Electric vehicles (EVs) are becoming increasingly popular, but one of the main concerns for potential buyers is the cost. While EVs offer numerous benefits, such as reduced environmental impact and lower running costs compared to traditional gasoline vehicles, the initial purchase price and ongoing expenses can be a significant barrier. This paragraph will explore the monthly costs associated with owning an electric vehicle, including electricity bills, charging infrastructure, insurance, and maintenance, to provide a comprehensive understanding of the financial implications for EV owners.
What You'll Learn
- Monthly Electricity Costs: Compare EV charging costs to traditional fuel expenses
- Maintenance and Repairs: Understand the long-term maintenance and repair expenses of EVs
- Insurance and Tax Benefits: Explore insurance discounts and tax incentives for electric vehicles
- Depreciation Rates: Analyze the depreciation of EVs over time
- Charging Infrastructure: Evaluate the cost of home and public charging station access

Monthly Electricity Costs: Compare EV charging costs to traditional fuel expenses
The cost of owning an electric vehicle (EV) is a topic of growing interest as more people consider making the switch from traditional gasoline-powered cars. One of the most significant expenses associated with EVs is electricity, which is used to power the vehicle's electric motor. Understanding the monthly electricity costs for EV charging is essential for potential buyers and current EV owners alike.
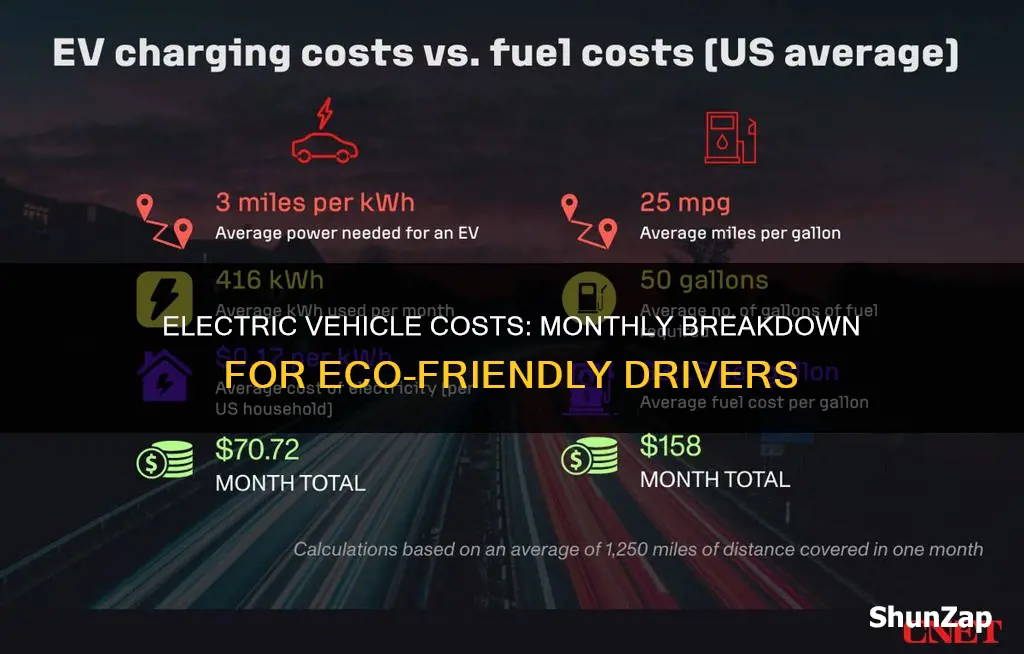
When comparing the monthly electricity costs of EV charging to traditional fuel expenses, it's important to consider several factors. Firstly, the cost of electricity varies depending on your location and the time of day. Many regions offer different rates for peak and off-peak hours, which can significantly impact your charging expenses. For instance, charging your EV during off-peak hours might be cheaper, allowing you to take advantage of lower electricity rates. Secondly, the efficiency of your EV plays a crucial role. Modern electric vehicles are designed to be energy-efficient, but the range and performance can vary. A more efficient EV will generally require less electricity to travel the same distance, resulting in lower monthly charging costs.
