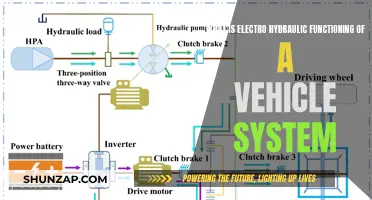
Electric vehicles (EVs) are revolutionizing the automotive industry by offering an eco-friendly and efficient mode of transportation. The power behind these vehicles lies in their advanced electric propulsion systems, which provide an alternative to traditional internal combustion engines. EVs are primarily powered by electric motors that run on electricity stored in batteries. This electricity is generated through various methods, including charging from power outlets or specialized charging stations, which replenish the battery's energy. The process involves converting electrical energy into mechanical power, allowing EVs to accelerate and drive without the need for gasoline or diesel fuel. This innovative technology not only reduces environmental impact but also offers a smooth and quiet driving experience, making electric vehicles an increasingly popular choice for environmentally conscious consumers.
What You'll Learn
- Battery Technology: Chemical reactions in batteries store and release energy for electric vehicles
- Charging Systems: Various methods and infrastructure for replenishing EV batteries efficiently
- Power Electronics: Converters and inverters manage energy flow between the battery and the motor
- Motor Control: Algorithms and systems regulate motor speed and torque for optimal performance
- Grid Interaction: EVs can interact with the power grid for charging and energy management

Battery Technology: Chemical reactions in batteries store and release energy for electric vehicles
The heart of an electric vehicle's power system is its battery pack, which relies on sophisticated chemical reactions to store and deliver energy efficiently. These reactions are the foundation of battery technology, enabling the conversion of chemical energy into electrical power. At the core of this process are electrochemical cells, the building blocks of batteries. Each cell consists of an anode, a cathode, and an electrolyte, all carefully designed to facilitate the movement of ions and electrons.
Chemical reactions within the battery involve the transfer of electrons between the anode and cathode through the electrolyte. During charging, a process known as electrolysis occurs, where an external power source forces electrons to flow from the cathode to the anode, causing a reduction in the cathode and an oxidation at the anode. This results in the storage of energy in the form of chemical bonds. When the vehicle is in use, the reverse reaction takes place. The chemical energy is released as the stored electrons flow back to the cathode, generating an electric current that powers the vehicle's motor.
The efficiency and performance of these chemical reactions are critical to the overall efficiency of electric vehicles. Researchers and engineers focus on optimizing the materials used in anodes and cathodes to enhance energy storage capacity and reduce energy loss during the charging and discharging cycles. Common materials include lithium, lead, and nickel, each offering unique advantages in terms of energy density, cost, and environmental impact. For instance, lithium-ion batteries, widely used in electric cars, provide high energy density and relatively low self-discharge rates, making them ideal for long-range vehicles.
Battery technology continues to evolve, with ongoing research aimed at improving battery life, charging speed, and sustainability. Scientists are exploring solid-state batteries, which replace the liquid electrolyte with a solid conductive material, offering potential benefits such as higher energy density and improved safety. Additionally, efforts are being made to recycle and reuse battery components, reducing the environmental impact of electric vehicles and ensuring a more sustainable future for the automotive industry.
In summary, the power of electric vehicles is harnessed through the intricate dance of chemical reactions within batteries. These reactions enable the storage and release of energy, driving the motors that propel the vehicles forward. As technology advances, the focus remains on enhancing battery performance, longevity, and environmental sustainability, ensuring that electric vehicles become an increasingly viable and attractive option for the transportation sector.
Electric Vehicles: Tax Benefits and Incentives Explained
You may want to see also

