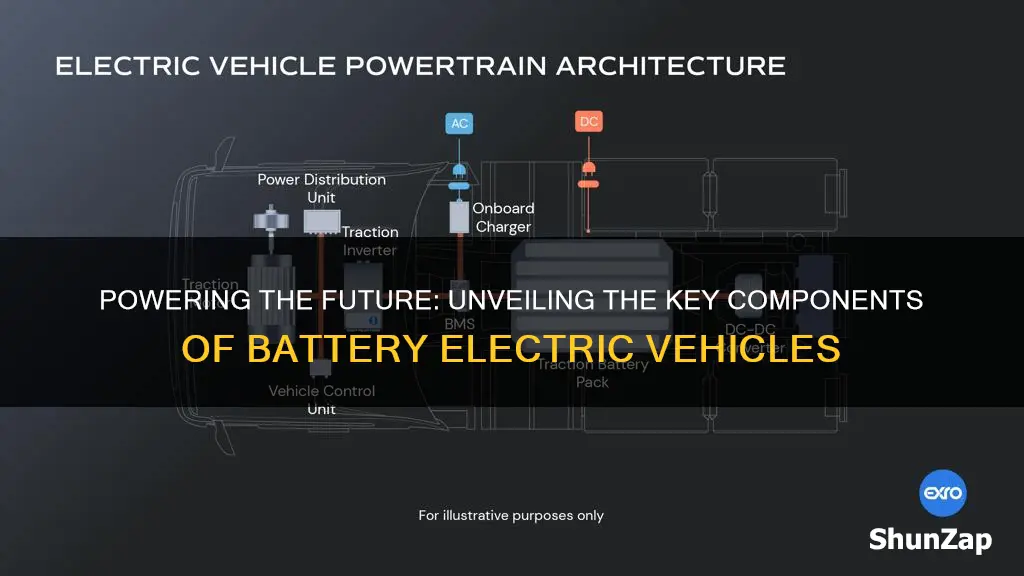
Battery electric vehicles (BEVs) are a rapidly growing segment of the automotive industry, offering an eco-friendly and efficient alternative to traditional internal combustion engine vehicles. These vehicles are powered by one or more electric motors, which are fueled by a high-capacity battery pack. The key components of a BEV include the battery pack, electric motor(s), inverter, power electronics, and a sophisticated control system. The battery pack stores electrical energy and provides the power needed to drive the vehicle, while the electric motor converts this electrical energy into mechanical energy to propel the car. The inverter and power electronics manage the flow of electricity between the battery and the motor, ensuring efficient and safe operation. The control system, often featuring advanced software, optimizes performance, range, and charging, making BEVs a highly sophisticated and environmentally friendly mode of transportation.
What You'll Learn
- Battery Pack: High-capacity lithium-ion cells, often in modules, store energy
- Electric Motor: Converts electrical energy into mechanical power for propulsion
- Power Electronics: Inverters and converters manage power flow between battery and motor
- Charging System: Includes chargers, cables, and ports for replenishing battery power
- On-Board Charger: Converts AC from external sources to DC for battery charging

Battery Pack: High-capacity lithium-ion cells, often in modules, store energy
The battery pack is the heart of any battery electric vehicle (BEV), and it is designed to store and supply the electrical energy required to power the vehicle. This component is a sophisticated system that utilizes high-capacity lithium-ion cells, which have become the industry standard for electric vehicles due to their exceptional performance and energy density.
Lithium-ion cells are the building blocks of the battery pack. These cells are composed of a positive electrode (cathode), a negative electrode (anode), and an electrolyte that facilitates the movement of ions between the electrodes during charging and discharging. The cathode is typically made of a lithium-based material, such as lithium cobalt oxide (LiCoO2), while the anode can be made of graphite or other carbon-based materials. The electrolyte is a conductive liquid or gel that ensures the flow of ions, allowing the cell to function.
Battery packs are often constructed in modules to optimize performance and safety. Each module contains multiple lithium-ion cells connected in series and parallel arrangements. In a series connection, the positive terminal of one cell is connected to the negative terminal of the next, increasing the overall voltage. Parallel connections, on the other hand, increase the overall current capacity by connecting multiple cells in parallel. This modular design allows for flexibility in pack configuration, enabling engineers to tailor the battery pack's energy and power output to the specific requirements of the vehicle.
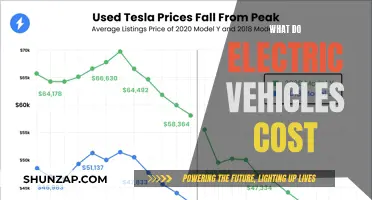
The energy storage capacity of a battery pack is measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh). High-capacity lithium-ion cells enable BEVs to achieve impressive range, which is a critical factor in the adoption of electric vehicles. Modern electric vehicles can have battery packs with capacities ranging from 30 kWh to over 100 kWh, providing sufficient energy to cover long distances without frequent charging.
Furthermore, the battery pack incorporates advanced management systems to monitor and control the performance of individual cells and the pack as a whole. These systems ensure optimal charging and discharging, maintain cell health, and provide protection against overcharging, over-discharging, and temperature extremes. The management system also includes communication interfaces that allow for data exchange with the vehicle's control unit, ensuring efficient and safe operation.
The Rapid Rise: Uncovering the Surprising Speed of Electric Vehicles' Adoption
You may want to see also

