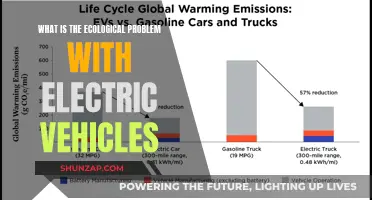
Despite the growing popularity of electric vehicles (EVs) and their numerous benefits, there is still a segment of the population that remains skeptical and even opposed to their adoption. This resistance can be attributed to several factors, including concerns about performance, range anxiety, and the initial cost. Some individuals worry that EVs may not offer the same driving experience as traditional gasoline vehicles, with potential issues related to acceleration, handling, and the lack of a familiar engine sound. Range anxiety, the fear of running out of battery power during a journey, is another significant deterrent, especially for those who frequently travel long distances. Additionally, the higher upfront cost of EVs compared to their gasoline counterparts can be a barrier, despite the long-term savings and environmental benefits. These factors, combined with a lack of comprehensive charging infrastructure in certain areas, contribute to the skepticism surrounding electric vehicles.
What You'll Learn
- Environmental Concerns: Some argue that EV production and disposal can harm the environment
- Battery Issues: Limited battery life, range anxiety, and charging infrastructure concerns
- Cost and Affordability: High upfront costs and ongoing maintenance can be a barrier
- Infrastructure and Charging: Inadequate charging stations and long charging times
- Job Displacement: The shift to EVs may impact jobs in the traditional auto industry

Environmental Concerns: Some argue that EV production and disposal can harm the environment
The environmental impact of electric vehicles (EVs) is a complex issue that has sparked debates among various stakeholders. While EVs are often promoted as a cleaner and more sustainable alternative to traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles, some argue that their production and disposal processes can have detrimental effects on the environment.
One of the primary concerns is the energy-intensive manufacturing process of EVs. The production of electric car batteries, in particular, requires substantial amounts of raw materials such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel. Mining these materials can lead to significant environmental degradation, including habitat destruction, soil erosion, and water pollution. For instance, the extraction of lithium, a critical component in lithium-ion batteries, often involves invasive techniques that can harm local ecosystems and water sources. Additionally, the manufacturing process itself contributes to greenhouse gas emissions, as it relies heavily on fossil fuels for energy generation.
Another critical aspect is the end-of-life management of EV batteries. As the demand for EVs increases, so does the need for efficient and environmentally friendly disposal methods. Improper disposal of EV batteries can result in hazardous waste, as they contain toxic chemicals and heavy metals. If not recycled or disposed of correctly, these batteries can leach harmful substances into the soil and water, posing risks to both human health and the environment. Furthermore, the recycling process itself is energy-intensive and may require significant amounts of water, raising concerns about water scarcity in certain regions.
Despite these challenges, it is essential to note that ongoing research and technological advancements aim to address these environmental concerns. Scientists and engineers are developing more sustainable extraction methods for raw materials, exploring recycling techniques that minimize waste, and designing more efficient battery technologies. Additionally, the shift towards renewable energy sources for manufacturing and recycling processes can significantly reduce the carbon footprint associated with EV production.
In conclusion, while EVs offer numerous benefits in terms of reduced emissions and improved energy efficiency, the environmental impact of their production and disposal cannot be overlooked. Addressing these concerns through sustainable practices and innovative technologies is crucial to ensuring that the widespread adoption of EVs contributes positively to the fight against climate change and environmental degradation.
Chevy Trax: Electric Vehicle or Not? Unveiling the Truth
You may want to see also

