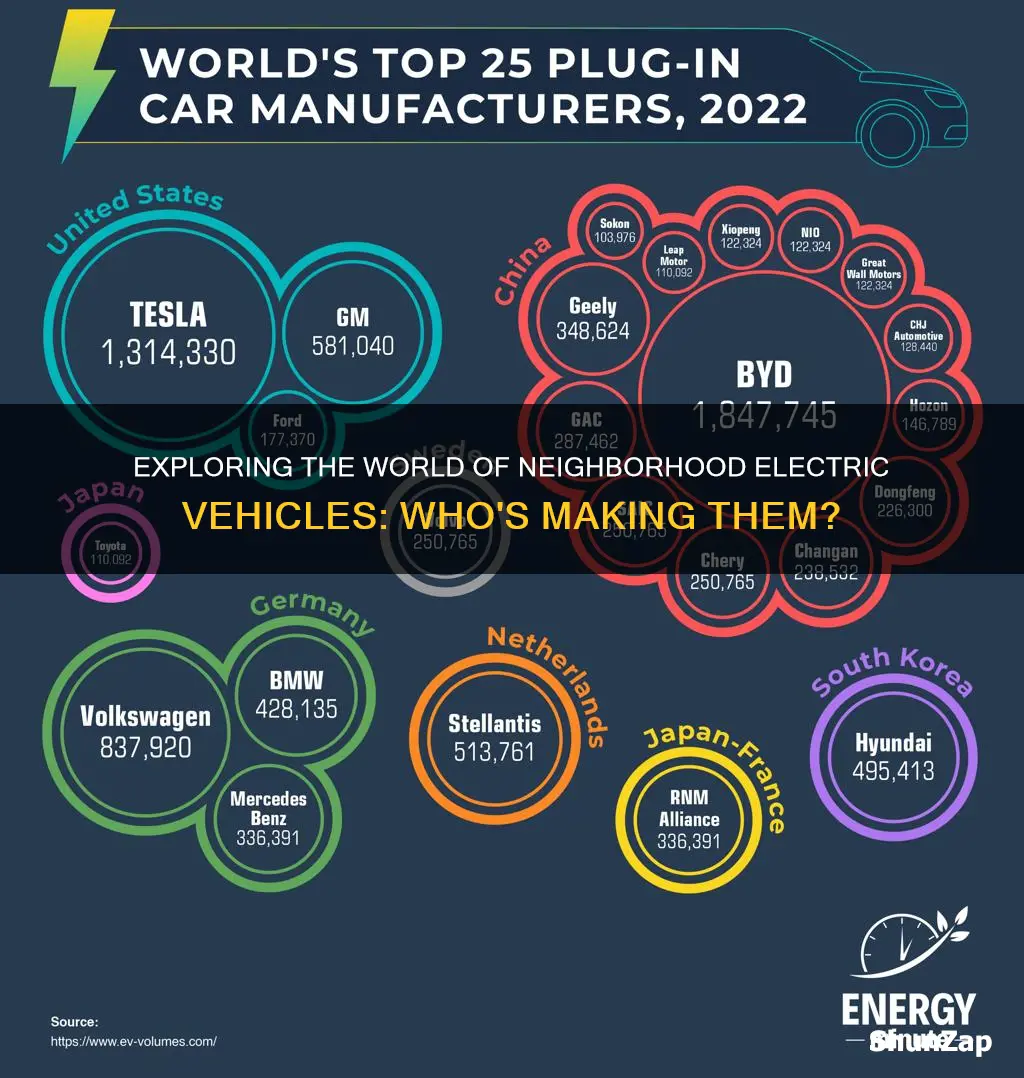
Neighborhood electric vehicles (NEVs) are a popular choice for short-distance transportation in urban areas, and several companies have entered the market to cater to this demand. These vehicles, designed for low-speed, short-range travel, are often used for commuting within neighborhoods, campus shuttling, and last-mile delivery services. Companies such as Zap, Club Car, and Propel are well-known producers of NEVs, offering a range of models from golf carts to more modern, electric-powered vehicles. Additionally, traditional automotive manufacturers like Ford, Chevrolet, and Mitsubishi have also ventured into the NEV market, providing consumers with more options and contributing to the growing popularity of these eco-friendly, efficient vehicles.
