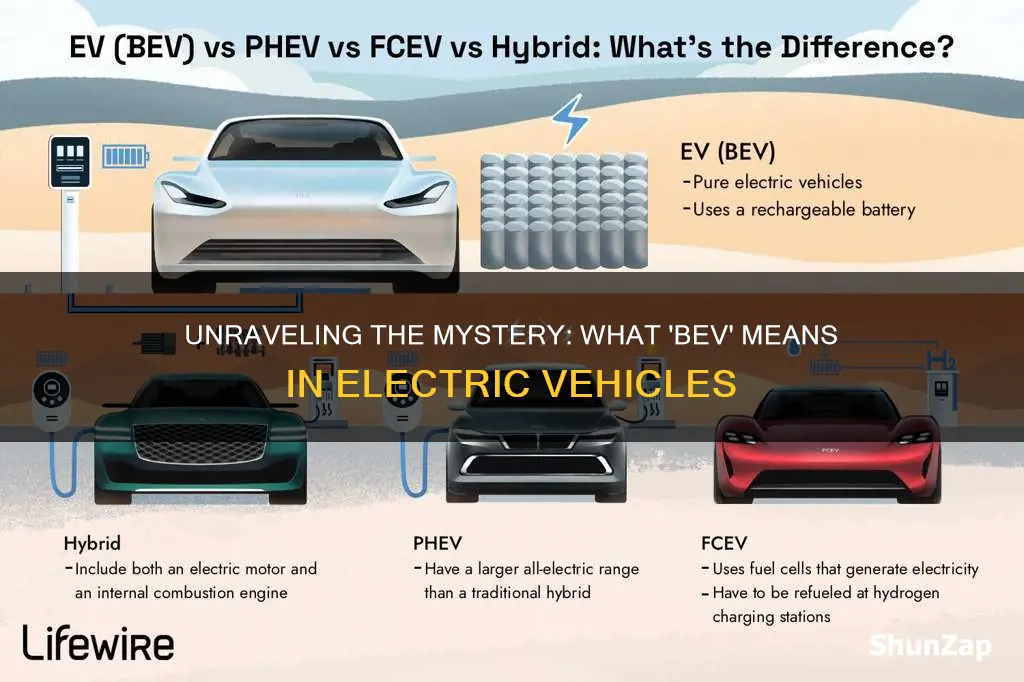
Bev is a popular acronym in the electric vehicle (EV) community, standing for Battery Electric Vehicle. These vehicles are powered solely by electric motors and batteries, without any internal combustion engines. Battery electric cars are a key component of the sustainable transportation movement, offering zero-emission driving and a more environmentally friendly alternative to traditional gasoline or diesel cars. Understanding the meaning of bev is essential for anyone interested in the EV market, as it highlights the growing importance of electric powertrains in the automotive industry.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV) | A fully electric vehicle powered by a battery pack, with no internal combustion engine. |
| Power Source | Battery |
| Emissions | Zero tailpipe emissions, contributing to a cleaner environment. |
| Performance | Often offers quick acceleration and smooth driving experience. |
| Range | Varies widely, typically ranging from 100 to 400+ miles on a single charge. |
| Charging | Requires charging at home, public charging stations, or fast-charging networks. |
| Efficiency | High energy efficiency, converting most of the battery's energy to power the vehicle. |
| Environmental Impact | Reduced carbon footprint compared to conventional vehicles. |
| Cost | Purchase and maintenance costs can vary, often with lower running costs over time. |
| Technology | Advanced driver assistance systems, autonomous capabilities, and infotainment features are common. |
| Market Trends | Growing popularity and availability, with many car manufacturers offering BEV options. |
What You'll Learn
- Battery Electric Vehicle: A fully electric car powered by a battery pack, with no internal combustion engine
- Charging Infrastructure: Networks of charging stations for EV batteries, ensuring convenient and efficient charging
- Range Anxiety: The fear of running out of battery power, a common concern for early EV adopters
- Performance Benefits: EVs offer instant torque, smooth acceleration, and superior handling compared to traditional cars
- Environmental Impact: Reduced carbon emissions and air pollution are key advantages of electric vehicles

Battery Electric Vehicle: A fully electric car powered by a battery pack, with no internal combustion engine
A Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV) is a type of electric vehicle that is entirely powered by an electric motor and a battery pack, without any internal combustion engine. This means that BEVs are a more environmentally friendly and sustainable mode of transportation compared to traditional gasoline-powered cars. The primary advantage of BEVs is their zero-emission nature, as they produce no harmful exhaust gases, making them a cleaner alternative for the environment.
