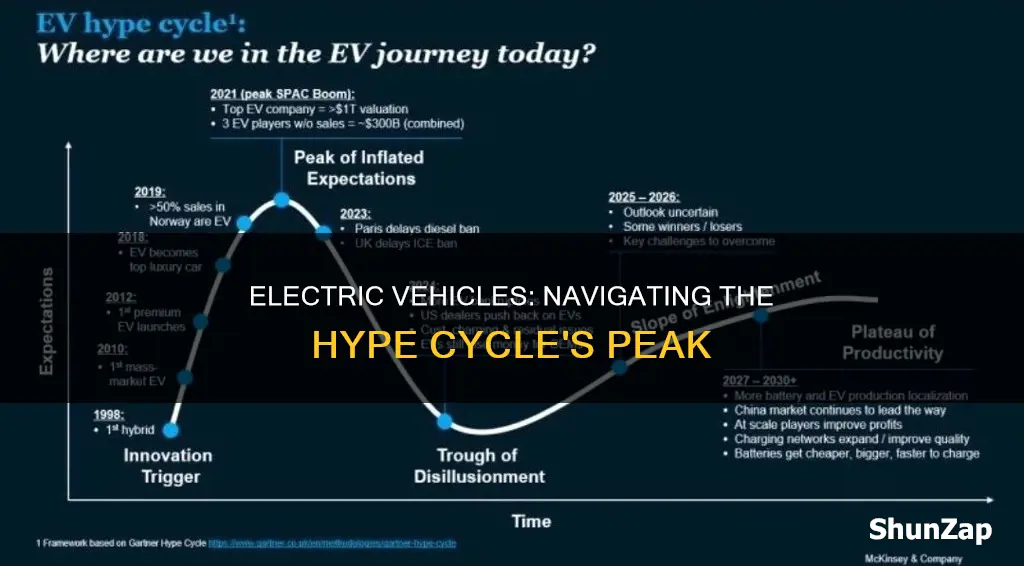
Electric vehicles (EVs) have been a hot topic in the automotive industry for several years, and their journey through the hype cycle has been an intriguing one. The hype cycle is a model that describes the typical pattern of excitement and adoption for emerging technologies, and EVs have certainly experienced their fair share of peaks and troughs. Initially, there was a surge of interest and media coverage, fueled by the promise of a greener future and the potential for reduced carbon emissions. However, as the initial hype wore off, the market faced challenges such as limited charging infrastructure, high costs, and concerns about battery technology. Despite these hurdles, EVs have continued to evolve and gain traction, with advancements in battery technology, increased range, and a growing network of charging stations. This paragraph introduces the discussion by highlighting the dynamic nature of the hype cycle and how it reflects the ongoing development and market reception of electric vehicles.
What You'll Learn
- Market Adoption: Slow growth, high expectations, and early adopters driving demand
- Infrastructure Development: Charging networks, battery tech, and grid integration are key
- Cost Reduction: Scaling production, battery costs, and government incentives are crucial
- Performance and Range: Advancements in battery tech and motor efficiency are essential
- Regulatory Support: Government policies, incentives, and standards shape the EV landscape

Market Adoption: Slow growth, high expectations, and early adopters driving demand
The electric vehicle (EV) market is currently experiencing a unique phase in its development, often referred to as the 'Market Adoption' stage within the hype cycle. This stage is characterized by a slow but steady growth in sales and adoption, despite high expectations and a strong presence of early adopters driving demand. The hype cycle, a popular model used to describe the lifecycle of new technologies, helps us understand the market dynamics and the journey of EV adoption.
In this phase, the market is witnessing a gradual shift towards electric mobility, with a growing number of consumers showing interest and making purchases. However, the growth rate is relatively slow compared to the initial excitement and hype that surrounded the introduction of EVs. This slow growth can be attributed to several factors. Firstly, the high upfront cost of electric vehicles remains a significant barrier, especially for price-sensitive consumers. Despite advancements in technology and increasing production volumes, EVs are still more expensive than their conventional counterparts, which can deter potential buyers. Additionally, the limited charging infrastructure in many regions poses a challenge, as it affects the convenience and range anxiety associated with electric cars.
