Electric vehicles (EVs) have gained significant popularity due to their environmental benefits, but it's important to consider the hidden emissions associated with their production and use. While EVs produce zero tailpipe emissions, the manufacturing process and the generation of electricity used to power them can contribute to environmental impacts. This paragraph will explore the often-overlooked emissions from the production of EV batteries, the extraction of raw materials, and the potential for increased energy consumption during manufacturing. Understanding these hidden emissions is crucial for a comprehensive evaluation of the environmental benefits of electric vehicles.
What You'll Learn
- Manufacturing: The environmental impact of rare earth minerals and heavy metals used in EV batteries
- Energy Use: High energy consumption during production and disposal of EV batteries
- Recycling: Challenges and potential environmental risks associated with recycling EV batteries
- Grid Impact: Increased strain on power grids from charging electric vehicles
- End-of-Life: Proper disposal and recycling methods for retired EV batteries

Manufacturing: The environmental impact of rare earth minerals and heavy metals used in EV batteries
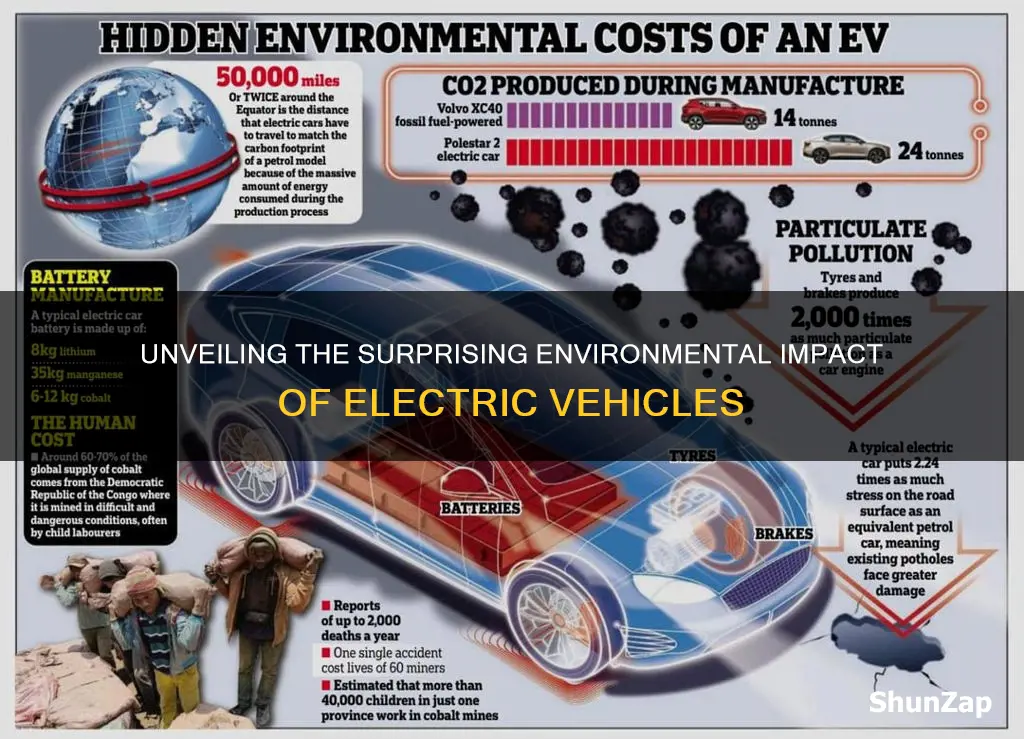
The manufacturing of electric vehicles (EVs) has brought about a revolution in the automotive industry, offering a more sustainable alternative to traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) cars. However, the environmental impact of EVs extends beyond their operational emissions, and one critical aspect is the manufacturing process, particularly the use of rare earth minerals and heavy metals in their batteries. These materials, essential for the production of high-performance batteries, have their own set of hidden environmental consequences.
