Electric vehicles (EVs) are a rapidly growing segment in the automotive industry, offering an eco-friendly and innovative alternative to traditional gasoline-powered cars. With advancements in technology, EVs have become increasingly popular due to their zero-emission nature, reduced running costs, and improved performance. This paragraph will explore the diverse range of electric vehicles available, from sleek and stylish sports cars to practical and efficient SUVs, and examine the factors that make them a viable choice for environmentally conscious consumers.
What You'll Learn
- Battery Technology: Innovations in battery chemistry and design for electric vehicles
- Charging Infrastructure: The development of charging stations and their impact on EV adoption
- Range Anxiety: Addressing consumer concerns about limited range and charging options
- Vehicle Types: Exploring electric cars, buses, trucks, and motorcycles
- Environmental Impact: The ecological benefits of electric transportation compared to fossil fuels

Battery Technology: Innovations in battery chemistry and design for electric vehicles
The evolution of electric vehicles (EVs) has been closely tied to advancements in battery technology, which has played a pivotal role in their development and widespread adoption. Innovations in battery chemistry and design have been instrumental in addressing the challenges associated with energy density, charging speed, and overall performance, making electric vehicles more practical and appealing to a broader audience.
One of the key areas of focus in battery technology is improving energy density. Researchers and engineers are constantly exploring new materials and architectures to pack more energy into a smaller space. This pursuit has led to the development of advanced lithium-ion batteries, which are currently the most prevalent technology in EVs. By optimizing the composition of the cathode and anode materials, scientists have achieved higher energy densities, allowing for longer driving ranges on a single charge. For instance, the use of nickel-rich cathodes in lithium-ion batteries has increased energy density, making it possible to fit more energy into the same volume.
Another critical aspect of battery innovation is enhancing charging speed. Fast-charging capabilities are essential to reduce the time required to recharge an EV's battery, making the technology more convenient for daily use. Researchers have been working on various approaches to accelerate charging, including improving the conductivity of electrode materials and developing advanced electrolytes. Solid-state batteries, for example, replace the liquid electrolyte with a solid conductive material, enabling faster charging and higher energy density. This technology is still in the development stage but holds great promise for the future of electric vehicles.
Battery design has also undergone significant transformations. The traditional cylindrical and prismatic cell designs have given way to more innovative forms, such as the pouch cell and the flexible, thin-film batteries. These new designs offer advantages in terms of weight reduction, improved safety, and customization. For instance, pouch cells, which are flexible and lightweight, are often used in electric bicycles and scooters, providing a more compact and efficient energy storage solution. Additionally, the integration of battery modules and packs with vehicle body structures is becoming more prevalent, allowing for better overall vehicle design and performance.
Furthermore, the development of battery management systems (BMS) has been crucial in optimizing the performance and longevity of electric vehicle batteries. BMS monitors and controls various parameters, such as temperature, voltage, and current, to ensure safe and efficient operation. These systems can also predict battery health, provide diagnostic information, and optimize charging strategies, thereby extending the battery's lifespan and improving the overall user experience.
In summary, the continuous innovation in battery chemistry and design has been a driving force behind the success of electric vehicles. As researchers and engineers strive to overcome the challenges of energy density, charging speed, and safety, they are pushing the boundaries of what is possible in battery technology. These advancements not only make electric vehicles more practical and efficient but also contribute to a more sustainable transportation future, reducing our reliance on fossil fuels and mitigating environmental impacts.
Amazon's Electric Vehicle Acquisition: A Green Revolution
You may want to see also

Charging Infrastructure: The development of charging stations and their impact on EV adoption
The widespread adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) is closely tied to the development of a robust charging infrastructure. As the number of EVs on the road increases, so does the demand for convenient and accessible charging solutions. This has led to a significant focus on building an extensive network of charging stations, which are essential for supporting the growing EV market.
Charging stations are designed to provide a quick and efficient way to replenish the battery of an electric vehicle. These stations come in various forms, including slow, fast, and rapid chargers, each catering to different charging needs. Slow chargers, typically found in residential areas and workplaces, provide a steady charge over several hours, making them ideal for overnight charging. Fast chargers, often located along highways and in public spaces, can replenish a significant portion of an EV's battery in 30-60 minutes, making them convenient for long-distance travel. Rapid chargers, the fastest among the three, can fully charge an EV in as little as 20-30 minutes, revolutionizing the concept of 'refueling' for electric cars.
