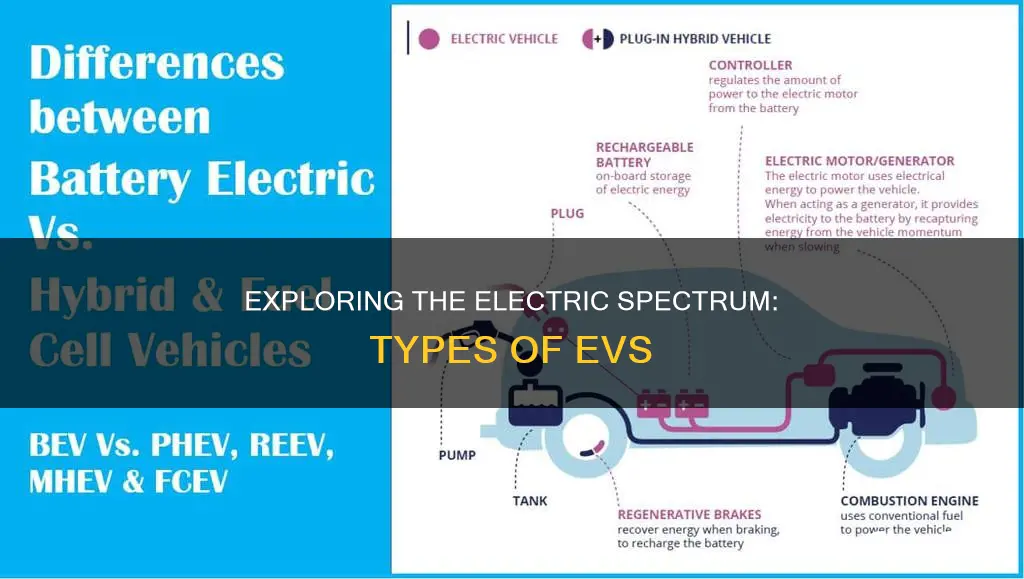
Electric vehicles (EVs) have revolutionized the automotive industry, offering a sustainable and eco-friendly alternative to traditional gasoline-powered cars. There are several types of electric vehicles, each with unique characteristics and advantages. The most common types include Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs), which run solely on electricity stored in batteries and produce zero tailpipe emissions. Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs) combine a conventional engine with an electric motor and battery, allowing for both electric and gasoline power. Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs) use a smaller battery and regenerative braking to capture and reuse energy, providing improved fuel efficiency without the need for direct charging. Additionally, Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles (FCEVs) utilize hydrogen as a fuel source, producing electricity through a chemical reaction and emitting only water vapor. These diverse types of electric vehicles cater to various consumer needs, offering a range of options for those seeking environmentally friendly transportation.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV) | Uses only electric motors and batteries, no internal combustion engine. |
| Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV) | Combines a traditional engine with an electric motor and a rechargeable battery. |
| Hybrid Electric Vehicle (HEV) | Features both an electric motor and a conventional engine, with the ability to recharge the battery through regenerative braking. |
| Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle (FCEV) | Powers the vehicle using hydrogen fuel cells, producing electricity through a chemical reaction with oxygen. |
| Range | Varies widely, from 100 to over 400 miles on a single charge, depending on the model and battery capacity. |
| Charging Time | Typically takes 30 minutes to 2 hours for a full charge, depending on the charger and battery size. |
| Efficiency | Electric vehicles are generally more efficient, converting over 77% of battery energy to power, compared to around 21% for conventional cars. |
| Environmental Impact | Zero tailpipe emissions, reducing air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions. |
| Performance | Often offer quick acceleration and smooth driving experience due to instant torque. |
| Maintenance | Less complex systems mean lower maintenance costs compared to traditional vehicles. |
| Cost | Purchase price can be higher, but running costs are lower over time due to reduced maintenance and fuel expenses. |
| Infrastructure | Requires access to charging stations, which are becoming more widely available. |
| Driving Experience | Quiet, smooth, and often provide a more engaging driving feel. |
| Technology | Advanced driver assistance systems and infotainment features are common in electric vehicles. |
| Resale Value | Resale values can be strong due to the growing demand for electric vehicles. |
What You'll Learn
- Battery EVs: Powered by rechargeable batteries, these vehicles are the most common type
- Hybrid EVs: Combine a traditional engine with an electric motor for improved efficiency
- Fuel Cell EVs: Use hydrogen to generate electricity, offering zero-emission driving
- Plug-in Hybrids: Charge the battery via a plug, providing both electric and hybrid capabilities
- Range Extenders: Feature a small internal combustion engine to extend the electric range

Battery EVs: Powered by rechargeable batteries, these vehicles are the most common type
Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs) are a popular and rapidly growing segment in the automotive industry, offering an eco-friendly and efficient mode of transportation. These vehicles are entirely powered by electric motors, eliminating the need for traditional internal combustion engines. The primary component that sets BEVs apart is their reliance on rechargeable batteries, which store electrical energy to drive the vehicle.
