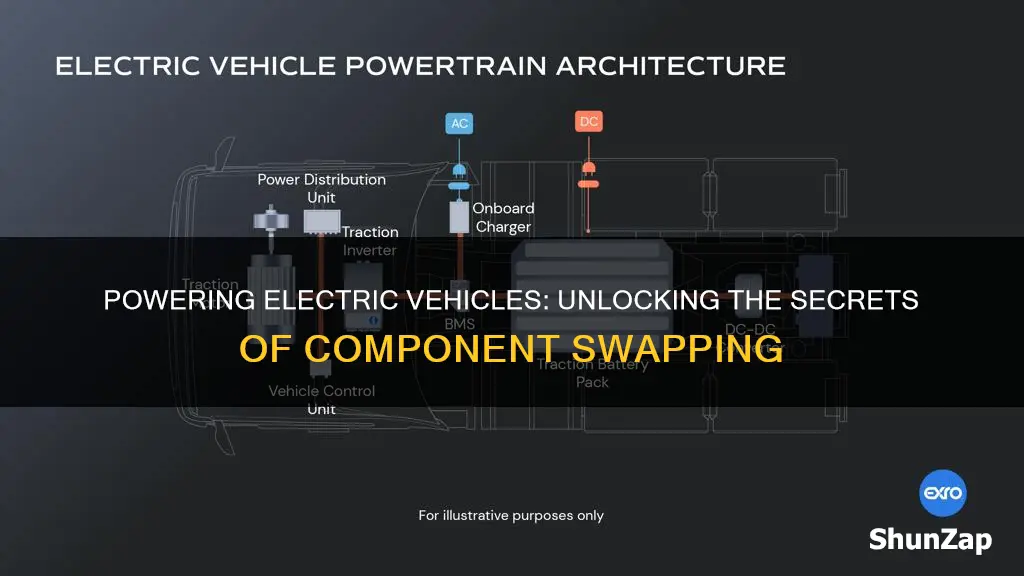
Electric vehicles (EVs) have revolutionized the automotive industry, offering a sustainable and efficient alternative to traditional internal combustion engine cars. One of the key components that set EVs apart is their electrical and electronic systems, which play a crucial role in their performance and functionality. In this paragraph, we will explore the various components that are switched or integrated in electric vehicles, including the electric motor, battery pack, power electronics, and advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS). These components work in harmony to provide a seamless driving experience, efficient energy management, and enhanced safety features, making electric vehicles a popular choice for environmentally conscious consumers.
What You'll Learn
- Battery Pack: High-capacity lithium-ion cells power the vehicle
- Motor: Electric motors convert energy into rotational motion
- Inverter: Converts direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC)
- Power Electronics: Controls and regulates power flow in the system
- Charging System: Manages the charging process and protects the battery

Battery Pack: High-capacity lithium-ion cells power the vehicle
The battery pack is a critical component of electric vehicles (EVs), serving as the primary power source that enables the vehicle to run. It is designed to store and supply the electrical energy required to operate the vehicle's electric motor and associated systems. At the heart of this battery pack are high-capacity lithium-ion cells, which have revolutionized the EV industry due to their exceptional energy density and performance.
Lithium-ion batteries are a popular choice for EVs because they offer several advantages over other battery technologies. Firstly, they provide a high energy-to-weight ratio, allowing for a compact and lightweight design, which is crucial for optimizing vehicle performance and range. These batteries also have a low self-discharge rate, meaning they can retain their charge for extended periods when not in use. This feature ensures that the vehicle is always ready for the next journey.
Each lithium-ion cell consists of an anode, a cathode, and an electrolyte. The anode is typically made of graphite, while the cathode can be composed of various materials such as lithium cobalt oxide (LiCoO2), lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4), or nickel manganese cobalt (NMC). The electrolyte, usually a lithium salt solution, facilitates the movement of lithium ions between the anode and cathode during charging and discharging. This electrochemical process enables the storage and release of electrical energy.
In an EV battery pack, multiple lithium-ion cells are connected in series and parallel configurations to achieve the desired voltage, current, and energy capacity. The cells are carefully arranged to ensure optimal performance and safety. Each cell is individually monitored to maintain balance and prevent overcharging or overheating, which could lead to performance degradation or safety hazards.
The high-capacity nature of lithium-ion batteries allows EVs to travel longer distances on a single charge compared to traditional internal combustion engine vehicles. This capability has been a significant factor in the growing popularity of electric vehicles, as it addresses a major concern among potential buyers—range anxiety. With advancements in battery technology, EVs are becoming more practical and appealing to a wider audience.
Grid-Integrated Electric Vehicles: Powering a Sustainable Future
You may want to see also