Electric Motor: Converts electrical energy into mechanical power for propulsion
The electric motor is a critical component of battery-electric vehicles (BEVs), playing a pivotal role in converting electrical energy into mechanical power for propulsion. This process is fundamental to the operation of BEVs, as it enables the vehicle to move forward. Electric motors are designed to operate efficiently and provide the necessary torque to drive the wheels, ensuring a smooth and responsive driving experience.
These motors are typically found in the drivetrain, positioned between the battery pack and the transmission. When the driver engages the accelerator, the battery sends electrical energy through the motor, which then transforms this energy into rotational motion. This rotational force is what turns the wheels, propelling the vehicle forward. The design of electric motors has evolved to be highly efficient, with minimal energy loss during the conversion process.
One of the key advantages of electric motors is their ability to provide instant torque. Unlike internal combustion engines, which require a certain amount of rotation before delivering full power, electric motors can generate maximum torque from a standstill. This results in quick acceleration and a responsive driving feel, making BEVs highly desirable for performance enthusiasts. The motor's efficiency is further enhanced by the use of advanced materials and cooling systems, ensuring optimal performance even under demanding conditions.
The power output of electric motors can vary, but they are generally designed to provide a substantial amount of force to meet the vehicle's driving requirements. For instance, high-performance BEVs often feature powerful motors that can deliver over 400 horsepower, enabling rapid acceleration and impressive top speeds. These motors are carefully calibrated to work in harmony with the battery pack and other vehicle systems, ensuring a well-balanced and efficient power delivery.
In summary, the electric motor is the heart of a battery-electric vehicle, responsible for the conversion of electrical energy into the mechanical power that drives the wheels. Its efficiency, instant torque delivery, and ability to work seamlessly with other vehicle components make it a vital element in the success of BEVs. As technology advances, electric motors continue to evolve, promising even more impressive performance and efficiency in the future of sustainable transportation.
Unveiling the Secrets: A Guide to Spotting Electric Vehicles
You may want to see also

Power Electronics: Inverters and converters manage power flow between battery and motor
Power electronics play a crucial role in the efficient operation of battery electric vehicles (BEVs). These vehicles rely on sophisticated power electronics systems to manage the complex interplay between the battery, motor, and other electrical components. At the heart of this system are inverters and converters, which are essential for controlling the flow of electrical energy.
Inverters are devices that convert direct current (DC) from the battery into alternating current (AC) that the motor can use. This process is vital because most electric motors operate on AC power. The inverter's primary function is to adjust the voltage and frequency of the output AC signal to match the motor's requirements. By doing so, it ensures that the motor receives the precise amount of power needed for efficient operation. Modern inverters also incorporate advanced control algorithms to optimize performance, improve efficiency, and protect the motor from potential damage.
Converters, on the other hand, are responsible for managing the power flow in the opposite direction, from the motor back to the battery. These devices convert the AC power generated by the motor back into DC power, which can then be stored in the battery pack. Converters play a critical role in maintaining the health and longevity of the battery by ensuring that the charging process is controlled and efficient. They also help in regulating the voltage and current levels, ensuring that the battery operates within safe and optimal parameters.
The efficiency and performance of BEVs heavily depend on the precision and responsiveness of these power electronics components. Inverters and converters must work in harmony to provide a seamless power supply to the motor while also managing the energy storage and recovery processes. This intricate dance of electrical energy ensures that BEVs can accelerate smoothly, maintain stable speeds, and efficiently recover energy during braking, all while maximizing the range and overall efficiency of the vehicle.
Furthermore, the design and implementation of these power electronics systems are areas of active research and development in the automotive industry. Engineers strive to create more compact, lightweight, and efficient inverters and converters to meet the growing demands of electric vehicle technology. These advancements contribute to the overall improvement of BEVs, making them more practical, affordable, and environmentally friendly.
Vehicle Chassis: Conducting the Electrical Circuit Path
You may want to see also

