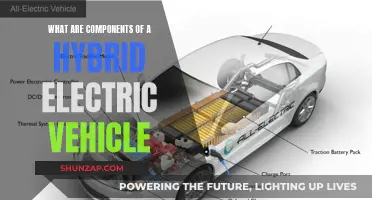
Electric vehicles (EVs) have gained significant popularity in recent years as a more environmentally friendly alternative to traditional gasoline-powered cars. One of the key questions that arises when considering the adoption of EVs is whether they are exempt from certain regulations, such as those set by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). The EPA plays a crucial role in setting and enforcing environmental standards, and its regulations impact various aspects of vehicle ownership and operation. In this paragraph, we will explore the relationship between electric vehicles and EPA regulations, examining the specific exemptions and considerations that EV owners and enthusiasts should be aware of.
What You'll Learn
- EPA Emissions Standards: Electric vehicles (EVs) are exempt from traditional tailpipe emissions testing under EPA standards
- Zero Emissions: EVs produce no direct emissions, meeting EPA zero-emission vehicle (ZEV) requirements
- Alternative Fuel: EVs are considered alternative fuel vehicles, exempt from certain EPA regulations
- Compliance Testing: EVs undergo different compliance testing, exempt from some EPA emission tests
- State Regulations: State rules may vary, but EVs often benefit from EPA exemptions

EPA Emissions Standards: Electric vehicles (EVs) are exempt from traditional tailpipe emissions testing under EPA standards
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has established emissions standards for vehicles to ensure that they meet specific environmental criteria. However, when it comes to electric vehicles (EVs), there is an important distinction to be made. EVs are indeed exempt from the traditional tailpipe emissions testing that is required for conventional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles. This exemption is a result of the unique nature of EV technology and its impact on the environment.
Under the EPA's regulations, EVs are considered to be 'zero-emission vehicles' because they produce no direct exhaust emissions during operation. This is a significant advantage over ICE vehicles, which release pollutants such as nitrogen oxides (NOx), volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and particulate matter (PM) into the atmosphere. The absence of tailpipe emissions from EVs means that they do not contribute to air pollution in the same way that traditional vehicles do.
The EPA's decision to exempt EVs from tailpipe emissions testing is based on the understanding that EVs have a different environmental footprint. While EVs themselves do not emit pollutants, their production and operation still have an impact on the environment. However, this impact is generally lower compared to the emissions generated by ICE vehicles over their lifetime. The focus of EPA standards is to encourage the adoption of cleaner technologies and reduce the overall environmental impact of the transportation sector.
This exemption allows EV manufacturers to design and produce vehicles without the need to meet the same stringent emissions standards as ICE vehicles. As a result, EVs can be engineered to prioritize performance, efficiency, and innovation, rather than solely focusing on emissions control. This has led to the rapid advancement of EV technology, with improvements in battery range, charging infrastructure, and overall vehicle performance.
In summary, the EPA's emissions standards recognize the unique characteristics of electric vehicles and their potential to reduce environmental impact. By exempting EVs from traditional tailpipe emissions testing, the EPA encourages the development and adoption of clean transportation technologies, ultimately contributing to a more sustainable future. This approach also highlights the importance of considering the entire lifecycle of a vehicle when evaluating its environmental performance.
Unraveling the Mystery: Hairball Phenomenon in Electric Vehicles
You may want to see also

