Despite the growing environmental concerns and technological advancements, electric vehicles (EVs) have not yet achieved widespread adoption among the general public. This paragraph aims to explore the reasons behind the relatively low demand for EVs. It will delve into various factors, including the initial high cost of purchase, limited charging infrastructure, range anxiety, and the lack of a comprehensive marketing strategy by traditional car manufacturers. Additionally, it will touch upon the psychological barriers, such as the fear of change and the perceived inconvenience of owning an EV, which further contribute to the slower uptake of these vehicles. Understanding these challenges is crucial for policymakers, industry leaders, and environmental advocates to develop effective strategies and incentives to accelerate the transition to a more sustainable transportation ecosystem.
What You'll Learn
- Cost and Affordability: High upfront costs and limited financing options deter potential buyers
- Charging Infrastructure: Inadequate charging stations and long charging times are major concerns
- Range Anxiety: Limited range and fear of running out of battery during long trips
- Battery Technology: Concerns about battery degradation, lifespan, and recycling capabilities
- Resale Value: Low resale value and limited used EV market create hesitation

Cost and Affordability: High upfront costs and limited financing options deter potential buyers
The high upfront cost of electric vehicles (EVs) is a significant barrier to their widespread adoption. While the long-term savings and environmental benefits of EVs are well-documented, the initial financial outlay can be a deterrent for many potential buyers. On average, electric cars carry a higher price tag compared to their gasoline counterparts, often due to the advanced technology and battery systems they employ. This premium pricing can be a substantial hurdle, especially for those on a tight budget or in regions where the cost of living is high.
The limited financing options available for EVs further exacerbate this issue. Many traditional lenders are hesitant to offer loans for electric vehicles due to the perceived higher risk and the relatively new market. As a result, buyers often face higher interest rates and more restrictive loan terms, making it even more challenging to afford the purchase. This lack of accessible financing can discourage potential buyers, especially those who might otherwise be interested in the environmental and economic benefits of EVs.
Additionally, the high cost of EVs can be a disincentive for those who are already in the market for a new car. Many consumers are price-sensitive and may opt for a more affordable gasoline-powered vehicle, even if it means forgoing the long-term advantages of an electric car. This decision can be influenced by the limited number of financing options, which may not provide the necessary support for buyers to make the switch.
To address this challenge, governments and automotive manufacturers are exploring various strategies. These include offering incentives such as tax credits and rebates, which can significantly reduce the upfront cost for buyers. Expanding financing options, such as specialized EV loans with lower interest rates, can also make EVs more accessible. Moreover, developing used EV markets and promoting trade-in programs can help lower the overall cost and encourage the second-hand sale of electric vehicles.
In summary, the high upfront costs and limited financing options for electric vehicles are critical factors that hinder their market growth. By implementing strategies to reduce costs and improve financing accessibility, the automotive industry can work towards making EVs more affordable and attractive to a broader consumer base. This approach will not only benefit the environment but also stimulate economic growth and innovation in the automotive sector.
Unraveling the Hybrid Mystery: A Comprehensive Guide to Identifying Hybrid Electric Vehicles
You may want to see also

Charging Infrastructure: Inadequate charging stations and long charging times are major concerns
The widespread adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) has been hindered by several factors, and one of the most significant concerns is the charging infrastructure. The current state of charging stations and the time required to charge an EV play a crucial role in shaping consumer behavior and perceptions.
Inadequate charging infrastructure is a critical issue that needs immediate attention. Many potential EV buyers are deterred by the fear of running out of power during long journeys or not having easy access to charging points. The availability of charging stations varies significantly across regions, with some areas lacking sufficient coverage. This disparity in charging infrastructure can lead to anxiety among EV owners, especially those who frequently travel long distances. For instance, rural areas often have limited or no charging stations, making it challenging for EV owners to plan their trips and maintain their vehicles' range.
Long charging times are another significant concern. While EVs offer numerous environmental and economic benefits, the process of recharging can be time-consuming, often taking several hours, which is a considerable drawback compared to the quick refueling of traditional gasoline vehicles. This extended charging time can be a significant barrier for those with busy schedules or those who need their vehicles for daily commutes. As a result, many individuals opt for conventional vehicles, even if they are environmentally conscious, due to the perceived inconvenience of long charging periods.
To address these challenges, significant investments in charging infrastructure are necessary. Governments and energy companies should collaborate to establish a comprehensive network of fast-charging stations along highways and in urban areas. These stations should be strategically placed to ensure accessibility and convenience for EV owners. Additionally, implementing smart charging technologies can optimize the charging process, reducing waiting times and improving overall efficiency.
Furthermore, encouraging the development of home charging solutions can empower individuals to charge their vehicles overnight or during off-peak hours, ensuring a reliable and convenient charging experience. By addressing the charging infrastructure concerns, the barriers to EV adoption can be significantly reduced, leading to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly transportation future.
Mastering EV Battery Sizing: A Comprehensive Guide to Powering Your Ride
You may want to see also

