Electric vehicles (EVs) are gaining popularity due to their environmental benefits and performance, but they often come with a higher price tag compared to traditional gasoline-powered cars. This cost can be attributed to several factors, including the advanced technology and materials used in EV production, such as powerful electric motors, advanced batteries, and sophisticated electronics. Additionally, the limited production volumes of many EVs can drive up prices due to higher development and research costs. The high cost of EVs is also influenced by government incentives and subsidies aimed at promoting the adoption of electric cars, which can further impact the overall price. Understanding these factors is essential for consumers considering the switch to electric vehicles.
What You'll Learn
- Battery Technology: Advanced lithium-ion batteries are expensive to produce
- Research and Development: High R&D costs for innovative EV designs
- Production Complexity: Complex manufacturing processes increase production costs
- Supply Chain Constraints: Limited availability of raw materials drives up prices
- Government Incentives: Tax credits and subsidies can offset initial high costs

Battery Technology: Advanced lithium-ion batteries are expensive to produce
The high cost of electric vehicles (EVs) is often attributed to the advanced battery technology they employ, specifically the lithium-ion batteries that power these vehicles. These batteries are a critical component of EVs, providing the necessary energy to run the vehicle and, in some cases, even offering the option for vehicle-to-grid (V2G) capabilities. However, the production of these advanced batteries is a complex and resource-intensive process, which contributes significantly to the overall cost of EVs.
Lithium-ion batteries consist of several key components, including the anode, cathode, electrolyte, and separator. Each of these components is carefully engineered to optimize performance, energy density, and safety. For instance, the anode and cathode materials are chosen for their ability to store and release lithium ions efficiently, while the electrolyte facilitates the movement of these ions between the electrodes. The separator, often made of a porous material, ensures that the electrodes do not come into direct contact, preventing short circuits and enhancing safety.
The manufacturing process of these batteries is intricate and requires specialized equipment and materials. The production of lithium-ion cells involves multiple steps, including mixing and casting electrode materials, assembling the cell components, and sealing the battery. Each step demands precise control over temperature, pressure, and chemical composition to ensure the battery's performance and longevity. The use of advanced materials, such as lithium cobalt oxide (LCO) or lithium iron phosphate (LFP) for the cathode, and graphite or silicon for the anode, further adds to the complexity and cost of production.
One of the primary reasons for the high cost of lithium-ion battery production is the limited availability and high price of raw materials. Lithium, cobalt, nickel, and other metals are essential for battery manufacturing, and their extraction and processing can be environmentally and socially challenging. For example, lithium mining often involves environmentally damaging techniques, and the extraction of cobalt, a key component in many cathodes, has been associated with ethical concerns and high costs. Additionally, the specialized equipment required for battery manufacturing, such as advanced mixing and casting machines, contributes to the overall production expense.
Research and development efforts are ongoing to address these cost challenges and improve battery technology. Scientists and engineers are exploring alternative materials and designs to reduce the reliance on expensive and limited resources. For instance, solid-state batteries, which replace the liquid electrolyte with a solid conductive material, offer potential improvements in energy density and safety. Other innovations include the development of more efficient recycling processes for used batteries and the optimization of manufacturing processes to reduce waste and increase efficiency. These advancements aim to make lithium-ion batteries more affordable and accessible, ultimately contributing to the broader goal of making electric vehicles more cost-effective and environmentally friendly.
Uncovering the Profitable Segments in the EV Supply Chain
You may want to see also

Research and Development: High R&D costs for innovative EV designs
The high cost of electric vehicles (EVs) is a multifaceted issue, and one significant contributor to this is the substantial investment required for research and development (R&D) in innovative EV designs. The automotive industry is undergoing a rapid transformation towards electrification, with a focus on developing more efficient, sustainable, and technologically advanced vehicles. This shift demands a significant R&D effort, which, in turn, adds to the overall cost of EVs.