Charging System: Includes chargers, cables, and ports for replenishing battery power
A battery electric vehicle (BEV) relies on a sophisticated charging system to replenish its power, ensuring it remains ready for the road. This system is a critical component, enabling the vehicle to be replenished and ready for use. Here's a breakdown of the key elements:
Chargers: These are the heart of the charging system. Chargers are typically located in the vehicle's engine bay or trunk, often integrated into the vehicle's design. They convert the alternating current (AC) from the power grid into direct current (DC), which is the form of electricity that the vehicle's battery can utilize. Chargers can be either alternating current (AC) or direct current (DC) types, with AC chargers being more common for home and public charging stations. The power output of chargers varies, with some capable of delivering rapid charging, while others provide a slower, more efficient charge.
Charging Ports: These are the physical interfaces where the charging cable connects to the vehicle. They are strategically placed for easy access and are often located near the vehicle's front or rear. Charging ports are designed to be user-friendly, with some featuring smart technology that communicates with the vehicle's system to optimize the charging process. This includes monitoring the battery's state of charge and adjusting the charging rate accordingly.
Cables: These are the flexible, insulated wires that connect the charger to the vehicle's charging port. Cables are designed to be durable and weather-resistant, ensuring safe and efficient charging. They come in various lengths and types, with some featuring quick-release connectors for convenient charging. The choice of cable can impact charging speed and safety, so it's essential to select the appropriate cable for the vehicle and charging station.
The charging system's efficiency and convenience are vital for the widespread adoption of BEVs. It allows for the replenishment of power, ensuring the vehicle is always ready for use. With the right combination of chargers, cables, and ports, BEVs can be charged at home, at work, or at public charging stations, providing flexibility and peace of mind to drivers.
Navigating the Tax Landscape: Electric Vehicles and Their Financial Implications
You may want to see also

On-Board Charger: Converts AC from external sources to DC for battery charging
The on-board charger is a crucial component in the charging infrastructure of battery electric vehicles (BEVs). Its primary function is to convert the alternating current (AC) from external power sources, such as wall outlets or charging stations, into direct current (DC) that can be used to charge the vehicle's battery. This process is essential for ensuring that the battery receives the correct voltage and current levels required for efficient and safe charging.
In the context of BEVs, the on-board charger typically operates in conjunction with a charging port, which is the physical interface where the vehicle connects to the external power source. When a BEV owner plugs their vehicle into a charging station or a home charging setup, the charger's role becomes evident. It receives the AC power supply, which is commonly in the form of a single-phase or three-phase AC voltage, and then performs the necessary conversion.
The conversion process involves several stages. Firstly, the charger's input stage filters and regulates the incoming AC voltage to ensure it meets the required specifications. This is crucial to prevent any damage to the charging system or the vehicle's battery. After regulation, the AC power is then converted into DC using an inverter. This inverter is a critical component, as it must handle the power levels required for efficient charging, which can vary significantly depending on the charging station's capabilities and the vehicle's battery capacity.
Once the AC is converted to DC, the output stage of the on-board charger ensures that the voltage and current levels are appropriate for the battery. This stage includes various electronic controls and sensors that monitor and adjust the charging parameters in real-time. The goal is to optimize the charging process, ensuring the battery is charged at the fastest possible rate while maintaining its health and longevity.
In summary, the on-board charger is a sophisticated device that plays a vital role in the charging process of BEVs. It enables the vehicle to accept and utilize external power sources, facilitating convenient and efficient charging for electric vehicle owners. Understanding the charger's function and its interaction with the charging infrastructure is essential for optimizing the performance and longevity of battery electric vehicles.
Mastering Vehicle Electrical Repairs: A Guide to Replacing Connectors
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
A battery electric vehicle is powered by an electric motor and a high-capacity battery pack. The key components include the battery pack, electric motor, power electronics, inverter, and the vehicle's control unit. The battery pack stores electrical energy and provides power to the motor, while the power electronics and inverter convert the direct current (DC) from the battery to alternating current (AC) for the motor. The control unit manages the entire system, optimizing performance and efficiency.
The battery pack is a collection of multiple individual batteries, typically lithium-ion cells, arranged in series and parallel configurations. These cells store electrical energy and can be charged through the vehicle's charging port or regenerative braking. When the driver accelerates, the control unit sends a signal to the inverter, which then converts the DC from the battery to AC to power the electric motor. The pack's capacity determines the vehicle's range, with larger packs offering more energy storage.
The electric motor is the primary component that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy, driving the vehicle's wheels. It is typically a high-torque, low-speed motor designed to provide instant torque for quick acceleration. The motor receives power from the inverter, which adjusts the voltage and frequency to match the motor's requirements. This system allows for efficient power delivery and smooth driving experience, making BEVs known for their responsive and quiet operation.