The question of whether all vehicles should be electric is a complex and multifaceted one, with valid arguments on both sides. On one hand, electric vehicles (EVs) offer numerous benefits, including reduced environmental impact, lower operating costs, and improved performance. They contribute to a cleaner, greener future by significantly reducing carbon emissions and air pollution compared to traditional internal combustion engine vehicles. Additionally, the rapid advancement of battery technology has made EVs more accessible and affordable, with longer ranges and faster charging times. However, there are still challenges to widespread adoption, such as the initial higher cost of EVs, the need for an extensive charging infrastructure, and the limited range of some models. This introduction sets the stage for a discussion on the pros and cons of electric vehicles and the potential implications of a fully electric vehicle market.
What You'll Learn
- Environmental Impact: Electric vehicles reduce carbon emissions and air pollution, but manufacturing has environmental costs
- Infrastructure: Widespread adoption requires extensive charging stations and renewable energy sources to support electric fleets
- Cost and Affordability: Initial costs and battery technology advancements are key factors in making electric vehicles accessible to all
- Range and Performance: Improvements in battery technology address range anxiety, but performance and charging times vary
- Grid Stability: Increased electric vehicle usage may strain power grids, requiring smart grid management and energy storage solutions

Environmental Impact: Electric vehicles reduce carbon emissions and air pollution, but manufacturing has environmental costs
The widespread adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) is a topic of growing interest and debate, especially in the context of environmental sustainability. While the environmental benefits of EVs are well-documented, it is essential to consider the full lifecycle of these vehicles, including their manufacturing processes, to gain a comprehensive understanding of their impact.
One of the most significant advantages of electric vehicles is their potential to reduce carbon emissions and air pollution. Traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles are major contributors to greenhouse gas emissions, primarily carbon dioxide (CO2), which is a leading driver of climate change. EVs, on the other hand, produce zero tailpipe emissions, meaning they do not release harmful pollutants during operation. This shift from fossil fuel combustion to electric power is a crucial step towards mitigating the environmental impact of transportation. For example, a study by the International Council on Clean Transportation found that, on average, EVs produce fewer lifecycle greenhouse gas emissions than conventional vehicles, even when accounting for the energy generation mix used to charge them.
However, the environmental benefits of EVs are not solely derived from their operation. The manufacturing process of these vehicles also plays a significant role in their overall environmental footprint. The production of electric vehicles involves the extraction and processing of raw materials, such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel, which are essential for battery and motor components. These extraction processes can have detrimental effects on ecosystems and local communities, including habitat destruction and water pollution. Additionally, the manufacturing of EV batteries and other components requires significant energy consumption, often derived from non-renewable sources, further contributing to the environmental impact.
The environmental costs of EV manufacturing are not limited to the initial production phase. The disposal and recycling of EV batteries and other electronic components also present challenges. While recycling technologies are improving, the process can still be energy-intensive and may release pollutants if not managed properly. Furthermore, the rapid evolution of EV technology leads to a high rate of obsolescence, with older models being discarded even before their useful life is fully utilized, creating a growing e-waste problem.
Despite these manufacturing considerations, the overall environmental impact of electric vehicles is still favorable compared to conventional ICE vehicles. The key lies in the long-term benefits of reduced carbon emissions and air pollution. As the world transitions to a more sustainable energy mix, the environmental costs of EV manufacturing are expected to decrease. Additionally, ongoing research and development efforts aim to improve recycling methods and reduce the environmental impact of raw material extraction, further enhancing the sustainability of the EV industry.
In conclusion, while the manufacturing of electric vehicles does have environmental costs, the benefits of reduced carbon emissions and air pollution are substantial. The transition to a more sustainable transportation system, powered by electric vehicles, is a crucial step towards mitigating climate change and improving air quality. As technology advances and sustainable practices are adopted, the environmental impact of EVs will continue to improve, making them an increasingly attractive and responsible choice for the future of transportation.
Vehicle Electrical Drain: Tips for Isolating Power to Prevent Drain
You may want to see also

