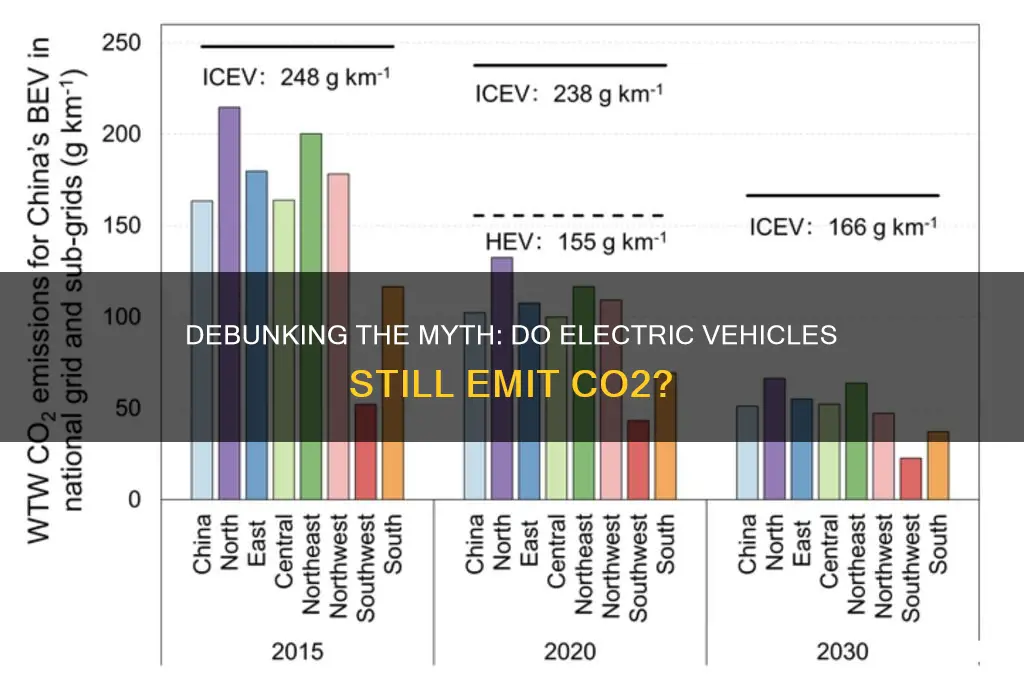
Electric vehicles (EVs) have gained significant popularity as a sustainable transportation alternative, but it's important to understand their environmental impact. One common question is whether EVs produce carbon dioxide (CO2), a greenhouse gas. The answer is nuanced: while traditional internal combustion engine vehicles emit CO2 during operation, EVs themselves do not produce CO2 directly. Instead, they generate electricity, which is typically sourced from power plants that may or may not be carbon-neutral. The environmental benefit of EVs lies in their ability to reduce tailpipe emissions, but the overall carbon footprint depends on the energy mix used to generate the electricity they consume.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Do electric vehicles produce CO2? | No, electric vehicles (EVs) do not produce CO2 emissions directly. They are powered by electric motors that run on electricity, which can be generated from various sources, including renewable energy. |
| CO2 Emissions from Charging | The CO2 emissions associated with EV charging depend on the electricity source. If charged using renewable energy, such as solar or wind power, the overall CO2 footprint is significantly lower compared to conventional vehicles. However, if charged with electricity generated from fossil fuels, there may be a higher CO2 impact. |
| Battery Production and Recycling | The manufacturing of EV batteries can have an environmental impact, including the use of rare earth metals and potential emissions during production. However, advancements in recycling technologies are being developed to minimize these effects. |
| Overall Environmental Impact | EVs have a much lower lifetime carbon footprint compared to internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles. They produce zero tailpipe emissions and contribute to reduced air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions when used extensively with a clean energy grid. |
| Range and Efficiency | Modern EVs have improved in range and efficiency, allowing for longer distances without the need for frequent charging. This further reduces the overall CO2 emissions associated with their use. |
| Charging Infrastructure | The development of charging infrastructure is crucial for widespread EV adoption. Smart charging systems can optimize energy usage, reducing the strain on the power grid and potentially lowering CO2 emissions. |
What You'll Learn
- Battery Production: Manufacturing EV batteries can emit CO2 due to raw material extraction and processing
- Charging Infrastructure: The electricity used to charge EVs can vary in CO2 emissions depending on the grid source
- Recycling Processes: Recycling EV batteries can reduce CO2 emissions compared to manufacturing new batteries
- Lifetime Emissions: Over their lifetime, EVs typically produce less CO2 than conventional vehicles
- Grid Decarbonization: As the grid becomes greener, EVs' CO2 impact decreases significantly

Battery Production: Manufacturing EV batteries can emit CO2 due to raw material extraction and processing
The manufacturing of electric vehicle (EV) batteries is an energy-intensive process that can contribute to carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions, primarily due to the extraction and processing of raw materials. The production of lithium-ion batteries, which are the most common type used in EVs, involves several stages, each with its own environmental impact.