Range Anxiety: Limited range and fear of running out of battery during long trips
The concern of running out of power during a journey, commonly known as range anxiety, is a significant barrier to the widespread adoption of electric vehicles (EVs). This fear is deeply rooted in the limited range of many early electric cars, which often fell short of the distances that gasoline-powered vehicles could cover on a single tank. As a result, potential EV buyers, especially those with long commutes or frequent road trips, worry about the availability of charging stations and the time required to recharge, often perceiving it as an inconvenience.
The range of electric cars has improved significantly over the years, with many modern EVs offering over 300 miles on a single charge. However, this still falls short of the average range of traditional vehicles, which can easily exceed 400 miles. The perception of limited range persists, especially among those accustomed to the convenience of gasoline stations, where refueling is a quick and often unnoticed process.
Addressing range anxiety requires a multi-faceted approach. Firstly, the development of an extensive and accessible charging infrastructure is vital. Governments and private entities are investing in the creation of charging networks, ensuring that EV owners have convenient access to charging stations during their journeys. This includes the installation of fast-charging stations along highways and the integration of charging points in residential areas and workplaces.
Secondly, car manufacturers are continually working on enhancing battery technology. Advances in lithium-ion battery chemistry and design have led to improved energy density, allowing for longer ranges. Additionally, the introduction of hybrid and plug-in hybrid vehicles provides a bridge between the traditional and electric worlds, offering extended range and the flexibility to choose between electric and conventional power sources.
Lastly, consumer education plays a crucial role in alleviating range anxiety. Many potential EV buyers are unaware of the advancements in battery technology and the growing accessibility of charging infrastructure. Providing accurate and up-to-date information about the capabilities of modern EVs can help dispel myths and encourage a shift towards electric mobility.
Electric Vehicles: Eco-Friendly, Sustainable, and Better for the Planet
You may want to see also

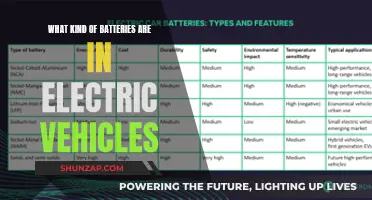
Battery Technology: Concerns about battery degradation, lifespan, and recycling capabilities
The widespread adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) has been a topic of interest and concern, especially regarding battery technology and its limitations. One of the primary reasons why more people are not embracing EVs is the persistent issue of battery degradation and its impact on vehicle performance and longevity.
Battery degradation refers to the gradual decline in a battery's ability to store and deliver energy efficiently over time. This phenomenon is a natural process and is influenced by various factors, including the chemical composition of the battery, temperature, charging and discharging rates, and overall usage patterns. As EV batteries age, they experience a reduction in capacity, meaning they can store less energy, which directly affects the vehicle's range. For instance, a study on lithium-ion batteries used in EVs found that after 10 years of operation, the battery capacity could be reduced by 20-30%, significantly impacting the vehicle's performance. This degradation is a critical concern for potential EV buyers, as it directly influences the overall cost of ownership and the convenience of long-distance travel.
The lifespan of EV batteries is another critical aspect that influences consumer behavior. While modern EV batteries have improved significantly, they are still limited in their endurance. High-end EVs with advanced battery packs might offer a range of 300-400 miles on a single charge, but this is still a far cry from the convenience of a traditional internal combustion engine vehicle. The limited range can be a significant deterrent for potential buyers, especially those who frequently travel long distances or live in regions with less-developed charging infrastructure. As a result, many consumers opt for hybrid or conventional vehicles, which provide more flexibility and peace of mind.
Recycling capabilities and the environmental impact of EV batteries are also essential considerations. The production and disposal of batteries can have significant ecological consequences. While EVs are generally more environmentally friendly than traditional vehicles, the extraction of raw materials and the end-of-life management of batteries are critical issues. Recycling technologies for lithium-ion batteries are improving, but the process is complex and costly. Consumers are increasingly conscious of the environmental impact of their purchases, and the lack of efficient recycling methods for EV batteries may deter some from making the switch.
Addressing these concerns requires ongoing innovation in battery technology. Researchers and engineers are working on developing more efficient and longer-lasting batteries, such as solid-state batteries, which promise higher energy density and improved safety. Additionally, advancements in recycling processes and the development of second-life applications for used batteries can help alleviate the environmental and economic concerns associated with battery degradation. As these technological advancements progress, the barriers to EV adoption may diminish, encouraging more people to embrace electric mobility.
Electrical Woes: Signs Your Car's System is Failing
You may want to see also