Infrastructure: Widespread adoption requires extensive charging stations and renewable energy sources to support electric fleets
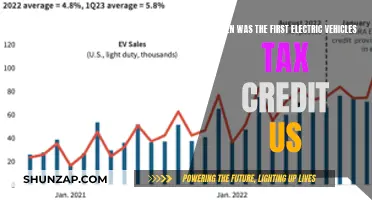
The transition to electric vehicles (EVs) on a large scale necessitates a robust and well-distributed infrastructure network, particularly in the realm of charging stations and renewable energy sources. This is a critical aspect often overlooked in the broader discussion of electric mobility. As the number of electric cars on the road increases, so does the demand for convenient and accessible charging options.
To facilitate widespread adoption, a comprehensive charging station network is essential. This network should be strategically designed to cater to various locations, including residential areas, urban centers, highways, and public spaces. Fast-charging stations, capable of replenishing batteries in a short time, are particularly crucial for long-distance travel and to alleviate range anxiety among potential EV owners. The placement of these stations should be optimized to ensure they are easily accessible and conveniently located, encouraging more people to make the switch.
Renewable energy sources play an equally vital role in supporting electric fleets. The integration of renewable energy into the power grid can significantly reduce the carbon footprint associated with EVs. Solar, wind, and hydroelectric power are some of the renewable sources that can be harnessed to generate electricity for charging stations. By utilizing these sustainable resources, the environmental benefits of electric vehicles can be maximized, contributing to a cleaner and greener transportation ecosystem.
Furthermore, the development of smart grid technologies can enhance the efficiency of charging infrastructure. Smart grids can dynamically manage energy distribution, allowing for real-time adjustments to optimize power usage during peak and off-peak hours. This ensures that charging stations are supplied with electricity from renewable sources when available, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and further decreasing emissions.
In summary, the success of electric vehicle adoption relies heavily on the establishment of a robust infrastructure. This includes the strategic placement of charging stations, ensuring convenience and accessibility, and the integration of renewable energy sources to power these stations. By addressing these infrastructure requirements, we can create a sustainable and efficient transportation system, paving the way for a greener future.
Uncover the Federal EV Tax Credit: A Green Car Incentive
You may want to see also

Cost and Affordability: Initial costs and battery technology advancements are key factors in making electric vehicles accessible to all
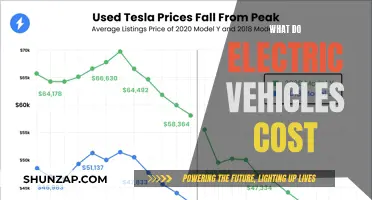
The transition to electric vehicles (EVs) is an important step towards a more sustainable future, but ensuring accessibility and affordability for all is crucial. One of the primary barriers to widespread adoption is the initial cost of purchasing an electric car, which often remains higher compared to traditional gasoline vehicles. This is primarily due to the advanced technology and high-performance batteries that power EVs. However, the good news is that the cost of electric vehicles is gradually decreasing as technology improves and production scales up.
Battery technology advancements play a pivotal role in reducing the overall cost of EVs. Modern electric car batteries have become more efficient, offering higher energy density and longer lifespans. This means that as battery technology progresses, the cost per kilowatt-hour of battery capacity decreases, making it more affordable to produce and purchase electric vehicles. For instance, the development of solid-state batteries promises higher energy density and potentially lower production costs, which could revolutionize the EV market by making it more accessible to a broader range of consumers.
To make electric vehicles truly accessible, governments and manufacturers can implement various strategies. Offering incentives such as tax credits, subsidies, and grants can help reduce the upfront cost for consumers. Additionally, promoting the development of charging infrastructure and providing access to charging stations can alleviate range anxiety, a common concern among potential EV buyers. By addressing these issues, the financial barrier to entry for electric vehicles can be significantly lowered.
Another approach to improving affordability is to encourage the use of second-life batteries. These are batteries that have been used in electric vehicles but are no longer suitable for high-performance applications. They can be repurposed for less demanding tasks, such as energy storage systems or backup power, making EV batteries more cost-effective and environmentally friendly. This practice can help drive down the cost of EV batteries and make electric vehicles more affordable for the average consumer.
In conclusion, while the initial cost of electric vehicles may still be a challenge, ongoing advancements in battery technology are making significant strides in reducing prices. By combining technological innovations with strategic incentives and infrastructure development, the accessibility and affordability of electric vehicles can be greatly improved, paving the way for a more sustainable transportation system. It is through these efforts that we can ensure that the benefits of electric mobility are available to all, regardless of their financial circumstances.
Revolutionizing EVs: Top Tips for Enhanced Performance and Efficiency
You may want to see also

Range and Performance: Improvements in battery technology address range anxiety, but performance and charging times vary
The transition to electric vehicles (EVs) is gaining momentum, and for good reason. With environmental concerns and the need to reduce carbon footprints, the push towards electrification is undeniable. However, one of the primary concerns that often arises in the discussion of EVs is range anxiety—the fear of running out of power before reaching a charging station. This anxiety has been a significant barrier to widespread EV adoption, but advancements in battery technology are making strides to alleviate this issue.
Battery technology has seen remarkable improvements in recent years, leading to longer driving ranges for electric cars. Modern EVs now offer ranges that can rival or even surpass those of their gasoline counterparts. For instance, the latest models from leading manufacturers can travel over 300 miles on a single charge, which is more than sufficient for the daily commutes of most individuals. This increased range is a direct result of advancements in lithium-ion battery technology, which has seen improvements in energy density, allowing for more energy storage in a smaller, lighter package.
Despite these advancements, range remains a critical factor in EV ownership. While longer ranges address the anxiety of long-distance travel, they do not eliminate the need for strategic planning. EV owners still need to consider their daily routines and ensure that charging infrastructure is readily available along their routes. Public charging networks are expanding, but the availability and accessibility of charging stations can vary significantly, especially in rural areas.
In addition to range, performance is another aspect that EV enthusiasts and potential buyers should consider. Electric motors offer instant torque, resulting in impressive acceleration and smooth power delivery. This performance characteristic is one of the reasons why EVs are often associated with sports cars and high-performance driving experiences. However, the performance of EVs can vary depending on the specific model and its intended use. For example, some EVs are designed for efficiency and long-range, which may result in a more conservative driving experience compared to high-performance variants.
Charging times also play a crucial role in the overall ownership experience. While charging times have improved with the development of faster charging stations, they can still be a significant consideration. Rapid charging stations, which can replenish a substantial amount of battery charge in a short time, are becoming more common, but they are not universally available. Standard home charging, which is typically slower, is more widely accessible but can take several hours to fully charge a battery, depending on the capacity. The variation in charging times highlights the importance of understanding the charging infrastructure and the specific charging options available to EV owners.
In summary, while improvements in battery technology have significantly addressed range anxiety, the performance and charging times of EVs remain important considerations. The ideal electric vehicle should offer a balance between an impressive range, robust performance, and efficient charging capabilities. As the market continues to evolve, manufacturers are focusing on these aspects to provide consumers with a seamless and satisfying EV ownership experience.
Illinois EV Fees: What Drivers Need to Know
You may want to see also

