The rise of electric vehicles (EVs) has sparked a new debate in the automotive world, with a growing number of people expressing concerns and even hostility towards these eco-friendly alternatives. Despite their numerous benefits, including reduced environmental impact and lower running costs, EVs have faced criticism and even physical attacks. This paragraph aims to explore the reasons behind this phenomenon, examining the various factors that contribute to the negative perception of electric vehicles, such as range anxiety, charging infrastructure challenges, and the fear of technological change.
What You'll Learn
- Environmental Backlash: Some oppose EVs due to perceived environmental harm from battery production and resource extraction
- Economic Concerns: High upfront costs and potential job losses in the automotive industry are common criticisms
- Infrastructure Challenges: Limited charging stations and long charging times are seen as barriers to widespread EV adoption
- Range Anxiety: Range limitations and the fear of running out of power during long trips are significant concerns
- Brand Image: Traditional car brands may resist EV integration, fearing a shift in brand identity and customer loyalty

Environmental Backlash: Some oppose EVs due to perceived environmental harm from battery production and resource extraction
The rise of electric vehicles (EVs) has sparked a heated debate, with one of the most prominent criticisms stemming from environmental concerns. Some individuals and groups argue that despite the overall environmental benefits of EVs, the production and resource extraction processes associated with their manufacturing can have detrimental effects on the planet. This backlash highlights the complex nature of sustainable transportation and the need for a comprehensive understanding of the entire lifecycle of these vehicles.
Battery production, a critical component of EVs, has been identified as a significant source of environmental impact. The manufacturing of lithium-ion batteries, in particular, requires substantial amounts of raw materials such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel. The extraction of these resources often involves energy-intensive processes and can lead to habitat destruction, soil erosion, and water pollution in the regions where they are sourced. For instance, the mining of cobalt, a key ingredient in battery cathodes, has been linked to environmental degradation and human rights issues in the Democratic Republic of Congo, a major cobalt producer.
Critics argue that the environmental costs of battery production are not fully offset by the reduced carbon emissions from driving EVs. They claim that the energy-intensive manufacturing process, coupled with the transportation of raw materials and the assembly of batteries, contributes to a significant carbon footprint. Additionally, the disposal and recycling of batteries at the end of their life cycle present further challenges, as the process requires specialized facilities and can release toxic substances if not managed properly.
The environmental backlash against EVs also extends to the issue of resource extraction for other vehicle components. The production of EVs requires a vast array of materials, including rare earth elements, which are extracted through mining and processing. These extraction processes can have severe ecological consequences, including soil and water contamination, habitat destruction, and the disruption of local ecosystems. Furthermore, the transportation of these raw materials over long distances can contribute to additional carbon emissions, further exacerbating the environmental impact.
Addressing these concerns requires a multi-faceted approach. Firstly, improving the efficiency of battery production and recycling processes can significantly reduce the environmental impact. Implementing stricter regulations and international cooperation can ensure responsible resource extraction and minimize the ecological footprint. Additionally, investing in renewable energy sources for manufacturing and transportation can help lower the carbon emissions associated with EV production. By addressing these challenges, the environmental benefits of EVs can be maximized, and the concerns of those who oppose them due to perceived environmental harm can be alleviated.
Unveiling the World of Light Electric Vehicles: A Comprehensive Guide
You may want to see also

Economic Concerns: High upfront costs and potential job losses in the automotive industry are common criticisms
The widespread adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) has sparked a range of debates and criticisms, with economic concerns being a prominent point of contention. One of the primary criticisms is the high upfront cost of EVs compared to traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles. While the long-term savings of EVs are well-documented, the initial financial outlay can be a significant barrier for many consumers. The purchase price of EVs, often several thousands of dollars more than their ICE counterparts, is a major deterrent, especially for price-sensitive buyers. This is further exacerbated by the limited availability of government incentives and subsidies to offset these costs, which are often insufficient to make EVs more affordable for the average consumer.
Another economic concern is the potential impact of EVs on the automotive industry and its workforce. The shift towards electrification is expected to disrupt the traditional automotive supply chain and manufacturing processes. As a result, there are fears of job losses, particularly in the manufacturing sector, where many jobs are directly linked to the production of ICE vehicles. The transition to EVs may lead to a reduction in the number of jobs in certain areas, such as engine assembly and fuel system production, which could have a significant economic impact on regions heavily reliant on the automotive industry. However, it is important to note that this transition also creates new job opportunities in EV manufacturing, battery production, and related technologies, which could help mitigate some of these concerns.
Critics argue that the rapid adoption of EVs could lead to a sudden and significant change in the automotive market, potentially causing economic instability. The fear is that the industry might struggle to adapt quickly enough, leading to a surplus of inventory and potential financial losses for manufacturers. Additionally, the shift in consumer demand towards EVs could result in a decline in the used car market, which is a vital segment for many automotive businesses. This could further contribute to economic concerns, especially for those who rely on the resale and maintenance of traditional vehicles.
Despite these criticisms, it is essential to consider the long-term economic benefits that the EV market can bring. The transition to a more sustainable transportation system could stimulate economic growth in new sectors, such as renewable energy and battery technology. Moreover, the reduction in fuel costs and environmental impact associated with EVs can lead to significant savings for consumers and businesses, which could have a positive economic ripple effect. Balancing these economic considerations is crucial in shaping a sustainable future for the automotive industry and the environment.
Unveiling Arizona's EV Registration Fee: A Comprehensive Guide
You may want to see also

