The invention of battery electric vehicles (BEVs) is a fascinating journey that has revolutionized the automotive industry. It all began in the late 19th century when pioneers like Robert Anderson and Thomas Davenport independently developed crude electric carriages, marking the initial spark of the BEV revolution. However, it was the visionary work of engineers like William Morrison in the early 20th century that laid the foundation for modern BEVs. Morrison's electric car, known as the Electric Wagon, was a significant milestone, but it was the contributions of more recent innovators, such as the Tesla team led by Elon Musk, that truly propelled BEVs into the mainstream. This evolution showcases the collective efforts of numerous inventors and engineers, each playing a crucial role in shaping the future of sustainable transportation.
What You'll Learn
- Early Pioneers: In the 19th century, pioneers like Robert Anderson and Thomas Davenport developed early electric carriages
- Global Innovations: Various countries contributed, with French inventor Gustave Trouvé and German inventor Andreas Flocken making significant early models
- Motor Development: The evolution of electric motors by inventors like Nikola Tesla and Charles Pollak was crucial for EV technology
- Battery Chemistry: Advances in battery chemistry, particularly lithium-ion batteries, revolutionized EV range and performance
- Modern Era: The 21st century saw rapid growth with companies like Tesla leading the way in mass-market electric vehicle adoption

Early Pioneers: In the 19th century, pioneers like Robert Anderson and Thomas Davenport developed early electric carriages
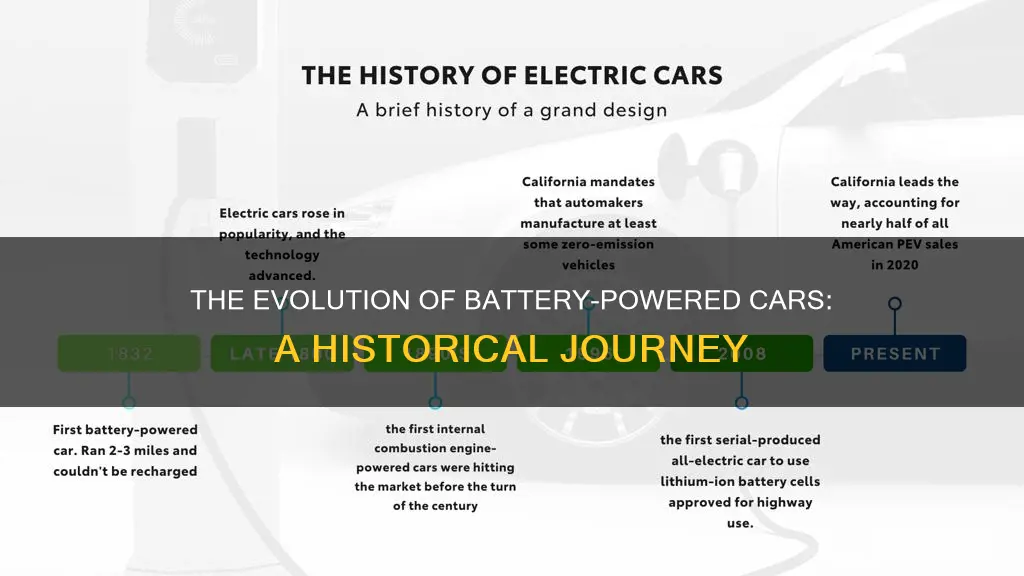
The concept of battery-powered electric vehicles has a rich history that dates back to the 19th century, with several early pioneers contributing to its development. One of the most notable figures during this period was Robert Anderson, a Scottish inventor who is often credited with creating one of the earliest electric carriages. Anderson's work in the 1830s laid the foundation for future advancements in electric mobility. His design involved a crude form of a battery-powered vehicle, which he demonstrated in Glasgow, Scotland. While Anderson's creation was not a practical or efficient means of transportation, it sparked interest and inspired others to explore the potential of electric power.
