and attractive to consumers. These incentives encouraged a rapid shift towards EVs, leading to a surge in sales and a growing number of electric vehicles on the road. However, with the incentives tapering off, the focus shifts to the long-term viability of this transportation shift.
One of the primary concerns is the strain on the charging network. The current infrastructure, designed to support a smaller number of EVs, may not be adequate to handle the increased demand. Public charging stations, in particular, could become congested, leading to longer wait times and potential frustration among EV owners. This issue is further exacerbated by the fact that many public charging stations are already in high demand, and their availability is limited, especially during peak hours.
The grid capacity is another critical aspect that requires careful management. As more EVs come online, the demand for electricity will increase significantly. This could lead to a strain on the power grid, potentially causing blackouts or brownouts in certain areas. The grid's ability to handle this additional load is a concern, especially during peak usage times, which could result in higher electricity prices and potential reliability issues. To address this, utilities and policymakers must work together to upgrade the grid infrastructure and ensure it can support the growing number of EVs without compromising the overall power supply.
To mitigate these challenges, a comprehensive strategy is necessary. This includes investing in the expansion of charging networks, both public and private, to ensure sufficient coverage and reduce congestion. Additionally, implementing smart charging solutions that optimize energy usage and reduce strain on the grid can be beneficial. Encouraging off-peak charging and providing incentives for home charging installations can also help manage the load more effectively. Furthermore, educating EV owners about responsible charging practices and the importance of grid stability will be crucial in ensuring a smooth transition as incentives fade.
The Evolution of Hybrid and Electric Cars: A Green Revolution
You may want to see also

Environmental Outcomes: Potential environmental benefits and drawbacks of reduced EV incentives
The potential environmental impact of reduced incentives for electric vehicles (EVs) in California is a critical consideration as the state aims to accelerate its transition to cleaner transportation. When incentives for EV purchases are reduced or eliminated, several key environmental outcomes can be expected.
Benefits:
- Reduced Greenhouse Gas Emissions: One of the most significant environmental advantages of EVs is their ability to lower greenhouse gas emissions. Without incentives, the market for EVs might slow down, leading to a temporary increase in the use of conventional gasoline vehicles. This could result in higher emissions of carbon dioxide (CO2) and other pollutants, which are major contributors to climate change. However, it's important to note that the overall environmental benefits of EVs, even without incentives, are still substantial due to their lower carbon footprint compared to traditional cars.
- Improved Air Quality: EVs produce zero tailpipe emissions, which directly contributes to improved air quality. With reduced incentives, the rate of EV adoption might decrease, potentially leading to a short-term increase in air pollution, especially in urban areas. This could negatively impact public health, as air pollutants are linked to respiratory and cardiovascular issues.
- Energy Efficiency: The reduced incentive program could encourage the development and adoption of more energy-efficient technologies. As the market for EVs matures, manufacturers might focus on improving battery efficiency, reducing energy consumption, and optimizing vehicle design, all of which have positive environmental implications.
Drawbacks:
- Slower Transition to Clean Energy: California's goal is to achieve carbon neutrality and significantly reduce its reliance on fossil fuels. Reduced incentives for EVs could hinder this transition, as EVs play a crucial role in the state's strategy to lower transportation-related emissions. A slower shift to EVs might result in prolonged reliance on gasoline vehicles, which are less environmentally friendly.
- Increased Traffic Congestion and Urban Pollution: With a potential decrease in EV sales, there is a risk of more conventional vehicles on the road, leading to increased traffic congestion and higher emissions in urban areas. This could negate some of the environmental gains made by the state's previous incentive programs.
- Impact on Battery Recycling and Second-Life Uses: The reduction in EV incentives might also affect the development of a robust recycling infrastructure for EV batteries. Proper disposal and recycling of batteries are essential to minimize environmental harm and ensure a sustainable supply of raw materials for future EV production. Without incentives, there could be less focus on establishing these recycling processes.
