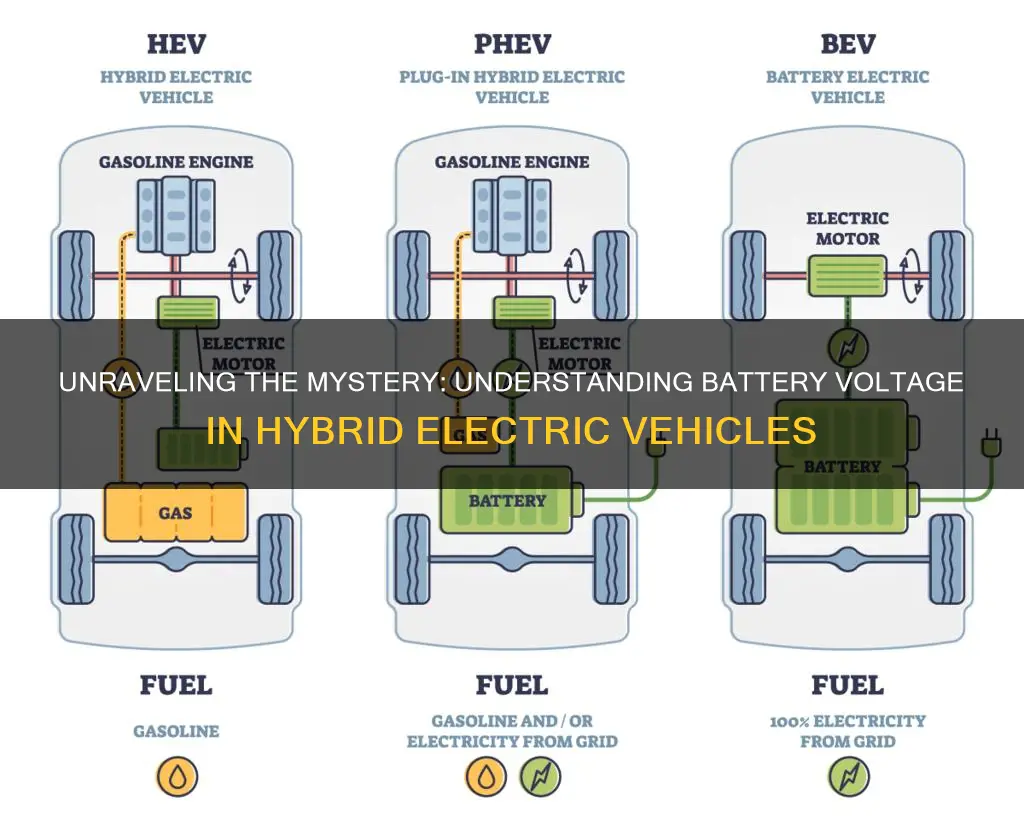
Hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) are a popular eco-friendly transportation option, and understanding their battery systems is crucial for optimizing performance and maintenance. The battery in an HEV is a critical component that powers the electric motor and assists the internal combustion engine. This battery system operates at a specific voltage, which is a key factor in determining the vehicle's efficiency and range. The voltage of the battery in an HEV can vary depending on the make and model, but it typically ranges from 200 to 300 volts, providing the necessary power to drive the vehicle efficiently while reducing emissions.
What You'll Learn
- Battery Voltage Range: Hybrid EVs typically operate within a 150-200V range
- Charging Systems: These vehicles use AC or DC charging to replenish battery power
- Voltage Regulation: Advanced systems maintain optimal voltage for efficient performance
- Voltage Drop: Driving conditions can cause voltage fluctuations, impacting vehicle efficiency
- Voltage Monitoring: Drivers can check battery voltage through dashboard displays

Battery Voltage Range: Hybrid EVs typically operate within a 150-200V range
Hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) have revolutionized the automotive industry by combining traditional internal combustion engines with electric motors, offering improved fuel efficiency and reduced emissions. At the heart of this technology is the battery pack, which plays a crucial role in powering the electric motor and assisting the internal combustion engine. The voltage of this battery pack is a critical factor in determining the vehicle's performance and efficiency.
In the context of HEVs, the battery voltage range is typically between 150 and 200 volts. This voltage range is carefully chosen to balance power and efficiency, ensuring the vehicle can deliver the required performance while optimizing energy usage. The higher voltage allows for more powerful electric motors, enabling the vehicle to accelerate quickly and provide a responsive driving experience. However, it also demands a more robust and efficient power electronics system to manage the high voltage and current.
The 150-200V range is a standard for many HEVs, providing a good compromise between performance and energy efficiency. This voltage allows for efficient energy recovery during braking, a process known as regenerative braking, where the electric motor acts as a generator, converting kinetic energy back into electrical energy to recharge the battery. This feature not only improves overall efficiency but also extends the vehicle's electric-only driving range, making it more practical for daily use.
Furthermore, the battery voltage in HEVs is designed to work in conjunction with the internal combustion engine. When the electric motor is not sufficient to power the vehicle, the engine can kick in, providing additional power. The voltage range ensures that the battery can supply the necessary energy to the motor while also allowing for seamless integration with the combustion engine, optimizing the vehicle's overall performance and fuel economy.
Understanding the battery voltage range in HEVs is essential for both manufacturers and consumers. It highlights the importance of battery technology in the development of efficient and environmentally friendly vehicles. As technology advances, we can expect to see further improvements in battery voltage and capacity, leading to even more powerful and efficient hybrid electric vehicles.
Unveiling the Power of Neighborhood Electric Vehicles: A Sustainable Revolution
You may want to see also