The design and functionality of BEVs are quite straightforward. When a driver engages the accelerator, the electric motor receives power from the battery pack, which is typically located in the vehicle's underbody or floor. This power is then distributed to the wheels, propelling the car forward. The beauty of this system lies in its simplicity and the absence of complex moving parts, resulting in reduced maintenance requirements compared to conventional vehicles.
One of the most significant advantages of BEVs is their environmental friendliness. As they produce zero tailpipe emissions, they contribute to improved air quality and reduced carbon footprints. This aspect has been a driving force behind the increasing popularity of BEVs, especially in regions with stringent environmental regulations. Additionally, the quiet operation of these vehicles makes them a more pleasant and less disruptive mode of transport.
The range of BEVs has been a concern for potential buyers, but advancements in battery technology have led to significant improvements. Modern BEVs offer a range of over 200 miles on a single charge, which is more than sufficient for daily commutes and even longer trips with careful planning. Fast-charging stations are also becoming more widespread, allowing for rapid recharging during longer journeys.
In summary, Battery Electric Vehicles are the most prevalent form of electric vehicles, offering a sustainable and efficient transportation solution. Their reliance on rechargeable batteries, combined with advancements in technology, has made them a viable and attractive option for environmentally conscious consumers. As the world shifts towards greener alternatives, BEVs are poised to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of the automotive industry.
Maserati's Electric Revolution: Unveiling the Future of Luxury
You may want to see also

Hybrid EVs: Combine a traditional engine with an electric motor for improved efficiency
Hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) are a fascinating innovation in the automotive industry, offering a unique blend of traditional combustion engines and electric power. These vehicles are designed to optimize efficiency and reduce environmental impact by combining the strengths of both worlds. At its core, a hybrid EV is a car that utilizes two distinct power sources: a conventional internal combustion engine (ICE) and one or more electric motors. This combination allows for a more flexible and efficient driving experience compared to traditional gasoline or diesel vehicles.
The key to the success of hybrid EVs lies in their ability to switch seamlessly between the two power sources. When the vehicle is stationary or during low-speed driving, the electric motor takes the lead, providing quiet, smooth, and efficient power. This is particularly beneficial in urban areas where frequent stops and starts are common. The electric motor can power the car independently, eliminating the need for gear changes and providing an instant torque boost, resulting in quick acceleration. During this mode, the vehicle operates like a pure electric car, offering a clean and environmentally friendly driving experience.
As the vehicle gains speed and the driver demands more power, the traditional engine kicks in. This engine is typically smaller and more fuel-efficient than those in conventional cars, as it only needs to provide additional power when required. The hybrid system ensures that the ICE operates at its most efficient range, reducing fuel consumption and emissions. The electric motor and the ICE can work in tandem, providing a seamless and powerful driving experience. For example, when accelerating on a highway, the electric motor provides an initial surge of power, and then the ICE takes over, ensuring a smooth and continuous flow of power.
One of the most significant advantages of hybrid EVs is their ability to recover energy during braking. When the driver applies the brakes, the electric motor acts as a generator, converting the kinetic energy back into electrical energy, which is then stored in the battery. This process, known as regenerative braking, not only improves efficiency but also extends the range of the vehicle, especially during city driving. The recovered energy can be used to power the electric motor or charge the battery, reducing the overall fuel consumption.
