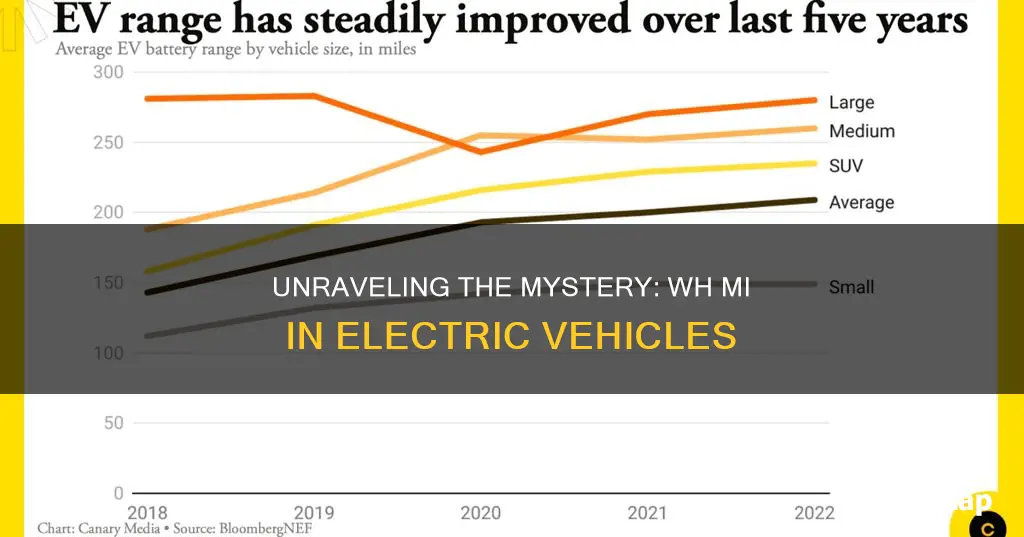
When discussing electric vehicles, you might come across the acronym WH MI. This stands for Watt-hours per Mile, a crucial metric that measures the energy efficiency of an electric vehicle. It indicates how many watt-hours of energy are required to travel one mile, providing insight into the vehicle's range and performance. Understanding WH MI is essential for consumers to assess the efficiency and sustainability of electric cars, helping them make informed decisions about their vehicle choices.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Wh (Watt-hour) | A unit of energy, typically used to describe the battery capacity of an electric vehicle. It represents the amount of energy a battery can store and provide over time. |
| Mi (Mileage) | Refers to the distance an electric vehicle can travel on a single charge. It is a crucial factor in assessing the vehicle's range and practicality. |
| Battery Capacity | The Wh value indicates the battery's capacity, often measured in kWh (kilowatt-hours). Higher Wh values generally mean a larger battery and potentially longer range. |
| Charging Time | The time required to fully charge the battery from empty to full. This depends on the charger, battery size, and other factors. |
| Range | The Mi value represents the estimated range an EV can achieve on a full charge. It varies based on driving conditions, efficiency, and other factors. |
| Efficiency | The relationship between energy input and output, often expressed as a percentage. Higher efficiency means less energy wasted during driving. |
| Power Output | The rate at which the battery can deliver energy to the vehicle's motor, measured in kW (kilowatts). |
| Voltage | The voltage of the battery pack, which can vary depending on the EV model. |
| Current | The amount of electric current flowing through the battery, measured in amperes (A). |
| Weight | The weight of the battery pack, which can impact the vehicle's overall performance and handling. |
What You'll Learn
- What: WH refers to Wireless Charging, a technology for charging EVs without physical connections
- How: WH technology uses electromagnetic fields to transfer energy, enabling efficient and convenient charging
- Mechanism: Wireless charging systems consist of a transmitter and receiver coils, converting AC to DC
- Impact: WH reduces wear on charging ports and cables, enhancing vehicle longevity and user experience
- Technology: WH is a rapidly evolving field, with ongoing research to improve efficiency and safety