Charging Systems: These vehicles use AC or DC charging to replenish battery power
Hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) have revolutionized the automotive industry by combining traditional combustion engines with electric motors, offering improved fuel efficiency and reduced emissions. At the heart of this technology is a sophisticated battery system that powers the electric motor and assists the internal combustion engine. Understanding the charging systems of these vehicles is crucial to optimizing their performance and longevity.
HEVs typically utilize a high-voltage battery pack, often ranging from 200 to 400 volts, depending on the specific model and manufacturer. This voltage level is significantly higher than that of conventional vehicles, which usually operate at 12 volts. The higher voltage in HEVs is essential to provide the necessary power to the electric motor and ensure efficient energy transfer. When it comes to charging these batteries, two primary methods are employed: AC (Alternating Current) and DC (Direct Current) charging.
AC charging is commonly used for HEVs, especially in home or public charging stations. This method involves converting the alternating current from the power grid to direct current, which is then used to recharge the battery pack. AC charging is generally slower compared to DC charging but is widely available and convenient for everyday use. During the charging process, the AC current is adjusted to match the battery's requirements, ensuring a safe and efficient recharge.
DC charging, on the other hand, is a faster method and is often used for rapid charging stations. It directly supplies direct current to the battery, bypassing the need for an intermediate conversion. This process is more efficient for replenishing the battery's power quickly. Many HEVs are equipped with DC fast-charging capabilities, allowing for shorter charging times, especially during long-distance travel. The charging system in these vehicles is designed to manage the high-voltage battery pack and ensure optimal charging conditions, maintaining the battery's health and performance over time.
In summary, HEVs rely on advanced charging systems to maintain their battery power, utilizing both AC and DC methods. The choice of charging technology depends on the specific application and infrastructure available. Understanding these charging systems is vital for vehicle owners and maintenance professionals to ensure the longevity and efficiency of hybrid electric vehicles. Proper charging practices contribute to the overall sustainability and performance of these innovative vehicles.
Unveiling the Secrets: A Comprehensive Guide to Testing Electric Vehicles
You may want to see also

Voltage Regulation: Advanced systems maintain optimal voltage for efficient performance
Voltage regulation is a critical aspect of hybrid electric vehicle (HEV) battery management, ensuring optimal performance and longevity. In HEVs, the battery system operates at specific voltage levels to provide efficient power to the electric motor and other vehicle components. Advanced voltage regulation systems are designed to maintain this optimal voltage, which is typically around 300-400 volts, depending on the vehicle's configuration. This precise voltage control is essential for several reasons.
Firstly, it enables efficient energy transfer and utilization. HEVs rely on the battery to supply power to the electric motor during acceleration and assist during regenerative braking. By maintaining a stable voltage, the system ensures that the energy is delivered effectively, maximizing the vehicle's overall efficiency. This is particularly important in hybrid systems, where the battery's state of charge needs to be carefully managed to balance power delivery and energy recovery.
Secondly, voltage regulation contributes to the longevity and health of the battery pack. Over time, batteries can experience voltage drops due to internal resistance and other factors. Advanced voltage regulation systems actively monitor and adjust the voltage to prevent excessive drops, which can lead to reduced battery capacity and performance. By keeping the voltage within an optimal range, these systems help maintain the battery's health and extend its lifespan, ensuring reliable performance over the vehicle's lifetime.
These systems employ various techniques to achieve precise voltage control. One common approach is the use of voltage regulators, which are electronic components that adjust the output voltage to match the desired level. These regulators can dynamically respond to changes in load and system conditions, ensuring that the voltage remains stable even during rapid acceleration or regenerative braking. Additionally, some HEVs utilize advanced battery management software that continuously monitors voltage levels and makes real-time adjustments to optimize performance.
In summary, voltage regulation in HEVs is a sophisticated process that ensures efficient energy utilization and battery health. Advanced systems maintain optimal voltage levels, typically around 300-400 volts, to provide the necessary power to the electric motor and other vehicle components. By actively managing voltage, these systems contribute to improved performance, extended battery lifespan, and overall reliability in hybrid electric vehicles.
Unlocking Savings: California's EV Tax Credit Explained
You may want to see also