Research and development in the EV sector involves a wide range of activities, including battery technology, electric motor design, power electronics, and vehicle architecture. Each of these areas requires extensive testing, prototyping, and refinement to meet the stringent performance, safety, and environmental standards. For instance, battery technology is a critical component of EVs, and R&D efforts are directed towards improving energy density, charging speed, and cycle life. This involves complex chemical formulations, advanced manufacturing processes, and rigorous safety testing to ensure the batteries are both powerful and safe.
Innovative designs also extend to the vehicle's overall architecture, aiming to optimize weight, aerodynamics, and efficiency. This includes the development of lightweight materials, efficient cooling systems, and streamlined body shapes. Such innovations require significant R&D investments, as they often involve collaboration between various engineering disciplines and the creation of specialized tools and equipment.
Furthermore, the regulatory environment for EVs is stringent, with various safety, emission, and performance standards that must be met. Compliance with these regulations adds another layer of complexity and cost to the R&D process. Manufacturers must ensure their vehicles meet or exceed these standards, which often requires extensive testing and validation, further increasing the R&D budget.
In summary, the high R&D costs for innovative EV designs are a critical factor in the overall cost of electric vehicles. This investment is necessary to drive technological advancements, improve performance, and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements. While these costs contribute to the higher upfront price of EVs, they are essential to fostering the development of sustainable and efficient transportation solutions for the future.
Electric Vehicle Battery Life: Unlocking the Future of Sustainable Driving
You may want to see also

Production Complexity: Complex manufacturing processes increase production costs
The production of electric vehicles (EVs) is a complex and intricate process that contributes significantly to their higher cost compared to traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles. One of the primary reasons for this complexity is the advanced technology and specialized components required in EV manufacturing.
Electric powertrains, for instance, consist of multiple components such as electric motors, power electronics, batteries, and sophisticated control systems. Each of these components demands precise engineering and manufacturing techniques. The electric motor, for example, requires advanced materials and intricate winding processes to achieve the necessary power and efficiency. Similarly, the power electronics module, which manages the flow of energy between the battery and the motor, must be highly efficient and compact, pushing manufacturers to employ complex assembly methods.
Battery technology is another critical aspect of EV production. Lithium-ion batteries, commonly used in EVs, are composed of numerous cells, each requiring meticulous assembly and testing. The manufacturing process involves intricate steps like cell stacking, electrolyte injection, and sealing, all of which contribute to higher production costs. Moreover, the stringent safety standards and regulations for batteries, especially in high-performance EVs, add layers of complexity and expense to the production process.
Furthermore, the integration of these advanced components into the vehicle's chassis and body is a challenging task. EVs often feature lightweight materials and innovative structural designs to optimize performance and efficiency. This requires sophisticated manufacturing techniques, such as advanced welding, bonding, and molding processes, which are more complex and time-consuming compared to traditional vehicle assembly.
The complexity of EV production extends beyond the individual components to the overall assembly process. EVs have a higher number of interconnected systems, requiring intricate wiring harnesses and sophisticated software integration. This complexity increases the time and resources needed for manufacturing, contributing to the higher costs associated with these vehicles.
In summary, the intricate manufacturing processes and the integration of advanced technologies in electric vehicles lead to increased production costs. This complexity is a direct result of the innovative engineering and specialized components required to power and control these vehicles, ultimately impacting their overall price.