Rare earth minerals, such as neodymium, praseodymium, and lanthanum, are crucial for the powerful permanent magnets used in EV motors. These minerals are extracted through mining, a process that can have severe environmental repercussions. The mining of rare earths often involves destructive practices, including open-pit mining, which can lead to habitat destruction, soil erosion, and water pollution. The harsh chemicals used in the extraction process can contaminate nearby water sources, affecting local ecosystems and communities. Furthermore, the energy-intensive nature of mining and refining these minerals contributes to a significant carbon footprint, often offsetting the environmental benefits of driving an EV.
Heavy metals, such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel, are also integral components of EV batteries. The extraction and processing of these metals present unique challenges. For instance, lithium mining requires extensive water resources, and the process can result in water scarcity in already arid regions. Cobalt, often sourced from conflict-affected areas in the Democratic Republic of Congo, has been associated with human rights abuses and environmental degradation. The extraction and transportation of these heavy metals can lead to soil and water contamination, posing risks to both human health and the environment.
The manufacturing process of EV batteries itself is energy-intensive, requiring large amounts of electricity, often sourced from fossil fuels in some regions. This energy consumption contributes to greenhouse gas emissions, further exacerbating the environmental impact. Additionally, the disposal of old batteries is another critical issue. If not managed properly, the heavy metals and rare earth minerals in these batteries can leach into the environment, causing soil and water pollution.
To address these hidden emissions, the EV industry must focus on sustainable sourcing and recycling practices. Implementing stricter regulations and standards for mining and manufacturing can help minimize environmental damage. Encouraging the development of renewable energy sources for battery production and promoting recycling technologies can significantly reduce the carbon footprint associated with EV manufacturing. By recognizing and mitigating these hidden environmental impacts, the EV market can continue to grow while contributing to a more sustainable future.
Electric Vehicles: Are They Worth the Price Tag?
You may want to see also

Energy Use: High energy consumption during production and disposal of EV batteries
The production and disposal of electric vehicle (EV) batteries contribute significantly to the hidden energy consumption associated with EVs. While EVs themselves have zero tailpipe emissions, the manufacturing and end-of-life processes of their batteries can have substantial environmental impacts.
The energy-intensive nature of EV battery production is primarily due to the extraction and processing of raw materials. Lithium, cobalt, and nickel are crucial components of EV batteries, and their mining and refining processes require vast amounts of energy. For instance, extracting lithium from brine or hard rock involves energy-intensive processes like evaporation or crushing, which often rely on fossil fuels. Similarly, the production of cobalt and nickel, essential for cathode and anode materials, also demands significant energy, often sourced from non-renewable means.
The manufacturing process itself further exacerbates energy consumption. Assembling battery cells, stacking them into modules, and integrating them into the vehicle's electrical system require substantial energy input. This manufacturing phase often occurs in energy-intensive facilities, and the transportation of raw materials and finished products adds to the overall energy footprint.
Moreover, the disposal and recycling of EV batteries present unique challenges. As batteries age or become obsolete, they need to be safely recycled or disposed of to prevent environmental contamination. The process of extracting valuable materials from spent batteries is energy-intensive and often involves chemical processes. Additionally, the transportation of batteries for recycling or disposal can contribute to the overall energy consumption associated with EVs.
Addressing the high energy consumption during the production and disposal of EV batteries is crucial for minimizing the environmental impact of the EV industry. Researchers and manufacturers are exploring more sustainable practices, such as improving recycling technologies, developing more energy-efficient extraction methods, and designing batteries with longer lifespans to reduce the need for frequent replacements. By focusing on these areas, the industry can work towards mitigating the hidden energy emissions associated with electric vehicles.
Electric Vehicles: The Rapid Overtake in the Automotive Industry
You may want to see also

Recycling: Challenges and potential environmental risks associated with recycling EV batteries
The recycling of electric vehicle (EV) batteries presents a complex set of challenges and potential environmental risks that are often overlooked. As the demand for EVs rises, so does the need for efficient and sustainable battery recycling methods. However, the process is not without its pitfalls.
