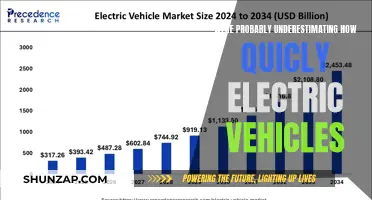
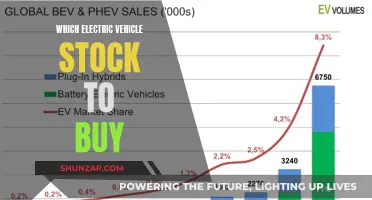
Electric vehicles (EVs) have been hailed as the future of transportation, promising a cleaner and more sustainable alternative to traditional internal combustion engines. However, recent reports and data suggest that the widespread adoption of EVs may be facing challenges and potential setbacks. Despite significant advancements in technology and infrastructure, concerns have emerged regarding their performance, reliability, and overall acceptance among consumers. This paragraph aims to explore the current state of electric vehicles and examine whether they are indeed failing to meet the expectations set by their proponents.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Market Share | As of 2023, electric vehicles (EVs) account for approximately 10% of new car sales in the United States, up from around 2% in 2020 but still a small fraction of the overall market. |
| Range | Modern EVs have improved significantly in range, with some models offering over 300 miles on a single charge. However, this is still a concern for long-distance travel. |
| Charging Infrastructure | The availability of charging stations varies widely by region. While charging networks are expanding, there are still areas with limited access to fast-charging stations. |
| Battery Technology | Advances in battery technology have led to improved energy density and faster charging times. However, battery degradation and the need for regular replacements are ongoing challenges. |
| Cost | The initial cost of EVs is still higher compared to traditional gasoline vehicles, although this gap is narrowing. Government incentives and subsidies can help offset these costs. |
| Environmental Impact | EVs produce zero tailpipe emissions, significantly reducing air pollution. However, the environmental benefits depend on the source of electricity used for charging. |
| Performance | Electric cars offer instant torque, resulting in quick acceleration. They also tend to have a lower center of gravity due to the battery placement, providing better handling. |
| Maintenance | EVs generally require less maintenance due to fewer moving parts. However, battery maintenance and potential replacement costs can be significant. |
| Resale Value | Resale values of EVs have been a concern, with some models depreciating faster than traditional cars. However, this is improving as more models become available. |
| Consumer Adoption | Consumer adoption of EVs is influenced by factors like range anxiety, charging infrastructure, and the overall cost of ownership. |
What You'll Learn
- Battery Technology: Limited range and charging infrastructure hinder widespread adoption
- Cost: High upfront costs and depreciation make EVs less affordable for many
- Infrastructure: Inadequate charging networks and limited public charging stations create convenience issues
- Reliability: Concerns about battery degradation and performance over time persist among consumers
- Environmental Impact: Manufacturing and disposal of EV components may have unforeseen ecological consequences

Battery Technology: Limited range and charging infrastructure hinder widespread adoption
The widespread adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) has been hindered by several key challenges, with battery technology and charging infrastructure playing pivotal roles. One of the primary concerns is the limited range that many EVs can currently offer. While early electric cars had even more restricted ranges, modern models have significantly improved, with some capable of traveling over 300 miles on a single charge. However, this still falls short of the range provided by conventional gasoline vehicles, which can easily exceed 400 miles on a single tank. The disparity in range means that EV owners often face the anxiety of running out of battery power during long journeys, a fear that is not as prevalent among gasoline vehicle drivers.
Battery technology has advanced, but it still has limitations. The energy density of current lithium-ion batteries is relatively low, meaning a substantial amount of space is required to store a significant amount of energy. This constraint impacts the design of EVs, often making them less sleek and more bulky compared to their gasoline counterparts. Additionally, the weight of the battery pack can affect the vehicle's performance, including its acceleration and handling. Despite ongoing research and development, the quest for higher energy density and faster charging times remains a complex and ongoing challenge.
Charging infrastructure is another critical aspect that has not kept pace with the growing popularity of EVs. The availability of charging stations varies widely across regions, and the process of finding and using these stations can be cumbersome. Fast-charging stations, which can significantly reduce charging times, are not as ubiquitous as gas stations, and their installation requires substantial investment and planning. As a result, EV owners often face the inconvenience of longer charging times, especially during long trips, which can deter potential buyers and impact the overall user experience.
The limited range and charging infrastructure issues are closely intertwined. A comprehensive charging network is essential to alleviate range anxiety and provide EV owners with the convenience of rapid charging. However, the development of such infrastructure is a complex process, requiring collaboration between governments, energy companies, and vehicle manufacturers. Without a robust and widely available charging network, the adoption of EVs will continue to face significant hurdles, especially in regions where the necessary infrastructure is lacking or poorly managed.
Addressing these challenges requires a multi-faceted approach. Battery technology companies are investing in research to improve energy density and charging speeds, while vehicle manufacturers are designing more efficient and aesthetically pleasing EVs. Simultaneously, governments and private entities are working on expanding and improving charging infrastructure, offering incentives for the installation of fast-charging stations and the development of smart charging networks. By tackling these issues head-on, the electric vehicle industry can overcome these barriers and pave the way for a more sustainable and widely adopted future of clean transportation.
Mastering EV Maintenance: A Guide to Servicing Electric Vehicles
You may want to see also

