The electric vehicle (EV) mandate is a growing topic of discussion and policy-making in many countries. With the global push towards sustainable transportation and the reduction of carbon emissions, governments are increasingly considering the implementation of regulations that require a certain percentage of new vehicle sales to be electric. This mandate aims to accelerate the transition to electric mobility, reduce air pollution, and promote technological advancements in the automotive industry. The idea is to incentivize manufacturers and consumers to invest in electric vehicles, ultimately leading to a cleaner and more sustainable future. As such, understanding the potential implications and benefits of an EV mandate is crucial for policymakers and stakeholders alike.
What You'll Learn
- Environmental Impact: How EV mandates reduce emissions and improve air quality
- Infrastructure Development: The need for charging stations and grid upgrades
- Economic Benefits: Job creation and cost savings for consumers
- Policy Challenges: Legal and regulatory hurdles in implementing EV mandates
- Public Acceptance: Overcoming consumer hesitancy and resistance to change

Environmental Impact: How EV mandates reduce emissions and improve air quality
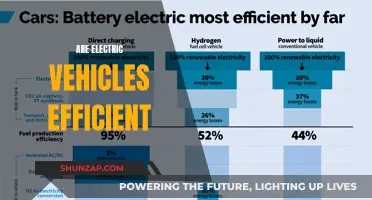
The concept of electric vehicle (EV) mandates is gaining traction globally as a powerful strategy to combat climate change and improve environmental sustainability. These mandates, often implemented by governments and local authorities, require a certain percentage of new vehicle sales to be electric or zero-emission vehicles. The primary environmental impact of such policies is the significant reduction in greenhouse gas emissions and the subsequent improvement in air quality.
One of the most significant advantages of EV mandates is their ability to accelerate the transition to a low-carbon economy. Traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles are major contributors to air pollution and carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions. By mandating the sale of EVs, governments can rapidly increase the number of electric cars, buses, and trucks on the road, thereby reducing the overall emissions footprint of the transportation sector. This is particularly crucial in densely populated urban areas where traffic congestion and air pollution levels are often at their highest.
The environmental benefits of EV mandates are twofold. Firstly, electric vehicles produce zero tailpipe emissions, meaning they do not release harmful pollutants like nitrogen oxides (NOx), particulate matter (PM), and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) during operation. This leads to improved air quality, especially in cities, where these emissions can have detrimental effects on human health, causing respiratory issues and contributing to the formation of smog. Secondly, the shift to EVs contributes to a reduction in CO2 emissions, a primary driver of global warming and climate change. As EVs are powered by electricity, their carbon footprint depends on the source of that electricity. However, with the increasing adoption of renewable energy sources like solar and wind power, the environmental benefits of EVs become even more pronounced.
Moreover, EV mandates can stimulate innovation and investment in the electric vehicle industry. Manufacturers are encouraged to develop more efficient and affordable EV models, leading to technological advancements and improved battery performance. This, in turn, can make EVs more accessible and desirable to consumers, creating a positive feedback loop that accelerates the market's growth. As the demand for EVs rises, so does the need for charging infrastructure, further supporting the development of a sustainable transportation ecosystem.
In summary, electric vehicle mandates play a crucial role in addressing environmental concerns. By mandating the sale of EVs, governments can rapidly reduce emissions, improve air quality, and foster a sustainable future. The transition to electric mobility is a significant step towards mitigating the environmental impact of the transportation sector, offering a cleaner and healthier environment for current and future generations. This approach also encourages technological advancements, making EVs more efficient, affordable, and widely available.
Li-ion: Powering the Future of Electric Vehicles?
You may want to see also