Resale Value: Low resale value and limited used EV market create hesitation
The hesitation to purchase electric vehicles (EVs) is often rooted in concerns about resale value and the limited second-hand market for these vehicles. One of the primary reasons for this hesitation is the relatively low resale value of EVs compared to their gasoline or diesel counterparts. This is primarily due to the rapid technological advancements in the EV market, which leads to frequent model updates and newer, more advanced versions being released within a short span of time. As a result, the older models may depreciate quickly, leaving owners with a vehicle that is still relatively new but has already lost a significant portion of its value.
The limited used EV market further exacerbates this issue. With a relatively small number of used EVs available, buyers often face a scarcity of options, which can make it challenging to find a vehicle that meets their specific needs and preferences. This scarcity can also drive up the prices of used EVs, making them less affordable for potential buyers. Additionally, the lack of a robust used EV market means that buyers may have fewer opportunities to negotiate on price, further discouraging the purchase of used EVs.
Another factor contributing to the low resale value of EVs is the relatively short lifespan of their batteries. As EVs age, their battery capacity tends to decrease, which can impact their performance and range. This reduction in battery health can make older EVs less desirable to potential buyers, who may be concerned about the long-term reliability and efficiency of the vehicle. Consequently, this can lead to a vicious cycle where the low resale value of EVs discourages buyers from purchasing used models, further limiting the development of a robust used EV market.
To address these concerns, several strategies can be considered. Firstly, manufacturers can play a crucial role by implementing more transparent and standardized battery health reporting. Providing detailed information about battery degradation and remaining capacity can help buyers make more informed decisions and potentially increase the perceived value of used EVs. Additionally, offering extended warranties or battery replacement programs can provide buyers with added peace of mind and potentially reduce the hesitation associated with the resale value of EVs.
Secondly, governments and industry stakeholders can collaborate to develop incentives and initiatives that promote the used EV market. This could include tax benefits for buyers of used EVs, subsidies for used EV dealers, and the establishment of certified pre-owned EV programs. By creating a more supportive environment for the used EV market, these measures can help increase the availability of used EVs, improve buyer confidence, and ultimately encourage more people to consider purchasing electric vehicles.
Revive Your Ride: A Guide to Putting Dead EVs in Neutral
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
There are several factors that contribute to the slower adoption of electric vehicles. Firstly, the initial cost of EVs is often higher compared to traditional gasoline or diesel cars, which can be a significant barrier for many consumers. However, this gap is narrowing as technology advances and more affordable EV options become available. Secondly, the range anxiety associated with EVs, the fear of running out of battery power during a journey, is a concern for potential buyers. While modern EVs have improved range, the infrastructure for charging stations is still developing, and the availability of convenient charging options remains a challenge in some regions. Lastly, consumer habits and preferences play a role; many people are comfortable with their current vehicles and may be hesitant to switch due to the perceived complexity of EV technology and the lack of a robust second-hand market for used EVs.
The high upfront cost of EVs can be tackled through various strategies. Governments and policymakers can offer incentives and subsidies to make EVs more affordable for consumers. These incentives could include tax credits, rebates, or grants that reduce the purchase price. Additionally, increasing the production volume of EVs can drive down costs due to economies of scale. As more EVs are manufactured, the cost of batteries, motors, and other components can decrease, making EVs more competitive in the market. Finally, encouraging the development of used EV markets can provide more affordable options for buyers, as the resale value of EVs is expected to improve over time.
Charging infrastructure is critical to the widespread adoption of electric vehicles. The availability and accessibility of charging stations directly impact consumer confidence in EV ownership. A comprehensive charging network ensures that EV drivers can conveniently charge their vehicles at home, work, or during their journeys. Governments and businesses need to invest in the development of fast-charging stations along highways and in urban areas to support long-distance travel and reduce range anxiety. Additionally, providing incentives for installing home charging points can encourage EV owners to charge their vehicles overnight, reducing the strain on the grid during peak hours.
While EVs have a lower environmental impact over their lifetime compared to conventional vehicles, there are still some concerns. The production and disposal of EV batteries can have environmental consequences, particularly if not managed sustainably. However, advancements in recycling technologies and the development of more eco-friendly battery materials are addressing these issues. Another consideration is the source of electricity used to charge EVs. If the electricity is generated from fossil fuels, the environmental benefits of EVs may be reduced. Encouraging the transition to renewable energy sources for charging can further enhance the environmental advantages of electric vehicles.
Educating consumers about the benefits and features of electric vehicles is essential to increasing sales. Many potential buyers may be unaware of the advancements in EV technology, the cost savings over time, or the environmental advantages. Running awareness campaigns, providing accurate information, and showcasing real-world experiences of EV owners can help dispel misconceptions. Additionally, offering test-drive programs and allowing potential buyers to experience the performance and convenience of EVs firsthand can be powerful marketing tools. By addressing common concerns and providing comprehensive information, the EV market can attract more buyers and accelerate the transition to sustainable transportation.