Another significant contributor to the early development of electric vehicles was Thomas Davenport, an American inventor. Davenport, in the 1830s, built an electric motor-powered carriage, which he successfully demonstrated in Vermont, USA. His invention was a significant step forward, as it utilized a lightweight, efficient electric motor to power the vehicle. Davenport's work attracted attention and led to further experimentation and improvements in electric vehicle technology.
These early pioneers, Anderson and Davenport, played crucial roles in the initial stages of electric vehicle development. Their efforts were instrumental in demonstrating the potential of electric power for transportation, even though the technology of the time had its limitations. The 19th century saw a surge in interest and experimentation, with numerous inventors and engineers contributing to the evolution of electric carriages. This period laid the groundwork for the modern electric vehicle industry, which has since become a leading force in sustainable transportation.
The 19th century's electric vehicle pioneers faced challenges in terms of battery technology, motor efficiency, and overall vehicle design. Despite these obstacles, their work was instrumental in shaping the future of electric mobility. Anderson and Davenport's contributions, along with those of other early innovators, paved the way for the development of more advanced and practical electric vehicles in the late 19th and early 20th centuries.
The legacy of these early pioneers continues to inspire modern electric vehicle manufacturers, who strive to build upon their groundbreaking work. The journey from these early electric carriages to the sophisticated electric cars and buses of today is a testament to the power of innovation and the dedication of countless inventors and engineers. As the world embraces sustainable transportation, the contributions of Robert Anderson and Thomas Davenport remain a vital part of the story.
Thermal Management: The Secret to EV Efficiency and Performance
You may want to see also

Global Innovations: Various countries contributed, with French inventor Gustave Trouvé and German inventor Andreas Flocken making significant early models
The development of battery-electric vehicles (BEVs) is a global story, with contributions from various countries and inventors over several decades. While the exact origins of the BEV are often attributed to a single inventor, it is important to recognize the cumulative efforts of many pioneers who laid the groundwork for modern electric mobility.
One of the earliest significant contributions came from France. Gustave Trouvé, a French engineer, is often credited with creating one of the first practical electric vehicles in the late 19th century. Trouvé's invention, known as the "Trouvé Electric Car," was a small, lightweight vehicle powered by a battery and an electric motor. This early model demonstrated the potential of electric propulsion and inspired further experimentation in the field.
In Germany, another pivotal figure emerged in the early 20th century. Andreas Flocken, a German engineer, is recognized for developing the first-ever electric automobile to be mass-produced. Flocken's company, Flocken Motorwerke, produced the "Flocken Elektrowagen" in 1888. This vehicle, while not as advanced as modern BEVs, showcased the feasibility of electric cars and sparked interest in electric transportation across Europe.
The contributions of these early inventors were instrumental in shaping the future of electric vehicles. Their work laid the foundation for the continuous advancements in battery technology, electric motors, and vehicle design that have led to the widespread adoption of BEVs today. Over time, the development of BEVs became a global effort, with countries and companies worldwide investing in research and development to create more efficient, sustainable, and environmentally friendly transportation solutions.
The story of BEVs is a testament to the power of international collaboration and innovation. While Gustave Trouvé and Andreas Flocken are notable pioneers, it is essential to acknowledge the countless other inventors and engineers who contributed to the evolution of electric vehicles. Their collective efforts have paved the way for a greener and more sustainable future in transportation.
Electric Vehicle Ownership: The American Shift to Green Transportation
You may want to see also

Motor Development: The evolution of electric motors by inventors like Nikola Tesla and Charles Pollak was crucial for EV technology
The development of electric motors played a pivotal role in the evolution of battery-powered vehicles, and several inventors contributed significantly to this technological advancement. One of the most renowned figures in this field is Nikola Tesla, a Serbian-American inventor and engineer. Tesla's work on alternating current (AC) motors in the late 19th century laid the foundation for the efficient and powerful electric motors used in modern electric vehicles (EVs). His AC induction motor design, which utilized a rotating magnetic field, was a breakthrough as it could operate at various speeds and provide high torque, making it ideal for automotive applications.