Motor: Electric motors convert energy into rotational motion
Electric motors are the heart of electric vehicles (EVs), and their primary function is to convert electrical energy into rotational motion, which is then used to power the vehicle's wheels. These motors are highly efficient and powerful, allowing EVs to accelerate quickly and provide a smooth driving experience. The design and functionality of electric motors have evolved significantly over the years, with advancements in technology leading to improved performance and reliability.
The construction of an electric motor involves several key components. Firstly, the stator, which is the stationary part of the motor, consists of coils of wire wound around a metal core. These coils are connected to the vehicle's battery, receiving electrical energy. When an electric current flows through these coils, it generates a magnetic field, creating a crucial interaction with the rotor.
The rotor, or the rotating part of the motor, is positioned within the stator. It is typically made of a permanent magnet or an electromagnet, which can be energized by the vehicle's electronics. When the magnetic field from the stator interacts with the rotor's magnetic field, it causes the rotor to rotate. This rotational motion is then transferred to the vehicle's drive system, ultimately propelling the car forward.
One of the advantages of electric motors is their ability to provide high torque from a standstill, resulting in excellent low-end performance. This is achieved through the use of powerful electromagnets or permanent magnets in the rotor, which can be precisely controlled by the vehicle's electronics. The motor's speed and torque can be adjusted in real-time, ensuring optimal performance and efficiency.
In electric vehicles, the motor's efficiency is further enhanced by the absence of traditional internal combustion engines. This allows for a more direct and efficient transfer of energy, as there are fewer moving parts and less energy loss. The motor's design also enables regenerative braking, where some of the energy generated during braking is captured and stored in the battery, improving overall efficiency.
Hybrid Electric Vehicles: Unveiling the Hidden Drawbacks
You may want to see also

Inverter: Converts direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC)
The inverter is a crucial component in electric vehicles (EVs) as it plays a vital role in the power conversion process. Its primary function is to convert the direct current (DC) electricity produced by the vehicle's battery into alternating current (AC) that can be used to power various electrical systems and accessories. This conversion is essential because most automotive electronics and motors operate on AC power.
In an EV, the inverter is typically a sophisticated electronic device that contains multiple power transistors and diodes. It is designed to handle high-voltage and high-current levels, ensuring efficient power distribution throughout the vehicle. When the driver engages the accelerator, the inverter receives a signal from the vehicle's control unit, which then activates the appropriate transistors to switch the DC power from the battery into AC. This AC power is then distributed to the vehicle's electrical system, including the motor, charging port, lights, and other accessories.
The switching process in the inverter is rapid and precise, allowing for quick adjustments to meet the varying power demands of the vehicle. This capability is crucial for maintaining optimal performance and efficiency, especially during acceleration and regenerative braking. During regenerative braking, the inverter also plays a role in converting the kinetic energy back into DC power, which can then be stored in the battery, thus improving overall energy efficiency.
Furthermore, the inverter's design and efficiency can significantly impact the vehicle's performance and range. Modern EVs often employ advanced inverter technology, such as pulse-width modulation (PWM) or voltage-source inverters, to optimize power conversion and minimize energy losses. These advancements contribute to improved acceleration, better overall efficiency, and extended driving range, making electric vehicles a viable and attractive alternative to traditional internal combustion engine cars.
In summary, the inverter is a critical switching component in electric vehicles, responsible for converting DC power from the battery into AC power for various electrical systems. Its efficient and rapid switching capabilities ensure optimal performance, energy efficiency, and a seamless driving experience, making it a key enabler in the widespread adoption of electric mobility.
Powering Hybrid Vehicles: Understanding the Battery Voltage
You may want to see also