What: WH refers to Wireless Charging, a technology for charging EVs without physical connections
Wireless Charging, or WH, is an innovative technology that enables the charging of electric vehicles (EVs) without the need for physical connections or cables. This method of charging is becoming increasingly popular and offers a convenient and efficient way to power EVs. The concept of wireless charging is based on the principle of electromagnetic induction, where a charging pad or station is placed under the vehicle, and a receiver coil is installed in the EV. When the vehicle is parked over the charging pad, an alternating current is induced in the receiver coil, which then converts it into direct current to charge the EV's battery.
The process of wireless charging is straightforward and user-friendly. Drivers simply need to park their vehicle over the designated charging area, and the system automatically initiates the charging process. This technology eliminates the hassle of searching for a charging station and plugging in the cable, making it especially convenient for home charging or public charging points. Wireless charging stations can be installed in various locations, including residential areas, parking lots, and even on the road, allowing for dynamic and flexible charging options.
One of the key advantages of WH technology is its efficiency. The wireless transfer of energy can be highly efficient, with minimal energy loss compared to traditional wired charging methods. This efficiency is crucial for optimizing the charging time and overall performance of electric vehicles. Additionally, wireless charging can help reduce the wear and tear on the vehicle's charging port and cable, as there are no physical connections to damage or degrade over time.
Implementing wireless charging infrastructure requires careful planning and consideration. The charging stations need to be strategically placed to ensure optimal coverage and accessibility. The range of wireless charging can vary, and factors such as the vehicle's position, the presence of metal objects, and environmental conditions can influence the charging efficiency. Therefore, proper alignment and placement of the charging pad and receiver coil are essential to ensure a successful and reliable charging experience.
Wireless Charging technology is an exciting development in the EV industry, offering a convenient, efficient, and potentially faster way to charge electric vehicles. As the technology advances and becomes more widely adopted, it has the potential to revolutionize the way we power our electric cars, making charging more accessible and user-friendly for drivers worldwide.
The Future of Transportation: Electric Vehicles Take Center Stage
You may want to see also

How: WH technology uses electromagnetic fields to transfer energy, enabling efficient and convenient charging
The WH technology, often associated with wireless charging, is a fascinating innovation in the electric vehicle (EV) industry. It utilizes electromagnetic fields to transfer energy, revolutionizing the way we charge our vehicles. This method offers a more efficient and convenient approach compared to traditional wired charging.
At its core, WH technology employs electromagnetic induction, a principle discovered by Michael Faraday. When a conductor, such as a coil of wire, is exposed to a changing magnetic field, it induces an electric current within the conductor. This phenomenon is the foundation of wireless charging. In the context of EVs, a transmitter coil is placed beneath the vehicle, creating a magnetic field. This field then induces a current in a receiver coil mounted on the bottom of the car, typically near the wheels.
The process begins with the EV being positioned above the charging pad or station. As the vehicle is lowered, the transmitter coil's magnetic field interacts with the receiver coil, generating an electric current. This current is then directed to the vehicle's battery, replenishing its power. The key advantage here is the absence of physical connections, eliminating the need for cables and reducing the risk of damage or wear over time.
The efficiency of WH technology is remarkable. It can transfer energy with minimal losses, ensuring that the battery receives a substantial charge. This efficiency is further enhanced by the ability to precisely control the charging process, allowing for faster and more controlled charging sessions. Additionally, the convenience of wireless charging means EV owners no longer need to search for specific parking spots or worry about plugging in their vehicles.
Implementing WH technology in electric vehicles requires careful design and consideration of various factors. Engineers must optimize the placement and size of the coils to maximize energy transfer efficiency. The frequency of the electromagnetic field also plays a crucial role, as it determines the range and effectiveness of the charging process. With ongoing research and development, WH technology continues to evolve, promising a future where charging electric vehicles is seamless and effortless.
Ford's Electric Future: A Doubtful Transition?
You may want to see also

Mechanism: Wireless charging systems consist of a transmitter and receiver coils, converting AC to DC
Wireless charging technology has revolutionized the way we power our devices, and it plays a crucial role in the functionality of electric vehicles (EVs). The acronym WH MI, which stands for "Wireless Charging Module," is an essential component in the wireless charging system of these vehicles. This module is responsible for enabling the efficient transfer of power from a charging station to the EV's battery.
The mechanism behind wireless charging involves a sophisticated interplay of electromagnetic fields and electrical conversions. At the heart of this process are two key components: the transmitter coil and the receiver coil. The transmitter coil is typically located in the charging station or the ground-based charging pad. It generates a high-frequency alternating current (AC) electromagnetic field when an electric current passes through it. This AC field is a fundamental aspect of wireless power transfer.
On the receiving end, the EV's battery incorporates the receiver coil, which is strategically positioned to capture the electromagnetic energy. When the transmitter coil's AC field induces a voltage in the receiver coil, an electric current is generated. This current then undergoes a crucial conversion process.
The conversion of AC to DC (direct current) is a critical step in wireless charging systems. This conversion ensures that the energy transferred to the EV's battery is in a usable form. The AC current from the receiver coil is fed into an electronic circuit, where it is transformed and rectified to become DC. This DC power is then directed to the vehicle's battery, allowing for efficient charging.
The efficiency and reliability of wireless charging depend on various factors, including the alignment and positioning of the transmitter and receiver coils, the frequency of the electromagnetic field, and the quality of the electronic components used in the conversion process. Modern wireless charging systems aim to provide a seamless and convenient charging experience for EV owners, ensuring that their vehicles are always ready for the road.
India's Electric Revolution: Are We Charged and Ready?
You may want to see also