Grid Stability: Increased electric vehicle usage may strain power grids, requiring smart grid management and energy storage solutions
The widespread adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) presents both opportunities and challenges for the power grid infrastructure. As more and more vehicles transition to electric power, the strain on the grid becomes a critical concern. The increased demand for electricity from charging stations can lead to significant peaks in power consumption, potentially overwhelming the grid's capacity. This is especially true during peak hours when multiple EVs are charging simultaneously, which could result in voltage fluctuations and even blackouts if not managed properly.
To address this issue, smart grid management systems are being developed and implemented. These systems utilize advanced technologies and algorithms to monitor and control the flow of electricity in real-time. By optimizing charging schedules and loads, smart grids can ensure that power distribution remains stable and efficient. For instance, dynamic pricing models can be employed to encourage EV owners to charge their vehicles during off-peak hours, reducing the burden on the grid during peak times. Additionally, smart meters provide detailed energy usage data, enabling grid operators to make informed decisions and predict potential strain points.
Energy storage solutions play a pivotal role in maintaining grid stability. Large-scale battery storage systems can store excess energy during periods of low demand and release it when the grid needs additional power. This helps in smoothing out the power curve and prevents sudden spikes in electricity usage. Furthermore, integrating renewable energy sources like solar and wind power with EV charging infrastructure can significantly reduce the strain on the grid. By harnessing clean energy, the environmental impact of increased EV usage can be minimized, and the grid's reliability improved.
Another strategy to manage the strain is the development of direct current (DC) fast charging stations. These stations can charge multiple EVs simultaneously without the need for an alternating current (AC) transformer, reducing the overall power consumption. Additionally, implementing vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technology allows EVs to not only draw power from the grid but also feed electricity back to it, further stabilizing the grid's load. V2G technology can be particularly useful in managing peak demand and providing additional power during emergencies.
In conclusion, while the shift towards electric vehicles is essential for reducing environmental impact, it is crucial to ensure that the power grid can handle the increased demand. Smart grid management and energy storage solutions are key to achieving this balance. By implementing these technologies, we can optimize the charging of EVs, reduce strain on the grid, and ensure a reliable and sustainable transportation system. This approach will not only benefit the environment but also enhance the overall efficiency and stability of our power infrastructure.
Powering Up: Understanding the Safety of Plugging In Your EV
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Electric vehicles (EVs) offer numerous benefits for the environment and society. They produce zero tailpipe emissions, reducing air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions, which is crucial for combating climate change. EVs also contribute to improved public health by minimizing the release of harmful pollutants, especially in densely populated urban areas.
Electric cars have several advantages. Firstly, they are more energy-efficient, converting a higher percentage of energy into power compared to internal combustion engines. This leads to reduced energy consumption and lower operating costs for drivers. Secondly, EVs offer a smoother and quieter driving experience due to their instant torque delivery and lack of gear shifts.
The infrastructure for charging electric vehicles is rapidly expanding globally. Many countries and cities are investing in charging station networks, both public and private, to support the growing number of EVs. Governments are also incentivizing the installation of home charging points, making it more convenient for EV owners to charge their vehicles overnight.
While the benefits are significant, there are challenges to consider. The initial cost of purchasing electric vehicles can be higher compared to their gasoline counterparts, although this is offset by long-term savings on fuel and maintenance. Additionally, the availability of charging stations in rural or less-developed areas may be limited, requiring investments in charging infrastructure to ensure widespread accessibility.
Encouraging the adoption of electric vehicles can be achieved through various means. Governments can play a crucial role by offering incentives such as tax credits, rebates, and reduced registration fees for EV owners. Additionally, raising awareness about the environmental and economic benefits of EVs through educational campaigns can help change consumer behavior.