What You'll Learn
- Battery Technology: Focus on advanced battery packs for efficient range
- Motor Design: Companies engineering powerful, lightweight electric motors
- Charging Infrastructure: Development of convenient and fast charging solutions
- Safety Features: Implementing advanced safety measures for urban vehicle use
- Regulatory Compliance: Adherence to local regulations for neighborhood vehicle standards

Battery Technology: Focus on advanced battery packs for efficient range
The development of advanced battery technology is a crucial aspect of the electric vehicle (EV) industry, especially for neighborhood electric vehicles (NEVs) designed for short-range urban mobility. NEVs are typically used for local transportation within cities and urban areas, and their battery packs need to be efficient, compact, and capable of providing sufficient range to meet the demands of daily commutes. Here, we delve into the advancements in battery technology that focus on enhancing the range and performance of these vehicles.
One of the key challenges in NEV battery design is achieving a balance between energy density, power output, and overall efficiency. Advanced battery packs aim to maximize the energy storage capacity while minimizing the weight and volume of the battery system. This is achieved through the use of cutting-edge materials and innovative cell designs. For instance, lithium-ion batteries have become the go-to technology for EVs due to their high energy density and relatively low self-discharge rate. Companies like Panasonic and LG Energy Solution have been at the forefront of developing lithium-ion cells with improved performance, including higher voltage and energy density, making them ideal for NEVs.
To further enhance range, researchers and engineers are exploring various strategies. One approach is to increase the number of cells in a battery pack while optimizing their arrangement. This can be achieved through advanced module designs, such as the use of prismatic or pouch cells, which offer higher energy density and improved thermal management. For example, Tesla's battery packs utilize a unique design where multiple cells are stacked in a prismatic format, allowing for a compact and lightweight structure. Another strategy is to incorporate solid-state batteries, which replace the liquid electrolyte with a solid conductive material, potentially offering higher energy density and faster charging capabilities.
In addition to cell technology, battery management systems (BMS) play a critical role in optimizing the performance and longevity of advanced battery packs. BMS monitors and controls various parameters, such as voltage, current, and temperature, to ensure safe and efficient operation. It also helps in balancing the cells within the pack, maximizing energy output and minimizing degradation. Companies like Continental and Robert Bosch have developed sophisticated BMS solutions that provide real-time data and analytics, enabling better decision-making for both manufacturers and end-users.
The focus on efficient range has also led to the development of fast-charging technologies, which are essential for NEVs to be practical for daily use. Advanced battery packs can be designed to support rapid charging, reducing the time required to recharge and improving overall convenience. This involves optimizing the charging process, including the use of high-power chargers and advanced cooling systems to manage the heat generated during charging. By combining these technological advancements, companies are working towards creating NEVs with extended ranges, faster charging times, and improved overall performance, making them a viable and attractive transportation option for urban environments.
Unlock EV Tax Savings: A Guide to Maximizing Your Credit
You may want to see also

Motor Design: Companies engineering powerful, lightweight electric motors
The development of electric motors is a crucial aspect of the neighborhood electric vehicle (NEV) industry, as these motors need to be powerful, efficient, and compact to meet the specific requirements of urban transportation. Several companies are at the forefront of motor design, pushing the boundaries of what's possible in terms of performance and weight reduction.
One such company is Tesla, Inc., which has revolutionized the automotive industry with its innovative electric powertrains. Tesla's electric motors are renowned for their high power density, allowing for rapid acceleration and responsive handling in their vehicles. These motors utilize advanced materials and cooling systems to manage heat dissipation, ensuring optimal performance even under demanding conditions. The company's commitment to lightweight construction techniques further enhances the overall efficiency of their NEVs.
Another key player in motor design is Lotus Engineering, a subsidiary of Geely Holding Group. Lotus has a rich history in the automotive industry, known for its expertise in lightweight construction and high-performance vehicles. Their electric motors are designed with a focus on minimizing weight while maximizing power output. By utilizing advanced manufacturing processes and materials, Lotus achieves exceptional power-to-weight ratios, making their NEVs highly efficient and agile.
In the realm of NEV production, ZAP (Zero Auto Products) stands out with its unique approach to motor design. ZAP offers a range of lightweight electric motors specifically tailored for neighborhood electric vehicles. These motors are designed to provide high torque and efficiency, ensuring smooth acceleration and extended driving range. ZAP's motors are also known for their compact size, allowing for flexible vehicle design and integration.
Additionally, companies like Proterra and BYD (BuildYourDream) have made significant contributions to motor technology for NEVs. Proterra focuses on developing high-performance electric motors for commercial and passenger vehicles, ensuring durability and efficiency. BYD, a Chinese multinational company, has also made strides in motor design, offering powerful and lightweight solutions for various electric vehicle applications. These companies' innovations have played a vital role in advancing the NEV market by providing efficient and reliable motor systems.