Hybrid vehicles also offer a unique driving experience by providing the driver with a choice of power sources. Many hybrid EVs have a 'power-split' function, allowing the driver to manually switch between electric-only and hybrid modes. This gives drivers the flexibility to choose the most suitable driving mode for their needs, whether it's the quiet and efficient electric mode or the powerful hybrid combination. This level of control and efficiency has made hybrid EVs increasingly popular, especially among environmentally conscious consumers.
The Green Revolution: Are Electric Vehicles the Ultimate Sustainable Choice?
You may want to see also

Fuel Cell EVs: Use hydrogen to generate electricity, offering zero-emission driving
Fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEVs) represent a significant advancement in the world of sustainable transportation, offering a unique approach to powering cars, buses, and other vehicles with zero direct emissions. These vehicles utilize a fascinating process to generate electricity, which then powers the vehicle's electric motor, providing a clean and efficient driving experience.
At the heart of FCEVs is a fuel cell, a device that combines hydrogen gas and oxygen from the air to produce electricity through a chemical reaction. This process is highly efficient and produces only water and heat as byproducts, making it an environmentally friendly alternative to traditional internal combustion engines. The fuel cell stack, often consisting of multiple cells, is designed to generate a steady supply of electricity, ensuring a continuous and reliable power source for the vehicle.
When a driver initiates the journey, the hydrogen gas is supplied to the fuel cell, where it undergoes a series of reactions. The hydrogen atoms split into protons and electrons, with the protons passing through a membrane to reach the oxygen. This reaction produces electricity, which is then used to power the vehicle's electric motor. The electrons, on the other hand, create a flow of current, which can be used to charge the vehicle's battery or directly power the motor. This efficient conversion of chemical energy to electrical energy results in a high energy density, allowing FCEVs to travel longer distances compared to some other electric vehicle types.
One of the key advantages of Fuel Cell EVs is their rapid refueling capability. Similar to conventional vehicles, FCEVs can be refueled with hydrogen gas in a matter of minutes, providing a convenient and time-efficient solution for drivers. This aspect addresses a common concern associated with electric vehicles, which often require longer charging times. With hydrogen refueling, FCEVs can offer a similar level of convenience to gasoline-powered cars, making them an attractive option for those seeking a sustainable yet practical transportation solution.
The environmental benefits of Fuel Cell EVs are substantial. As mentioned, these vehicles produce zero direct emissions, significantly reducing air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions. This is particularly important in urban areas, where traffic congestion and air quality are major concerns. By utilizing hydrogen, FCEVs contribute to a cleaner and healthier environment, making them a crucial part of the transition towards a more sustainable transportation ecosystem.
In summary, Fuel Cell EVs represent a cutting-edge technology in the electric vehicle market, offering a unique and efficient way to power vehicles with zero emissions. Their ability to generate electricity through hydrogen fuel cells, coupled with rapid refueling and environmental benefits, makes them a promising solution for the future of sustainable transportation. As research and development in this field continue to advance, FCEVs are likely to play a significant role in shaping a greener and more environmentally conscious world.
Unlock EV Tax Savings: A Guide to Qualification
You may want to see also

Plug-in Hybrids: Charge the battery via a plug, providing both electric and hybrid capabilities
Plug-in hybrids are an innovative class of electric vehicles that offer a unique blend of traditional combustion engine and electric motor capabilities. These vehicles are designed to provide the best of both worlds, combining the efficiency and environmental benefits of electric power with the range and flexibility of a conventional engine. One of the key features of plug-in hybrids is their ability to charge their batteries via a plug, which sets them apart from conventional hybrids.
In terms of charging, plug-in hybrids can be charged using a standard electrical outlet or a dedicated charging station. This allows for convenient and flexible charging options, making it easier for drivers to keep their vehicles powered up. When it comes to driving, plug-in hybrids offer a seamless transition between electric and hybrid modes. During electric mode, the vehicle runs solely on the electric motor, providing a smooth and quiet driving experience with minimal emissions. This is particularly beneficial for short-distance travel, such as commuting in urban areas, where the vehicle can operate in zero-emission mode.