The heart of a BEV is its battery pack, which stores electrical energy and powers the vehicle. These batteries are typically lithium-ion-based and have improved over time, offering higher energy density and longer lifespans. When a BEV is in use, the battery pack supplies electricity to the electric motor, which then drives the wheels, propelling the car forward. This process is efficient and produces minimal waste heat, unlike internal combustion engines.
One of the key features of BEVs is their regenerative braking system. When the driver applies the brakes, the electric motor reverses, acting as a generator, converting kinetic energy back into electrical energy and recharging the battery. This feature not only improves energy efficiency but also enhances the overall driving experience by providing a smooth and responsive braking sensation.
BEVs offer several benefits over conventional vehicles. Firstly, they have simpler mechanical systems, which can lead to lower maintenance costs. Without the need for oil changes, spark plug replacements, or complex exhaust systems, BEVs require less frequent servicing. Additionally, the electric drivetrain provides instant torque, resulting in quick acceleration and a more engaging driving experience.
The range of BEVs has been a concern in the past, but advancements in battery technology have significantly improved their performance. Modern BEVs can travel over 200 miles on a single charge, and some high-end models even exceed 300 miles. This range is more than sufficient for daily commutes and many long-distance trips, especially when considering the availability of charging stations along highways and in urban areas.
The Evolution of the Milkman's Electric Vehicle: A Historical Perspective
You may want to see also

Charging Infrastructure: Networks of charging stations for EV batteries, ensuring convenient and efficient charging
The development of charging infrastructure is a critical aspect of supporting the widespread adoption of electric vehicles (EVs). As the number of EVs on the road increases, so does the demand for a robust and accessible charging network. This infrastructure is the backbone of the EV ecosystem, ensuring that drivers can conveniently and efficiently recharge their vehicle's batteries.
Charging stations are the physical locations where EVs can connect to power sources. These stations are strategically placed along highways, in urban areas, and in residential neighborhoods to provide flexibility and convenience. The design and placement of these stations are crucial to their success. For instance, fast-charging stations, equipped with high-power connectors, can significantly reduce charging times, making them ideal for long-distance travel. These stations are typically found along major routes, allowing drivers to quickly replenish their battery levels during extended journeys.
The charging infrastructure network also includes a variety of charging options to cater to different needs. Level 1 charging, for example, uses a standard household outlet and is suitable for overnight charging at home. Level 2 charging, on the other hand, employs dedicated charging stations and provides faster charging times, making it convenient for public and private parking lots. Rapid or fast-charging stations, often found in highway rest areas and urban hubs, can recharge batteries to 80% capacity in as little as 20-30 minutes, addressing range anxiety and facilitating rapid long-distance travel.
Ensuring the efficient and convenient operation of this network requires careful planning and management. This includes optimizing station placement to cover key travel routes and high-demand areas, ensuring sufficient power supply to handle the load, and implementing smart charging technologies that balance energy demand and supply. Smart charging systems can communicate with the grid and adjust charging rates based on real-time energy prices and availability, helping to prevent grid overload and reduce charging costs for EV owners.
Furthermore, the development of charging infrastructure also involves addressing potential environmental impacts. As EVs are generally more environmentally friendly than traditional internal combustion engine vehicles, the focus should be on minimizing the carbon footprint of the charging process. This can be achieved through the use of renewable energy sources for power generation and the implementation of energy-efficient charging technologies.
Powering Your Ride: Understanding Vehicle Electrical Connectors
You may want to see also

Range Anxiety: The fear of running out of battery power, a common concern for early EV adopters
Range anxiety is a real concern for many early electric vehicle (EV) adopters, and it's an issue that has been a significant barrier to widespread EV adoption. This anxiety stems from the fear of running out of battery power while driving, which can lead to a sense of unease and even panic. For those new to EVs, the experience of driving a conventional car with an internal combustion engine is quite different from an EV. With a traditional car, you can easily check the fuel gauge and estimate how far you can go before needing to refuel. In contrast, EVs rely on battery power, and the range varies depending on the model and driving conditions.