One significant source of CO2 emissions is the extraction of raw materials. Lithium, a key component in EV batteries, is primarily obtained through mining. The process of extracting lithium from the ground can release greenhouse gases, especially during the initial stages of mining and the subsequent transportation of the raw material to manufacturing facilities. For instance, the open-pit mining of lithium often requires large amounts of energy and can result in the release of methane, a potent greenhouse gas, from the surrounding soil and rock.
Additionally, the processing of raw materials to create the battery components further contributes to CO2 emissions. This includes the purification and refining of lithium, as well as the production of other essential materials such as nickel, cobalt, and manganese. These processes often involve energy-intensive steps, such as roasting, leaching, and electroplating, which require significant amounts of electricity and can lead to the release of CO2, especially when fossil fuels are used to generate the power.
The manufacturing process itself also has a substantial environmental footprint. Assembling the battery cells, stacking them into modules, and integrating them into the final EV battery pack require specialized equipment and energy-intensive processes. The use of industrial solvents, adhesives, and other materials in these processes can also contribute to emissions, although the impact is generally lower compared to raw material extraction and processing.
Despite these emissions, it's important to note that the overall lifecycle emissions of EVs are still lower compared to traditional internal combustion engine vehicles. The reason is that EVs produce no direct tailpipe emissions during operation, and their batteries can be charged using electricity from renewable sources, which have a much lower carbon footprint. However, the manufacturing process highlights the need for sustainable practices and the development of more efficient, environmentally friendly methods in the EV battery production chain.
Electric Vehicles: Manual or Automated? Transmission Explained
You may want to see also

Charging Infrastructure: The electricity used to charge EVs can vary in CO2 emissions depending on the grid source
The environmental impact of electric vehicles (EVs) is a topic of growing interest as the world shifts towards more sustainable transportation. One aspect often overlooked is the carbon footprint associated with charging these vehicles. The electricity used to power EVs can vary significantly in terms of its CO2 emissions, depending on the source of the grid. This is a critical factor to consider when evaluating the overall environmental benefits of electric cars.
Charging infrastructure plays a pivotal role in this context. The CO2 emissions from EV charging can be influenced by several factors, primarily the energy mix of the local power grid. In regions where the grid relies heavily on renewable sources like solar, wind, or hydropower, the carbon footprint of charging EVs is relatively low. These clean energy sources produce little to no direct CO2 emissions during electricity generation. As a result, charging EVs in such areas contributes to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly process.
Conversely, areas with a grid heavily dependent on fossil fuels, such as coal or natural gas, will have higher CO2 emissions during the charging process. The burning of these fuels releases significant amounts of greenhouse gases, which can offset the environmental advantages of driving electric vehicles. For instance, if a region's power grid is primarily sourced from coal, the CO2 emissions from charging EVs could be substantial, potentially negating some of the benefits of switching to electric cars.
To address this issue, governments and energy providers are increasingly investing in renewable energy infrastructure. This includes expanding wind and solar farms, as well as improving grid efficiency. By diversifying the energy mix and reducing reliance on fossil fuels, the carbon emissions associated with EV charging can be significantly lowered. This, in turn, enhances the overall environmental credentials of electric vehicles.
