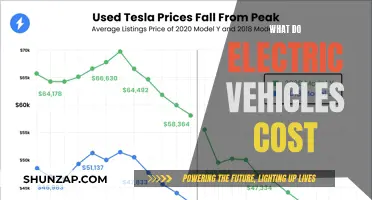
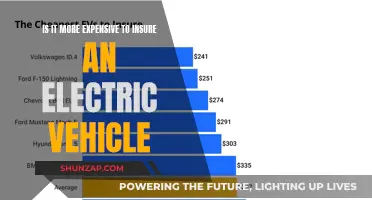
The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) offers standard mileage rates for tax deductions, but what about electric vehicles? This paragraph introduces the topic by addressing the question of whether the standard mileage rates for tax deductions are applicable to electric vehicles. It highlights the importance of understanding the tax implications for electric vehicle owners, especially those who use their vehicles for business or charitable purposes. The discussion will explore the potential benefits and considerations for electric vehicle owners when it comes to claiming mileage-based deductions.
What You'll Learn
- Electric Vehicle Mileage Rates: IRS provides standard mileage rates for electric vehicles, similar to traditional cars
- Deductibility for EVs: Business expenses for electric vehicles can be deducted using standard mileage rates
- Tax Benefits: Electric vehicle owners can claim tax deductions for business-related travel using standard mileage rates
- Rate Calculation: Standard mileage rates for electric vehicles are calculated based on IRS guidelines and vehicle specifications
- Documentation: Proper documentation is required to claim standard mileage rates for electric vehicle business expenses

Electric Vehicle Mileage Rates: IRS provides standard mileage rates for electric vehicles, similar to traditional cars
The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) offers standard mileage rates that can be used to calculate the deductible expenses for electric vehicles, mirroring the treatment for traditional cars. This policy is particularly relevant for individuals and businesses that own or lease electric vehicles and wish to claim tax deductions for their usage. The standard mileage rate is a fixed amount per mile that can be used to estimate the vehicle's operating costs, including expenses for fuel, maintenance, and depreciation.
For electric vehicles, the IRS provides the same mileage rates as for conventional cars, ensuring a consistent approach to tax deductions. As of the latest updates, the standard mileage rate for the calendar year 2023 is 65.5 cents per mile for business use and 58.5 cents per mile for medical or moving purposes. These rates are adjusted annually and are based on the IRS's analysis of the average operating costs associated with vehicles.
When calculating expenses for an electric vehicle, taxpayers can choose to use either the standard mileage rate or actual expenses, whichever method provides a greater deduction. The standard mileage rate simplifies the process by eliminating the need to track and document individual expenses, making it a convenient option for many vehicle owners. However, it's important to note that the actual expense method allows for a more precise calculation, considering factors such as fuel efficiency, electricity costs, and vehicle maintenance.
To claim the mileage deduction for an electric vehicle, taxpayers must provide specific documentation. This includes records of the vehicle's usage for business, medical, or moving purposes, as well as evidence of the vehicle's acquisition or lease. The IRS requires that the vehicle be used predominantly for business purposes to qualify for the standard mileage rate deduction. Additionally, taxpayers should maintain records of the vehicle's mileage and any relevant expenses incurred.
In summary, the IRS's standard mileage rates provide a straightforward method for calculating deductible expenses for electric vehicles, similar to traditional cars. Taxpayers can choose between the standard rate or actual expenses, ensuring they maximize their tax deductions. By understanding and utilizing these rates, individuals and businesses can effectively manage their vehicle-related expenses and take advantage of the tax benefits offered by the IRS.
Ford's Electric Future: Rumors of Cancellation Unveiled
You may want to see also