The anxiety often arises from the limited range of early EVs, which was a common complaint among early adopters. Many early electric cars had a range of around 100-150 miles on a single charge, which could be a challenge for long-distance travel or for those who frequently drive in areas with limited charging infrastructure. This range limitation was a significant factor in the perception that EVs were not practical for daily use, especially for those who needed to travel long distances regularly.
To manage range anxiety, EV manufacturers have made significant strides in improving battery technology and charging infrastructure. Modern EVs now offer ranges of 200 miles or more on a single charge, addressing the initial concerns of many potential buyers. Additionally, the development of extensive charging networks has made it more convenient to recharge EVs while on the go. Public charging stations, fast-charging facilities, and home charging options have alleviated the fear of running out of power during a journey.
For those experiencing range anxiety, several strategies can help. Firstly, planning routes with charging stations along the way can provide peace of mind. Many navigation apps now offer EV-specific routing, suggesting the most efficient paths with regular charging stops. Secondly, understanding the factors that affect EV range, such as driving speed, climate control use, and vehicle efficiency, can help drivers make informed decisions to maximize their range. Lastly, for those who are still hesitant, car rental services and access to shared EVs can provide a convenient way to test drive different models and alleviate range-related concerns.
In conclusion, range anxiety has been a significant hurdle for early EV adopters, but it is a challenge that has been effectively tackled through technological advancements and infrastructure development. With improved battery ranges and a growing charging network, the fear of running out of power is becoming less of a barrier to EV ownership, making electric vehicles an increasingly attractive and practical choice for drivers worldwide.
Ford's Electric Future: Rumors of a Shift Unveiled
You may want to see also

Performance Benefits: EVs offer instant torque, smooth acceleration, and superior handling compared to traditional cars
The term 'BEV' stands for Battery Electric Vehicle, and it represents a new era in automotive technology, offering a range of performance advantages that are transforming the driving experience. One of the most notable performance benefits of EVs is their ability to deliver instant torque. Unlike traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles, electric motors provide a surge of torque from a standstill, resulting in rapid acceleration. This instant torque delivery gives EVs a significant advantage in terms of performance, especially when compared to conventional cars. When you press the accelerator pedal in an EV, the electric motor responds immediately, propelling the vehicle forward with a smooth and powerful surge. This instant response is particularly beneficial in everyday driving scenarios, such as merging onto highways or quickly overtaking other vehicles.
The smooth acceleration of EVs is another aspect that sets them apart. As you gradually increase the pressure on the accelerator, the electric motor seamlessly delivers power to the wheels, resulting in a linear and fluid acceleration experience. This contrasts sharply with the gradual build-up of power in traditional cars, which often require a more gradual and controlled application of force to the accelerator. The smooth and linear power delivery of EVs contributes to a more comfortable and responsive driving feel, making everyday driving more enjoyable and less fatiguing.
In terms of handling, EVs excel due to their lightweight design and well-distributed weight. The absence of a heavy internal combustion engine allows for better weight distribution, resulting in improved stability and agility. Additionally, the low center of gravity, often achieved through the placement of the battery pack, further enhances handling by reducing body roll during cornering. This combination of lightweight construction and optimized weight distribution gives EVs superior handling characteristics, making them more responsive and predictable in various driving conditions.
The performance benefits of EVs extend beyond just the driving experience. The instant torque and smooth acceleration also contribute to improved safety. The rapid response of the electric motor allows for quicker reactions in emergency situations, such as sudden stops or lane changes. The superior handling characteristics of EVs provide better control and stability, reducing the risk of skidding or losing traction, especially in adverse weather conditions. Furthermore, the absence of a traditional transmission in many EVs simplifies the driving experience, reducing the chances of mechanical failures that can occur in complex transmission systems.