Mastering EV Maintenance: A Guide to Servicing Electric Vehicles
You may want to see also

Supply Chain Constraints: Limited availability of raw materials drives up prices
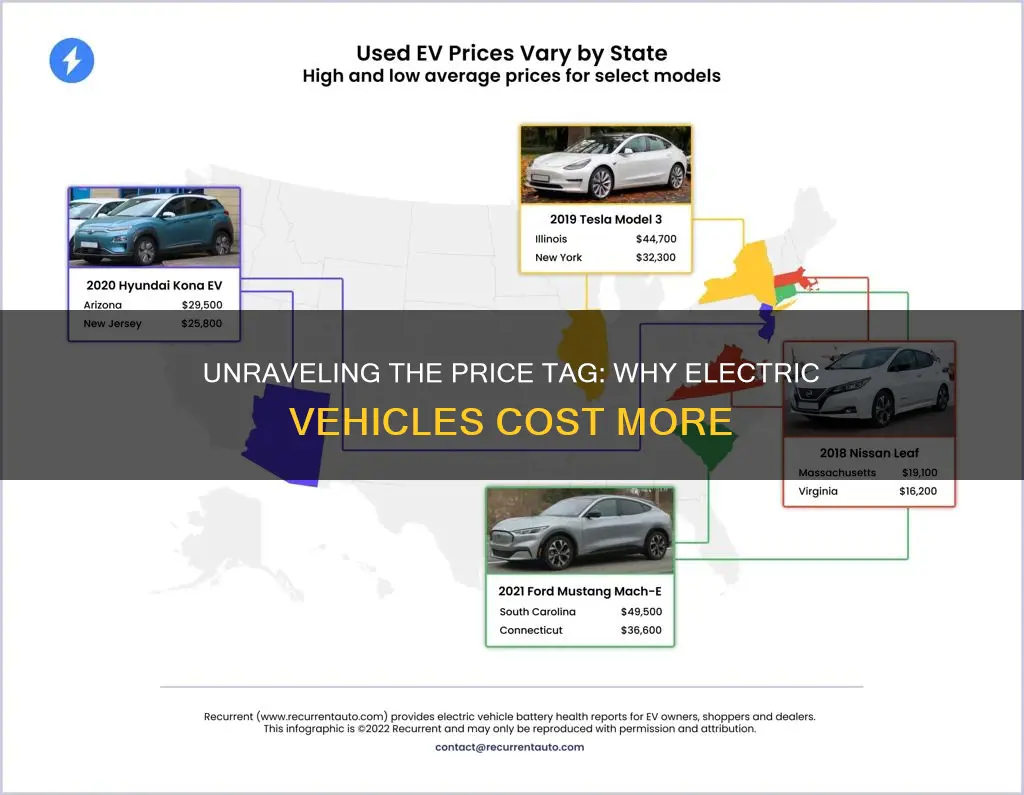
The high cost of electric vehicles (EVs) is a topic of growing interest as the automotive industry undergoes a significant shift towards electrification. One of the primary reasons behind this cost is the intricate supply chain and the limited availability of raw materials required to produce these vehicles. The supply chain for EVs is complex, involving multiple stages and a vast network of suppliers. It encompasses the extraction of raw materials, such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel, which are essential for battery production. These materials are not only scarce but also face geopolitical tensions and environmental concerns associated with their extraction.
The limited availability of these raw materials is a significant constraint. For instance, lithium, a key component in lithium-ion batteries, is primarily sourced from a few countries, including Chile, Australia, and Argentina. The concentration of production in these regions makes the supply vulnerable to geopolitical issues and natural disasters. Similarly, cobalt, another critical material, is predominantly mined in the Democratic Republic of Congo, raising ethical and environmental concerns. The supply chain's reliance on a few sources makes it susceptible to price fluctuations and supply disruptions.
As a result, the prices of these raw materials have been on a steady rise, impacting the overall cost of EVs. The demand for lithium, cobalt, and nickel has outpaced their supply, leading to a situation where manufacturers are often at the mercy of market dynamics. This is further exacerbated by the fact that these materials are not easily substitutable, and their extraction and processing require specialized technologies and infrastructure. The limited availability and the subsequent price volatility create a challenging environment for EV manufacturers, forcing them to navigate the complexities of the supply chain while ensuring the sustainability and affordability of their products.