Charging Systems: Various methods and infrastructure for replenishing EV batteries efficiently
Electric vehicles (EVs) rely on sophisticated charging systems to replenish their batteries, ensuring they remain ready for use. The charging infrastructure is a critical component of the EV ecosystem, offering various methods to efficiently power these vehicles. One common approach is the use of AC (Alternating Current) charging stations, which are widely available and provide a convenient way to recharge EVs. These stations convert the AC power from the grid to DC (Direct Current) to charge the vehicle's battery. The charging speed can vary depending on the power output of the station and the vehicle's onboard charger capacity. Typically, AC charging stations are categorized into different levels, with Level 1 being the slowest and providing a charging rate of around 5 miles per hour (mph) of range per hour of charging, and Level 3 being the fastest, capable of replenishing a significant portion of the battery in just minutes.
DC fast-charging stations are another essential part of the EV charging infrastructure. These stations deliver high-voltage DC power directly to the vehicle's battery, bypassing the onboard charger. This method significantly reduces charging times, making it ideal for long-distance travel. Fast-charging stations are often found along highways and in strategic locations, allowing EV owners to quickly top up their batteries during journeys. The charging power can range from 50 kW to 350 kW, with the latter providing an impressive charging rate of up to 100 miles of range in just 20 minutes.
The charging infrastructure also includes wireless charging systems, which eliminate the need for physical cables. This technology uses electromagnetic fields to transfer energy between a ground-based charging pad and a receiver on the vehicle's undercarriage. Wireless charging offers convenience and the potential for automated parking and charging, making it an attractive feature for future EV developments. However, the efficiency of wireless charging can be lower compared to wired methods, and the technology is still evolving to address range and reliability concerns.
In addition to charging stations, home charging solutions are becoming increasingly popular. Many EV owners opt to install charging points in their garages or driveways, providing a convenient and cost-effective way to recharge their vehicles overnight. These home charging systems can be connected to the grid and offer various charging speeds, depending on the power supply and the vehicle's requirements. Some modern EVs even support bi-directional charging, allowing them to supply power back to the grid or other devices during periods of high demand.
The development of efficient charging systems and infrastructure is crucial for the widespread adoption of electric vehicles. As the demand for EVs grows, so does the need for a robust and accessible charging network. Governments and private entities are investing in expanding charging station networks, ensuring that EV owners have convenient access to charging points. This includes the installation of fast-charging stations along major routes and the integration of smart charging technologies that optimize energy usage and reduce strain on the power grid.
Kia K4: Electric or Not? Unveiling the Truth
You may want to see also

Power Electronics: Converters and inverters manage energy flow between the battery and the motor
Power electronics play a crucial role in electric vehicles (EVs) by efficiently managing the flow of energy between the battery and the electric motor. This technology enables the conversion and regulation of electrical power, ensuring optimal performance and efficiency in these vehicles.
At the heart of this process are converters and inverters, which are essential components in the power electronics system. Converters are responsible for converting the direct current (DC) from the battery into alternating current (AC) that the motor requires. This conversion is vital as it allows the vehicle to utilize the stored energy in the battery effectively. The converters ensure that the voltage and frequency of the electrical power are suitable for the motor's operation, providing the necessary energy for propulsion.
Inverters, on the other hand, are used to convert the AC power from the converters back into DC power, which can then be supplied to the motor. This step is necessary because the electric motor typically operates on DC power. Inverters also play a critical role in controlling the speed and torque of the motor, allowing for precise regulation of the vehicle's performance. By adjusting the frequency and voltage of the AC power, inverters can influence the motor's speed, ensuring smooth acceleration and efficient energy utilization.
The interaction between converters and inverters is seamless and rapid, allowing for real-time adjustments to meet the dynamic demands of the vehicle. This dynamic control is essential for maintaining stability and performance, especially during acceleration, deceleration, and changes in driving conditions. Power electronics enable the EV to optimize energy usage, ensuring that the battery power is utilized effectively while also protecting the battery from over-discharge or over-charge conditions.
Furthermore, these power electronics systems contribute to the overall efficiency of electric vehicles. By minimizing energy losses during power conversion, they help extend the vehicle's range and reduce energy consumption. This efficiency is a key advantage of electric vehicles, making them an attractive and sustainable transportation option. The continuous development of power electronics technology is driving the advancement of EV performance, reliability, and overall driving experience.
Universal EV Charger: One Size Fits All?
You may want to see also

Motor Control: Algorithms and systems regulate motor speed and torque for optimal performance
Motor control is a critical aspect of electric vehicle (EV) technology, ensuring that the electric motors operate efficiently and effectively to power the vehicle. The primary goal of motor control systems is to regulate the speed and torque of the motor, allowing for precise control over the vehicle's performance and driving experience. This involves a complex interplay of algorithms and control systems that have evolved significantly over the years to meet the demands of modern EVs.
At the heart of motor control are the algorithms that process data and make real-time decisions. These algorithms are designed to optimize the motor's performance by adjusting its speed and torque based on various inputs and conditions. For instance, when an EV driver accelerates, the control system calculates the required torque to achieve the desired speed, taking into account factors such as road grip, battery capacity, and vehicle weight. This calculation is crucial for delivering a smooth and responsive driving experience while ensuring the motor operates within its optimal range.
The control systems in electric vehicles employ feedback mechanisms to monitor the motor's performance continuously. Sensors provide data on the motor's speed, temperature, and current, which is then fed into the control algorithms. These algorithms use advanced mathematical models to analyze the sensor data and make adjustments to the motor's operation. For example, if the motor's speed deviates from the desired value, the control system can quickly calculate the necessary corrections to bring it back to the target speed. This rapid response capability is essential for maintaining stability and control during various driving conditions.
One of the key challenges in motor control is managing the trade-off between speed and torque. Electric motors can deliver high torque at low speeds, which is advantageous for quick acceleration. However, excessive torque can lead to wheel spin and reduced traction. Motor control algorithms address this by dynamically adjusting the torque output based on the vehicle's speed and the driver's input. This ensures that the motor provides the right amount of power at the right time, optimizing performance and safety.
Advanced motor control systems also consider energy efficiency and battery management. By optimizing the motor's operation, these systems can reduce energy consumption, thereby extending the vehicle's range. This is particularly important for electric vehicles, where battery capacity and charging infrastructure are significant considerations. Through precise control of the motor, EVs can achieve higher energy efficiency, making them more practical and appealing to a wider range of consumers.
In summary, motor control algorithms and systems play a pivotal role in the performance and efficiency of electric vehicles. They enable EVs to deliver smooth acceleration, maintain stability, and optimize energy usage. The continuous development of these control mechanisms contributes to the advancement of electric vehicle technology, making it a viable and increasingly popular alternative to traditional internal combustion engines.
Powering Your Ride: Understanding Vehicle Electrical Circuits
You may want to see also