In summary, the performance benefits of BEVs are substantial and have a significant impact on the overall driving experience. The instant torque, smooth acceleration, and superior handling capabilities of EVs offer a more responsive, comfortable, and safe driving environment compared to traditional cars. As technology advances and more manufacturers focus on electric powertrains, the performance gap between EVs and conventional vehicles continues to widen, making electric vehicles an increasingly attractive choice for those seeking a more dynamic and efficient driving experience.
Beyond the Range: Uncovering EV's Hidden Limitations
You may want to see also

Environmental Impact: Reduced carbon emissions and air pollution are key advantages of electric vehicles
The term 'BEV' stands for 'Battery Electric Vehicle', and it refers to a type of electric vehicle that is powered solely by an electric motor and a battery pack, without any internal combustion engine. This technology is at the forefront of the automotive industry's efforts to reduce its environmental footprint. One of the most significant environmental impacts of BEVs is their contribution to reducing carbon emissions. Traditional internal combustion engine vehicles are a major source of greenhouse gas emissions, primarily carbon dioxide (CO2), which is a primary driver of climate change. Electric vehicles, on the other hand, produce zero direct tailpipe emissions, meaning they do not release any harmful pollutants or greenhouse gases during operation. This is a crucial advantage in the fight against climate change, as it directly addresses one of the most pressing environmental issues of our time.
The environmental benefits of BEVs extend beyond just the reduction of carbon emissions. These vehicles also play a vital role in improving air quality, especially in urban areas. Internal combustion engines emit a range of pollutants, including nitrogen oxides (NOx), particulate matter (PM), and volatile organic compounds (VOCs), which contribute to smog and air pollution. BEVs, being emission-free, eliminate these harmful pollutants from the equation, leading to cleaner air and improved public health. This is particularly important in densely populated cities, where air pollution can have severe health impacts, including respiratory and cardiovascular diseases.
The environmental impact of BEVs is further enhanced by the potential for renewable energy integration. As the world moves towards a more sustainable energy model, electric vehicles can be charged using electricity generated from renewable sources such as solar, wind, or hydropower. This clean energy supply ensures that the entire lifecycle of a BEV, from production to operation, has a minimal environmental impact. Moreover, the widespread adoption of BEVs can contribute to a more efficient and sustainable energy grid, as the demand for electricity can be managed and distributed more effectively.
In addition to the direct environmental benefits, the shift towards BEVs can also have a positive economic impact. As the technology advances, the cost of producing electric vehicles has decreased, making them more affordable for consumers. This accessibility can lead to a rapid increase in the number of electric vehicles on the road, further accelerating the reduction of carbon emissions and air pollution. Additionally, the development of a robust electric vehicle infrastructure, including charging stations, can create new job opportunities and stimulate economic growth in the green sector.
In summary, BEVs offer a compelling solution to the environmental challenges posed by traditional vehicles. Their ability to reduce carbon emissions and air pollution is a significant step towards a more sustainable and healthier future. With ongoing technological advancements and increasing consumer interest, the widespread adoption of electric vehicles is becoming more feasible, paving the way for a greener and more environmentally conscious transportation system. This transition is essential to mitigate the environmental impact of the automotive industry and contribute to global efforts in combating climate change.
Demystifying the Scrap Process: A Guide to Recycling Electric Vehicles
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
In the electric vehicle (EV) industry, 'Bev' is an abbreviation for 'Battery Electric Vehicle'. It refers to a type of EV that is powered solely by an electric motor and a battery pack, without any internal combustion engine.
Bevs are distinct from other electric vehicles, such as hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) or plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs), as they exclusively rely on electricity for propulsion. They do not have a conventional fuel tank or an internal combustion engine, making them zero-emission vehicles.
Battery electric vehicles offer several benefits. They produce zero tailpipe emissions, reducing air pollution and contributing to a cleaner environment. Bevs are also known for their smooth and quiet operation, providing an efficient and enjoyable driving experience. Additionally, the cost of electricity is generally lower than gasoline, making them economically advantageous in the long run.
Absolutely! Home charging is a convenient option for Bev owners. Most electric vehicles come with a home charging cable and can be plugged into a standard electrical outlet or a dedicated charging point. This allows for convenient overnight charging, ensuring the vehicle is ready for daily use.