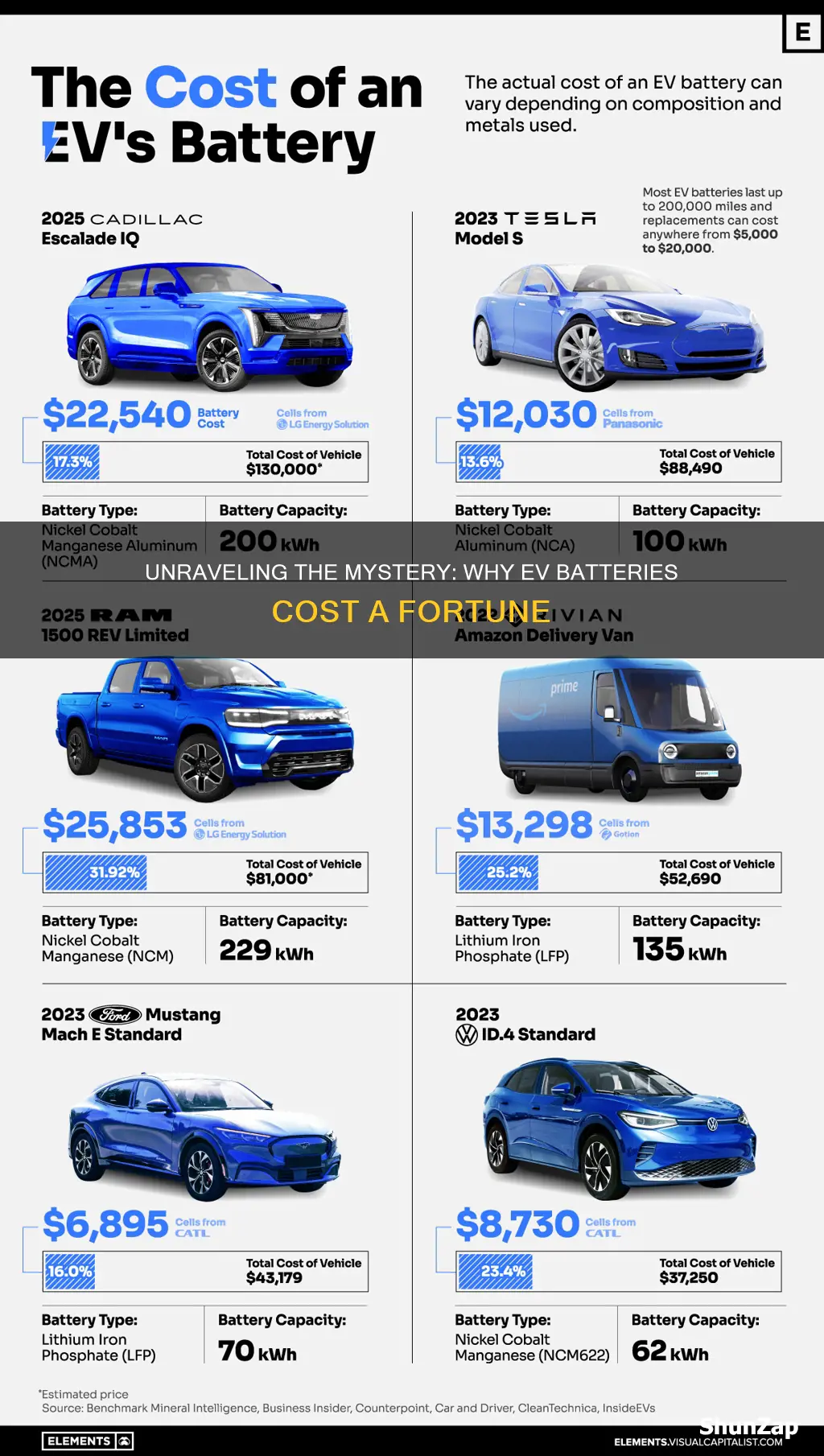
Electric vehicle batteries are a significant component of the cost of electric vehicles, and their high price is a major barrier to widespread adoption. The expense of these batteries is primarily due to the cost of the raw materials, such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel, which are essential for their production. Additionally, the complex manufacturing process and the need for specialized equipment contribute to the high cost. This paragraph will explore the factors that make electric vehicle batteries so expensive and discuss potential solutions to reduce their cost.