Battery Issues: Limited battery life, range anxiety, and charging infrastructure concerns
Battery issues have been a significant barrier to the widespread adoption of electric vehicles (EVs), and they are often cited as a primary concern by those hesitant to make the switch from traditional gasoline-powered cars. One of the most pressing problems is the limited battery life, which directly impacts the vehicle's range. Modern EVs typically offer a range of around 200-300 miles on a single charge, which, while sufficient for daily commutes for many, falls short for longer journeys or those who frequently travel to remote areas without easy access to charging stations. This limitation can be particularly challenging for those living in regions with colder climates, as battery performance tends to decrease in such conditions.
Range anxiety is a real and growing concern among potential EV buyers. It refers to the fear of running out of battery power during a journey, which can lead to stressful situations and potentially dangerous ones if a suitable charging station is not nearby. The anxiety is further exacerbated by the limited availability of fast-charging infrastructure, which can significantly reduce charging times but is not yet widely accessible. As a result, many people worry about the practicality of long-distance travel with an EV, often preferring the convenience of a gasoline car for such trips.
The charging infrastructure for EVs is still developing and improving, but it remains a critical aspect of battery-related concerns. While home charging solutions are becoming more common, public charging stations are still not as prevalent as gas stations. This lack of accessibility can make it challenging for EV owners to find convenient and reliable charging options, especially during long trips. The time required to charge an EV, often significantly longer than a gasoline fill-up, can be a significant deterrent for those seeking a seamless driving experience.
Additionally, the charging process itself can be complex and time-consuming. Unlike the quick and simple process of refueling a gasoline car, charging an EV requires a specific type of connector and can take anywhere from 30 minutes to several hours, depending on the charging station and the vehicle's battery capacity. This prolonged charging time is a significant factor in the hesitation of some consumers, who may prefer the instant convenience of a traditional vehicle.
Addressing these battery issues is crucial for the EV industry to gain broader acceptance. Improvements in battery technology, such as developing more efficient and higher-capacity batteries, are essential to increase the range and reduce charging times. Expanding the charging infrastructure network, both public and private, is also vital to alleviate range anxiety and provide a more convenient and accessible charging experience for EV owners.
Ford Maverick: Electric Vehicle or Not? Unveiling the Truth
You may want to see also

Cost and Affordability: High upfront costs and ongoing maintenance can be a barrier
The high upfront cost of electric vehicles (EVs) is a significant barrier for many potential buyers. While the long-term savings of EVs are well-documented, the initial investment can be daunting. On average, electric cars carry a higher price tag than their gasoline counterparts, often due to the advanced technology and battery systems they employ. This higher cost is further exacerbated by the limited production volumes of many EVs, which can drive up prices. For instance, luxury electric SUVs can easily cost over $100,000, making them out of reach for many families and individuals on a tight budget.
The high price point is not the only financial hurdle. Even after purchasing an EV, owners may face substantial ongoing costs. Maintenance, for example, can be more expensive due to the complexity of electric powertrains. While traditional engines have fewer moving parts, electric motors and battery packs require specialized care and can be more costly to repair. Additionally, the availability of service centers and technicians skilled in EV maintenance can vary, potentially leading to longer wait times and higher costs for repairs.
The financial burden doesn't end with maintenance. The cost of electricity to power an EV can add up over time, especially for those who drive long distances or frequently. While home charging can be a cost-effective solution, not everyone has access to a dedicated charging point. Public charging stations, while becoming more widespread, often come with higher rates, which can quickly accumulate for frequent users. This is particularly challenging for those in rural areas, where public charging infrastructure is less developed.
Despite these challenges, the financial benefits of EVs are undeniable. Over time, the reduced fuel and maintenance costs can significantly offset the higher upfront expense. However, for many, the initial financial hurdle remains a significant barrier to entry. To address this, governments and manufacturers are exploring various incentives and subsidies to make EVs more affordable. These include tax credits, rebates, and low-interest loans, which can help bridge the gap between the high upfront cost and the long-term savings.
In conclusion, the high upfront costs and ongoing maintenance of electric vehicles present a significant affordability challenge. While the long-term benefits are clear, the initial financial outlay can be a deterrent for many. However, with increasing awareness and a growing range of incentives, the accessibility of EVs is improving, making them a more viable option for a broader range of consumers.
South Carolina's EV Tax Exemption: A Green Car Owner's Guide
You may want to see also