In summary, the charging infrastructure is a key consideration when assessing the environmental impact of electric vehicles. The variability in CO2 emissions depends on the grid's energy sources, with renewable-rich grids offering lower emissions. As the world moves towards a more sustainable energy future, the focus on clean charging infrastructure will be essential in maximizing the benefits of electric vehicles in reducing carbon footprints.
Electric Vehicles: The Truth About Clutches
You may want to see also

Recycling Processes: Recycling EV batteries can reduce CO2 emissions compared to manufacturing new batteries
The environmental impact of electric vehicles (EVs) is a topic of growing interest, and one of the key considerations is their role in reducing carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions. While it is true that EVs themselves do not produce CO2 during operation, the production and disposal of their batteries can have environmental consequences. However, the recycling processes associated with EV batteries offer a significant opportunity to mitigate these effects.
Recycling EV batteries is an essential step towards a more sustainable future. The process involves recovering valuable materials from spent batteries, such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel, which can then be reused in the manufacturing of new batteries or other products. This recycling process is crucial because it reduces the need for extracting and processing raw materials, which often involves energy-intensive and environmentally damaging methods. By reusing these materials, we can decrease the overall carbon footprint associated with battery production.
The benefits of recycling EV batteries extend beyond material recovery. The process itself is an energy-efficient alternative to primary production. Manufacturing new batteries from scratch requires substantial energy input, much of which is derived from fossil fuels, leading to significant CO2 emissions. In contrast, recycling batteries consumes less energy and generates fewer emissions, especially when compared to the extraction and processing of raw materials. This is particularly evident in the case of lithium-ion batteries, where the recycling process can reduce CO2 emissions by up to 95% compared to manufacturing new batteries.
Furthermore, the recycling infrastructure for EV batteries is already being developed, ensuring a more sustainable approach to managing these resources. Specialized recycling facilities can efficiently process spent batteries, separating and recovering the valuable components. This not only reduces the environmental impact but also contributes to a circular economy, where resources are reused and recycled, minimizing waste.
In summary, recycling EV batteries is a critical process that significantly reduces CO2 emissions. By reusing materials and minimizing the need for energy-intensive extraction processes, recycling offers a more sustainable alternative to manufacturing new batteries. As the demand for EVs continues to grow, implementing and optimizing recycling processes will play a vital role in ensuring that electric vehicles remain an environmentally friendly transportation option.
Unveiling Electro-Hydraulic Power: The Heart of Modern Vehicle Systems
You may want to see also

Lifetime Emissions: Over their lifetime, EVs typically produce less CO2 than conventional vehicles
The concept of 'lifetime emissions' is crucial when comparing the environmental impact of electric vehicles (EVs) to conventional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles. While EVs are often criticized for their emissions during the manufacturing and charging processes, a comprehensive analysis of their entire lifecycle reveals a different story. Over their lifetime, EVs generally produce fewer greenhouse gases, particularly carbon dioxide (CO2), compared to their conventional counterparts.
The primary reason for this lies in the energy sources used to power EVs. Most EVs are charged using electricity generated from renewable sources like solar, wind, and hydropower, which have significantly lower carbon footprints compared to the burning of fossil fuels in ICE vehicles. As the global energy mix shifts towards cleaner sources, the environmental advantage of EVs becomes even more pronounced. For instance, in regions where electricity generation is heavily reliant on coal, the CO2 savings of EVs can be substantial.
The manufacturing process of EVs also contributes to their lower lifetime emissions. While the production of electric motors, batteries, and other components does require energy and resources, the overall energy efficiency of EV manufacturing is improving. Additionally, the longevity of EVs, often exceeding 10 years, means that the emissions associated with their production are spread out over a longer period, further reducing the lifetime emissions.
In contrast, conventional vehicles have a much higher CO2 output over their lifetime. The burning of gasoline or diesel in ICE engines releases a significant amount of CO2, and this emission is concentrated in the vehicle's operational phase. Over the typical lifespan of a conventional vehicle, which is around 15 years, the cumulative CO2 emissions can be several times higher than those of an EV.