Deductibility for EVs: Business expenses for electric vehicles can be deducted using standard mileage rates
The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) offers a simplified method for calculating business expenses related to electric vehicles (EVs) through standard mileage rates, which can be a valuable deduction for EV owners. This approach is particularly useful for businesses that use EVs for work-related purposes, as it provides a straightforward way to claim expenses without the need for detailed records of each trip.
When it comes to EVs, the standard mileage rate is calculated based on the vehicle's class and usage. For tax years 2023 and beyond, the standard mileage rate for EVs is 65.5 cents per mile for business miles driven. This rate is slightly lower than the rate for conventional vehicles, reflecting the generally higher efficiency and lower operating costs of EVs. This deduction is available for both new and used EVs, making it accessible to a wide range of business owners.
To claim this deduction, you'll need to provide specific documentation. You must keep records of the vehicle's acquisition, usage, and any related expenses. This includes mileage logs, which should detail the date, purpose, and distance of each trip. Additionally, you should maintain records of any maintenance, repairs, and charging costs associated with the EV. These records are essential to support your deduction and ensure compliance with IRS regulations.
One of the advantages of using standard mileage rates is the simplicity it brings to expense tracking. Instead of keeping detailed receipts for every business-related mile, you can use the mileage rate to calculate your deduction. This method is especially beneficial for businesses with high mileage and those who find it challenging to track individual trip expenses. By using the standard rate, you can ensure a consistent and accurate deduction process.
It's important to note that while standard mileage rates provide a convenient method, there are still considerations to keep in mind. You must ensure that the EV is used predominantly for business purposes to qualify for the deduction. Additionally, any personal use of the vehicle should be documented separately. Consulting with a tax professional can provide further guidance on how to maximize deductions while adhering to IRS guidelines.
Ford's Future: Electric Vehicles in Transition
You may want to see also

Tax Benefits: Electric vehicle owners can claim tax deductions for business-related travel using standard mileage rates
Electric vehicle (EV) owners who use their cars for business purposes can take advantage of tax deductions, and one of the key benefits is the ability to claim tax deductions for business-related travel using standard mileage rates. This is a significant advantage for EV owners, as it simplifies the process of calculating and claiming tax deductions compared to traditional vehicle expenses.
The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) allows EV owners to use the standard mileage rate method to calculate the deductible amount for business miles driven. This rate is set annually and is based on the cost of operating a vehicle. For the tax year 2023, the standard mileage rate is 65.5 cents per mile. This rate is applied to the total business miles driven, providing a straightforward way to estimate and claim deductions.
To calculate the deduction, you multiply the standard mileage rate by the total business miles driven during the year. For example, if an EV owner drove 12,000 business miles in a year, the calculation would be: 12,000 miles * $0.655 = $7,860. This amount can then be claimed as a deduction against business income. It's important to note that this method simplifies the process, especially for those who find it challenging to track and document individual business-related expenses.
EV owners should also be aware of the limitations and rules associated with this deduction. The standard mileage rate is generally used when it is more convenient or when the vehicle is used for both business and personal purposes. Additionally, there are specific guidelines for calculating the deduction when the vehicle is used for both business and personal travel, ensuring that the tax benefits are applied accurately.
In summary, electric vehicle owners can take advantage of tax deductions by using the standard mileage rate method for business-related travel. This approach simplifies the calculation and claiming process, providing a valuable benefit for those who use their EVs for work. Understanding the IRS guidelines and limitations is essential to ensure proper utilization of this tax deduction opportunity.
EVs' Size and Color Constraints: A Technical Deep Dive
You may want to see also

Rate Calculation: Standard mileage rates for electric vehicles are calculated based on IRS guidelines and vehicle specifications
The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) provides standard mileage rates that can be used to calculate the deductible expenses for vehicle use, including electric vehicles. These rates are a convenient method for taxpayers to estimate their vehicle-related expenses without the need for detailed mileage logs. When it comes to electric vehicles, the calculation process is similar to that of conventional vehicles, but with some specific considerations.
The IRS guidelines for standard mileage rates are based on a set of predefined rates that are adjusted annually. For electric vehicles, the rates are calculated using a formula that takes into account various factors, including the vehicle's battery capacity, range, and efficiency. The IRS provides specific tables and rates for different vehicle types, including electric cars, trucks, and motorcycles. These rates are designed to reflect the unique characteristics of electric vehicles, such as their zero-emission nature and potential for higher energy efficiency.
To calculate the standard mileage rate for an electric vehicle, you need to follow these steps: First, determine the vehicle's battery capacity and range. The IRS provides guidelines on how to measure and report these specifications. Then, refer to the IRS tables that outline the standard mileage rates for electric vehicles. These rates are typically higher than those for conventional vehicles due to the higher energy efficiency and potential environmental benefits of electric cars. Multiply the vehicle's annual mileage by the appropriate rate to calculate the deductible expense.
It's important to note that the IRS provides detailed instructions and forms to help taxpayers accurately calculate their vehicle expenses. These resources ensure that taxpayers can properly report their electric vehicle-related expenses and take advantage of the available tax deductions. Additionally, taxpayers should keep records of their vehicle usage, maintenance, and any other relevant expenses to support their calculations and provide evidence for tax purposes.
In summary, the standard mileage rates for electric vehicles are calculated based on IRS guidelines and specific vehicle specifications. By following the IRS's instructions and using the provided rates, taxpayers can accurately determine their deductible expenses for electric vehicle usage, ensuring compliance with tax regulations and maximizing their tax benefits.
The Future of Driving: When Will the Next EV Arrive?
You may want to see also

