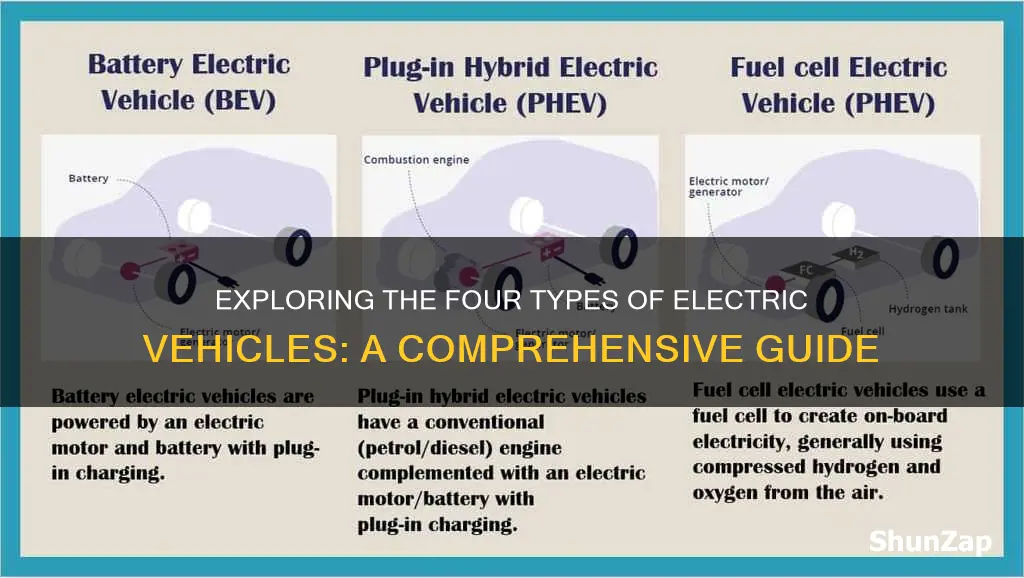
The world of electric vehicles (EVs) is rapidly expanding, offering a diverse range of options for eco-conscious drivers. These vehicles can be broadly categorized into four main types, each with unique characteristics and advantages. The first type is battery electric vehicles (BEVs), which are fully powered by batteries and produce zero tailpipe emissions. Next are plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs), which combine a traditional combustion engine with an electric motor and can be charged from an external power source. Hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) are another popular choice, utilizing both an electric motor and a conventional engine to provide efficient and environmentally friendly performance. Finally, fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEVs) use hydrogen as a fuel source to generate electricity, offering a zero-emission driving experience. Understanding these different types of EVs is essential for consumers to make informed decisions when choosing their preferred mode of sustainable transportation.
What You'll Learn
- Battery-Powered EVs: Cars and buses run on rechargeable batteries
- Hybrid EVs: Combines a traditional engine with an electric motor for efficiency
- Plug-in Hybrids: Like hybrids but can be fully charged from an external source
- Fuel Cell EVs: Uses hydrogen to generate electricity, emitting only water vapor
- Solar-Powered EVs: Vehicles that harness solar energy for propulsion or auxiliary power

Battery-Powered EVs: Cars and buses run on rechargeable batteries
Battery-powered electric vehicles (EVs) are a cornerstone of the automotive industry's shift towards sustainable transportation. These vehicles rely on rechargeable batteries as their primary power source, offering a cleaner and more efficient alternative to traditional internal combustion engines. The concept is simple: instead of burning fossil fuels, battery-powered EVs convert electrical energy into mechanical power, enabling them to move. This technology has seen remarkable advancements, making it a viable and increasingly popular choice for both personal and public transportation.
At the heart of battery-powered EVs are advanced rechargeable batteries. These batteries are typically lithium-ion, known for their high energy density and ability to store a significant amount of energy in a relatively compact space. The design of these batteries is crucial, as it determines the vehicle's range, charging speed, and overall performance. Modern EVs often feature sophisticated battery management systems that optimize charging, monitor temperature, and ensure the longevity of the battery pack.
The application of battery-powered EVs extends beyond personal cars. Electric buses, for instance, are becoming a common sight in many cities. These buses utilize the same rechargeable battery technology as cars but are designed to accommodate a larger number of passengers. The benefits of electric buses include reduced noise pollution, lower operating costs, and a smaller environmental footprint compared to traditional diesel buses. Many cities are now investing in electric bus fleets to improve public transportation and reduce urban air pollution.
One of the key advantages of battery-powered EVs is their ability to provide a smooth and quiet driving experience. Unlike traditional engines, electric motors offer instant torque, resulting in quick acceleration. This makes electric cars and buses responsive and enjoyable to drive. Additionally, the absence of the typical engine noise contributes to a quieter and more comfortable environment for passengers.
As technology advances, battery-powered EVs continue to evolve, addressing challenges such as charging infrastructure and battery range. The development of fast-charging stations and the improvement of battery technology are crucial steps in making electric vehicles more accessible and convenient for the masses. With ongoing research and development, the future of battery-powered EVs looks promising, paving the way for a more sustainable and environmentally friendly transportation ecosystem.
The Electric Revolution: Ford's Model T Redefined the Automotive World
You may want to see also

