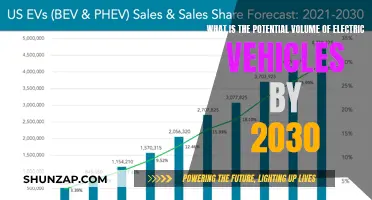
The sales of electric vehicles (EVs) have been slower than expected, despite the growing environmental concerns and technological advancements in the industry. This paradoxical situation can be attributed to several factors, including high upfront costs, limited charging infrastructure, and consumer skepticism about battery technology and range anxiety. Additionally, the traditional automotive industry's resistance to change and the lack of incentives for consumers to make the switch from conventional vehicles have further contributed to the slow adoption of EVs. Understanding these challenges is crucial for stakeholders to develop effective strategies to accelerate the transition to a more sustainable transportation ecosystem.
What You'll Learn
- High upfront cost: Electric vehicles (EVs) often have a higher purchase price compared to traditional gasoline cars
- Limited charging infrastructure: The availability of charging stations is still insufficient in many areas, causing range anxiety
- Battery technology limitations: Current battery technology restricts range and charging times, impacting long-distance travel and convenience
- Consumer perception: Some consumers perceive EVs as less reliable or less stylish, hindering widespread adoption
- Government incentives: Inadequate or inconsistent incentives and subsidies can discourage potential buyers from making the switch

High upfront cost: Electric vehicles (EVs) often have a higher purchase price compared to traditional gasoline cars
The high upfront cost of electric vehicles (EVs) is a significant barrier to their widespread adoption. While the long-term savings and environmental benefits of EVs are well-documented, the initial financial outlay can be a deterrent for many potential buyers. On average, electric cars carry a premium of around $5,000 to $10,000 more than their gasoline counterparts, even when accounting for similar features and specifications. This premium is primarily due to the advanced technology and battery systems that power EVs, which are more expensive to manufacture and integrate into the vehicle.
The higher purchase price is often a result of several factors. Firstly, the development and production of electric powertrains require significant investment in research and development, leading to higher component costs. The batteries, in particular, are a major expense, as they account for a substantial portion of the vehicle's total weight and cost. These batteries are complex systems, requiring advanced materials and manufacturing processes, which contribute to the elevated price tag. Additionally, the infrastructure needed to support EV charging, such as charging stations and power grid upgrades, adds to the overall cost, making EVs less affordable for many consumers.
Another factor is the lower production volumes of EVs compared to traditional cars. With lower sales, manufacturers often face higher per-unit production costs due to economies of scale. This is further exacerbated by the limited availability of certain raw materials and components, which can drive up prices. As a result, the high upfront cost of EVs can be a significant challenge for budget-conscious consumers, especially those who are price-sensitive and prefer to buy vehicles with a lower initial investment.
Despite the higher purchase price, it is essential to consider the long-term savings and potential return on investment. Electric vehicles offer reduced fuel and maintenance costs, as they have fewer moving parts and require less frequent servicing. Over time, these savings can offset the initial higher cost, making EVs a more economical choice. However, the transition period to a more sustainable transportation system requires a shift in consumer mindset and financial incentives to make EVs more accessible and affordable to a broader audience.
In conclusion, the high upfront cost of electric vehicles is a critical factor in the slow sales of EVs. While the technology and environmental benefits are undeniable, the financial barrier needs to be addressed through various means, including government incentives, improved charging infrastructure, and increased production efficiency. By reducing the initial cost and making EVs more affordable, the industry can accelerate the adoption of electric vehicles and contribute to a more sustainable future.
The Green Evolution: When EVs Outshine Fossil Fuels
You may want to see also