Infrastructure Development: The need for charging stations and grid upgrades
The widespread adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) is an essential step towards a sustainable future, and it has sparked a critical discussion about the necessary infrastructure to support this transition. As more and more people opt for electric cars, the demand for charging stations and grid upgrades becomes increasingly apparent. This infrastructure development is not just a matter of convenience but a strategic move to ensure a seamless and efficient EV ecosystem.
The current state of EV charging infrastructure varies globally, with some regions lagging in providing adequate charging options. This disparity can hinder the widespread adoption of electric vehicles, as potential buyers may face concerns about range anxiety and the availability of charging stations. To address this, governments and private entities must invest in a comprehensive network of charging stations, ensuring accessibility and convenience for EV owners. Public charging stations, especially those with fast-charging capabilities, will play a pivotal role in encouraging long-distance travel and reducing the time spent refueling.
Grid upgrades are an equally vital aspect of this infrastructure development. The rise in EV ownership will significantly impact the electrical grid, requiring enhancements to handle the additional load. Upgrading the grid involves increasing its capacity, improving voltage regulation, and implementing smart grid technologies. These upgrades ensure that the power supply remains stable and reliable, even during peak EV charging times. Smart grid systems can also optimize energy distribution, allowing for more efficient charging and potentially reducing the strain on the power grid.
The benefits of investing in this infrastructure are twofold. Firstly, it addresses the immediate concerns of EV owners, providing them with the confidence to make the switch. Secondly, it positions countries and cities to take a leading role in the global transition to sustainable transportation. By implementing these measures, governments can attract EV manufacturers and encourage the development of a robust EV market, fostering economic growth and environmental sustainability.
In summary, the need for charging stations and grid upgrades is a critical component of any electric vehicle mandate. It requires a collaborative effort between governments, energy providers, and private investors to create a robust and accessible charging infrastructure. This development will not only support the growing EV market but also contribute to a greener and more sustainable future for transportation.
Powering Up: Understanding the Safety of Plugging In Your EV
You may want to see also

Economic Benefits: Job creation and cost savings for consumers
The implementation of an electric vehicle (EV) mandate can have significant economic benefits, particularly in terms of job creation and cost savings for consumers. Here's an overview of these advantages:
Job Creation: The transition to electric mobility has the potential to stimulate job growth in various sectors. Firstly, the automotive industry will experience a shift towards EV manufacturing and assembly. This transition will require skilled labor for EV production, battery technology development, and the establishment of charging infrastructure. As a result, new job opportunities will emerge for engineers, technicians, and support staff. Additionally, the expansion of the EV market can create jobs in related industries such as battery recycling, renewable energy, and sustainable transportation services. These sectors often provide well-paying jobs and contribute to a more diverse and resilient economy.
Cost Savings for Consumers: Electric vehicles offer long-term cost savings compared to traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles. Firstly, EVs have lower fuel costs since electricity is generally cheaper than gasoline or diesel. This translates to significant savings for drivers over the vehicle's lifetime. Additionally, electric cars have fewer moving parts, resulting in reduced maintenance expenses. Owners of EVs often report lower maintenance costs due to the absence of oil changes, complex engine systems, and the need for less frequent part replacements. As the technology advances and production scales, the overall cost of EVs is expected to decrease, making them even more affordable for consumers.
The mandate for electric vehicles can drive investment in EV-related infrastructure, creating jobs in construction and maintenance. This includes the installation of charging stations in public spaces, residential areas, and workplaces, ensuring convenient access to charging facilities. Furthermore, the development of a robust EV charging network can attract businesses and encourage the growth of related services, such as charging station management and maintenance.
In summary, an electric vehicle mandate can foster economic growth by creating jobs in various sectors, including automotive manufacturing, renewable energy, and infrastructure development. Simultaneously, it offers consumers substantial cost savings through reduced fuel and maintenance expenses, making electric mobility an economically attractive and sustainable choice.
Ford's Electric Future: Rumors and Reality
You may want to see also

Policy Challenges: Legal and regulatory hurdles in implementing EV mandates
The concept of electric vehicle (EV) mandates, which require a certain percentage of new vehicle sales to be zero-emission, is gaining traction globally as a strategy to combat climate change and reduce air pollution. However, the implementation of such mandates presents a range of policy challenges, particularly in the areas of legal and regulatory frameworks. These challenges can significantly impact the success and effectiveness of EV mandates, and careful consideration is required to navigate them.
One of the primary legal hurdles is the potential conflict with existing automotive regulations and trade laws. Many countries have established standards and requirements for vehicle safety, emissions, and fuel efficiency, which may not align with the rapid transition to EVs. For instance, the safety and performance standards for traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles might not directly apply to EVs, leading to a need for new or adapted regulations. This includes considerations for charging infrastructure, battery safety, and the unique characteristics of electric powertrains.
Regulatory bodies often face the challenge of keeping pace with the rapidly evolving EV market. As technology advances, new models and charging solutions emerge, requiring regulators to update and interpret existing laws to accommodate these changes. This dynamic nature of the industry can make it difficult to establish clear and consistent policies that provide a stable environment for both manufacturers and consumers. For example, the integration of smart grid technologies and vehicle-to-grid (V2G) systems, which allow EVs to interact with the power grid, introduces new regulatory considerations for energy management and grid stability.
Another significant issue is the potential impact on the automotive industry's established supply chains and market dynamics. A sudden mandate could disrupt the market, affecting not only vehicle manufacturers but also suppliers of traditional automotive parts. This includes the potential phase-out of ICE vehicle production, which may lead to complex legal and contractual issues, especially for companies heavily invested in ICE technology and infrastructure. Balancing the incentives for EV adoption with the need to support a just transition for the automotive workforce and related industries is a delicate task for policymakers.
Furthermore, the enforcement of EV mandates raises questions about jurisdiction and international cooperation. With global supply chains and vehicle markets, ensuring compliance across borders can be challenging. International agreements and harmonization of standards are essential to address these challenges, but they also require significant diplomatic efforts and consensus-building among nations.
In summary, the legal and regulatory hurdles in implementing EV mandates are multifaceted and require careful planning and collaboration between governments, industry stakeholders, and environmental advocates. Addressing these challenges is crucial to ensure a smooth transition to a sustainable transportation system, where EVs play a central role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions and improving air quality.
The Future of EV Tax Credits: What You Need to Know
You may want to see also