The impact of this charging infrastructure development is twofold. Firstly, it addresses the range anxiety associated with EVs, a common concern among potential buyers. With a well-distributed network of charging stations, EV owners can plan their journeys with greater confidence, knowing they can easily find a charging point when needed. This, in turn, encourages more people to make the switch from traditional gasoline vehicles to electric ones. Secondly, the expansion of charging infrastructure creates new business opportunities. Companies are investing in the construction and management of charging stations, providing services that range from providing charging points in public spaces to installing home charging units for individual customers.
The development of charging infrastructure also has environmental benefits. As EVs become more prevalent, the overall carbon footprint of the transportation sector can be significantly reduced. Electric vehicles produce zero tailpipe emissions, and by ensuring efficient charging, the energy consumption and environmental impact of EV charging can be optimized. This is particularly important as the world moves towards a more sustainable and green energy future.
In summary, the creation of a comprehensive charging network is a critical aspect of the EV revolution. It not only addresses the practical concerns of potential EV owners but also opens up new avenues for economic growth and contributes to a more sustainable future. As the demand for electric vehicles continues to rise, the importance of investing in and improving charging infrastructure cannot be overstated.
The Green Revolution: Is the EV Shift Worth It?
You may want to see also

Range Anxiety: Addressing consumer concerns about limited range and charging options
The concept of electric vehicles (EVs) has gained significant traction in recent years, with many consumers embracing the idea of a greener, more sustainable mode of transportation. However, one of the most common concerns that potential EV buyers often express is 'range anxiety'—the fear of running out of battery power before reaching a charging station. This anxiety is a significant barrier to widespread EV adoption, as it can lead to hesitation and uncertainty among those considering the switch from traditional gasoline-powered cars.
To address this concern, it's essential to understand the factors contributing to range anxiety. Firstly, early electric vehicles had indeed limited ranges, often restricted to around 100-150 miles on a single charge, which was not sufficient for long-distance travel. However, modern EVs have made substantial strides in this regard. Contemporary electric cars offer a much-improved range, with many models now boasting over 300 miles on a full charge, thanks to advancements in battery technology and more efficient powertrains. This significant increase in range has largely alleviated the anxiety associated with long-distance travel in EVs.
Another aspect to consider is the charging infrastructure. The availability and accessibility of charging stations play a pivotal role in reducing range anxiety. Governments, automotive manufacturers, and energy companies are investing heavily in expanding charging networks. Public charging stations, including fast-charging options, are becoming increasingly common along highways and in urban areas. These stations enable drivers to recharge their vehicles quickly during long journeys, ensuring they can cover extended distances without the worry of running out of power. Additionally, home charging solutions are now more accessible and convenient, allowing drivers to charge their EVs overnight or during periods of low demand, further reducing the anxiety associated with range limitations.
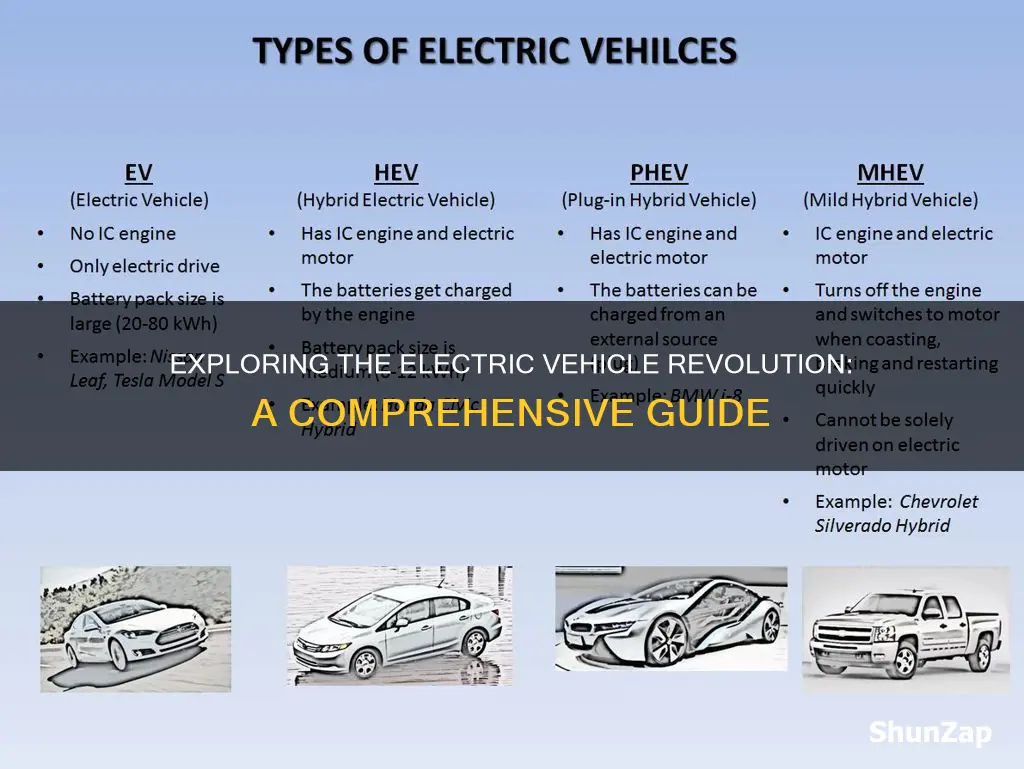