Hybrid EVs: Combines a traditional engine with an electric motor for efficiency
Hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) are a popular and efficient type of electric vehicle that combines the best of both worlds: a traditional internal combustion engine and an electric motor. This innovative design allows for improved fuel efficiency and reduced emissions, making it an attractive option for environmentally conscious drivers.
The key feature of HEVs is their ability to switch between the electric motor and the traditional engine seamlessly. When driving at lower speeds or during short distances, the vehicle primarily relies on the electric motor, which provides quiet, smooth, and efficient power. This is particularly beneficial in urban areas where frequent stops and starts are common. The electric motor can power the vehicle independently, eliminating the need for gear changes and providing a responsive driving experience.
As the vehicle's speed increases or during more demanding driving conditions, the traditional engine takes over. This engine can run independently or in conjunction with the electric motor, depending on the vehicle's needs. For example, when accelerating rapidly, both motors work together to provide a powerful boost, ensuring a smooth and responsive drive. This dual-power system allows HEVs to offer better performance and efficiency compared to conventional vehicles.
One of the significant advantages of hybrid technology is its ability to recover and store energy. When the vehicle brakes or decelerates, the electric motor acts as a generator, converting kinetic energy back into electrical energy. This energy is then stored in the vehicle's battery, which can be used later to power the electric motor or assist the traditional engine. This regenerative braking system not only improves efficiency but also extends the overall range of the vehicle.
HEVs are designed to provide a seamless driving experience, often feeling similar to a conventional vehicle in terms of performance and handling. However, the electric motor's instant torque provides a responsive and smooth acceleration, making the drive more enjoyable. Additionally, the combination of both power sources ensures that the vehicle can cover longer distances without the need for frequent refueling, making it a practical choice for daily commutes and long-distance travel.
In summary, hybrid electric vehicles offer a unique and efficient solution by merging traditional combustion engines with electric motors. This design provides improved fuel efficiency, reduced emissions, and a seamless driving experience. With their ability to recover and store energy, HEVs are a step towards a more sustainable and environmentally friendly transportation future.
Electric Vehicle Tax Credit: Annual or One-Time?
You may want to see also

Plug-in Hybrids: Like hybrids but can be fully charged from an external source
Plug-in hybrids are a unique breed of electric vehicle (EV) that combines the best of both worlds: the efficiency and environmental benefits of electric power with the convenience and range of a traditional combustion engine. These vehicles are designed to be charged from an external power source, typically an electrical outlet or a charging station, which sets them apart from conventional hybrids.
In essence, plug-in hybrids offer the flexibility to choose how and when to power the vehicle. Unlike conventional hybrids, which rely on a combination of electric and gasoline power, plug-in hybrids can be driven exclusively on electric power for a certain distance, thanks to their larger battery packs. This electric-only range can vary depending on the model, but it often provides enough power for daily commutes, especially in urban areas with shorter distances. When the battery is depleted, the vehicle seamlessly switches to a hybrid mode, utilizing both the electric motor and the internal combustion engine to extend the range.
The key advantage of plug-in hybrids is their ability to be fully charged from an external source. This means that unlike some fully electric vehicles, which require specialized charging infrastructure, plug-in hybrids can be conveniently charged at home, work, or public charging stations. This accessibility makes them more practical for a wide range of drivers, especially those who may not have access to dedicated EV charging facilities.
Charging a plug-in hybrid is straightforward. Most models come with a standard 120-volt charger that can be plugged into a regular electrical outlet, making it easy to charge at home. For faster charging, dedicated charging stations or 240-volt outlets can be used, reducing the time required to replenish the battery. This flexibility in charging options ensures that plug-in hybrids can be easily integrated into existing energy infrastructure.
In summary, plug-in hybrids represent a significant step towards a more sustainable transportation system. They offer the environmental benefits of electric power, the convenience of a combustion engine, and the flexibility to choose how and when to charge. With their ability to be fully charged from an external source, plug-in hybrids are an attractive option for those seeking a more efficient and environmentally friendly vehicle without compromising on range or convenience.
Debunking Myths: Are Electric Vehicles' Range Claims Reliable?
You may want to see also