One of the primary challenges is the composition of EV batteries. Most modern EVs use lithium-ion batteries, which contain valuable materials like cobalt, nickel, and lithium. While these materials are recyclable, the process itself can be energy-intensive and environmentally detrimental. The extraction and processing of these metals often involve hazardous chemicals and can lead to soil and water contamination if not managed properly. For instance, the leaching of cobalt and lithium from battery components can result in the pollution of nearby water sources, posing risks to aquatic ecosystems and potentially affecting human health.
Another concern is the potential release of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) during the recycling process. These compounds can contribute to air pollution and have adverse effects on human health. Additionally, the recycling facilities must be designed to handle these hazardous materials safely, ensuring that workers and the surrounding environment are protected. This includes implementing proper ventilation systems and waste management protocols to minimize the release of harmful substances.
Furthermore, the recycling infrastructure for EV batteries is still developing. The collection and transportation of used batteries to recycling centers can be logistically challenging, especially considering the weight and potential hazards of these batteries. Specialized facilities and transportation methods are required to handle the large volume of batteries generated by the growing EV market. Inadequate infrastructure can lead to delays in recycling, allowing potentially hazardous materials to remain in storage for extended periods.
Despite these challenges, there are ongoing efforts to improve recycling technologies and processes. Researchers are exploring more efficient and environmentally friendly methods, such as developing advanced recycling techniques that can recover a higher percentage of materials without the need for aggressive chemical treatments. Additionally, the development of second-life applications for EV batteries, where they can be repurposed for less demanding uses, can extend their lifespan and reduce the overall demand for new recycling.
In conclusion, while recycling EV batteries is crucial for a sustainable future, it is essential to address the associated challenges and potential environmental risks. By implementing stricter regulations, investing in research and infrastructure, and promoting responsible recycling practices, the industry can work towards minimizing the hidden emissions and environmental impact of EV battery recycling. This will contribute to a more sustainable and environmentally conscious approach to the growing EV market.
Parking Privileges: Unlocking Free EV Parking Benefits
You may want to see also

Grid Impact: Increased strain on power grids from charging electric vehicles
The widespread adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) is revolutionizing the automotive industry, offering a cleaner and more sustainable alternative to traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) cars. However, beneath the surface, there are several hidden environmental impacts associated with the rise of EVs, particularly concerning their impact on power grids. As the number of EVs on the road increases, so does the demand for charging infrastructure, which can have significant implications for the stability and reliability of our electrical grids.
One of the primary concerns is the strain on power grids during peak charging times. When a large number of EVs are charged simultaneously, it can lead to a surge in electricity demand, potentially overwhelming the grid's capacity. This is especially critical in urban areas where multiple EVs are charged at home or in public charging stations. During peak hours, such as early mornings and late evenings, the grid may struggle to meet this sudden increase in load, leading to potential power outages or voltage fluctuations. For instance, a study by the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) in the United States revealed that charging EVs during peak hours could result in a 15-20% increase in grid load, posing challenges for grid operators.
To address this issue, grid operators and utility companies are exploring various strategies. One approach is to implement smart charging systems that optimize charging times based on grid conditions. These systems can adjust charging rates to match the grid's available capacity, ensuring a more stable and efficient power distribution. Additionally, the development of vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technology allows EVs to not only draw power from the grid but also feed electricity back to it during periods of high demand, helping to balance the load.
Another aspect to consider is the environmental impact of the increased electricity generation required to power EVs. While EVs themselves produce zero tailpipe emissions, the electricity used to charge them may come from various sources, some of which can be less environmentally friendly. For example, if a significant portion of EV charging occurs during periods when the grid relies heavily on coal or natural gas power plants, it could indirectly contribute to higher greenhouse gas emissions. This highlights the importance of transitioning to a more sustainable and renewable energy mix to support the growing EV market.
In conclusion, the rise of electric vehicles brings about a unique set of challenges for power grids. Managing the strain on grids during peak charging times and ensuring a sustainable energy supply for EV charging are crucial aspects that require innovative solutions. By implementing smart grid technologies and promoting renewable energy sources, we can mitigate the hidden environmental impacts of EVs and ensure a more resilient and eco-friendly transportation system.