Zero Emissions: EVs produce no direct emissions, meeting EPA zero-emission vehicle (ZEV) requirements
Electric vehicles (EVs) are not exempt from the Environmental Protection Agency's (EPA) regulations, but they do meet the agency's zero-emission vehicle (ZEV) requirements. This is a crucial distinction, as it highlights the unique environmental benefits of EVs.
The EPA's ZEV program aims to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and improve air quality by promoting the adoption of zero-emission vehicles. EVs, powered by electric motors and rechargeable batteries, produce no direct emissions from their tailpipes, which is a significant advantage over traditional internal combustion engine vehicles. This means that EVs contribute to cleaner air and a reduction in carbon footprints, especially in urban areas where pollution levels are often higher.
The absence of direct emissions from EVs is a key factor in their compliance with the EPA's ZEV standards. These standards set specific targets for vehicle manufacturers to meet, ensuring a certain percentage of zero-emission vehicles in their sales portfolio. By producing no tailpipe emissions, EVs easily fulfill these requirements, making them an essential part of the automotive industry's efforts to combat climate change and promote sustainable transportation.
Furthermore, the EPA's ZEV program encourages the development and sale of EVs, providing incentives and regulations that support the transition to a more environmentally friendly transportation sector. This includes financial incentives for consumers, as well as standards for vehicle manufacturers, ensuring a steady growth in the EV market.
In summary, while EVs are not exempt from the EPA's regulations, they are well-suited to meet the agency's zero-emission vehicle requirements due to their zero-emission nature. This compliance is vital for the automotive industry's contribution to environmental sustainability and the reduction of harmful emissions.
Exploring the World of Non-GamePass Electric Vehicles: A Comprehensive Guide
You may want to see also

Alternative Fuel: EVs are considered alternative fuel vehicles, exempt from certain EPA regulations
Electric vehicles (EVs) are indeed classified as alternative fuel vehicles, which has significant implications for their regulation and compliance with environmental standards. This classification is primarily due to the fact that EVs are powered by electricity, a source of energy that is considered alternative to traditional gasoline or diesel. As a result, EVs are exempt from certain regulations set by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in the United States, which primarily governs the emissions and fuel efficiency standards for conventional vehicles.
The EPA has established specific guidelines and standards for vehicles that run on conventional fuels, such as gasoline and diesel. These regulations aim to reduce harmful emissions and improve fuel efficiency. However, since EVs do not burn gasoline or diesel, they are not subject to the same stringent emission tests and fuel economy standards. This exemption allows EV manufacturers to design and produce vehicles with different performance characteristics and emissions profiles.
One of the key benefits of this exemption is the ability to optimize EV performance and efficiency. Without the constraints of traditional emission control systems, EV engineers can focus on maximizing energy efficiency, improving battery technology, and enhancing overall vehicle performance. This has led to the development of high-performance electric cars that can accelerate rapidly and offer impressive range, all while emitting zero tailpipe pollutants.
Additionally, the EPA's alternative fuel vehicle classification opens up opportunities for innovation in the automotive industry. It encourages the development of advanced battery technologies, charging infrastructure, and sustainable energy sources. This includes the integration of renewable energy systems, such as solar panels or wind turbines, to power EVs, further reducing their environmental impact.
However, it's important to note that while EVs are exempt from certain EPA regulations, they still undergo rigorous testing and certification processes to ensure they meet specific safety and performance standards. These standards include requirements for battery safety, vehicle stability, and overall reliability. Despite the exemption, EVs must adhere to these guidelines to ensure they are safe and reliable for consumers.
Electric Vehicles: Heavier or Lighter? Unveiling the Truth
You may want to see also