To estimate your monthly electricity costs, you need to know the charging speed of your EV and the capacity of its battery. Faster charging rates can be more convenient but may also increase electricity consumption. The battery capacity, measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh), determines how much electricity your EV uses during a charge. A larger battery will generally require more electricity, leading to higher monthly charges. Additionally, the type of charging station you use matters. Home charging stations are typically more cost-effective than public fast-charging stations, as they can be connected to your household electricity supply at a lower rate.
Let's illustrate with an example. Suppose you own a mid-range electric sedan with a 60 kWh battery and a home charging station that can fully charge the car in 8 hours. If your electricity rate is 15 cents per kWh during off-peak hours, your monthly electricity cost for charging this EV would be approximately $15.00. However, if you frequently use fast-charging stations at a rate of 45 cents per kWh, your monthly cost could increase to around $45.00. This comparison highlights the importance of understanding your charging habits and electricity rates to manage your EV's monthly expenses effectively.
In summary, monthly electricity costs for EV charging can vary widely depending on location, charging habits, and vehicle efficiency. By comparing these costs to traditional fuel expenses, potential EV owners can make informed decisions about their vehicle choices. It is advisable to research local electricity rates, consider the efficiency of different EV models, and plan for charging infrastructure to ensure a well-informed and cost-effective ownership experience.
The Future is Electric: Unlocking the Potential of EVs
You may want to see also

Maintenance and Repairs: Understand the long-term maintenance and repair expenses of EVs
When considering the long-term costs of owning an electric vehicle (EV), maintenance and repair expenses are an important factor to consider. While EVs are known for their efficiency and reduced environmental impact, they do require specific maintenance and can have unique repair considerations compared to traditional gasoline or diesel vehicles. Understanding these aspects can help potential EV owners make informed decisions and budget accordingly.
One of the key advantages of electric vehicles is their generally lower maintenance requirements. Traditional internal combustion engines have more moving parts, which can lead to more frequent service needs and potential issues. EVs, on the other hand, have fewer complex mechanical systems, resulting in reduced wear and tear. For instance, there are no oil changes or spark plug replacements required, which can save both time and money over the vehicle's lifetime. The absence of these routine services means that EV owners typically spend less on maintenance, making it an attractive long-term investment.
However, it's important to note that while routine maintenance is less frequent, specialized knowledge and equipment are often required for EV maintenance. Electric motors and battery packs have unique characteristics that demand specific diagnostic tools and techniques. As a result, finding qualified technicians who can service EVs might be more challenging and potentially more expensive than for conventional vehicles. It is advisable to research and identify reputable EV-certified repair shops in your area to ensure you receive the necessary expertise and care for your vehicle.
The cost of repairs for EVs can vary widely depending on the specific issue and the make and model of the vehicle. Common issues with electric vehicles may include battery-related problems, such as degradation or cell failures, which can be costly to replace or repair. Additionally, the complexity of the electrical systems in EVs means that diagnosing and fixing issues might require specialized equipment and training, potentially increasing repair costs. It is essential to have a clear understanding of the warranty coverage and any extended warranty options available to protect yourself from unexpected high-cost repairs.
In summary, while electric vehicles offer reduced maintenance costs in the long run due to fewer routine services, they may require more specialized knowledge and equipment for maintenance and repairs. Potential EV owners should research and understand the specific maintenance needs of their chosen vehicle and be prepared for potential repair costs. Being proactive in finding qualified technicians and staying informed about warranty coverage can help ensure a positive and cost-effective ownership experience.