Simplifying the Process: A Guide to Registering Your Electric Car
You may want to see also

End-of-Life: Proper disposal and recycling methods for retired EV batteries
The end-of-life management of retired electric vehicle (EV) batteries is a critical aspect often overlooked in the discussion of the environmental benefits of EVs. As the demand for electric mobility grows, so does the need for a sustainable approach to handle the batteries that power these vehicles when they reach the end of their useful life. Proper disposal and recycling methods are essential to minimize the environmental impact and ensure the responsible handling of these powerful energy storage systems.
When an EV battery pack is no longer functional or has reached the end of its lifespan, it should be carefully removed and prepared for recycling. This process begins with a thorough inspection to identify any physical damage or defects. The battery pack should be disconnected from the vehicle, ensuring that all power sources are isolated to prevent any safety hazards. Specialized equipment is then used to carefully extract the individual battery cells, modules, and packs, separating them from the vehicle's structure. This step is crucial to facilitate the recycling process and ensure the safety of the handling personnel.
Recycling EV batteries involves a complex process to recover valuable materials and minimize environmental harm. The first step is to dismantle the battery pack, separating the various components such as the cathode, anode, electrolyte, and casing. These materials are then processed through specialized recycling techniques. For instance, the cathode and anode materials can be recycled to produce new battery cells, reducing the need for mining and processing of raw materials. The electrolyte can be recovered and reused, while the casing and other non-metallic components can be recycled for other industrial applications.
One of the key challenges in EV battery recycling is the safe handling of lithium-ion batteries, which contain hazardous materials. These batteries can pose risks if not managed properly, including the potential for thermal runaway and the release of toxic gases. Specialized facilities and equipment are required to safely dismantle and process these batteries, ensuring that any hazardous materials are contained and managed appropriately. This includes the use of advanced recycling technologies that can effectively separate and recover valuable materials while minimizing the environmental impact.
In addition to recycling, proper disposal methods are also crucial. While recycling is the preferred approach, there may be instances where batteries cannot be recycled due to their condition or composition. In such cases, specialized disposal methods should be employed to prevent environmental contamination. This may involve secure containment and treatment processes to neutralize or stabilize the batteries, ensuring that any potential hazards are mitigated.
In summary, the end-of-life management of EV batteries requires a comprehensive approach that includes proper removal, recycling, and disposal methods. By implementing these practices, we can ensure that the environmental benefits of electric vehicles are not undermined by improper handling of retired batteries. It is essential for manufacturers, policymakers, and consumers to collaborate and establish sustainable practices to address the hidden emissions and environmental impact associated with the lifecycle of EV batteries.
Can Income Limit Your Electric Vehicle Credit?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
While electric vehicles are known for their zero tailpipe emissions, it's important to consider the entire lifecycle of these cars. The production and disposal of EV batteries can lead to significant emissions, often referred to as 'hidden emissions'. Manufacturing processes, especially those involving rare earth minerals, can have a substantial environmental impact. However, it's worth noting that these emissions are generally lower compared to traditional internal combustion engine vehicles over their lifetime.
Calculating hidden emissions is a complex task as it involves various factors, including the type of energy used for electricity generation, the manufacturing process, and the end-of-life disposal methods. You can use lifecycle assessment tools or consult environmental impact studies specific to the EV model you're interested in. These studies often provide estimates of greenhouse gas emissions, resource consumption, and other environmental impacts throughout the vehicle's lifecycle.
Absolutely! The automotive industry and researchers are actively working on improving the sustainability of electric vehicles. This includes developing more efficient battery production methods, recycling technologies for used batteries, and transitioning to renewable energy sources for electricity generation. Many governments and organizations also promote the use of clean energy and sustainable practices to minimize the overall environmental footprint of EVs.
Yes, there are various ways to offset or counteract the hidden emissions. You can consider investing in renewable energy projects, such as wind or solar farms, which help reduce the carbon intensity of electricity generation. Additionally, supporting reforestation initiatives or purchasing carbon credits can contribute to environmental conservation and help balance out the emissions associated with EV production and use.