The hybrid mode, on the other hand, utilizes both the electric motor and the internal combustion engine. This mode is activated when the battery needs additional power or when the vehicle requires higher performance. In hybrid mode, the vehicle can switch between the electric motor and the engine, optimizing fuel efficiency and providing a more dynamic driving experience. This dual-power system ensures that plug-in hybrids can cover longer distances without range anxiety, as the conventional engine can take over when the battery is low.
The design of plug-in hybrids often includes a range extender, which is a small, efficient internal combustion engine that provides additional power when needed. This range extender ensures that the vehicle can continue its journey even if the battery is fully depleted. Additionally, plug-in hybrids typically have larger batteries compared to conventional hybrids, allowing for longer electric-only driving ranges. This combination of electric and hybrid capabilities makes plug-in hybrids an attractive option for environmentally conscious consumers who also value the convenience and versatility of a traditional vehicle.
In summary, plug-in hybrids offer a compelling solution for those seeking an eco-friendly yet practical mode of transportation. With the ability to charge via a plug, these vehicles provide the flexibility to drive in electric mode for short distances while also ensuring long-range capability through the integration of a conventional engine. As the automotive industry continues to evolve, plug-in hybrids represent a significant step towards a more sustainable and diverse electric vehicle market.
Unlocking Savings: California's EV Tax Credit Explained
You may want to see also

Range Extenders: Feature a small internal combustion engine to extend the electric range
Range extenders are a unique feature in the world of electric vehicles (EVs), designed to address the common concern of limited driving range that many early EVs faced. This technology is particularly useful for those who want the benefits of electric driving but also need the reassurance of a longer range for longer journeys or when charging infrastructure is less accessible.
The core concept behind range extenders is simple: a small, efficient internal combustion engine (ICE) is coupled with an electric motor. When the battery power is low, the ICE springs into action, generating electricity to recharge the battery and extend the vehicle's range. This system ensures that the vehicle can continue its journey without the anxiety of running out of power.
These engines are typically smaller and more fuel-efficient compared to their conventional counterparts, often using advanced technologies like direct fuel injection and turbocharging to maximize performance while minimizing fuel consumption. The ICE is not used as the primary power source but rather as a backup, which is a key advantage over traditional hybrid vehicles where the ICE is more prominently featured.
One of the significant benefits of range extenders is their ability to provide a seamless driving experience. When the battery is fully charged, the vehicle operates solely on electric power, delivering the smooth and quiet performance that electric vehicles are known for. As the battery level drops, the ICE gently kicks in, seamlessly transitioning the vehicle to a hybrid mode, ensuring the driver doesn't notice any disruption in their journey.
This technology has been a game-changer for many EV manufacturers, allowing them to offer vehicles with extended range without compromising the environmental benefits of electric driving. It provides a practical solution for a wide range of consumers, from those who commute daily to those who occasionally need to travel long distances. With range extenders, the limitations of early electric vehicles are significantly reduced, making the transition to electric mobility more accessible and appealing to a broader audience.
Chrysler's Electric Evolution: A New Era of Sustainable Mobility
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Electric vehicles can be broadly classified into three main types: Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs), Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs), and Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs). BEVs are fully electric and run solely on electricity, while PHEVs have both an electric motor and an internal combustion engine. HEVs use a combination of an electric motor and a traditional engine, but the electric power is typically used to recharge the battery rather than drive the vehicle.
BEVs are powered by one or more electric motors that run on electricity stored in batteries. These vehicles are charged by plugging into an external power source, typically an electric socket or a charging station. The batteries store electrical energy, which is then used to power the motor(s), propelling the vehicle forward. BEVs produce zero direct emissions and are a popular choice for environmentally conscious consumers.
Plug-in Hybrids (PHEVs) and Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs) both use a combination of electric and traditional fuel sources. However, PHEVs can be charged by plugging into an external power source, allowing them to run in electric-only mode for a certain distance before switching to hybrid mode. HEVs, on the other hand, cannot be plugged in and typically use regenerative braking to recharge their batteries. HEVs are more common in the market and offer improved fuel efficiency compared to traditional vehicles.