Compliance Testing: EVs undergo different compliance testing, exempt from some EPA emission tests
Electric vehicles (EVs) have revolutionized the automotive industry, offering an eco-friendly alternative to traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles. As the popularity of EVs rises, it's essential to understand the regulatory framework surrounding their environmental impact, particularly regarding emissions testing. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) plays a crucial role in setting emission standards and conducting tests to ensure vehicles meet these criteria. However, EVs are subject to specific compliance testing procedures that differ from those of conventional cars.
Compliance testing for EVs focuses on evaluating their performance and emissions in various conditions. Unlike ICE vehicles, EVs do not produce tailpipe emissions, which are a significant concern for traditional emission tests. As a result, certain EPA emission tests are waived for EVs, allowing for a more tailored assessment process. This exemption is primarily due to the unique nature of EV powertrains, which operate without the need for combustion, thus eliminating the release of harmful pollutants during regular driving.
The testing process for EVs involves several key areas of evaluation. Firstly, manufacturers must demonstrate that the vehicle meets the required energy efficiency standards, ensuring optimal performance per unit of energy consumed. This is crucial for promoting sustainable transportation and reducing overall energy consumption. Secondly, EVs are tested for their electric range, which is the distance they can travel on a single charge. This aspect is vital for consumer confidence and encourages the adoption of EVs by addressing range anxiety.
Additionally, compliance testing for EVs includes assessments of their battery performance, charging efficiency, and overall system reliability. These tests aim to ensure that EVs provide a safe, efficient, and reliable driving experience. The focus on battery performance is particularly important, as it directly impacts the vehicle's range, charging speed, and overall longevity. By subjecting EVs to these comprehensive tests, regulatory bodies can ensure that they meet the necessary standards without compromising the unique characteristics of electric powertrains.
In summary, the compliance testing process for EVs is designed to address the specific attributes of electric vehicles, allowing them to be exempt from certain EPA emission tests. This tailored approach ensures that EVs are evaluated based on their unique strengths while still adhering to regulatory requirements. As the EV market continues to grow, understanding these compliance testing procedures is essential for both manufacturers and consumers, fostering a more sustainable and environmentally conscious transportation ecosystem.
EVs: Why Your Green Car Costs More to Insure
You may want to see also

State Regulations: State rules may vary, but EVs often benefit from EPA exemptions
Electric vehicles (EVs) have gained significant popularity in recent years, and their environmental benefits are well-documented. While the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has played a crucial role in regulating vehicle emissions, the relationship between EVs and EPA regulations is complex, especially when considering state-by-state variations.
In the United States, the EPA has established certain exemptions for electric vehicles, particularly in the context of state regulations. These exemptions allow EVs to bypass certain federal emission standards, which can vary from state to state. This flexibility is essential as it enables states to adapt to the unique characteristics of electric vehicles and their impact on the environment. For instance, some states may have different air quality standards or specific environmental goals that require tailored approaches to vehicle emissions.
State regulations regarding EVs often focus on the benefits of electric mobility. Many states offer incentives, tax credits, and other benefits to encourage the adoption of electric vehicles. These measures can include exemptions from certain fees, reduced registration taxes, or access to carpool lanes, even for single-occupancy vehicles. Such incentives not only promote the use of EVs but also contribute to a cleaner and more sustainable transportation ecosystem.
The EPA's role in this context is to provide a framework that allows states to implement their own programs while ensuring a certain level of environmental protection. This approach empowers states to make decisions based on their specific needs and challenges. For example, a state with a high concentration of electric vehicles might choose to waive certain emission tests, recognizing that the technology itself contributes to reduced pollution.
It is important to note that while EVs often benefit from EPA exemptions, the specific regulations and benefits can vary widely across different states. Therefore, EV owners and potential buyers should be aware of the local rules and incentives to fully understand the advantages and responsibilities associated with electric vehicle ownership.
Colorado EV Tax Credit: Refundable or Not?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
No, electric vehicles are not exempt from Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulations. While EVs produce zero tailpipe emissions, they are still subject to various EPA standards and emissions testing. These regulations ensure that EVs meet specific performance, safety, and environmental criteria, contributing to their overall sustainability and compliance with environmental laws.
Yes, electric cars do require emissions testing, but the process differs from traditional internal combustion engine vehicles. Instead of testing for tailpipe emissions, EV testing focuses on the vehicle's battery performance, range, and efficiency. This ensures that the EV meets the required standards and provides accurate information about its environmental impact.
Absolutely. The EPA has implemented specific guidelines for EVs to address their unique characteristics. These considerations include testing for battery degradation, ensuring accurate range estimates, and evaluating the environmental impact of battery production and disposal. The EPA's regulations aim to promote the responsible development and use of electric vehicles while minimizing their environmental footprint.
Electric vehicles have a significant impact on EPA emissions standards. Since EVs produce zero direct emissions, they help reduce overall air pollution and improve air quality. However, the EPA still regulates the manufacturing and sale of EVs to ensure they meet specific standards. This includes guidelines for battery performance, charging infrastructure, and the environmental impact of the entire vehicle lifecycle, from production to end-of-life recycling.