The Evolution of Electric Vehicles: A Historical Perspective
You may want to see also

Policy Adjustments: Strategies California might adopt to sustain EV adoption without incentives
California has been a pioneer in promoting electric vehicle (EV) adoption through various incentives and policies, but the question of what happens when these incentives phase out is a critical one. As the state aims to sustain and accelerate the transition to EVs, several policy adjustments and strategies could be considered to ensure continued growth without relying heavily on financial incentives. Here are some approaches that California could adopt:
Streamline and Standardize Regulations: One of the key challenges in EV adoption is the complexity of various incentives and regulations across different counties and cities. California could centralize and streamline these policies, ensuring a consistent and transparent framework for EV owners and manufacturers. By standardizing regulations, the state can simplify the process of purchasing, registering, and maintaining EVs, making it more attractive for residents and businesses. This might involve creating a unified state-wide program that replaces or complements existing county-specific incentives.
Focus on Infrastructure Development: The expansion of EV charging infrastructure is essential to support widespread EV ownership. California should invest in a comprehensive charging network, ensuring that charging stations are easily accessible across the state. This includes installing fast-charging stations along major highways and in urban areas, addressing range anxiety, and providing incentives for businesses to install chargers in parking lots and public spaces. A well-planned infrastructure network will encourage more people to make the switch, knowing that convenient charging options are readily available.
Implement Tax Policies Favorable to EVs: Tax incentives can play a significant role in sustaining EV adoption. California could consider introducing or expanding tax credits or exemptions for EV purchases and maintenance. For instance, offering a state-wide sales tax exemption for EVs or providing tax credits for the installation of home charging stations. Additionally, the state could explore ways to reduce or eliminate taxes on EV-related services, such as registration fees or road taxes, making ownership more affordable and attractive.
Promote Public Transportation and Car-Sharing: To reduce the overall number of vehicles on the road, California should continue to invest in and improve public transportation systems, making them more efficient, affordable, and attractive to residents. This includes expanding bus and rail networks, offering incentives for public transit usage, and promoting car-sharing services. By encouraging shared mobility, the state can decrease the demand for individual vehicle ownership, which in turn reduces the need for incentives focused on personal vehicle purchases.
Educate and Engage the Public: Public awareness and education are vital to sustaining EV adoption. California can launch awareness campaigns to highlight the environmental and economic benefits of EVs, dispel misconceptions, and provide information on available resources and incentives. Engaging with communities, especially in underserved areas, can help address concerns and ensure that the transition to EVs is inclusive and accessible to all. Providing educational programs in schools and community centers can also foster a culture of sustainable transportation.
By implementing these policy adjustments, California can create a robust and sustainable framework for EV adoption, reducing its reliance on incentives while still encouraging residents and businesses to embrace electric mobility. A well-structured approach that focuses on infrastructure, regulation, taxation, and public engagement will be crucial in maintaining the state's leadership in the EV market.