Despite the slow growth, the EV market is far from stagnant. High expectations and a strong belief in the long-term benefits of electric mobility continue to drive demand. Early adopters, who are often environmentally conscious and tech-savvy, are playing a crucial role in this phase. These individuals are willing to invest in EVs despite the current limitations, as they recognize the potential for a more sustainable future. They advocate for the technology, share their positive experiences, and influence others to make the switch. This word-of-mouth promotion and the growing awareness of environmental issues are contributing to a positive shift in consumer perception.
The market adoption of EVs is also being influenced by government incentives and policies. Many countries are offering subsidies, tax benefits, and other incentives to encourage the purchase of electric vehicles. These measures aim to reduce the financial burden on consumers and make EVs more affordable. Furthermore, the increasing collaboration between automotive manufacturers and technology companies is leading to the development of innovative solutions, such as improved battery technology and faster charging systems, which will further enhance the appeal of electric cars.
In summary, the electric vehicle market is in the 'Market Adoption' phase of the hype cycle, marked by slow but promising growth. High expectations and the influence of early adopters are driving demand, despite the current challenges. As the technology matures and infrastructure improves, the market is expected to accelerate, leading to a more widespread adoption of electric vehicles and a significant impact on the automotive industry. This phase is crucial for the long-term success of EVs, as it lays the foundation for a sustainable and environmentally friendly transportation system.
Electric Vehicle Sales: The 1-Million Milestone Reached
You may want to see also

Infrastructure Development: Charging networks, battery tech, and grid integration are key
The development of electric vehicle (EV) infrastructure is a critical aspect of the EV's journey through the hype cycle, transforming the potential of EVs into a tangible reality. This infrastructure encompasses several key components, each playing a vital role in the widespread adoption of electric mobility.
Charging Networks: The establishment of a robust charging network is essential to address the range anxiety associated with EVs. Public and private charging stations need to be strategically deployed across urban and rural areas. Fast-charging stations, in particular, are crucial for long-distance travel, allowing EV owners to quickly recharge their batteries during journeys. The development of a comprehensive charging network infrastructure involves identifying optimal locations, ensuring accessibility, and implementing smart charging solutions that optimize energy usage and reduce strain on the power grid.
Battery Technology: Advances in battery technology are pivotal in the EV revolution. The development of more efficient, powerful, and sustainable batteries directly impacts the performance and appeal of electric vehicles. Researchers and engineers are focusing on improving energy density, reducing charging times, and extending battery life. Solid-state batteries, for instance, offer higher energy density and faster charging capabilities, addressing some of the current limitations of lithium-ion batteries. Additionally, recycling and sustainable sourcing of battery materials are essential to ensure the long-term viability of the EV industry.
Grid Integration: Integrating EV charging with the existing power grid is a complex but necessary task. As more EVs hit the roads, the grid must be able to handle the additional load. Smart grid technologies enable two-way communication between the grid and EVs, allowing for dynamic charging based on grid demand and availability. This integration ensures that charging sessions are optimized, reducing the risk of power outages and promoting a stable energy supply. Grid integration also involves developing energy storage solutions to manage the intermittent nature of renewable energy sources, which are increasingly being used to power charging stations.
The synergy between these three aspects of infrastructure development is crucial. A well-designed charging network, coupled with advanced battery technology, ensures that EV owners have convenient and efficient charging options. Simultaneously, grid integration enables the power grid to accommodate the growing number of EVs, facilitating a sustainable and reliable energy system. As the hype cycle progresses, addressing these infrastructure challenges will be pivotal in driving the widespread adoption of electric vehicles and reshaping the transportation landscape.
Unveiling the Mystery: Ice in Electric Vehicles
You may want to see also

Cost Reduction: Scaling production, battery costs, and government incentives are crucial
The electric vehicle (EV) market is at a pivotal point in its development, navigating the hype cycle, and addressing key challenges to ensure its long-term success. One of the most critical areas requiring attention is cost reduction, which encompasses several interrelated factors. Firstly, scaling production is essential to drive down costs. As the number of EVs produced increases, economies of scale can be realized, leading to lower manufacturing expenses. This is a fundamental principle of mass production, where the cost per unit decreases as production volume increases. For instance, Tesla's approach to vertical integration, where they control various stages of production, has allowed them to optimize costs and maintain a competitive edge.