What You'll Learn
- Raw Materials: Limited supply and high demand for lithium, cobalt, and nickel drive up costs
- Manufacturing Complexity: Advanced battery production requires specialized equipment and intricate processes
- Research & Development: High R&D costs for innovation and technology improvements contribute to higher prices
- Supply Chain: Long and complex supply chains increase costs due to transportation and logistics
- Market Demand: High demand for EVs leads to increased battery prices as manufacturers meet growing consumer needs

Raw Materials: Limited supply and high demand for lithium, cobalt, and nickel drive up costs
The high cost of electric vehicle (EV) batteries is largely attributed to the raw materials used in their production, particularly lithium, cobalt, and nickel. These materials are essential components of the lithium-ion batteries that power EVs, and their availability and demand significantly impact the overall expense.
Firstly, lithium is a critical element in the battery's cathode, which stores and releases energy. The supply of lithium is limited, and its extraction is an energy-intensive process. The primary sources of lithium are hard-rock mining and brine extraction, both of which have environmental implications. The finite nature of these resources and the increasing global demand for lithium have led to a surge in prices. As a result, EV manufacturers are faced with the challenge of securing a consistent supply of lithium at a reasonable cost, which directly influences the battery's price.
Cobalt, another key component, is primarily used in the cathode material, lithium cobalt oxide (LCO). Cobalt is a rare metal, and its mining is associated with ethical concerns, including child labor and environmental degradation in some regions. The limited availability of cobalt, coupled with its high demand, contributes to its expensive nature. The global supply chain for cobalt is complex, and any disruptions or geopolitical tensions can cause significant price fluctuations, further impacting the EV battery's cost.
Nickel, used in the battery's anode, is also a critical raw material. While nickel is more abundant than lithium and cobalt, its extraction and processing can be challenging. The high demand for nickel, driven by the growing EV market, has led to increased prices. Additionally, the recycling of nickel-containing batteries is a complex process, and the recovery rate is relatively low, adding to the overall cost.
The limited supply and high demand for these raw materials create a delicate balance in the market. As the global shift towards EVs accelerates, the demand for these materials is expected to rise further. This situation has led to increased investment in exploration and mining, as well as efforts to improve recycling technologies. However, until these measures can significantly increase the supply, the cost of raw materials will likely remain a significant factor in the expense of EV batteries.
Green Incentives: Why Go Electric?
You may want to see also

Manufacturing Complexity: Advanced battery production requires specialized equipment and intricate processes
The high cost of electric vehicle (EV) batteries is largely attributed to the intricate manufacturing processes and specialized equipment required to produce these advanced energy storage systems. Battery production involves a series of complex steps, each demanding precision and advanced technology.
One of the primary reasons for the complexity is the need for specialized equipment. Manufacturing lithium-ion batteries, the most common type used in EVs, requires sophisticated machinery. These machines are designed to handle the precise assembly of various components, including the cathode, anode, electrolyte, and separator. Specialized equipment ensures that each component is accurately positioned and aligned, which is crucial for the battery's performance and safety. For instance, advanced coating machines are used to apply thin layers of materials to the electrodes, requiring high precision to achieve the desired thickness and uniformity.
The manufacturing process itself is a multi-step journey. It begins with the preparation of raw materials, which are then processed and transformed into the various battery components. The cathode, for example, is made by mixing and drying lithium-based compounds, followed by a complex process of coating and rolling to create a thin, flexible layer. Similarly, the anode is produced through a process of mixing and shaping graphite particles. Each step requires precise control of temperature, pressure, and chemical composition to ensure the quality and performance of the final product.
Furthermore, the intricate design of lithium-ion batteries demands a meticulous assembly process. This involves carefully stacking the cathode and anode layers, separating them with a thin polymer membrane, and then encapsulating the entire assembly. Each layer must be precisely aligned to ensure optimal performance and safety. The assembly process also includes the integration of various electronic components, such as the battery management system, which monitors and controls the battery's operation.