Charles Pollak, an American engineer, also made significant contributions to electric motor technology. In the early 20th century, Pollak developed a unique type of electric motor known as the "Pollak Motor." This motor was designed with a specific focus on efficiency and was used in various applications, including early electric vehicles. Pollak's motor utilized a unique commutator design, which allowed for improved power transmission and reduced energy losses, making it a significant advancement in electric motor technology.
The evolution of electric motors by these inventors and others was crucial for the development of battery-powered vehicles. As the demand for cleaner and more sustainable transportation grew, the need for efficient and reliable electric motors became apparent. Tesla's AC induction motor design provided the basis for many early electric vehicles, offering a practical and powerful solution for powering cars. The advancements in motor technology allowed for higher energy densities, improved efficiency, and longer driving ranges, making electric vehicles a viable alternative to traditional internal combustion engine cars.
The impact of these inventors' work can be seen in the modern electric vehicle market, where companies like Tesla, Inc., have revolutionized the industry. Tesla's use of advanced electric motors and battery technology has set new standards for performance, efficiency, and sustainability. The continuous development and refinement of electric motors by various engineers and researchers have led to the creation of high-performance electric vehicles that can compete with their gasoline counterparts in terms of speed, range, and overall driving experience.
In summary, the evolution of electric motors, driven by the efforts of inventors like Nikola Tesla and Charles Pollak, has been instrumental in the advancement of battery-electric vehicle technology. Their contributions have paved the way for a greener and more sustainable transportation future, offering efficient and powerful solutions for powering vehicles without the need for traditional internal combustion engines. The ongoing research and development in electric motor technology will continue to shape the EV industry, making it an exciting and rapidly evolving field.
The Evolution of Hybrid and Electric Cars: A Green Revolution
You may want to see also

Battery Chemistry: Advances in battery chemistry, particularly lithium-ion batteries, revolutionized EV range and performance
The evolution of battery electric vehicles (BEVs) has been significantly influenced by advancements in battery chemistry, with lithium-ion batteries playing a pivotal role in revolutionizing the range and performance of these vehicles. The development of lithium-ion batteries can be traced back to the 1970s, primarily through the work of Stanley Whittingham, a British chemist. Whittingham's research focused on developing a rechargeable battery that could store a large amount of energy in a lightweight and compact form, which was crucial for the emerging electric vehicle market. His efforts laid the foundation for the modern lithium-ion battery.
The key to the success of lithium-ion batteries lies in their ability to store and release energy efficiently. These batteries utilize a unique chemistry that involves the movement of lithium ions between two electrodes, typically a lithium metal oxide anode and a carbonaceous cathode. This process allows for the storage of electrical energy, which can then be converted back into mechanical energy to power the vehicle. The development of advanced lithium-ion battery technology has led to several breakthroughs in EV performance.
One significant advancement is the increase in energy density. Lithium-ion batteries have achieved much higher energy densities compared to their predecessors, such as lead-acid and nickel-cadmium batteries. This higher energy density translates to longer driving ranges for electric vehicles. Modern lithium-ion batteries can store more energy in a smaller and lighter package, allowing for the creation of more efficient and powerful EVs. For example, the introduction of lithium-ion phosphate (LiFePO4) batteries has further improved safety and extended the lifespan of these batteries, making them ideal for electric vehicles.
Another critical aspect of battery chemistry advancements is the improvement in charging speed and cycle life. Modern lithium-ion batteries can charge much faster than earlier versions, reducing the time required for a full charge. This is particularly important for EV owners who need to quickly recharge their vehicles during long journeys. Additionally, the cycle life of lithium-ion batteries has been extended, meaning they can withstand more charge-discharge cycles without significant performance degradation. This longevity ensures that electric vehicles retain their performance and reliability over an extended period.