Electric Revolution: Who Wins in the EV Market?
You may want to see also

Charging Infrastructure: Development of convenient and fast charging solutions
The development of charging infrastructure is a critical aspect of the widespread adoption of neighborhood electric vehicles (NEVs). NEVs, designed for short-range urban mobility, rely on efficient and accessible charging solutions to ensure their practicality and appeal to potential users. As the market for these vehicles grows, so does the need for robust charging networks that can support the increasing number of NEVs on the road.
One key aspect of developing convenient charging infrastructure is the implementation of fast-charging technologies. Traditional charging methods, while functional, are often slow and can deter potential EV owners. Fast-charging stations, typically found along highways and in strategic urban locations, can significantly reduce charging times. Companies like Tesla have pioneered this technology, allowing their vehicles to recharge to 80% capacity in under an hour. This rapid charging capability is essential for NEVs, which are often used for daily commutes and short-distance travel.
To ensure convenience, charging stations should be strategically placed in residential areas, commercial hubs, and along common travel routes. This placement encourages the adoption of NEVs by addressing the concern of limited charging options. For instance, installing charging points in parking lots, residential complexes, and public spaces can provide easy access to charging for NEV owners. This approach mirrors the convenience of traditional fuel stations, making the transition to electric vehicles more appealing.
The development of charging infrastructure also involves collaboration between various stakeholders. Governments play a crucial role in incentivizing the installation of charging stations by offering subsidies or tax benefits to businesses and individuals. Additionally, partnerships between NEV manufacturers and energy companies can lead to the creation of comprehensive charging networks. These networks can include a variety of charging options, from slow-charging home stations to rapid-charging stations, catering to different user needs.
Furthermore, the integration of smart charging technologies is essential for efficient and convenient charging. Smart charging systems can optimize energy usage, reduce strain on the power grid, and provide real-time data on charging status. These systems can also be integrated with renewable energy sources, further enhancing the sustainability of NEV charging infrastructure. By combining fast-charging capabilities with strategic placement and smart technologies, the development of charging infrastructure can significantly contribute to the success of the NEV market.
Exploring the Four Types of Electric Vehicles: A Comprehensive Guide
You may want to see also

Safety Features: Implementing advanced safety measures for urban vehicle use
In the realm of urban transportation, the development of neighborhood electric vehicles (NEVs) has gained significant traction, offering a sustainable and efficient solution for short-distance travel. As these vehicles become more prevalent, prioritizing safety becomes paramount, especially in densely populated urban areas. This article delves into the implementation of advanced safety features tailored for NEV use, ensuring a secure and reliable experience for both drivers and pedestrians.
One of the key safety measures is the integration of advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS). These systems employ a range of sensors and cameras to monitor the vehicle's surroundings, enabling it to detect potential hazards and assist the driver in avoiding accidents. For instance, forward-collision warning systems use radar or cameras to identify impending obstacles and automatically apply the brakes if the driver fails to respond in time. Similarly, lane-keeping assist systems help maintain the vehicle's position within its lane, reducing the risk of lane drift and potential collisions. These ADAS features are particularly crucial in urban settings, where traffic density and unpredictable road conditions demand heightened awareness.
Additionally, implementing robust braking systems is essential for NEV safety. Regenerative braking, a technology often associated with electric vehicles, allows for efficient energy recovery while providing a smooth and responsive braking experience. This system captures the kinetic energy generated during deceleration and converts it into electrical energy, recharging the vehicle's battery. Furthermore, anti-lock braking systems (ABS) ensure that the wheels do not lock up during braking, allowing the driver to maintain control and steer around obstacles. Combining regenerative braking with ABS enhances overall braking performance, making NEVs more responsive and safer in various urban driving conditions.
Another critical aspect of safety is the design and construction of the vehicle itself. NEVs should incorporate lightweight materials and robust structural frameworks to minimize the risk of damage in collisions. Additionally, implementing advanced crash-test simulations during the design phase can help identify potential weak points and ensure that the vehicle meets or exceeds safety standards. Side-impact protection, for example, can be enhanced through the use of advanced composites and reinforced pillars, providing added security for occupants during potential side-collision scenarios.
Furthermore, the integration of advanced communication systems can significantly contribute to NEV safety. Vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) communication enables NEVs to exchange data with nearby vehicles, alerting drivers to potential dangers and improving overall situational awareness. This technology can also facilitate communication with infrastructure, such as traffic lights and road signs, providing real-time updates on traffic conditions and potential hazards. By leveraging V2V communication, NEVs can become more proactive in avoiding accidents and optimizing urban traffic flow.