Infrastructure Challenges: Limited charging stations and long charging times are seen as barriers to widespread EV adoption
The widespread adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) is facing significant challenges, and one of the primary obstacles is the inadequate charging infrastructure. Limited charging stations and the time required to charge EVs are major concerns that have been widely discussed and criticized. This issue is a critical barrier to the widespread acceptance and integration of electric vehicles into our daily lives.
The current charging infrastructure is not keeping pace with the rapid growth of the EV market. As more people switch to electric cars, the demand for charging stations increases exponentially. However, the availability of charging points remains a significant problem, especially in urban areas where parking spaces are limited. Many cities and towns have a shortage of charging stations, making it inconvenient for EV owners to find a suitable place to charge their vehicles. This lack of accessibility can lead to range anxiety, a common fear among potential EV buyers, who worry about running out of battery power without access to charging facilities.
Moreover, the time required to charge an EV is another critical factor. Traditional charging methods, such as using a standard household outlet, can take several hours to fully charge a battery. While faster charging options are available, they are not widely accessible and often require specialized equipment. Public charging stations, which are supposed to provide a quick top-up, can still take a considerable amount of time, especially during peak hours when multiple vehicles are connected. Long charging times discourage potential buyers and contribute to the perception that EVs are impractical for daily use, especially for those with busy schedules or limited time for charging.
To address these infrastructure challenges, significant investments are needed in the development and expansion of charging networks. Governments and private companies must collaborate to install more charging stations in residential areas, workplaces, and public spaces. Implementing faster charging technologies and ensuring their widespread availability will be crucial in reducing charging times. Additionally, incentives and subsidies can encourage the installation of charging points in residential areas, making it more convenient for EV owners to charge their vehicles at home.
In conclusion, the limited charging infrastructure and long charging times are significant barriers to the widespread adoption of electric vehicles. These challenges require immediate attention and action from various stakeholders to create a more supportive environment for EV owners. By improving the charging infrastructure, we can address range anxiety, make EVs more practical, and accelerate the transition to a sustainable transportation system.
Unlock EV Savings: Your Guide to Electric Vehicle Tax Credits
You may want to see also

Range Anxiety: Range limitations and the fear of running out of power during long trips are significant concerns
The concept of range anxiety is a critical factor in the widespread adoption of electric vehicles (EVs). It refers to the fear and worry that EV drivers experience when contemplating the potential limitations of their vehicle's range, especially during long-distance travel. This anxiety is primarily driven by the concern that the battery might not provide sufficient power to complete a journey, leaving the driver stranded on the road. The range of early EVs was indeed limited, often ranging from 100 to 300 miles on a single charge, which was far from adequate for many drivers' needs. This led to a sense of insecurity and hesitation among potential buyers, especially those who frequently embark on long-distance trips or require a vehicle for their daily commute.
Modern EVs have made significant strides in addressing this issue. Contemporary electric cars offer ranges that can easily surpass 300 miles on a single charge, with some high-end models reaching over 400 miles. This substantial improvement in range has significantly alleviated range anxiety for many drivers. However, for some, the fear persists, especially when considering the availability and accessibility of charging stations along their intended routes. The challenge lies in the fact that charging infrastructure is still developing, and not all areas have an extensive network of charging stations. This lack of infrastructure can lead to situations where drivers might not find a charging station when needed, exacerbating their anxiety.
To combat range anxiety, EV manufacturers are continually working on enhancing battery technology. This includes developing more efficient batteries with higher energy densities, allowing for increased range. Additionally, advancements in battery management systems enable more precise monitoring of battery health and performance, providing drivers with real-time data to make informed decisions about their journey. These technological improvements are crucial in building confidence among EV owners, especially those who were initially hesitant due to range concerns.
Another strategy to address range anxiety is the integration of smart charging and energy management systems. These systems optimize charging times and locations, ensuring that drivers can efficiently charge their vehicles when needed. By providing personalized charging recommendations based on driving patterns and preferences, these systems contribute to a more relaxed and confident driving experience. Furthermore, the development of wireless charging technology offers an innovative solution, eliminating the need for physical charging cables and providing a more convenient and efficient charging process.
In conclusion, while range anxiety was a significant barrier to the widespread adoption of electric vehicles, the industry has made remarkable progress in addressing this concern. Through technological advancements, improved charging infrastructure, and innovative energy management systems, the fear of running out of power during long trips is becoming less of a deterrent. As the EV market continues to evolve, these efforts will play a pivotal role in encouraging more drivers to make the switch to electric mobility, ultimately contributing to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly transportation ecosystem.
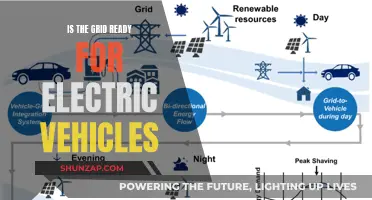
Grid-Integrated Electric Vehicles: Powering a Sustainable Future
You may want to see also