Grid Interaction: EVs can interact with the power grid for charging and energy management
Electric vehicles (EVs) have revolutionized the automotive industry, offering an eco-friendly and sustainable alternative to traditional internal combustion engine cars. One of the key aspects of EV technology is its ability to interact with the power grid, enabling efficient charging and energy management. This grid interaction is a crucial feature that enhances the overall performance and environmental benefits of electric vehicles.
When EVs are connected to the power grid, they can engage in a process known as vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technology. This technology allows EVs to not only draw power from the grid for charging but also to feed electricity back into the grid when needed. During periods of high electricity demand, EVs can act as temporary energy storage devices, absorbing excess power from the grid and storing it in their batteries. This capability is particularly useful in stabilizing the grid and ensuring a consistent power supply. For instance, during peak hours, EVs can be programmed to charge at reduced rates, allowing the grid to manage the increased load more efficiently.
The interaction between EVs and the power grid is facilitated through smart charging systems. These systems use advanced algorithms and communication protocols to optimize charging times and rates. Smart chargers can adjust the charging speed based on the grid's availability and the vehicle's battery capacity. For example, during off-peak hours when electricity prices are lower, EVs can be charged at faster rates, maximizing the use of cheaper energy. Conversely, during peak hours, charging can be slowed down to avoid overloading the grid and to take advantage of potentially lower electricity rates.
Furthermore, V2G technology enables EVs to participate in demand response programs. In these programs, vehicles can be remotely controlled to charge or discharge batteries based on grid instructions. This is especially valuable in emergency situations or when the grid requires rapid response to changing energy demands. For instance, during a power outage, EVs equipped with V2G capabilities can provide backup power by supplying electricity to the grid or even to nearby homes, ensuring a more resilient and flexible energy infrastructure.
The benefits of grid interaction in EVs extend beyond energy management. It also contributes to a more sustainable and cost-effective transportation system. By optimizing charging and discharging processes, EVs can help reduce the overall strain on the power grid, leading to lower electricity costs for both vehicle owners and utility companies. Additionally, the ability to store and manage energy locally can decrease the reliance on centralized power plants, thereby reducing greenhouse gas emissions and improving air quality.
In summary, the interaction between electric vehicles and the power grid is a vital aspect of EV technology. It enables efficient charging, energy storage, and management, while also contributing to a more stable and sustainable energy infrastructure. As the adoption of EVs continues to grow, the integration with the power grid will play a significant role in shaping a greener and more resilient future for transportation and energy systems.
Unveiling New York's EV Inspection: A Comprehensive Guide
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Electric vehicles are powered by one or more electric motors that run on electricity. This electricity is typically stored in batteries, which are the main power source for the vehicle. EVs can be charged by plugging them into an electrical outlet or a charging station, which replenishes the battery's energy.
The most common type of battery used in electric vehicles is the lithium-ion battery. These batteries are known for their high energy density, lightweight design, and ability to store a significant amount of energy. Lithium-ion batteries power most EVs on the market today.
Charging an electric vehicle involves connecting it to a power source. This can be done through a standard electrical outlet, often referred to as Level 1 charging, which provides a slow charging rate. Faster charging is achieved through Level 2 chargers, which require a special charging station and a higher voltage. Some EVs also support rapid charging, using specialized equipment that can replenish the battery in a matter of minutes.
Absolutely! Electric vehicles can be charged using electricity generated from renewable sources such as solar, wind, or hydroelectric power. Many EV owners opt for solar panels to power their vehicles, reducing their carbon footprint and reliance on the traditional power grid.
When an electric vehicle's battery is depleted, the driver will need to recharge it. This can be done at home, at a public charging station, or using a mobile charger. Some EVs also have a range extender, which is a smaller, secondary power source that can provide additional miles when the main battery is low.