For those who are still hesitant, there are several strategies to mitigate range anxiety. One approach is to plan trips carefully, taking into account the range of the vehicle and the availability of charging stations along the route. Many modern EVs come equipped with onboard navigation systems that can provide real-time charging station information, helping drivers stay informed and make informed decisions. Another strategy is to consider dual-purpose vehicles, such as hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) or plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs), which offer the best of both worlds—a longer range and the flexibility to switch to gasoline power when needed. These options provide a practical solution for those who want to gradually transition to fully electric vehicles without the immediate range concerns.
In conclusion, while range anxiety was a valid concern in the early days of electric vehicles, it is no longer a significant barrier to adoption. Modern EVs offer impressive ranges, and the charging infrastructure is rapidly expanding to support long-distance travel. By understanding the advancements in technology and planning trips accordingly, consumers can confidently embrace the electric vehicle revolution, knowing that their range-related worries are becoming a thing of the past.
Electric Vehicles: Green or Greenwashing? Unveiling the Environmental Impact
You may want to see also

Vehicle Types: Exploring electric cars, buses, trucks, and motorcycles
The world of transportation is undergoing a quiet revolution, with electric vehicles (EVs) increasingly becoming a common sight on our roads, in our cities, and on our highways. This shift towards electrification is not just about personal cars; it's a movement that encompasses various vehicle types, each contributing to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly future. Let's delve into the diverse world of electric vehicles and explore the different types that are paving the way for a greener tomorrow.
Electric Cars: Perhaps the most iconic and widely recognized electric vehicle, electric cars have gained immense popularity in recent years. These vehicles are powered by one or more electric motors, which draw energy from rechargeable batteries. The appeal of electric cars lies in their zero-emission nature, offering a cleaner and quieter driving experience. Modern electric cars come in various shapes and sizes, from compact city cars to luxurious SUVs, providing an eco-friendly alternative to traditional gasoline or diesel vehicles. With improved battery technology, these cars now offer longer ranges, making them a practical choice for daily commutes and long-distance travel.
Electric Buses: Public transportation is also embracing electrification, and electric buses are leading the charge. These buses are designed to operate on electric power, often utilizing overhead wires or ground-level power supplies for charging. Electric buses offer numerous advantages, including reduced noise pollution, lower operating costs, and zero tailpipe emissions, making them an environmentally friendly choice for urban transportation. Many cities are now investing in electric bus fleets to improve air quality and reduce their carbon footprint. The design and size of these buses vary, from small shuttles to larger articulated buses, catering to different urban mobility needs.
Electric Trucks: The trucking industry is not immune to the electric revolution. Electric trucks are becoming increasingly popular, especially for short-haul deliveries and urban logistics. These trucks are powered by electric motors and batteries, offering a more sustainable alternative to diesel-powered vehicles. Electric trucks can be found in various sizes, from small delivery vans to heavy-duty haulers. They are particularly useful for reducing noise and emissions in urban areas, making them ideal for last-mile deliveries and local transportation. With advancements in battery technology, electric trucks are now capable of hauling heavy loads over longer distances, making them a viable option for various commercial applications.