The complexity of manufacturing EV batteries is further exacerbated by the need for quality control and safety measures. Stringent testing and inspection procedures are implemented at each stage of production to ensure that the batteries meet the required standards. This includes electrical testing, thermal analysis, and safety assessments to identify and mitigate potential risks. The high cost of production is, therefore, a result of the specialized equipment, intricate processes, and rigorous quality control measures required to deliver reliable and safe energy storage solutions for electric vehicles.
Electric Revolution: Soaring Demand for Green Cars
You may want to see also

Research & Development: High R&D costs for innovation and technology improvements contribute to higher prices
The high cost of electric vehicle (EV) batteries is a significant barrier to widespread adoption, and research and development (R&D) plays a pivotal role in this context. The development of advanced battery technologies is an intricate and costly process, requiring substantial investments in research and innovation. One of the primary reasons for the high R&D costs is the need for continuous technological advancements. Battery manufacturers strive to improve energy density, charging speed, cycle life, and safety, all of which are critical factors in the performance and appeal of EVs. These advancements often demand cutting-edge materials, novel manufacturing processes, and sophisticated engineering solutions, all of which contribute to increased R&D expenses.
For instance, lithium-ion batteries, the most common type used in EVs, have seen significant improvements over the years, but the quest for higher energy density and faster charging rates continues. Researchers are exploring solid-state batteries, which promise higher energy density and faster charging, but these technologies are still in the early stages of development and require substantial R&D investments. The complexity of battery chemistry and the need for specialized materials, such as lithium metal or silicon-based anodes, further drive up R&D costs.
Additionally, the regulatory landscape and safety standards for batteries are stringent, requiring extensive testing and validation. This process is resource-intensive and time-consuming, adding to the overall R&D burden. Manufacturers must ensure their batteries meet or exceed safety standards, which often involves rigorous safety protocols and extensive testing, all of which contribute to higher prices.
Furthermore, the high R&D costs are also a result of the competitive nature of the EV battery market. Companies are constantly vying for market share and technological leadership, driving them to invest heavily in research and innovation. This competitive environment encourages continuous improvement and differentiation, which, in turn, raises the bar for R&D expenditures. As a result, the pursuit of technological superiority and market dominance becomes a significant factor in the pricing dynamics of EV batteries.
In summary, the high R&D costs associated with electric vehicle batteries are a multifaceted issue. They stem from the need for continuous technological advancements, the complexity of battery chemistry, stringent regulatory requirements, and the competitive market dynamics. These factors collectively contribute to the higher prices of EV batteries, presenting a challenge for the widespread adoption of electric vehicles. Addressing these R&D challenges is crucial for driving down costs and making EVs more accessible to the general public.
Unlock Savings: Florida's EV Tax Credit Explained
You may want to see also

Supply Chain: Long and complex supply chains increase costs due to transportation and logistics
The high cost of electric vehicle (EV) batteries is a multifaceted issue, and one significant contributor to this expense is the intricate and lengthy supply chain involved in their production. The supply chain for EV batteries is a complex web of processes, materials, and transportation, which collectively adds to the overall cost.
In the realm of EV battery manufacturing, the supply chain often begins with the extraction and processing of raw materials. These materials, including lithium, cobalt, nickel, and manganese, are sourced from various regions around the world. The transportation of these raw materials over long distances incurs significant costs, especially when considering the specialized logistics required for handling such commodities. For instance, lithium, a critical component, is often transported via cargo ships or trains, a journey that can span thousands of miles, leading to substantial transportation expenses.
As the supply chain progresses, the raw materials undergo a series of processing steps, each requiring energy-intensive processes and specialized equipment. These manufacturing processes are often located in specific regions, creating another layer of complexity in logistics. For instance, the production of lithium-ion batteries involves a multi-stage process, from cell manufacturing to assembly, which may be spread across different countries or even continents. This distributed nature of the supply chain means that each stage incurs transportation and logistics costs, contributing to the overall expense.
Furthermore, the transportation of intermediate goods and finished batteries adds to the complexity. Batteries are heavy and bulky, requiring specialized shipping methods, such as large container trucks or even cargo planes for international shipments. These specialized transportation methods are not only expensive but also contribute to the environmental impact of the supply chain. The long-distance transportation of batteries also means that they are more susceptible to damage during transit, leading to potential quality control issues and additional costs for reworks or replacements.