Power Electronics: Controls and regulates power flow in the system
Power electronics play a crucial role in electric vehicles (EVs) by managing the complex power flow within the system. These components are responsible for controlling and regulating the electrical energy, ensuring efficient and safe operation. The primary function of power electronics in EVs is to switch and convert electrical power between different forms, enabling the vehicle to operate effectively.
One of the key components in this process is the power inverter. Inverters are responsible for converting direct current (DC) power from the battery into alternating current (AC) power required by the electric motor. This conversion is essential for the motor's operation, as it needs AC power to function optimally. The inverter's switching frequency and waveform control directly impact the motor's performance, including its speed, torque, and efficiency.
Additionally, power electronics are used for motor control, which involves adjusting the voltage and current supplied to the electric motor. This control is achieved through pulse-width modulation (PWM) techniques, where the inverter switches the power electronics components on and off rapidly. By modulating the switching pattern, the inverter can regulate the motor's speed and torque, allowing for precise control during acceleration, deceleration, and while maintaining a steady speed.
Another critical aspect is the management of power electronics in charging and discharging the battery. During charging, the inverter must handle the reverse power flow, converting AC power from the charging station to DC power for the battery. This process requires careful control to ensure the battery is charged efficiently and safely. When the vehicle is in regenerative braking mode, the power electronics also play a vital role in converting the kinetic energy back into electrical energy, recharging the battery.
The power electronics in EVs are designed to handle high-voltage and high-current levels, making them robust and reliable. These components are often made using insulated-gate bipolar transistors (IGBTs) or silicon carbide (SiC) MOSFETs, which offer fast switching speeds and excellent thermal management. The efficiency and performance of these power electronics are essential for the overall efficiency and driving range of electric vehicles, making them a critical technology in the automotive industry.
Powering Up: Understanding the Safety of Plugging In Your EV
You may want to see also

Charging System: Manages the charging process and protects the battery
The charging system of an electric vehicle (EV) is a critical component that ensures the efficient and safe replenishment of the vehicle's battery. This system is designed to manage the complex process of converting alternating current (AC) from an external power source into direct current (DC) suitable for the battery, while also providing protection against potential hazards.
At the heart of the charging system is the charger itself, which can be either an onboard charger integrated into the vehicle or an external charger connected to the vehicle's charging port. Onboard chargers are typically found in plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs) and some fully electric cars. These chargers are designed to handle the specific voltage and current requirements of the vehicle's battery pack. When an EV is connected to a charging station, the charger regulates the power flow, ensuring that the battery is charged at the appropriate rate to prevent damage. The charger's efficiency is crucial, as it directly impacts the time it takes to recharge the battery.
One of the key functions of the charging system is to protect the battery from overcharging. Overcharging can lead to reduced battery life and, in extreme cases, may cause the battery to overheat and potentially catch fire. To prevent this, the charging system employs various safety mechanisms. For instance, it may include a timer that limits the charging duration to a specific period, ensuring the battery doesn't remain connected for too long. Additionally, some chargers have a maximum voltage or current limit, preventing the battery from receiving more power than it can handle. These safety features are essential, especially when charging at home, where users might forget to disconnect the charger.
Another critical aspect of the charging system is its ability to manage the charging process dynamically. This involves adjusting the charging rate based on factors such as battery temperature, state of charge, and available power from the charging source. For example, during cold weather, the battery may require a slower charging rate to avoid excessive heat generation. Modern EVs often feature smart charging systems that communicate with the charging station to optimize the charging process, ensuring a safe and efficient recharge.
In summary, the charging system in an electric vehicle is a sophisticated arrangement that not only facilitates the battery's replenishment but also safeguards it from potential harm. It employs various mechanisms to manage the charging process, protect against overcharging, and adapt to different environmental conditions, ultimately ensuring the longevity and reliability of the EV's battery. Understanding these components and their functions is essential for EV owners and enthusiasts to maximize the vehicle's performance and safety.
Chevy Trax: Electric Vehicle or Not? Unveiling the Truth
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
In an electric vehicle, several critical components are switched or activated to ensure the proper functioning of the car. These include the battery pack, which stores and provides the electrical energy needed to power the vehicle. When the driver engages the accelerator, the battery switches on, supplying power to the electric motor. The electric motor then switches on, converting electrical energy into mechanical energy to propel the car forward. Additionally, the inverter is a crucial component that switches the direct current (DC) from the battery to alternating current (AC) for the motor, allowing for efficient power distribution.
The switching process in an EV's drivetrain is a sophisticated system. When the driver selects 'Drive' or 'Reverse', the transmission or gear selector switches internally to route power to the appropriate wheels. This action is often controlled by an electronic control unit (ECU) that manages the entire switching process. The ECU sends signals to the inverter, which then switches the power flow to the motor accordingly. This switching mechanism ensures the vehicle can accelerate, decelerate, and change gears smoothly without the need for a traditional gear stick and manual gear changes.
Absolutely! Electric vehicles have a range of switches and sensors that monitor and control various functions. For instance, the charging port switch is activated when the vehicle is plugged into a charging station, allowing the charging process to begin. There are also switches for the air conditioning system, climate control, and various driver-assistance features like cruise control or lane-keeping assist. These switches are often integrated into the vehicle's dashboard or center console, providing a user-friendly interface for the driver to control and monitor the EV's performance and comfort features.