To address this issue, the industry is exploring various strategies. One approach is to diversify the supply chain by identifying new sources of raw materials and developing more sustainable extraction methods. Additionally, recycling and reusing materials from retired batteries can help reduce the demand for new raw materials. Another strategy involves improving the efficiency of battery production processes to minimize waste and optimize material usage. These efforts aim to mitigate the supply chain constraints and make EVs more cost-effective, ultimately contributing to a more sustainable and widely accessible transportation future.
Deadhead Miles: The Hidden Cost of Electric Vehicle Ownership
You may want to see also

Government Incentives: Tax credits and subsidies can offset initial high costs
The high upfront cost of electric vehicles (EVs) is a significant barrier to their widespread adoption, and governments around the world are implementing various incentives to encourage the transition to cleaner transportation. One of the most effective tools in this regard is the provision of tax credits and subsidies, which can substantially reduce the initial financial burden for consumers.
Tax credits are a direct financial benefit to buyers, typically calculated as a percentage of the vehicle's purchase price. For instance, many countries offer tax credits that can cover a substantial portion of the EV's cost, making them more affordable. These credits are often designed to stimulate the market and promote the adoption of environmentally friendly vehicles. For example, in the United States, the Inflation Reduction Act provides a tax credit of up to $7,500 for new electric vehicles, which can significantly lower the overall price for consumers. Similarly, in Norway, the government offers a tax deduction of up to 50% of the vehicle's value, making EVs highly competitive compared to traditional gasoline cars.
Subsidies, on the other hand, take the form of financial grants or rebates, often provided by local or national governments. These subsidies aim to reduce the effective price of EVs, making them more accessible to a broader range of consumers. For instance, some regions offer subsidies that cover a fixed amount of the vehicle's price, directly reducing the out-of-pocket expense for buyers. In the UK, the Plug-in Car Grant provides up to £3,000 towards the purchase of an electric car, while in Canada, the federal government offers a rebate of up to $5,000 for eligible electric vehicles. These subsidies not only make EVs more affordable but also encourage manufacturers to invest in and produce more electric models.
The combination of tax credits and subsidies can significantly impact the EV market. By providing financial relief to consumers, governments can stimulate demand and accelerate the shift towards electric mobility. This, in turn, leads to increased sales, which can drive down production costs over time, making EVs even more cost-effective. Moreover, these incentives can help reduce the environmental impact of transportation by encouraging the adoption of cleaner, more sustainable vehicles.
In summary, government incentives in the form of tax credits and subsidies play a crucial role in addressing the high costs associated with electric vehicles. These measures not only make EVs more affordable for consumers but also contribute to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly future. As the world continues to prioritize reducing carbon emissions, such incentives will likely become even more prevalent and effective in promoting the widespread adoption of electric vehicles.
Electric Vehicle Market: Top Competitors and Their Strategies
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The primary reason for the higher cost of EVs is the advanced technology and components they utilize. Electric cars require powerful electric motors, advanced batteries, and sophisticated electronics, which are more expensive to manufacture and assemble compared to the internal combustion engines found in conventional vehicles. Additionally, the production of EVs is a relatively new process, and the economies of scale are not yet fully realized, contributing to the higher upfront cost.
Yes, many governments worldwide offer incentives to promote the adoption of electric cars. These incentives can include tax credits, rebates, or grants that significantly reduce the purchase price for buyers. For example, some countries provide tax breaks for EV buyers, while others offer direct subsidies or low-interest loans. These financial incentives can make EVs more affordable and attractive to consumers, especially when considering the long-term savings on fuel and maintenance.
Absolutely. While the initial purchase price may be higher, EVs offer several cost advantages over time. Firstly, electricity is generally cheaper than gasoline, resulting in significant savings on fuel costs. Secondly, electric motors are known for their simplicity and reliability, often requiring less maintenance than traditional engines. This can lead to reduced service and repair expenses. Lastly, the longevity of EV batteries is improving, and many manufacturers provide warranties, ensuring that the cost of battery replacement is minimal or non-existent for many years.