Battery technology is another significant contributor to the overall cost of EVs. The development of more efficient and cost-effective batteries is crucial for the widespread adoption of electric vehicles. Research and investment in battery chemistry and manufacturing processes can lead to breakthroughs that reduce battery costs significantly. For example, solid-state batteries, which replace the liquid electrolyte with a solid conductive material, promise higher energy density and potentially lower production costs. As battery technology advances, the range and performance of EVs will improve, addressing consumer concerns about range anxiety and making electric vehicles more appealing to a broader market.
Government incentives play a pivotal role in accelerating the adoption of electric vehicles and driving down costs. Financial incentives, such as tax credits, rebates, and subsidies, can make EVs more affordable for consumers. These incentives not only reduce the upfront cost of purchasing an EV but also encourage the development of supporting infrastructure, such as charging stations, which are essential for EV ownership. Moreover, governments can implement policies that promote the recycling and second-life use of batteries, further reducing the environmental impact and cost associated with battery production and disposal.
In addition to these strategies, collaboration between governments, automotive manufacturers, and technology companies is vital. Joint efforts can lead to the development of standardized components and manufacturing processes, reducing the complexity and cost of production. Standardization can also facilitate the sharing of resources and expertise, accelerating the pace of innovation. By working together, these stakeholders can overcome the challenges of cost reduction and make electric vehicles more accessible and competitive in the market.
In summary, the journey of electric vehicles through the hype cycle requires a comprehensive approach to cost reduction. Scaling production, advancing battery technology, and leveraging government incentives are essential steps to make EVs more affordable and attractive to consumers. As the industry continues to evolve, addressing these cost-related challenges will be pivotal in ensuring the long-term sustainability and success of the electric vehicle market. This multi-faceted approach will contribute to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly transportation ecosystem.
Unveiling the Electric Vehicle Range: A Comprehensive Overview
You may want to see also

Performance and Range: Advancements in battery tech and motor efficiency are essential
The electric vehicle (EV) industry has been on a remarkable journey, and its progress can be best described as a rollercoaster ride, with the hype cycle being a fitting metaphor. As we delve into the heart of this cycle, it's crucial to recognize that the performance and range of electric vehicles are at the core of this discussion. These two factors are the driving forces behind the industry's evolution, pushing it forward and shaping its future.
Battery technology and motor efficiency are the twin pillars that support the entire EV ecosystem. Over the years, significant advancements have been made in both these areas, leading to improved performance and extended range. The development of lithium-ion batteries, for instance, has been a game-changer. These batteries offer higher energy density, allowing EVs to travel longer distances on a single charge. The introduction of solid-state batteries, which promise even greater energy density and faster charging, is on the horizon, further enhancing the appeal of electric vehicles.
Motor efficiency is another critical aspect. Electric motors have become more powerful and efficient, enabling EVs to accelerate faster and deliver better overall performance. The use of advanced materials and improved cooling systems has played a pivotal role in enhancing motor efficiency. As a result, electric vehicles now offer a more engaging driving experience, challenging the notion that EVs are sluggish and unresponsive.
The impact of these advancements is twofold. Firstly, it addresses a significant pain point for potential EV buyers—range anxiety. With improved battery technology and motor efficiency, EVs can now cover longer distances without the need for frequent charging stops, making them more practical for daily use. Secondly, it opens up new possibilities for EV manufacturers. The ability to offer longer ranges and better performance encourages more people to make the switch from traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles to electric ones.
In conclusion, the performance and range of electric vehicles are at the forefront of the hype cycle, driving the industry forward. The continuous advancements in battery technology and motor efficiency are not just improving the current state of EVs but also setting the stage for future innovations. As the industry matures, these advancements will play a pivotal role in shaping the perception of electric vehicles, making them more desirable and accessible to a broader audience.