Limited charging infrastructure: The availability of charging stations is still insufficient in many areas, causing range anxiety
The widespread adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) has been hindered by a critical challenge: limited charging infrastructure. This issue is a significant barrier to potential EV buyers, especially those in rural or suburban areas where access to charging stations is scarce. The fear of running out of battery charge, known as range anxiety, remains a primary concern for many, despite the continuous improvement in EV battery technology.
The current charging infrastructure is inadequate to support the growing number of EVs on the road. Many public charging stations are often occupied or located far from residential areas, making it inconvenient for daily use. This lack of accessibility means that drivers often rely on home charging, which can be slow and may not always be feasible due to limited access to suitable power outlets or the need for additional equipment. As a result, the convenience and practicality of owning an EV are compromised, especially for those with longer commutes or specific travel needs.
To address this, governments and businesses must invest in expanding the charging network. This includes installing more charging stations in public spaces, such as shopping malls, parking lots, and rest stops, making them more widely available. Additionally, incentivizing the installation of home charging stations can provide a convenient solution for many EV owners. These measures will not only alleviate range anxiety but also encourage more people to make the switch to electric vehicles.
Furthermore, the development of fast-charging technologies can significantly reduce charging times, making the process more efficient and appealing. While the initial investment in infrastructure may be substantial, the long-term benefits are clear. Improved charging infrastructure will not only boost the sales of EVs but also contribute to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly transportation system.
In summary, the limited availability of charging stations is a critical factor in the slow sales of electric vehicles. By addressing this issue through infrastructure development and technological advancements, we can make EVs more accessible and appealing to a wider audience, ultimately contributing to a greener future.
Electric Vehicle Mileage Tax: Fair or Unfair for Drivers?
You may want to see also

Battery technology limitations: Current battery technology restricts range and charging times, impacting long-distance travel and convenience
The widespread adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) has been hindered by several factors, and one of the most significant challenges lies in battery technology. The current limitations in battery technology have a direct impact on the sales and overall appeal of EVs. One of the primary concerns is the range anxiety associated with electric cars. Despite advancements, modern electric vehicles still struggle to match the range of their gasoline counterparts, especially for long-distance travel. This is primarily due to the energy density of the batteries, which needs to be significantly improved to store more energy in a smaller and lighter package. As a result, drivers often feel the need to plan their trips meticulously, ensuring access to charging stations along the route, which can be a cumbersome and time-consuming process.
The charging time for electric vehicles is another critical issue. Current battery technology requires substantial time to recharge, often several hours, which is a significant drawback compared to the mere minutes needed to refuel a conventional car. This extended charging time can be a major inconvenience for daily commuters and those with busy schedules, making it less appealing for regular use. The inefficiency in charging technology is a barrier to the widespread adoption of EVs, especially in regions where charging infrastructure is not well-developed.
Furthermore, the physical size and weight of batteries pose challenges. To achieve the desired range, batteries need to be large and heavy, which can negatively impact the vehicle's performance, handling, and overall driving experience. This is particularly evident in sports cars and luxury vehicles, where the weight of the battery pack can compromise the vehicle's agility and acceleration. As a result, manufacturers are constantly seeking innovative solutions to reduce the size and weight of batteries without compromising energy storage capacity.
In summary, battery technology limitations are a significant hurdle in the widespread acceptance of electric vehicles. The range and charging time constraints, coupled with the physical size and weight of batteries, create a complex set of challenges. Overcoming these limitations will require substantial investments in research and development, leading to more efficient and powerful battery systems that can address the concerns of potential EV buyers.
Unlock Savings: Florida's EV Tax Credit Explained
You may want to see also

Consumer perception: Some consumers perceive EVs as less reliable or less stylish, hindering widespread adoption
Consumer perception plays a significant role in the slow adoption of electric vehicles (EVs), and it is a critical factor that manufacturers and marketers must address. One of the primary concerns that potential buyers have is the perceived reliability of EVs. Despite significant advancements in technology, some consumers still associate electric cars with a lack of dependability, often due to the relatively recent introduction of these vehicles to the market. This perception of lower reliability can be attributed to the limited understanding of EV technology and the fear of potential issues related to battery life, charging infrastructure, and the overall lifespan of the vehicle. As a result, many consumers are hesitant to make the switch from traditional gasoline or diesel vehicles, fearing that an EV might break down more frequently or require more frequent and costly maintenance.
Additionally, the style and aesthetics of EVs are often overlooked by critics, who argue that these vehicles lack the visual appeal and sophistication of their conventional counterparts. This perception is particularly relevant in the luxury car market, where consumers are accustomed to sleek designs and powerful engines. Electric vehicles, with their emphasis on sustainability and environmental friendliness, sometimes come across as utilitarian or even unattractive to those seeking a more traditional and stylish driving experience. The design challenge for EV manufacturers is to strike a balance between creating a visually appealing vehicle that aligns with the latest trends in the automotive industry while also conveying a sense of innovation and environmental consciousness.
To address these concerns, car companies should focus on transparent communication about the reliability and performance of their electric models. Providing detailed information about the advanced safety features, long-term durability, and the extensive charging network available can help alleviate buyer's worries. Moreover, investing in design research and development to create aesthetically pleasing EVs without compromising on performance and efficiency is essential. This approach would not only appeal to a broader consumer base but also contribute to the overall success of the EV market by challenging the notion that electric vehicles are less reliable or stylish.
In summary, consumer perception significantly impacts the sales of electric vehicles, with reliability and style being key factors in their decision-making process. By addressing these concerns through improved communication and innovative design, the automotive industry can work towards increasing the adoption of EVs and contributing to a more sustainable future. It is through these strategic efforts that the market can overcome the current barriers to widespread EV ownership.
Unraveling the Mystery: Electric Vehicle Index Demystified
You may want to see also