Electric Vehicles: Powering the Future, Yet Lacking Essential Features
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
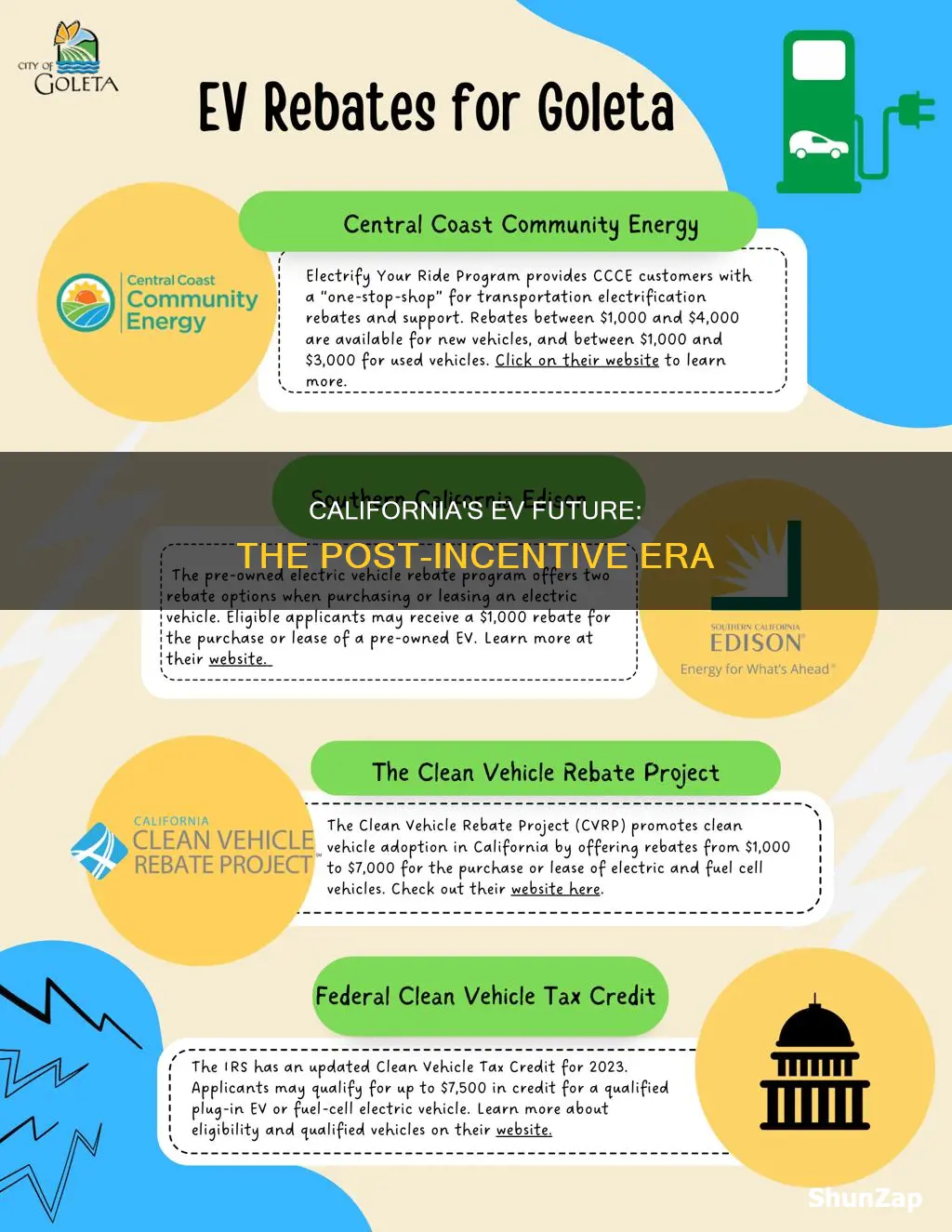
The California Air Resources Board (CARB) has announced that the current incentive programs for electric vehicles (EVs) will phase out by 2025. This includes the Hybrid and Zero-Emission Vehicle (ZEV) Program, which provides rebates for the purchase of new electric cars, and the Clean Vehicle Rebate Project, which offers incentives for the purchase of used electric vehicles. The exact timeline and details of the phase-out will be determined by the state's budget and environmental goals.
After the incentives are discontinued, the cost of electric vehicles in California may increase, making them less affordable for some consumers. However, it's important to note that the state's commitment to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting sustainable transportation is expected to continue. The focus will shift towards other policies and programs, such as building a robust charging infrastructure, implementing stricter vehicle emission standards, and potentially offering other financial incentives or tax benefits for EV owners.
Yes, California has a comprehensive strategy to support the transition to zero-emission vehicles. While the specific details of future incentives are yet to be finalized, the state has indicated its intention to continue providing support for EV adoption. This could include funding for charging stations, tax credits, or other financial assistance programs. Additionally, the federal government's incentives, such as the federal tax credit for electric vehicles, may still be available to California residents, providing further financial benefits for EV buyers.