Exploring the Electric Spectrum: Types of EVs
You may want to see also

Insurance and Tax Benefits: Explore insurance discounts and tax incentives for electric vehicles
When considering the financial aspects of owning an electric vehicle (EV), it's important to explore the various insurance and tax benefits that can significantly reduce your overall costs. Many governments and insurance companies worldwide recognize the environmental benefits of EVs and have implemented incentives to encourage their adoption. Here's an overview of how you can take advantage of these advantages:
Insurance Discounts:
Electric vehicles often qualify for specialized insurance discounts due to their unique characteristics. Many insurance providers offer reduced rates for EVs because of their lower insurance claim rates compared to traditional gasoline vehicles. This is primarily due to the reduced risk of engine-related damage and the lower likelihood of certain types of accidents. For instance, you might find that comprehensive insurance coverage for your EV is more affordable than for a conventional car. Additionally, some insurance companies provide discounts for EV owners who opt for usage-based insurance, where premiums are adjusted based on driving habits and mileage.
Tax Incentives:
Governments at various levels often provide tax incentives to promote the use of electric vehicles. These incentives can be substantial and vary depending on your location. For example, in some countries, you may be eligible for a tax credit or rebate when purchasing an EV, which can offset a significant portion of the vehicle's cost. These incentives are designed to encourage the transition to cleaner transportation and can make EVs more affordable upfront. Moreover, some regions offer tax exemptions or reduced rates on sales tax for EV purchases, further lowering the initial financial burden.
Environmental Benefits and Long-Term Savings:
Beyond the immediate insurance and tax advantages, owning an electric vehicle can lead to long-term savings. EVs produce fewer emissions, which can result in reduced air pollution and potential savings on healthcare costs associated with respiratory issues. Many cities and states offer incentives for EV owners to participate in car-sharing or ride-sharing programs, further decreasing the overall cost of vehicle ownership. Additionally, the decreasing cost of EV batteries over time means that charging an EV is becoming more affordable, making it a cost-effective choice in the long run.
Exploring these insurance and tax benefits can significantly impact your EV ownership experience. It's advisable to research the specific incentives and discounts available in your region, as they can vary widely. By taking advantage of these opportunities, you can make owning an electric vehicle more financially viable and environmentally friendly. Remember, the initial investment in an EV can be higher, but the long-term savings and benefits make it a compelling choice for many drivers.
The Future of Driving: Embracing All-Electric Vehicles
You may want to see also

Depreciation Rates: Analyze the depreciation of EVs over time
The depreciation of electric vehicles (EVs) is a critical aspect to consider when evaluating the long-term cost of ownership. Unlike traditional gasoline vehicles, EVs have unique depreciation patterns due to various factors, including technological advancements, market demand, and environmental regulations. Analyzing these depreciation rates can provide valuable insights for potential EV buyers and investors.
One of the primary reasons for the distinct depreciation of EVs is their relatively short lifespan in the market. As technology advances rapidly, newer models with improved performance and features are introduced frequently. This constant innovation leads to a higher rate of obsolescence, especially for early-generation EVs. For instance, a study by the University of Michigan found that the average annual depreciation of early-model EVs (2011-2014) was significantly higher, ranging from 15% to 20%, compared to conventional vehicles. This rapid depreciation can be attributed to the desire for the latest technology and the fear of missing out on potential performance improvements.
However, as the EV market matures and production volumes increase, depreciation rates may start to stabilize. The law of supply and demand comes into play here. With more EVs on the road, the initial excitement and rapid adoption may slow down, leading to a more gradual depreciation over time. This trend is evident in the second-hand EV market, where prices of slightly older models have shown a tendency to stabilize or even increase in value, especially for those with high-performance characteristics or unique features.
Another factor influencing EV depreciation is the battery technology and its associated performance. The battery pack is a significant component of an EV's cost, and its health and longevity are crucial. Over time, lithium-ion batteries degrade, leading to a decrease in range and overall performance. This degradation is not uniform across all EVs and depends on various factors, including driving habits, climate conditions, and maintenance. Some studies suggest that the depreciation of EVs can be closely linked to battery health, with well-maintained batteries retaining their value better.
Understanding the depreciation rates of EVs is essential for making informed financial decisions. For individuals, it can help determine the optimal time to buy a used EV, potentially saving costs. For businesses and investors, analyzing depreciation trends can guide investment strategies, especially in the emerging EV market. Additionally, governments and policymakers can use this information to develop incentives and regulations that encourage the adoption of EVs while managing the environmental impact of vehicle disposal.