In summary, the supply chain for EV batteries is a critical factor in their high cost. The long and complex nature of this supply chain, involving international transportation, multiple processing stages, and specialized logistics, all contribute to the overall expense. Addressing these supply chain challenges is essential for making electric vehicles more affordable and accessible to a broader market.
Power Down: Strategies for When Your EV's Battery Fails
You may want to see also

Market Demand: High demand for EVs leads to increased battery prices as manufacturers meet growing consumer needs
The market demand for electric vehicles (EVs) has been on a remarkable rise, and this surge in popularity is a significant contributor to the escalating costs of EV batteries. As more consumers are drawn to the environmental benefits and technological advancements of electric cars, the demand for these vehicles has skyrocketed. This increased demand creates a ripple effect throughout the supply chain, particularly in the battery manufacturing sector.
Manufacturers of electric vehicle batteries are faced with the challenge of meeting the growing consumer appetite for EVs. The production of batteries requires a complex process involving rare earth metals, lithium, and other specialized materials. These raw materials are finite and often sourced from specific regions, which can lead to supply constraints. When demand exceeds supply, prices tend to rise, and this is exactly what has been happening in the EV battery market.
The high demand for EVs is not just a result of consumer preference but also influenced by government incentives and regulations. Many countries and regions have implemented policies to encourage the adoption of electric vehicles, such as tax credits, subsidies, and even mandates. These incentives have further stimulated the market, driving up the demand for EVs and, consequently, the demand for their batteries. As a result, manufacturers are under pressure to scale up production to fulfill these growing orders, often at the expense of maintaining lower prices.
The relationship between market demand and battery prices is a delicate balance. While increased demand provides manufacturers with the opportunity to expand production, it also puts pressure on their ability to control costs. To meet the rising demand, companies may need to invest in additional infrastructure, research and development, and raw material sourcing, all of which contribute to higher production costs. These increased costs are then often passed on to consumers in the form of higher battery prices.
In summary, the high demand for electric vehicles is a primary driver of the rising costs of EV batteries. As manufacturers strive to meet the growing consumer needs, they face challenges in managing production costs while also ensuring a steady supply of batteries. This dynamic market situation highlights the intricate relationship between consumer preferences, government policies, and the resulting impact on the prices of essential components like EV batteries.
Green Machines: Unveiling Hybrid's Eco-Friendly Secrets
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The primary reason for the high cost of electric vehicle (EV) batteries is the use of rare and expensive materials. Lithium-ion batteries, which are commonly used in EVs, require materials like lithium, cobalt, nickel, and manganese. These elements are not only rare but also have complex extraction processes, making them costly to source and refine. Additionally, the large-scale production of batteries requires significant investment in manufacturing facilities and specialized equipment, further contributing to the overall expense.
Yes, the automotive industry and battery manufacturers are actively working on strategies to decrease battery costs. Research and development efforts focus on improving battery chemistry, optimizing production processes, and exploring alternative materials. For instance, solid-state batteries, which use solid electrolytes instead of liquid ones, have the potential to offer higher energy density and lower costs. Scaling up production and achieving economies of scale can also help drive down prices over time.
Battery prices for electric vehicles have been historically higher than the cost of traditional ICE vehicle engines. However, this gap is narrowing as technology advances and production volumes increase. The total cost of ownership (TCO) of EVs, including battery costs, maintenance, and fuel savings, is often lower over the vehicle's lifetime compared to ICE vehicles. Moreover, government incentives and subsidies in many regions aim to make EVs more affordable and competitive.
Absolutely! Technological advancements play a crucial role in reducing battery costs. Improvements in battery chemistry can enhance energy density, allowing for smaller and lighter batteries without compromising performance. Advancements in manufacturing processes, such as automation and more efficient assembly lines, can also drive down production costs. Additionally, recycling and second-life applications for used batteries can help reduce overall costs and promote sustainability.
Yes, battery prices can vary significantly between different EV models and manufacturers. Factors such as battery capacity, energy density, brand reputation, and target market influence pricing. High-end luxury EVs often feature larger, more advanced batteries, which contribute to higher costs. However, as the market matures and production volumes increase, we can expect to see a wider range of battery options and prices, making EVs more accessible to a broader consumer base.