Electric vehicles (EVs) are gaining popularity as a sustainable transportation alternative, but their environmental impact is a complex issue. While EVs produce zero tailpipe emissions, their production, use, and disposal can have various ecological consequences. Manufacturing EVs requires significant energy and resources, potentially leading to increased greenhouse gas emissions and environmental degradation. However, the overall environmental benefits of EVs are significant, as they help reduce air pollution and carbon footprints compared to traditional internal combustion engine vehicles. This paragraph introduces the topic by highlighting the dual nature of EVs' environmental impact and the need to consider their entire lifecycle for a comprehensive understanding.
What You'll Learn
- Reduced Air Pollution: EVs emit fewer pollutants, improving air quality and public health
- Lower Carbon Footprint: Electric cars produce fewer greenhouse gases, mitigating climate change
- Energy Efficiency: EVs convert more energy into motion, reducing overall energy consumption
- Noise Reduction: Electric motors are quieter, lowering noise pollution in urban areas
- Recycling and Battery Life: Proper disposal and recycling of batteries are essential for environmental sustainability

Reduced Air Pollution: EVs emit fewer pollutants, improving air quality and public health
The widespread adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) has been a significant step towards mitigating air pollution and its detrimental effects on human health and the environment. One of the most notable advantages of EVs is their minimal emission of pollutants compared to traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles.
Internal combustion engines, particularly those in older vehicles, release a myriad of harmful pollutants into the atmosphere. These include nitrogen oxides (NOx), volatile organic compounds (VOCs), carbon monoxide (CO), and particulate matter (PM). These pollutants contribute to the formation of smog, acid rain, and have severe impacts on respiratory and cardiovascular health. In contrast, electric vehicles produce zero tailpipe emissions, meaning they do not release these harmful pollutants during operation.
The reduction in air pollution from EVs is particularly beneficial in urban areas, where traffic congestion and high vehicle density can lead to elevated pollution levels. By replacing conventional vehicles with EVs, cities can significantly improve air quality, especially in densely populated neighborhoods. This improvement is crucial as it directly correlates with better public health outcomes, reducing the risk of respiratory diseases, heart problems, and other health issues associated with air pollution.
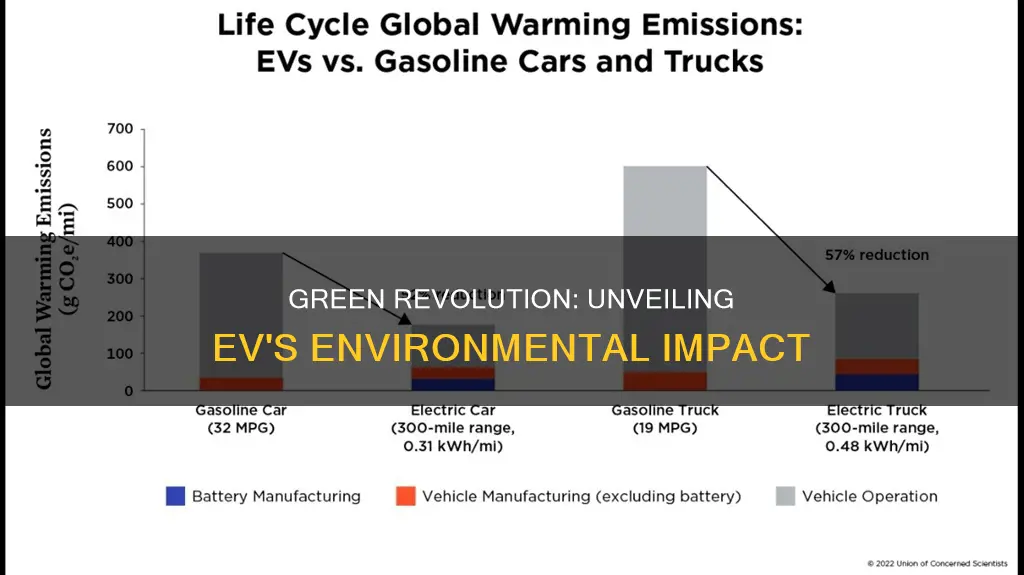
Furthermore, the environmental benefits of EVs extend beyond the immediate reduction in local air pollution. The production and use of EVs also contribute to a decrease in greenhouse gas emissions, which are a major driver of climate change. While the manufacturing process of EVs may have a higher carbon footprint compared to ICE vehicles, the overall lifecycle emissions are significantly lower, especially when charged with electricity from renewable energy sources.
In summary, electric vehicles play a pivotal role in reducing air pollution and improving public health. Their zero-emission nature at the point of use directly contributes to cleaner air, particularly in urban areas. Additionally, the long-term environmental benefits of EVs, including reduced greenhouse gas emissions, further emphasize their importance in the global effort to combat climate change and create a more sustainable future.
Unveiling Tesla's Electric Vehicle: A Patent Mystery
You may want to see also