Infrastructure and Charging: Inadequate charging stations and long charging times
The widespread adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) has been hindered by several concerns, and one of the primary obstacles is the lack of adequate charging infrastructure. As the number of EVs on the road increases, the demand for charging stations becomes more critical, yet the current infrastructure falls short. Many potential EV buyers are deterred by the fear of running out of power during long journeys or not having easy access to charging points. This issue is particularly prominent in rural areas, where the availability of charging stations is limited, and the distances between them can be vast.
The current charging infrastructure is not designed to handle the rapid growth in EV ownership. Traditional charging stations, often located in public areas or along highways, are typically slow chargers, taking several hours to fully recharge a battery. This is a significant drawback compared to the convenience of refueling a conventional vehicle in just a few minutes. As a result, long charging times discourage potential buyers who value the efficiency and convenience of a quick top-up.
To address this problem, significant investments are required in expanding and improving charging networks. This includes installing more charging stations in residential areas, workplaces, and public spaces, ensuring that EV owners have convenient access to charging facilities. Rapid charging stations, which can significantly reduce charging times, are also essential. These stations use advanced technology to charge batteries much faster, making them ideal for long-distance travel and reducing the anxiety associated with running out of power.
Governments and energy companies play a crucial role in this transformation. They can incentivize the development of charging infrastructure by offering subsidies or tax benefits to businesses and individuals investing in charging stations. Additionally, implementing smart charging solutions can optimize the use of existing infrastructure. These solutions involve dynamic pricing and load management, ensuring that charging stations are utilized efficiently during peak and off-peak hours.
In summary, the inadequate charging infrastructure and long charging times are significant barriers to the widespread adoption of electric vehicles. To overcome this challenge, a comprehensive approach is necessary, involving the development of a robust charging network, the deployment of rapid charging stations, and the implementation of smart charging technologies. By addressing these issues, the transition to electric mobility can be smoother, and the concerns of potential buyers can be alleviated, fostering a more sustainable and environmentally friendly transportation future.
Electric Revolution: Replacing Gasoline's Reign with Sustainable Alternatives
You may want to see also

Job Displacement: The shift to EVs may impact jobs in the traditional auto industry
The transition to electric vehicles (EVs) is an ongoing revolution in the automotive industry, but it has sparked concerns about job displacement within the traditional auto sector. As the world moves towards more sustainable transportation, the shift towards EVs could potentially disrupt the employment landscape for those working in the internal combustion engine (ICE) industry. This transition is not just about environmental benefits; it also presents a complex challenge for the workforce.
One of the primary reasons for job displacement is the change in technology. EVs rely on electric motors and batteries, which are fundamentally different from the internal combustion engines that have been the backbone of the auto industry for decades. This shift requires a re-skilling of the workforce, as traditional auto mechanics and engineers may need to adapt to new technologies and repair methods. The demand for ICE-specific skills will naturally decline, leading to potential job losses for those who specialize in engine repair, maintenance, and manufacturing.
The impact on employment is already being felt in some regions. As EV manufacturers gain popularity, there is a growing need for skilled workers in battery production, electric motor assembly, and charging infrastructure development. However, this shift also means that jobs related to ICE production, maintenance, and repair may become obsolete faster than new positions can be created. For instance, roles like engine assemblers, transmission specialists, and ICE-related engineers might find themselves in a vulnerable position as their expertise becomes less relevant.
Moreover, the pace of this transition is crucial. A rapid shift to EVs could lead to a skills gap, where the industry struggles to find workers with the necessary expertise in EV-related fields. This could result in a temporary shortage of skilled labor, potentially causing further job displacement as companies struggle to adapt. On the other hand, a gradual transition might provide enough time for workers to retrain and adapt, ensuring a smoother transition for the workforce.
Addressing this issue requires a comprehensive approach. Governments and industry leaders should invest in retraining programs to help workers transition to new roles within the EV sector. This could include providing financial support, vocational training, and apprenticeships to ensure that the workforce is equipped with the skills needed for the future of transportation. Additionally, creating new job opportunities in the EV supply chain and infrastructure development can help mitigate the negative impact on employment.
The Ultimate Guide to Electric Scooter Shopping
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
One of the primary concerns is the initial cost of EVs, which can be significantly higher than traditional gasoline vehicles. However, it's important to note that the total cost of ownership over the vehicle's lifetime can be lower due to reduced fuel and maintenance expenses. Range anxiety is another issue, as early EVs had limited driving ranges, but modern EVs offer longer ranges and rapid charging options, addressing this concern. Lastly, the availability of charging infrastructure is a valid worry, but governments and private companies are investing in expanding charging networks to support the growing EV market.
While environmentalists generally support the transition to EVs, they also have some reservations. One concern is the source of electricity used to power these vehicles. If the electricity comes from fossil fuel-based power plants, it may not significantly reduce carbon emissions. However, as renewable energy sources become more prevalent, this issue is being addressed. Additionally, some environmentalists worry about the extraction and processing of raw materials for EV batteries, which can have environmental impacts.
The rise of EVs could have both positive and negative economic effects. On the positive side, it may stimulate job growth in the automotive industry, particularly in battery manufacturing and charging infrastructure development. However, a rapid shift to EVs could disrupt the traditional automotive market, potentially leading to job losses in the internal combustion engine (ICE) sector. Additionally, the increased demand for raw materials used in EVs might impact global markets and supply chains, affecting various industries.