Brand Image: Traditional car brands may resist EV integration, fearing a shift in brand identity and customer loyalty
The transition to electric vehicles (EVs) presents a significant challenge for traditional car manufacturers, who have long dominated the automotive industry. These established brands often face a complex dilemma when it comes to embracing EV technology: the potential threat to their brand image and customer loyalty. The fear of a shift in brand identity is a critical aspect of this resistance, as it directly impacts the core of a company's reputation and the trust it has built over the years.
Traditional car brands have cultivated a strong association with certain values and qualities that have defined the automotive industry for decades. These include a sense of power, performance, and, in some cases, a certain ruggedness and reliability. For instance, brands like Ford, General Motors, and Toyota have built their reputations on delivering robust, high-performance vehicles that are often seen as status symbols. The idea of these iconic brands becoming synonymous with electric cars, which are often perceived as less powerful and more environmentally conscious, can be unsettling. Customers who have long associated these brands with a certain lifestyle and image may resist the change, fearing that the essence of their favorite car company is being diluted.
The concern is not just about the physical attributes of the vehicles but also the emotional connection that customers have with these brands. For many, a car is more than just a mode of transportation; it is an extension of one's personality and lifestyle. The fear of losing this emotional attachment is a powerful motivator for resistance. Traditional car manufacturers understand that their customers have strong brand loyalty, and any perceived shift in the brand's identity could lead to a loss of trust and, consequently, a decline in sales.
Moreover, the integration of EVs into their product line may also lead to a reevaluation of the brand's positioning in the market. Traditional car brands often have a specific niche and target audience, and introducing a new, potentially different type of vehicle could disrupt this carefully crafted market image. For example, a luxury car brand known for its high-performance, gas-powered SUVs might struggle to transition to EVs without causing a rift between its traditional customers and the new, potentially more environmentally-focused audience.
To address this challenge, traditional car brands must carefully consider their approach to EV integration. A strategic and gradual transition, coupled with effective communication, can help mitigate the fears of a brand identity shift. By highlighting the continued presence of their iconic, high-performance models alongside the new EV offerings, these brands can reassure customers that their values and experiences remain intact. Additionally, emphasizing the technological advancements and performance capabilities of EVs can help bridge the gap between traditional and electric vehicles, ensuring that the brand's image remains relevant and desirable in an evolving market.
Understanding Electric Auxillary Controls: Powering Vehicle Convenience
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Attacks on electric vehicles (EVs) can be driven by various factors, often rooted in misinformation, fear, or a lack of understanding. One common reason is the perception of noise pollution, where some individuals believe that EVs are too quiet and pose a risk to pedestrians, especially children. This has led to calls for mandatory noise-making devices in EVs. Another factor is the fear of technological change, where some people are resistant to the idea of a rapidly evolving automotive industry, and may view EVs as a threat to traditional car ownership and the jobs associated with the internal combustion engine sector.
The environmental benefits of EVs are well-known, but this can sometimes be a double-edged sword. Some individuals may feel that promoting EVs is a form of 'greenwashing,' especially if they believe that the production and disposal of batteries and other components have significant environmental impacts. Additionally, the idea that EVs are a solution to climate change might be met with skepticism by those who argue that the focus should be on more immediate and tangible solutions, such as improving public transport or promoting cycling.
Social and cultural factors can play a significant role in shaping public opinion about EVs. In some cases, attacks on EVs may be a manifestation of broader societal tensions. For instance, the increasing popularity of EVs might be seen as a symbol of a changing social order, where traditional car ownership is becoming less prevalent. This could evoke feelings of resentment or a sense of being left behind, especially among certain demographic groups who feel their values or way of life are being threatened by the rise of EVs.
Media coverage and public discourse can greatly impact the way people perceive and react to EV-related issues. Sensationalized headlines or biased reporting can often exaggerate the frequency or severity of attacks, leading to an exaggerated sense of danger. Moreover, the way media portrays the 'othering' of EV owners, such as presenting them as wealthy elites or eco-warriors, can influence public sentiment. This can create a narrative that EV owners are a distinct and potentially hostile group, which may contribute to the perception of attacks.