Lower Carbon Footprint: Electric cars produce fewer greenhouse gases, mitigating climate change
The environmental benefits of electric vehicles (EVs) are significant, particularly in the context of reducing greenhouse gas emissions and combating climate change. One of the most notable advantages is their lower carbon footprint compared to conventional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles.
Electric cars are powered by electric motors that run on electricity, which is typically generated from renewable sources such as solar, wind, or hydropower. When an EV is charged and driven, it produces zero tailpipe emissions, meaning it emits no harmful pollutants or greenhouse gases during operation. This is in stark contrast to ICE vehicles, which release substantial amounts of carbon dioxide (CO2), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and particulate matter as a result of burning fossil fuels. Greenhouse gases, including CO2, are the primary drivers of global warming and climate change. By eliminating these emissions, electric vehicles play a crucial role in reducing the carbon footprint of the transportation sector.
The process of charging an EV also contributes to its environmental advantage. As long as the electricity used for charging comes from renewable sources, the overall carbon emissions associated with the vehicle's lifecycle are significantly lower. Many countries and regions are increasingly adopting renewable energy, which further enhances the environmental benefits of electric cars. For instance, in regions with a high penetration of wind or solar power, the carbon savings from driving an electric vehicle can be substantial.
The impact of widespread EV adoption could be substantial. As more electric cars hit the roads, the collective reduction in greenhouse gas emissions will help slow down the rate of climate change. This shift in transportation can contribute to meeting international climate goals and commitments, such as those set by the Paris Agreement, which aims to limit global temperature rise.
In summary, electric vehicles offer a promising solution to reduce the carbon footprint of the transportation sector. Their zero-emission nature during operation and the potential for clean energy sources in their charging process make them a powerful tool in the fight against climate change. Encouraging the adoption of electric cars, along with the development of sustainable energy infrastructure, can lead to a more environmentally friendly and sustainable future.
The Electric Revolution: Are We Prepared for the EV Takeover?
You may want to see also

Energy Efficiency: EVs convert more energy into motion, reducing overall energy consumption
Electric vehicles (EVs) have gained significant attention as a potential solution to reduce environmental impact and improve energy efficiency in the transportation sector. One of the key advantages of EVs is their ability to convert a higher percentage of energy into motion compared to traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles. This enhanced energy efficiency is a critical factor in reducing overall energy consumption and minimizing the environmental footprint of the transportation industry.
The traditional ICE vehicles waste a substantial amount of energy as heat, which is a result of the combustion process. This inefficiency means that only a fraction of the energy from the fuel is actually used to propel the vehicle forward. In contrast, electric motors in EVs are highly efficient, converting a larger proportion of electrical energy into mechanical power. This efficiency is further improved by the use of advanced battery technology, which stores and delivers energy more effectively. As a result, EVs can achieve higher energy conversion rates, ensuring that more of the energy supplied is utilized for actual movement.
The benefits of this increased energy efficiency are twofold. Firstly, it directly contributes to reducing the overall energy demand for transportation. With EVs, more energy is utilized for their intended purpose, reducing the need for excessive fuel consumption. This is particularly important in a world where energy resources are finite, and the transportation sector is a significant consumer of fossil fuels. Secondly, the improved efficiency helps lower the environmental impact associated with energy production and distribution. By utilizing energy more effectively, EVs can reduce the demand for energy generation, which often relies on carbon-intensive processes, thereby decreasing greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution.
The design and engineering of EVs also play a crucial role in maximizing energy efficiency. Modern EVs are built with lightweight materials, aerodynamic designs, and optimized drivetrains, all of which contribute to improved performance and reduced energy wastage. These factors, combined with the high efficiency of electric motors, ensure that EVs can travel further on a single charge or tank of fuel, making them a more practical and environmentally friendly choice for consumers.
In summary, electric vehicles offer a more energy-efficient alternative to traditional cars, converting a higher percentage of energy into motion. This efficiency is a result of advanced technology, including powerful electric motors and sophisticated battery systems. By reducing the overall energy consumption in transportation, EVs contribute to a more sustainable future, lowering the demand for energy generation and, consequently, the environmental impact associated with the production and use of energy. This aspect of EVs is a significant step towards mitigating the environmental challenges posed by the transportation industry.
Chevy Spark: Electric Vehicle or Gas-Powered Mystery?
You may want to see also