Electric Vehicle Tax Credit: Unlocking Savings for All Income Levels
You may want to see also

Charging Infrastructure: Evaluate the cost of home and public charging station access
The cost of charging an electric vehicle (EV) is an essential consideration for potential buyers, as it directly impacts the overall ownership and running expenses. When evaluating the charging infrastructure, it's crucial to understand the costs associated with both home and public charging stations.
Home Charging:
Setting up a home charging station is a convenient and often cost-effective solution for EV owners. The initial investment involves purchasing a charging unit, which can range from $300 to $1,000 or more, depending on power output and additional features. Installation costs can vary depending on your location and the complexity of the electrical setup. Some EV manufacturers offer home charging packages, which may include the charger and installation, making it a more comprehensive solution. The electricity consumption of home charging depends on the vehicle's battery capacity and the charger's efficiency. On average, charging an EV at home can cost between $0.10 and $0.30 per kWh, but this can vary based on regional electricity rates and the time of day you charge. For instance, charging during off-peak hours might be cheaper.
Public Charging Stations:
Accessing public charging stations is another option, especially for those who don't have the means to install home charging. Public chargers can be found in various locations, including shopping malls, parking lots, and roadside rest areas. The cost of using public charging stations varies widely. Some stations offer free charging, while others charge per session or per minute. Prices can range from $0.20 to $0.50 per kWh or more, depending on the station's location, type, and network. Fast-charging stations, which provide a quicker charge, often charge a premium. It's essential to plan your routes and consider charging costs when traveling long distances. Many public charging networks offer membership or subscription plans, providing discounted rates for frequent users.
When evaluating the overall cost of EV ownership, it's beneficial to calculate the monthly expenses. This includes the electricity cost for home charging and the estimated usage of public charging stations if applicable. For instance, if an EV owner charges their vehicle at home for 20 days a month at an average rate of $0.25 per kWh, the monthly cost would be approximately $50. Adding public charging expenses, if any, will provide a more comprehensive view of the monthly outlay.
In summary, the cost of charging infrastructure is a critical aspect of EV ownership. Home charging offers convenience and potential cost savings, while public charging stations provide flexibility for those without home charging options. Understanding the rates and costs associated with both systems is essential for making informed decisions about EV ownership and charging habits.
Unveiling the Perfect Voltage: Optimizing Power for Electric Vehicles
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The monthly charging cost for an EV can vary significantly depending on several factors. On average, an EV owner might spend between $30 to $100 per month on electricity. This estimate is based on driving an EV with a range of 200-300 miles, which typically requires about 30-40 kWh of electricity for a full charge. The actual cost will depend on your local electricity rates, the efficiency of your EV, and your charging habits.
Yes, apart from the electricity cost, there are a few other expenses to consider. These include the initial purchase price of the EV, which can vary widely based on the make, model, and range. Additionally, some EVs may have higher maintenance costs compared to traditional gasoline vehicles due to their complex electric drivetrains. However, many EV owners report lower overall maintenance expenses over time.
Absolutely! You can estimate your monthly charging cost by first calculating your daily or weekly driving distance and then determining the corresponding electricity usage. For instance, if you drive 100 miles per day, and your EV has a range of 250 miles on a full charge, you'll need to charge it approximately 0.4 times per day. Multiplying this by the average daily electricity cost can give you a monthly estimate.
Yes, many governments worldwide offer incentives and subsidies to promote the adoption of electric vehicles. These financial benefits can significantly reduce the overall cost of ownership. For example, some regions provide tax credits, rebates, or grants to EV buyers, which can offset the initial purchase price and, in some cases, even the monthly charging expenses. It's advisable to research local incentives to maximize these savings.
On average, the monthly cost of owning an electric vehicle is lower than that of a conventional gasoline-powered car. This is primarily due to the reduced fuel costs and, in some cases, lower maintenance expenses. While the initial purchase price of an EV might be higher, the long-term savings on fuel and maintenance can make it a more economical choice. Additionally, the cost of electricity is generally more stable and predictable compared to fluctuating gasoline prices.