Cost: High upfront costs and depreciation make EVs less affordable for many
The high upfront cost of electric vehicles (EVs) is a significant barrier to their widespread adoption. While the long-term savings of EVs are well-documented, the initial purchase price often exceeds that of traditional gasoline vehicles, leaving many potential buyers priced out of the market. This is further exacerbated by the limited availability of government incentives and subsidies, which are crucial in making EVs more affordable.
The depreciation of EVs is another critical factor. Unlike conventional cars, which retain a significant portion of their value over time, EVs depreciate at a much faster rate. This is primarily due to the rapid technological advancements in the EV market, which render older models less desirable and valuable. As a result, buyers often face a significant loss in value when selling their EVs, making them a less attractive investment.
The high upfront costs and rapid depreciation of EVs can be attributed to several factors. Firstly, the technology used in EVs is relatively new and still evolving, which drives up production costs. Secondly, the limited production volumes of many EV models result in higher per-unit costs. Lastly, the lack of a well-established used EV market means that buyers have fewer options for purchasing pre-owned vehicles at a lower price point.
To address these affordability challenges, several strategies can be employed. Firstly, governments can play a pivotal role by offering more substantial incentives and subsidies for EV purchases, especially for lower-income households. Secondly, manufacturers can work towards reducing production costs through economies of scale and technological advancements. Additionally, the development of a robust used EV market, with standardized pricing and certification, can provide buyers with more affordable options while also reducing the overall depreciation rate.
In conclusion, the high upfront costs and rapid depreciation of EVs are significant hurdles that need to be addressed to make electric vehicles more accessible and affordable for the general public. By implementing strategies that reduce costs and improve the used EV market, the potential for widespread EV adoption can be realized, contributing to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly transportation future.
India's Electric Revolution: Strategies for a Sustainable Future
You may want to see also

Infrastructure: Inadequate charging networks and limited public charging stations create convenience issues
The widespread adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) is facing a significant hurdle due to inadequate charging infrastructure, which is a critical aspect often overlooked in the debate about the success or failure of EVs. The current state of public charging stations and charging networks is not keeping pace with the rapid growth of the EV market, leading to several convenience issues for EV owners.
One of the primary concerns is the limited availability of public charging stations. Many EV drivers report difficulty finding available charging points, especially during peak hours or in densely populated urban areas. This scarcity often forces drivers to rely on home charging, which can be time-consuming and may not always be feasible, especially for those living in apartments or with limited parking spaces. As a result, long-distance travel becomes a challenge, and the convenience of EVs is compromised.
The issue of inadequate charging networks is further exacerbated by the varying charging speeds and compatibility issues. While some charging stations offer rapid charging, which can significantly reduce charging times, not all stations are equipped with such technology. Additionally, different EVs may require specific charging connectors, and the lack of standardized charging infrastructure means that drivers might encounter compatibility problems, further limiting their ability to charge on the go.
To address these challenges, governments and energy companies must invest in expanding the charging network infrastructure. This includes installing more public charging stations in strategic locations, ensuring rapid charging capabilities, and implementing smart charging systems that optimize energy distribution. By doing so, the convenience and practicality of owning an EV will be significantly improved, encouraging more consumers to make the switch from traditional internal combustion engine vehicles.
In summary, the success of electric vehicles relies heavily on the development of a robust and extensive charging infrastructure. The current limitations in charging networks and public stations create significant convenience issues for EV owners, hindering the widespread adoption of this environmentally friendly transportation alternative. Addressing these infrastructure challenges is crucial to ensuring the long-term viability and appeal of electric vehicles.
Unveiling the Green Impact: Electric Vehicles and Their Carbon Footprint
You may want to see also