Electric Motorcycles: For those seeking a two-wheeled electric experience, electric motorcycles are a thrilling and eco-friendly option. These motorcycles are powered by electric motors and offer a smooth and quiet ride. Electric motorcycles come in various styles, from sleek street bikes to rugged off-roaders. They are lightweight and agile, making them perfect for urban commuting and short-distance travel. With improved battery life and charging infrastructure, electric motorcycles are becoming a popular choice for environmentally conscious riders who don't want to compromise on performance.
The exploration of electric vehicles goes beyond these specific types, as the market continues to innovate and diversify. From electric boats and planes to hydrogen fuel cell vehicles, the possibilities are endless. As technology advances and environmental concerns grow, the adoption of electric transportation will likely expand, offering a more sustainable and efficient way to move people and goods. This shift towards electrification is a testament to the power of innovation and the collective effort to create a greener future.
Government Incentives: Accelerating the Shift to Electric Vehicles
You may want to see also

Environmental Impact: The ecological benefits of electric transportation compared to fossil fuels
The shift towards electric vehicles (EVs) is a pivotal movement in the transportation sector, offering a cleaner and more sustainable alternative to traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles. This transition is driven by the urgent need to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate the environmental impact of the transportation industry. Electric transportation, encompassing a range of vehicle types from cars and buses to motorcycles and trucks, presents several ecological advantages over their fossil fuel-powered counterparts.
One of the most significant environmental benefits of electric vehicles is the elimination of tailpipe emissions. ICE vehicles release a myriad of pollutants, including nitrogen oxides (NOx), particulate matter (PM), and carbon monoxide (CO), which contribute to air pollution and have detrimental effects on human health and the environment. In contrast, electric cars produce zero direct emissions, significantly improving air quality, especially in densely populated urban areas. This reduction in air pollution can lead to fewer respiratory and cardiovascular diseases, benefiting both public health and the environment.
The ecological benefits of electric transportation extend beyond the reduction of local air pollution. The widespread adoption of EVs can contribute to a substantial decrease in greenhouse gas emissions, primarily carbon dioxide (CO2), which is a major driver of climate change. Electric vehicles, when powered by renewable energy sources, offer a pathway to a low-carbon future. For instance, the use of EVs in urban fleets can help cities meet their emission reduction targets, as demonstrated by the success of electric bus fleets in cities like London and Amsterdam.
Furthermore, the environmental impact of electric transportation is not limited to the vehicles themselves. The entire lifecycle of an EV, from production to end-of-life, can be more sustainable compared to ICE vehicles. Electric cars, for example, have a lower carbon footprint during manufacturing due to the use of fewer heavy metals and the potential for recycling of battery components. Additionally, the charging infrastructure for EVs can be designed to incorporate renewable energy sources, further reducing the overall environmental impact.
In summary, electric transportation offers a compelling solution to the environmental challenges posed by the transportation sector. The ecological benefits include reduced air pollution, lower greenhouse gas emissions, and a more sustainable lifecycle compared to fossil fuel-powered vehicles. As technology advances and infrastructure develops, the widespread adoption of electric vehicles can contribute significantly to global efforts to combat climate change and create a cleaner, healthier environment. This transition is a crucial step towards a more sustainable and environmentally conscious future for transportation.
Out-of-State EV Owners: Register Your Car in California
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Electric vehicles (EVs) come in various forms, including cars, trucks, buses, motorcycles, scooters, and even airplanes. The most common and widely recognized electric vehicles are electric cars, which are powered by one or more electric motors and rechargeable batteries.
Electric vehicles operate using an electric motor that runs on electricity stored in batteries. When the driver engages the accelerator, the motor delivers power to the wheels, providing propulsion. EVs typically have a single-speed transmission, and the power is directly transferred to the wheels, resulting in smooth acceleration.
Electric cars offer several advantages, such as reduced environmental impact due to zero tailpipe emissions, lower operating costs compared to traditional gasoline or diesel vehicles, and high energy efficiency. EVs also provide a quiet and comfortable driving experience and often have advanced safety features and connectivity options.
One of the most obvious indicators is the presence of a charging port, usually located on the front or side of the vehicle. Electric vehicles also often have a different badge or logo on the grille or hood, indicating their electric nature. Additionally, some car manufacturers display a small 'e' or 'EV' icon on the dashboard to remind drivers of the vehicle's electric power source.