Jeep's Electric Revolution: Rumors of a Green Future
You may want to see also

Regulatory Support: Government policies, incentives, and standards shape the EV landscape
The adoption and integration of electric vehicles (EVs) into mainstream transportation are significantly influenced by regulatory support, which includes government policies, incentives, and standards. These measures play a pivotal role in accelerating the EV revolution by addressing various challenges and fostering a conducive environment for EV manufacturers, consumers, and infrastructure developers.
Government policies are the cornerstone of EV promotion. Many countries have implemented regulations that mandate a certain percentage of new vehicle sales to be electric or zero-emission. These policies, often referred to as 'zero-emission vehicle' (ZEV) standards, encourage manufacturers to invest in EV technology and ensure a steady supply of EVs in the market. For instance, California's ZEV program has been instrumental in driving EV sales and technology development, setting an example for other regions to follow. Such policies not only promote EV sales but also create a long-term market for EV-related services and infrastructure.
Incentives, in the form of subsidies, tax credits, and rebates, are another powerful tool in the government's arsenal to boost EV adoption. These financial incentives reduce the upfront cost of purchasing EVs, making them more affordable and attractive to consumers. Many governments offer tax credits for EV purchases, with some countries providing additional benefits for the installation of home charging stations. For instance, the United States' federal tax credit for EV buyers can be up to $7,500, while some states offer additional incentives, further lowering the cost of ownership. These incentives not only benefit individual consumers but also stimulate the local economy by creating jobs in the EV manufacturing and service sectors.
Standards and regulations also play a critical role in the development and deployment of EV infrastructure. Governments set standards for charging stations, ensuring compatibility and interoperability across different EV models and charging networks. These standards facilitate the widespread adoption of EVs by providing a consistent and reliable charging experience for consumers. Additionally, regulations governing the safety and performance of EVs, such as those related to battery design and manufacturing, ensure that the technology is reliable and safe for consumers. This regulatory oversight is essential to building public trust in EVs and encouraging their long-term use.
The impact of regulatory support extends beyond the immediate benefits to consumers and manufacturers. It contributes to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly transportation sector. By encouraging the use of EVs, governments can reduce greenhouse gas emissions, improve air quality, and decrease dependence on fossil fuels. Moreover, the development of a robust EV ecosystem, supported by regulatory measures, can attract significant investments in research and development, fostering innovation and technological advancements in the field.
In summary, regulatory support, encompassing government policies, incentives, and standards, is a critical enabler in the EV landscape. These measures drive the market, reduce barriers to adoption, and create a sustainable future for transportation. As the EV industry continues to evolve, the role of governments in providing the necessary regulatory framework will be essential to accelerate the transition to a more environmentally friendly and efficient mobility system.
Green Revolution: Unveiling the Environmental Impact of Electric Vehicles
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The hype cycle is a graphical representation used in business and technology to describe the typical lifecycle of a technology or innovation, from its initial excitement and hype to its eventual maturity and adoption. In the context of EVs, the hype cycle illustrates the journey of this technology, showing the peaks of expectations, the troughs of disillusionment, and the eventual plateau of productivity.
Yes, EVs have been at the peak of the hype cycle for several years now. This is due to the growing awareness of climate change, government incentives, and the increasing availability of charging infrastructure. Consumers are becoming more interested in EVs, and the market is responding with a wide range of new electric car models, often with impressive performance and innovative features.
The trough of disillusionment is a critical phase where the initial hype fades, and the technology faces practical challenges. For EVs, some of the key issues include limited driving range, long charging times, high purchase costs, and the availability of charging stations. These factors can lead to customer dissatisfaction and a temporary dip in interest, as people wait for improvements in these areas.
To progress towards the plateau of productivity, the EV industry needs to address the challenges mentioned above. This includes investing in battery technology to increase range, reducing charging times, making EVs more affordable, and expanding the charging infrastructure network. Additionally, educating consumers about the benefits of EVs, such as lower running costs and reduced environmental impact, can help shift the perception and move the market towards a more sustainable and mature adoption phase.