In conclusion, ensuring the safety of neighborhood electric vehicles in urban environments requires a multi-faceted approach. By implementing advanced driver-assistance systems, enhancing braking performance, focusing on vehicle design and construction, and utilizing advanced communication technologies, NEVs can become even safer and more reliable. As the demand for sustainable urban transportation continues to grow, investing in these safety features will play a pivotal role in shaping a future where NEVs are a trusted and integral part of city life.
Electric Vehicle Tax Credit: Deduction or Itemization?
You may want to see also

Regulatory Compliance: Adherence to local regulations for neighborhood vehicle standards
The production of neighborhood electric vehicles (NEVs) is a specialized field, and several companies have dedicated themselves to meeting the unique requirements of these low-speed, short-range vehicles. These companies often have a strong focus on regulatory compliance, ensuring their products adhere to local and regional standards. NEVs are designed for urban environments and are subject to specific regulations regarding speed, range, and safety.
One of the key aspects of regulatory compliance in NEV production is meeting the local speed limits. These vehicles are typically restricted to speeds of 25 mph or less, which requires careful engineering to ensure the vehicle's performance aligns with these standards. Companies like Proterra, a leading manufacturer of electric buses and NEVs, have designed their vehicles with advanced braking systems and speed control mechanisms to comply with these regulations. Their vehicles are equipped with regenerative braking, which slows the vehicle down while also recharging the battery, contributing to energy efficiency.
Additionally, NEVs must adhere to range requirements, often limited to 25 miles or less on a single charge. This specification is crucial for urban transportation, where vehicles need to navigate through densely populated areas with frequent stops and starts. Companies such as Taylor Mobility and Workhorse Group have developed NEVs with extended-range options, allowing for greater flexibility while still meeting the regulatory range limits. These vehicles often feature advanced battery technology and efficient powertrains to maximize range without compromising performance.
Safety is another critical area of regulatory compliance. NEVs must meet specific safety standards, including crashworthiness, lighting requirements, and visibility. Manufacturers invest in rigorous testing and certification processes to ensure their vehicles comply with local regulations. For instance, the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) in the United States sets safety standards for NEVs, and companies like E-Auto, a Chinese manufacturer, have designed their vehicles with advanced safety features to meet these standards.
Furthermore, companies producing NEVs must navigate the complex landscape of local and regional regulations. These may include licensing requirements, emission standards, and specific design guidelines. For example, in some cities, NEVs are subject to unique licensing processes, and companies must ensure their vehicles meet the necessary criteria for registration and operation. Staying abreast of these regulations is essential for manufacturers to ensure their products are legally compliant and accessible to potential customers.
GM's Electric Revolution: Unveiling the Future of Green Cars
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
NEVs are primarily produced by a range of companies, including specialized EV manufacturers, automotive startups, and even some traditional car brands. Some notable names include Proterra, Workhorse Group, and Niu Technologies, which focus specifically on electric vehicles for urban mobility. Additionally, companies like Ford, General Motors, and Nissan have also ventured into the NEV market with models like the Ford E-Series van and the Nissan e-NV200 van.
Yes, several well-known automotive brands have expanded their portfolios to include NEVs. For instance, Toyota has the bZ4X, a compact crossover designed for urban environments. Volkswagen's ID. Buzz is another example, offering a modern take on the iconic microbus for city driving. These brands bring their expertise in vehicle engineering and design to the NEV market.
NEVs offer several benefits for urban transportation. They are typically designed for short-range, low-speed travel within neighborhoods, making them ideal for last-mile connectivity. These vehicles are often more affordable and environmentally friendly compared to traditional cars. NEVs usually have lower maintenance costs, reduced noise levels, and can help decrease carbon emissions in urban areas.
NEVs are specifically designed for urban, low-speed applications, whereas traditional cars are built for higher speeds and longer distances. NEVs often have a smaller footprint, making them more maneuverable in tight city spaces. They may also feature unique designs and configurations, such as the iconic two-seater layout or the van-like structure of some models.
Absolutely! NEVs are versatile and can be utilized for various commercial applications. For example, companies like Workhorse Group produce electric delivery vans for last-mile package delivery. Niu Technologies offers electric scooters and bikes for urban cargo transport. These vehicles provide an eco-friendly and cost-effective solution for businesses operating in city centers.