Noise Reduction: Electric motors are quieter, lowering noise pollution in urban areas
The environmental benefits of electric vehicles (EVs) extend beyond reduced greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution. One often overlooked advantage is the significant reduction in noise pollution, particularly in urban areas. Electric motors, a key component of EVs, operate at much lower noise levels compared to traditional internal combustion engines. This quiet operation contributes to a more peaceful and less stressful urban environment.
Noise pollution has been a growing concern in cities, with excessive noise from traffic and other sources impacting the quality of life for residents. Electric vehicles play a crucial role in mitigating this issue. The quiet nature of electric motors is primarily due to their design and the absence of the loud, high-pitched sounds associated with gasoline or diesel engines. This reduction in noise is not just beneficial for drivers but also for pedestrians, cyclists, and other road users who may be exposed to less disruptive sounds.
The impact of noise reduction in urban areas is multi-faceted. Firstly, it contributes to improved public health. Lower noise levels can lead to better sleep quality, reduced stress, and improved overall well-being for city dwellers. This is especially important in densely populated areas where noise from traffic and industrial activities can be a constant source of disturbance. By reducing noise pollution, electric vehicles help create a more tranquil and healthy urban environment.
Secondly, the quiet operation of electric motors enhances road safety. With less noise, pedestrians and cyclists are more likely to hear approaching vehicles, potentially preventing accidents. This is particularly relevant in urban settings where visibility might be limited, and the absence of engine noise could otherwise go unnoticed. The reduction in noise pollution also extends to residential areas, where the peacefulness of neighborhoods can be preserved, ensuring a better quality of life for residents.
In summary, the environmental impact of electric vehicles goes beyond emissions and includes a significant contribution to noise reduction. Electric motors' quiet operation lowers noise pollution in urban areas, benefiting public health, road safety, and the overall quality of life for city residents. As cities continue to grapple with the challenges of noise pollution, the adoption of electric vehicles can play a pivotal role in creating more livable and environmentally friendly urban spaces.
Kia K4: Electric or Not? Unveiling the Truth
You may want to see also

Recycling and Battery Life: Proper disposal and recycling of batteries are essential for environmental sustainability
The environmental benefits of electric vehicles (EVs) are well-known, but a crucial aspect often overlooked is the proper management of their batteries at the end of their life cycle. As the demand for EVs rises, so does the need for responsible recycling practices to ensure a sustainable future.
EV batteries, primarily composed of lithium-ion cells, contain valuable materials such as cobalt, nickel, and lithium, as well as potentially hazardous substances like lead and cadmium. When these batteries reach the end of their useful life, improper disposal can lead to severe environmental consequences. If not recycled, the heavy metals and toxic chemicals within the batteries can leach into the soil and water, causing soil degradation and water pollution. This is especially critical as the global supply of lithium, for instance, is finite, and mining for it can have detrimental effects on ecosystems and communities.
Recycling EV batteries is a complex process that requires specialized facilities and techniques. It involves several stages, starting with the safe disassembly of the battery packs to separate the various components. The recycling process aims to recover valuable materials while minimizing the environmental impact. For instance, lithium can be recycled and reused in new batteries, reducing the need for additional mining. Additionally, recycling helps conserve natural resources, as it reduces the reliance on raw material extraction, which often involves energy-intensive and environmentally damaging processes.
Proper disposal and recycling of EV batteries are essential for several reasons. Firstly, it prevents the release of harmful substances into the environment, protecting ecosystems and human health. Secondly, it promotes resource efficiency by allowing the recovery of valuable materials. This, in turn, can reduce the environmental impact of mining and manufacturing new batteries. Furthermore, responsible recycling ensures that the growing number of retired EV batteries can be managed sustainably, contributing to the long-term viability of the EV industry.
In summary, the environmental sustainability of electric vehicles is not solely dependent on their operation but also on the responsible end-of-life management of their batteries. By implementing effective recycling practices, we can ensure that the benefits of EVs extend beyond reduced emissions, contributing to a cleaner and more sustainable future. It is a critical aspect that requires collaboration between manufacturers, recyclers, and policymakers to establish efficient and environmentally friendly battery recycling systems.
Hyundai Kona: Electric Vehicle or Not?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Electric vehicles produce zero tailpipe emissions, which means they do not release harmful pollutants like nitrogen oxides (NOx), volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and particulate matter (PM) into the air during operation. This is a significant improvement over traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles, which are major contributors to air pollution and smog formation.
When EVs are charged using electricity generated from renewable sources such as solar, wind, or hydropower, the environmental impact is minimal. Renewable energy sources produce little to no greenhouse gas emissions, reducing the carbon footprint associated with EV ownership. This makes EVs even more environmentally friendly when compared to conventional vehicles.
Yes, absolutely. EVs play a crucial role in mitigating climate change by reducing greenhouse gas emissions. The burning of fossil fuels in ICE vehicles is a major source of carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions, a primary driver of global warming. By transitioning to electric powertrains, we can significantly lower CO2 emissions and improve air quality.
Electric vehicles have a positive impact on water resources. Unlike ICE vehicles, EVs do not require cooling systems that use a significant amount of water. This reduces the strain on local water supplies and minimizes the risk of water pollution from engine coolant leaks. Additionally, the absence of exhaust systems in EVs means no harmful fluids or gases are released into water bodies.
While the production of EV batteries, particularly lithium-ion batteries, can have some environmental implications, these impacts are generally lower compared to the overall benefits of EVs. The manufacturing process may involve the extraction of raw materials, which can have ecological consequences if not managed sustainably. However, ongoing research and development aim to improve battery recycling, reduce material usage, and minimize the environmental footprint of battery production.