Public Acceptance: Overcoming consumer hesitancy and resistance to change
The transition to electric vehicles (EVs) is an essential step towards a sustainable future, but it faces a significant challenge: public acceptance. Many consumers are hesitant to embrace this change due to various factors, including concerns about performance, range anxiety, and the perceived higher cost compared to traditional vehicles. Overcoming this resistance is crucial for the successful implementation of any electric vehicle mandate. Here are some strategies to address and mitigate consumer hesitancy:
Addressing Range Anxiety: One of the primary concerns for potential EV buyers is the fear of running out of battery power during long journeys. To alleviate this, governments and vehicle manufacturers can work together to improve charging infrastructure. Establishing a comprehensive network of charging stations across urban and rural areas will make long-distance travel in EVs more feasible and less stressful. Public awareness campaigns can also educate consumers about the increasing range of modern EVs and the convenience of charging options available.
Performance and Technology Education: Some consumers might be skeptical about the performance and technology of EVs, especially those who are accustomed to conventional vehicles. It is essential to provide detailed information and demonstrations to showcase the capabilities of electric cars. This can include organizing test drive events, offering virtual tours of EV features, and sharing real-world experiences of satisfied EV owners. By providing tangible evidence of improved performance, efficiency, and the latest technological advancements, manufacturers can build trust and confidence among the public.
Financial Incentives and Subsidies: The initial cost of purchasing an EV is often a significant barrier for many consumers. Governments can play a pivotal role by offering financial incentives and subsidies to make EVs more affordable. These incentives could include tax credits, rebates, or grants that directly reduce the purchase price. Additionally, providing long-term financing options with lower interest rates can make owning an EV more financially attractive to the average consumer.
Community Engagement and Education: Building a positive perception of EVs requires engaging with the public and addressing their concerns directly. Local communities can organize events, workshops, and information sessions to educate people about the benefits of electric mobility. These initiatives can highlight the environmental impact of reducing carbon emissions, the long-term cost savings, and the positive experiences of early EV adopters. By fostering a sense of community and shared responsibility, it becomes easier to influence public opinion and encourage the adoption of EVs.
Gradual Transition and Support: A successful electric vehicle mandate should consider a phased approach, allowing for a gradual transition. This gives consumers time to adapt and build confidence. Providing support and resources during this transition, such as dedicated customer service, extended warranties, and easy return policies, can significantly reduce resistance. Additionally, offering a range of EV models and styles to cater to diverse consumer preferences will make the transition more appealing.
Unleash the Power: Is an Electric Vehicle Your Next Ride?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The electric vehicle mandate, also known as the EV mandate, is a policy or regulation that aims to accelerate the transition to electric mobility by setting specific targets or requirements for the adoption of electric vehicles (EVs). These mandates are often implemented by governments to encourage the use of cleaner and more sustainable transportation options.
An EV mandate typically involves setting a timeline or a percentage-based goal for the number of new vehicle sales or registrations that must be electric vehicles. For example, a government might mandate that a certain percentage of all new car sales in a region should be electric by a specific year. This could be further broken down into segments, such as passenger cars, light commercial vehicles, or public transportation fleets.
The primary benefits include reduced greenhouse gas emissions, improved air quality, and a shift towards a more sustainable and environmentally friendly transportation system. Mandates can also stimulate innovation in the automotive industry, drive investment in EV infrastructure, and create new job opportunities related to EV manufacturing and charging station development.
One challenge is the potential burden on consumers, especially those with lower incomes, who may struggle to afford the higher upfront costs of electric vehicles. Critics also argue that mandates might not be as effective as incentives or voluntary measures in encouraging EV adoption. Additionally, ensuring a robust charging infrastructure network is crucial to support the increased demand, and governments need to invest in this aspect to make EV mandates successful.