The impact of these advancements in battery chemistry is evident in the widespread adoption of electric vehicles. As lithium-ion batteries became more efficient, affordable, and reliable, they became the standard power source for BEVs. This shift has led to a significant reduction in the environmental impact of transportation, as electric vehicles produce zero tailpipe emissions. Moreover, the continuous development of battery chemistry is driving further improvements in EV technology, such as the integration of solid-state batteries, which promise even higher energy densities and faster charging times.
Unlocking California's EV Future: Exploring Tax Credits and Incentives
You may want to see also

Modern Era: The 21st century saw rapid growth with companies like Tesla leading the way in mass-market electric vehicle adoption
The 21st century has witnessed a remarkable acceleration in the development and adoption of battery-electric vehicles (BEVs), with a significant shift towards a more sustainable and environmentally friendly transportation sector. This era has seen the rise of innovative companies that have revolutionized the automotive industry, with Tesla being at the forefront of this electric vehicle (EV) revolution.
Tesla, founded by a group of engineers, including Martin Eberhard and Marc Tarpenning, in 2003, has played a pivotal role in bringing electric cars to the mainstream market. The company's initial focus on creating a stylish and high-performance electric sports car, the Roadster, helped to spark interest in BEVs among a wider audience. However, it was their subsequent models, such as the Model S, that truly propelled Tesla into the spotlight and set a new standard for electric vehicles. These models offered impressive range, rapid acceleration, and a sleek design, challenging the notion that electric cars were slow and unattractive.
The success of Tesla has had a profound impact on the automotive industry, encouraging traditional car manufacturers to invest heavily in electric vehicle technology. As a result, the market has seen a rapid increase in the availability of electric cars, with various brands introducing their own BEVs to compete with Tesla. This competition has driven innovation, leading to improved battery technology, faster charging times, and more efficient electric motors. The 21st century has also seen the development of advanced battery management systems, which optimize power distribution and extend the range of electric vehicles, addressing one of the primary concerns of early EV adopters.
In addition to technological advancements, the 21st century has brought about a shift in consumer behavior and government policies that have further fueled the growth of the BEV market. Many countries have implemented incentives and subsidies to encourage the purchase of electric cars, while also investing in charging infrastructure to support widespread adoption. This combination of consumer demand and supportive policies has created a favorable environment for the mass-market acceptance of electric vehicles.
The impact of this rapid growth in the electric vehicle sector is far-reaching. It has not only reduced the environmental footprint of the transportation industry but has also sparked a new era of innovation and competition. As more companies enter the market, the focus on sustainability and green technology is expected to intensify, driving further advancements in battery technology and overall vehicle performance. The 21st century, indeed, marks a significant turning point in the history of battery-electric vehicles, with Tesla and other pioneers leading the charge towards a more sustainable future.
Unveiling the Power of Mild Hybrid Electric Vehicles: A Comprehensive Guide
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The invention of the first battery-powered vehicle is often attributed to Robert Anderson, a Scottish inventor, who created a crude electric carriage in the 1830s.
No, while Thomas Davenport, an American inventor, is known for his contributions to electric motors and batteries, he did not invent the electric car. His work laid the foundation for future developments in electric transportation.
The first practical and successful battery-electric vehicle was the 'Electric Horse' or 'Electric Carriage' invented by Robert Anderson and Robert Davidson in the 1830s and 1840s, respectively.
Many pioneers and companies have contributed to the evolution of modern electric vehicles. For instance, William Morrison, an American inventor, built the first practical electric car in the late 19th century. In the 21st century, companies like Tesla, led by Elon Musk, have revolutionized the electric car market with innovative designs and technology.
Yes, several early pioneers include Thomas Parker, a British inventor, who built the first practical production electric carriage in the 1880s. In the early 20th century, the Woods Motor Vehicle Company, founded by William Wood, produced electric cars. These early innovators paved the way for the modern electric vehicle industry.