Government incentives: Inadequate or inconsistent incentives and subsidies can discourage potential buyers from making the switch
The low sales of electric vehicles (EVs) can be attributed to various factors, and one significant aspect often overlooked is the role of government incentives and subsidies. While many countries have recognized the importance of promoting sustainable transportation, the effectiveness of these incentives varies greatly, and in some cases, they may even be counterproductive.
Incentives play a crucial role in encouraging consumers to adopt electric vehicles. These incentives can take the form of tax credits, rebates, or subsidies that directly reduce the purchase price of EVs. For instance, some governments offer substantial tax breaks for EV buyers, making these vehicles more affordable and attractive. However, the impact of such incentives is often limited due to their short-term nature. Many buyers are hesitant to invest in a technology that may not be supported or incentivized in the long term. This uncertainty creates a sense of risk, especially for those who are considering a significant financial commitment.
Inadequate or inconsistent incentives can lead to confusion and frustration among potential EV buyers. When governments change their policies frequently, it becomes challenging for consumers to make informed decisions. For example, a sudden shift in subsidies or the introduction of new, conflicting incentives can leave buyers unsure about the future value of their purchase. This uncertainty may prompt buyers to opt for traditional vehicles, which are generally more reliable in terms of long-term ownership costs.
Furthermore, the inconsistency in incentives across different regions or countries can also hinder the widespread adoption of EVs. A buyer in one region might benefit from generous subsidies, while someone in another area receives minimal support. This disparity creates an unfair market and may discourage potential buyers from considering electric vehicles, especially if they are aware of the better deals available elsewhere.
To address this issue, governments should aim for a more consistent and long-term approach to incentives. Providing stable and reliable support for EV buyers can build trust and encourage the market to grow. Additionally, educating consumers about the benefits of electric vehicles and the potential long-term savings can help mitigate the concerns caused by inconsistent incentives. By ensuring a more predictable and supportive environment, governments can play a vital role in accelerating the transition to electric mobility.
Green Incentives: Why Go Electric?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The low sales of electric vehicles can be attributed to several factors. Firstly, the initial cost of purchasing an EV is often higher compared to traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles, which can be a significant deterrent for many consumers. However, this gap is narrowing as technology advances and more affordable EV options become available. Secondly, the charging infrastructure for EVs is still developing, and the availability of charging stations varies across regions, causing range anxiety among potential buyers. Lastly, consumer habits and preferences play a role, as many people are accustomed to the convenience of refueling ICE vehicles and may be hesitant to switch to a different charging method.
Yes, there are certain market segments that show a higher interest in electric vehicles. For instance, environmentally conscious consumers who prioritize sustainability and are willing to invest in eco-friendly alternatives are more likely to consider EVs. Additionally, younger demographics, such as millennials and Gen Z, tend to be early adopters of new technologies and are more open to the idea of electric mobility. Furthermore, urban dwellers who rely on public transportation might see EVs as a convenient and cost-effective solution for their daily commute.
Government policies and incentives can significantly influence the sales of electric vehicles. Many countries and regions offer tax credits, rebates, or subsidies to encourage consumers to purchase EVs. These financial incentives can make the upfront cost more manageable and attractive to buyers. Moreover, governments are also investing in improving charging infrastructure, making it more accessible and convenient for EV owners. By combining these measures, governments aim to accelerate the transition to electric mobility and reduce the environmental impact of the transportation sector.
Absolutely, the lack of awareness and education about electric vehicles can be a significant barrier to their adoption. Many potential buyers might not fully understand the benefits, features, and long-term cost savings of EVs. Educating the public about the environmental advantages, performance, and convenience of electric vehicles is crucial. This can be achieved through awareness campaigns, community events, and partnerships with automotive manufacturers and environmental organizations. By increasing awareness, the industry can address misconceptions and encourage more people to consider electric vehicles as a viable option.