Voltage Drop: Driving conditions can cause voltage fluctuations, impacting vehicle efficiency
The voltage in a hybrid electric vehicle (HEV) battery system is a critical aspect of its performance and efficiency. When driving, various factors can influence the voltage drop, leading to potential issues and reduced efficiency. Understanding these voltage fluctuations is essential for optimizing the vehicle's performance and ensuring a reliable driving experience.
One of the primary causes of voltage drop in HEVs is the driving conditions themselves. As the vehicle accelerates, decelerates, or navigates through different terrains, the electrical load on the battery changes. During acceleration, the battery provides power to the electric motor, demanding more energy and potentially causing a voltage drop. Conversely, during deceleration or braking, the regenerative braking system recharges the battery, reducing the load and allowing the voltage to recover. However, this dynamic nature of driving can lead to voltage fluctuations, especially when rapid changes in speed and load occur.
Voltage drop can have a significant impact on the overall efficiency of the HEV. When the voltage drops, the battery's ability to supply power to the electric motor and other electrical components is compromised. This may result in reduced acceleration, decreased performance, and even limited driving range. Modern HEVs are designed with sophisticated voltage regulation systems to mitigate these issues, but understanding the driving conditions that cause voltage fluctuations is crucial for maintaining optimal performance.
Several factors contribute to voltage drop during driving. Firstly, the resistance of the electrical system plays a role. As current flows through the wiring and components, it encounters resistance, leading to a voltage drop. This is more pronounced at higher currents and lower voltages. Secondly, the efficiency of the battery itself is a critical factor. Older batteries or those with degraded performance may not hold a charge as effectively, leading to voltage drops during driving. Additionally, external factors like temperature can affect battery voltage; extreme temperatures can impact the chemical reactions within the battery, altering its voltage output.
To address voltage drop and ensure optimal performance, HEV manufacturers employ various strategies. These include advanced battery management systems that monitor voltage levels and adjust charging/discharging rates accordingly. Some vehicles also utilize voltage regulators to maintain a stable voltage output. Regular maintenance and monitoring of the battery's health can help identify potential issues related to voltage drop. Additionally, drivers can contribute to efficient voltage management by adopting smooth driving habits, avoiding rapid acceleration, and utilizing regenerative braking when possible.
Green Incentives: Why Go Electric?
You may want to see also

Voltage Monitoring: Drivers can check battery voltage through dashboard displays
In hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs), monitoring the battery voltage is an essential aspect of vehicle management and can be easily done by drivers through the dashboard displays. This feature provides real-time information about the battery's state of charge, which is crucial for efficient driving and maintaining the vehicle's performance.
The dashboard display in an HEV is typically equipped with a dedicated section or gauge specifically for battery voltage monitoring. This display is often located within the driver's line of sight, ensuring quick access to vital information. When the vehicle is running, the driver can glance at the dashboard to see the current voltage level of the battery. This voltage reading gives an immediate indication of the battery's health and power availability.
Modern HEVs often employ a color-coded system to represent different voltage ranges. For instance, a green indicator might signify a healthy voltage level, while a yellow or red warning could alert the driver to potential issues. This visual representation makes it easier for drivers to interpret the battery's status at a glance. Some vehicles may also provide numerical values alongside the color-coded indicators for more precise voltage monitoring.
In addition to the visual cues, some HEVs offer audio alerts or haptic feedback to notify drivers of significant changes in battery voltage. These additional layers of feedback ensure that drivers are promptly informed about any deviations from the normal operating range. By providing both visual and auditory cues, the vehicle's safety and efficiency are enhanced, allowing drivers to take appropriate actions.
Regularly checking the battery voltage through dashboard displays is a recommended practice for HEV owners. It enables drivers to identify potential issues early on, such as voltage drops that may indicate battery degradation or charging problems. This proactive approach to monitoring can help prevent unexpected breakdowns and ensure the longevity of the hybrid system. Additionally, understanding the battery's voltage can assist drivers in optimizing their driving habits to maximize energy efficiency.
The Future of EV Tax Credits: What You Need to Know
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The voltage of the battery in an HEV can vary depending on the specific model and manufacturer. Typically, HEVs use nickel-metal hydride (NiMH) batteries, which commonly operate at a nominal voltage of 200-300 volts.
Battery voltage plays a crucial role in the vehicle's performance and efficiency. Higher voltage batteries can provide more power and improve acceleration, while lower voltage batteries may result in reduced power output and slower performance.
Yes, you can monitor the battery voltage in your HEV. Some vehicles provide voltage readings on the dashboard or through the onboard computer system. You can also consult the vehicle's manual for specific instructions on how to access this information.
A significant drop in battery voltage can impact the vehicle's performance and range. In some cases, the vehicle may enter a 'low voltage' mode, reducing power to non-essential systems to maintain essential operations. It is recommended to maintain regular battery maintenance to prevent voltage drops.
Yes, there are several ways to optimize battery voltage. Proper maintenance, such as regular battery charging and keeping the battery at an optimal temperature, can help maintain voltage levels. Additionally, adopting energy-efficient driving habits and utilizing regenerative braking can contribute to better battery voltage management.