Documentation: Proper documentation is required to claim standard mileage rates for electric vehicle business expenses
When it comes to claiming standard mileage rates for electric vehicle (EV) business expenses, proper documentation is crucial. The IRS requires detailed records to support your deductions, ensuring that your claims are accurate and compliant with tax regulations. Here's a breakdown of the documentation requirements:
Mileage Logs: Start by maintaining a comprehensive mileage log for each business trip or journey involving your EV. Record the date, purpose of the trip, starting and ending odometer readings, and the distance traveled. This log should be kept for at least one year from the date of filing your tax return. Include any relevant details, such as the route taken, any stops made, and the total time spent on the trip.
Vehicle Usage Records: Document how you use your EV for business purposes. This includes recording the purpose of each trip (e.g., client meetings, deliveries, office visits) and the corresponding mileage. Keep track of the total business miles driven over a specific period, ensuring you have a clear distinction between personal and business usage.
Supporting Evidence: For each business trip or journey, provide supporting evidence to back up your mileage claims. This could include receipts for fuel purchases, toll booth receipts, or any other expenses incurred during the trip. If you charge your EV at a public station, keep records of the dates and amounts paid. Additionally, if you receive any tax credits or incentives for EV ownership, include the relevant documentation.
Consistency and Accuracy: Consistency is key when documenting your mileage. Ensure that your records are accurate and consistent with the IRS guidelines. Double-check your calculations and ensure that the mileage rates applied are correct for the tax year in question. Any discrepancies or missing documentation could lead to audits or delays in processing your tax return.
Record-Keeping Tips: Consider using digital tools or apps that can help you track mileage and expenses efficiently. These tools often provide templates and reminders to ensure you capture all necessary information. Proper organization of your records is essential, so consider creating a system that works best for you, whether it's folders, digital storage, or a combination of both.
By maintaining detailed and accurate documentation, you can ensure that your standard mileage rate claims for electric vehicle business expenses are valid and accepted by the IRS. Proper record-keeping not only helps with tax compliance but also provides valuable data for tracking your EV's business usage and expenses over time.
The Rise of Electric Vehicle Manufacturing: States Leading the Charge
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Yes, the IRS provides the same standard mileage rates for electric vehicles as it does for conventional gasoline or diesel-powered vehicles. The rates are based on the vehicle's use and are calculated based on the IRS's guidelines.
Absolutely! You can use the standard mileage rate for your electric vehicle regardless of its primary use. Whether it's for business or personal trips, you can deduct the mileage expenses accordingly.
The calculation is straightforward. You multiply the IRS's standard mileage rate by the total miles driven for business purposes. For example, if the rate is 58 cents per mile and you drove 10,000 miles for business, your deduction would be $5,800.
No, there is no specific limit on the number of miles you can deduct. You can deduct the actual expenses incurred for business-related travel in a vehicle, including electric vehicles, up to the IRS's standard mileage rate.
Yes, it's recommended to keep records of your electric vehicle usage, including the purpose of the trip, distance traveled, and any relevant expenses. Proper documentation will ensure a smooth tax return process and may be required if the IRS requests further evidence.