Fuel Cell EVs: Uses hydrogen to generate electricity, emitting only water vapor
Fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEVs) are a fascinating and innovative type of electric vehicle that utilizes a unique power source to propel itself. These vehicles are a cutting-edge technology in the automotive industry, offering a sustainable and efficient mode of transportation. Here's an overview of how fuel cell EVs work and their environmental benefits:
Power Generation: At the heart of a fuel cell EV is a fuel cell stack, which is essentially a device that converts chemical energy into electrical energy through a process called electrochemical reaction. The primary fuel used in these vehicles is hydrogen, which is stored in high-pressure tanks on board. When the vehicle is in operation, the hydrogen gas is fed into the fuel cell stack along with oxygen from the air. Through a series of complex reactions, the hydrogen atoms combine with oxygen to form water, releasing a significant amount of energy in the process. This energy is then used to power the vehicle's electric motor, providing the necessary force to move the car.
Emission-Free Operation: One of the most remarkable aspects of fuel cell EVs is their environmental friendliness. Unlike traditional internal combustion engines, fuel cell vehicles produce zero tailpipe emissions. The only byproduct of the electrochemical reaction is water vapor, which is released into the atmosphere. This means that fuel cell EVs do not contribute to air pollution, making them a clean and sustainable transportation option. The absence of harmful emissions also makes these vehicles attractive for urban areas, where air quality is a significant concern.
Performance and Efficiency: These vehicles offer excellent performance and efficiency. The electric motor provides instant torque, resulting in quick acceleration and a smooth driving experience. The energy conversion process in fuel cells is highly efficient, typically converting over 60% of the chemical energy in hydrogen to electricity, which is then used to drive the vehicle. This efficiency, combined with the high energy density of hydrogen, allows fuel cell EVs to achieve impressive driving ranges, often exceeding 300 miles on a single hydrogen tank.
Refueling and Infrastructure: Refueling a fuel cell EV is a relatively quick process, similar to refueling a conventional gasoline vehicle. Hydrogen can be supplied through high-pressure hoses or specialized refueling stations that use compressed hydrogen gas or hydrogen gas from a pipeline. The infrastructure for refueling stations is gradually being developed, ensuring that fuel cell vehicle owners have convenient access to the necessary fuel.
Applications and Future Potential: Fuel cell EVs have the potential to revolutionize the automotive industry and contribute to a more sustainable future. They are particularly well-suited for long-distance travel, heavy-duty applications, and commercial fleets due to their high energy efficiency and rapid refueling. As technology advances, we can expect to see more fuel cell vehicles on the roads, offering an alternative to traditional battery-electric vehicles and internal combustion engine cars.
Unlocking the Future: A Beginner's Guide to Electric Vehicle Ownership
You may want to see also

Solar-Powered EVs: Vehicles that harness solar energy for propulsion or auxiliary power
Solar-powered electric vehicles (EVs) represent a unique and innovative approach to sustainable transportation, offering an alternative means of propulsion and auxiliary power generation. These vehicles harness the abundant energy of the sun, converting it into electricity to power the vehicle's electric motor or to charge the battery. This technology has gained traction as a promising solution to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and decrease the environmental impact of transportation.
The concept of solar-powered EVs is based on the use of photovoltaic (PV) cells, also known as solar panels. These panels are strategically placed on the vehicle's body, often on the roof or hood, to maximize sun exposure. When sunlight hits these panels, the PV cells absorb the solar energy and convert it directly into electricity through the photovoltaic effect. This electricity can then be utilized to power the vehicle's electric motor, drive the wheels, or charge the onboard battery.
One of the key advantages of solar-powered EVs is their ability to provide auxiliary power. These vehicles can generate electricity not only for propulsion but also for various onboard systems and accessories. For example, solar energy can be used to power air conditioning, heating systems, lights, and even entertainment devices, reducing the strain on the vehicle's main battery. This feature is particularly beneficial for long-distance travel, as it allows for more efficient energy management and can extend the vehicle's range.
Designing and engineering solar-powered EVs present unique challenges. The efficiency of solar panels is crucial, as they need to convert a significant amount of sunlight into usable electricity. Researchers and engineers are constantly working on improving the efficiency of PV cells and optimizing their placement on the vehicle to capture the maximum amount of solar energy. Additionally, the weight and space requirements of solar panels must be carefully considered to ensure they do not compromise the vehicle's performance and aesthetics.
Despite the challenges, solar-powered EVs offer a compelling solution for sustainable transportation. They contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions, decreasing noise pollution, and providing a renewable energy source. While the technology is still evolving and may not be suitable for all driving conditions or long-range travel, it represents a significant step towards a greener and more environmentally friendly future for the automotive industry. As research and development continue, solar-powered EVs may become a more viable and widespread option, offering an innovative and sustainable mode of transportation.
The Future of Driving: Electric Vehicles: A Sustainable Choice?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The four primary categories of electric vehicles are Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs), Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs), Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs), and Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles (FCEVs).
BEVs are fully electric and run exclusively on electricity stored in their batteries. They do not have a traditional internal combustion engine and produce zero direct emissions. These vehicles are charged by plugging into an electrical source, and the battery powers the motor, which turns the wheels.
PHEVs combine a conventional internal combustion engine with an electric motor and a rechargeable battery. They can be driven in electric mode for short distances using the battery, and when the battery is depleted, the gasoline engine takes over. PHEVs offer flexibility and can be charged by plugging into an outlet or refueled at a gas station.
HEVs, also known as conventional hybrids, use a combination of an internal combustion engine and an electric motor. However, the electric motor primarily assists the engine and does not provide a separate power source. HEVs recharge their batteries through regenerative braking and the internal combustion engine, but they cannot be plugged in to an external power source.