Furthermore, the environmental benefits of EVs extend beyond CO2. EVs produce zero tailpipe emissions, which means they do not release harmful pollutants like nitrogen oxides (NOx) and particulate matter during driving. This aspect is particularly important in urban areas, where air pollution from vehicles contributes to various health issues. While the manufacturing and charging processes of EVs do have some environmental impacts, the overall lifetime emissions of EVs are significantly lower, making them a more environmentally friendly choice for transportation.
Unveiling PEVs and BEVs: The Electric Vehicle Revolution
You may want to see also

Grid Decarbonization: As the grid becomes greener, EVs' CO2 impact decreases significantly
The concept of grid decarbonization is a crucial aspect of the broader transition to electric vehicles (EVs), as it directly influences the environmental impact of EVs. Grid decarbonization refers to the process of reducing the carbon footprint of the electricity grid by increasing the share of renewable energy sources and decreasing reliance on fossil fuels. This shift in the energy mix has a significant impact on the carbon emissions associated with EV charging.
As the grid becomes greener, the electricity used to power EVs is generated from cleaner, renewable sources such as solar, wind, and hydropower. These renewable sources produce little to no greenhouse gas emissions during electricity generation. When an EV is charged using electricity from a decarbonized grid, its carbon footprint is significantly reduced compared to charging with electricity from a grid heavily reliant on fossil fuels. This is because the carbon emissions associated with EV charging are directly proportional to the carbon intensity of the grid.
The environmental benefits of grid decarbonization are twofold. Firstly, it reduces the overall carbon emissions of the transportation sector, which is a major contributor to global CO2 emissions. Secondly, it improves the efficiency of EV ownership by ensuring that the energy used to charge these vehicles is as clean and sustainable as possible. As a result, the CO2 impact of EVs decreases significantly, making them an even more attractive and environmentally friendly mode of transportation.
The transition to a greener grid is already underway in many regions, driven by government policies, technological advancements, and public awareness. This shift is essential to meet the growing demand for EVs and to ensure that the transportation sector aligns with global climate goals. As more renewable energy sources come online, the grid's carbon intensity will continue to decrease, further reducing the environmental impact of EVs.
In summary, grid decarbonization plays a pivotal role in minimizing the CO2 emissions associated with electric vehicles. By increasing the share of renewable energy in the grid, the carbon footprint of EV charging is significantly reduced. This development is a crucial step towards a more sustainable transportation system, where EVs can contribute to a cleaner and greener future without producing CO2 emissions during operation.
Unlocking the Potential: Range-Extending Electric Vehicles Explained
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
No, electric vehicles do not directly produce CO2 emissions. EVs are powered by electric motors that run on electricity, which can be generated from various sources, including renewable energy like solar and wind power, or from traditional power plants. When EVs are charged, the electricity used is often cleaner compared to the burning of fossil fuels in conventional vehicles, leading to lower overall CO2 emissions.
Electric vehicles play a significant role in reducing CO2 emissions in several ways. Firstly, they eliminate tailpipe emissions, which means no direct CO2 release during driving. Secondly, as mentioned earlier, the electricity used to charge EVs can be sourced from renewable energy, further reducing the carbon footprint. This shift from internal combustion engines to electric motors is a crucial step towards mitigating climate change.
It's true that some CO2 emissions can still occur during the electricity generation process for EVs, especially if the power grid relies heavily on fossil fuels. However, this is a temporary issue as the transition to renewable energy sources continues. Many countries and regions are investing in renewable energy infrastructure, which will significantly reduce the carbon intensity of electricity production. Additionally, the overall CO2 savings from widespread EV adoption can outweigh these temporary emissions.
Absolutely! Electric vehicles offer numerous environmental advantages. They produce zero tailpipe emissions, reducing air pollution and improving public health. EVs also contribute to lower noise pollution compared to traditional vehicles. Furthermore, the shift to electric mobility can help reduce the demand for oil, which has significant geopolitical and environmental benefits. As the technology advances and infrastructure improves, electric vehicles will continue to play a vital role in creating a more sustainable and environmentally friendly transportation system.