Reliability: Concerns about battery degradation and performance over time persist among consumers
The reliability of electric vehicles (EVs) has been a topic of concern and discussion among consumers, especially regarding the longevity and performance of their batteries. Despite the advancements in EV technology, some users still express worries about battery degradation, which can significantly impact the overall driving experience and the vehicle's resale value.
Battery degradation is a natural process that occurs over time as the chemical components of the battery age and undergo repeated charge-discharge cycles. While modern EVs are designed to manage this degradation, the fear of rapid or excessive decline in battery capacity remains a hurdle for potential buyers. This concern is further exacerbated by the limited understanding of battery health and the varying performance metrics across different EV models.
One of the primary reasons for consumer hesitation is the potential for reduced range and performance. As batteries age, they may not hold a charge as efficiently, leading to a decrease in the vehicle's driving range. This can be particularly problematic for long-distance travelers or those relying on EVs for daily commutes. Additionally, some users report noticeable performance drops, such as slower acceleration or reduced power output, which can affect the overall driving experience and satisfaction.
Manufacturers have been working on addressing these concerns by implementing various strategies. Advanced battery management systems are now employed to monitor and optimize battery performance, ensuring that it operates within safe parameters. These systems can also provide valuable insights to drivers, allowing them to understand and manage their battery usage effectively. Furthermore, the development of faster charging technologies and the introduction of larger, more efficient batteries have contributed to improving the overall reliability of EVs.
However, consumer confidence in the long-term reliability of EVs remains a challenge. To address this, manufacturers should focus on transparent communication about battery health and performance. Providing detailed information about expected degradation rates and offering comprehensive warranties can help alleviate consumer worries. Additionally, ongoing research and development efforts to enhance battery technology and extend their lifespan will be crucial in establishing EVs as a reliable and sustainable transportation option.
Unveiling Active Discharge: Powering Electric Vehicles Efficiently
You may want to see also

Environmental Impact: Manufacturing and disposal of EV components may have unforeseen ecological consequences
The environmental impact of electric vehicles (EVs) is a critical aspect often overlooked in the broader discussion of their success or failure. While EVs offer numerous benefits in terms of reduced emissions and energy efficiency, the manufacturing and disposal processes of their components can have significant ecological consequences. As the demand for EVs continues to rise, it is essential to examine these processes to ensure that the overall environmental impact is minimized.
The manufacturing of EV components, particularly batteries, requires substantial energy and raw materials. Lithium-ion batteries, a common choice for EVs, demand lithium, cobalt, and nickel, which are extracted through mining processes. These extraction methods can lead to habitat destruction, soil erosion, and water pollution if not managed sustainably. For instance, the lithium mining process often involves the use of large amounts of water, which can deplete local water sources and impact ecosystems that rely on these water bodies. Additionally, the energy-intensive nature of battery production contributes to a significant carbon footprint, especially if the energy used is derived from non-renewable sources.
As EVs age and reach the end of their useful lives, the proper disposal of their components becomes another environmental concern. EV batteries, in particular, contain hazardous materials that require specialized handling and recycling. If not disposed of or recycled correctly, these batteries can release toxic substances into the environment, posing risks to both human health and ecosystems. For example, the release of lithium, cobalt, and other heavy metals into the soil and water can lead to long-term ecological damage, affecting soil fertility and aquatic life.
Furthermore, the disposal of other EV components, such as motors and electronics, also presents challenges. These components often contain rare earth metals and other valuable materials that can be recovered through recycling. However, if not recycled properly, they may end up in landfills, leading to soil and water contamination. The improper disposal of these materials can have severe environmental consequences, especially in regions with inadequate waste management infrastructure.
To address these unforeseen ecological consequences, it is crucial to implement sustainable practices throughout the EV lifecycle. This includes adopting more efficient and environmentally friendly extraction methods for raw materials, improving recycling technologies for batteries and other components, and establishing robust waste management systems. Governments, manufacturers, and consumers all have a role to play in ensuring that the environmental benefits of EVs are not overshadowed by the manufacturing and disposal processes. By doing so, we can work towards a more sustainable future where electric vehicles truly succeed in reducing our environmental impact.
Powering the Engine: The Secret to Vehicle Electricity
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Not at all! While there have been some challenges and concerns regarding the widespread adoption of EVs, they are not failing. The technology has advanced significantly, and many of the initial issues have been addressed. Range anxiety, for instance, has been reduced with improved battery technology and the expansion of charging infrastructure. EVs are becoming more affordable, and their performance, efficiency, and sustainability are attracting a growing number of consumers.
There are a few reasons for the skepticism. Firstly, the initial high cost of purchase and the limited range of early models were significant barriers. However, these issues are being tackled with time and technological advancements. Secondly, the reliance on fossil fuel-based charging infrastructure and the time required for charging can be seen as drawbacks compared to traditional refueling. Lastly, the environmental impact of battery production and disposal is a concern, but many manufacturers are focusing on sustainable practices to address this.
Some common complaints include the higher upfront cost, which can be a deterrent for potential buyers, especially in price-sensitive markets. The limited charging infrastructure in certain areas can also cause range anxiety, especially for those who frequently travel long distances. Additionally, the time required to charge an EV, which is longer than refueling a conventional car, might be inconvenient for some users. Lastly, the availability of specific models and colors may vary, leading to potential wait times for customers.
Manufacturers are actively working on solutions. They are investing in research and development to reduce battery costs and increase energy density, making EVs more affordable and efficient. The expansion of charging networks is also a priority, with governments and private companies collaborating to improve accessibility. Many brands are also focusing on offering a wide range of models and colors to cater to diverse customer preferences. Furthermore, the industry is committed to making EV production and recycling processes more environmentally friendly.