Impact: WH reduces wear on charging ports and cables, enhancing vehicle longevity and user experience
The WH technology, an innovative feature in electric vehicles, significantly contributes to the longevity and reliability of charging systems. This technology is designed to minimize wear and tear on the charging ports and cables, ensuring a smoother and more efficient charging process. By implementing WH, manufacturers aim to address the common issue of charging port degradation, which can lead to frequent maintenance and potential safety hazards.
One of the primary impacts of WH is its ability to reduce mechanical stress on the charging interface. Traditional charging methods often involve repetitive physical connections, causing friction and potential damage over time. WH technology introduces a more gentle approach by utilizing advanced materials and designs. It employs a mechanism that minimizes the contact pressure between the charging connector and the port, thus reducing wear on the mating surfaces. This innovation is particularly crucial for high-frequency charging scenarios, where the strain on the charging ports can be substantial.
The benefits of WH extend beyond the physical aspects of charging. By extending the lifespan of charging ports and cables, WH contributes to the overall longevity of the electric vehicle. This is especially important given the increasing popularity of electric vehicles and the need for reliable charging infrastructure. With WH, users can expect their vehicles to maintain optimal charging performance over an extended period, reducing the likelihood of costly repairs or replacements.
Furthermore, WH technology positively impacts the user experience. Efficient and reliable charging is essential for electric vehicle owners, as it provides peace of mind and convenience. By minimizing the risk of charging port damage, WH ensures that users can charge their vehicles without the worry of frequent maintenance or potential breakdowns. This reliability encourages a more seamless integration of electric vehicles into daily routines, fostering a positive user experience.
In summary, the WH technology in electric vehicles has a profound impact on reducing wear and tear on charging ports and cables. Its implementation enhances vehicle longevity by minimizing mechanical stress and potential damage. Additionally, WH contributes to a better user experience by providing reliable and efficient charging, ensuring that electric vehicle owners can enjoy the benefits of their vehicles without frequent maintenance concerns. This innovation is a significant step towards a more sustainable and user-friendly electric vehicle ecosystem.
Unlocking Savings: California's EV Tax Credit Explained
You may want to see also

Technology: WH is a rapidly evolving field, with ongoing research to improve efficiency and safety
The field of WH technology in electric vehicles (EVs) is an exciting and rapidly advancing area of research and development. WH stands for Wireless Hybrid, a concept that combines wireless charging and hybrid electric systems to enhance the performance and efficiency of EVs. This technology is a significant step forward in the evolution of electric mobility, offering a more sustainable and convenient driving experience.
The core idea behind WH is to eliminate the need for traditional charging infrastructure by utilizing wireless power transfer. This involves inductive charging systems where a charging pad or station is installed on the ground, and the EV's battery is designed to receive power wirelessly when parked over it. This technology is particularly useful for public transportation fleets, parking lots, and residential areas, ensuring a seamless and efficient charging process.
In terms of efficiency, WH technology aims to optimize energy usage and reduce power losses. By employing advanced wireless charging systems, the energy transfer process becomes more efficient, minimizing the energy wasted during the charging cycle. This is crucial for extending the range of electric vehicles and reducing the time required for recharging, making EVs more practical for long-distance travel and everyday use.
Safety is another critical aspect of WH technology. Researchers and engineers are working tirelessly to ensure that wireless charging systems are safe and reliable. This includes developing advanced sensors and control mechanisms to detect and prevent potential hazards, such as foreign objects or incorrect parking positions. Additionally, the integration of hybrid electric systems can provide a failsafe mechanism, allowing the vehicle to switch to its internal combustion engine if wireless charging encounters any issues.
Ongoing research in the WH field focuses on improving the overall system design, including the development of more compact and efficient wireless power transfer components. Scientists are also exploring ways to integrate WH technology with other EV innovations, such as advanced battery management systems and smart grid infrastructure. The goal is to create a seamless and sustainable transportation ecosystem, where electric vehicles can be charged efficiently, safely, and conveniently, contributing to a greener and more efficient future.
Powering the Future: Unveiling the Key Components of Battery Electric Vehicles
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
WH MI stands for "Wireless Charging and Mileage Indicator." It is a feature commonly found in modern electric vehicles (EVs) that allows for convenient wireless charging and provides an indication of the vehicle's remaining range or mileage.
Wireless charging technology uses electromagnetic fields to transfer energy between a charging pad or station and a receiver installed in the vehicle. The charging pad is placed on the ground, and when the EV is parked over it, the electromagnetic field induces a current in the receiver, which then charges the vehicle's battery.
The mileage indicator in WH MI displays the remaining range or mileage of the electric vehicle. It provides real-time information about the distance the vehicle can travel on a fully charged battery, helping drivers plan their trips and manage their energy usage efficiently.
WH MI is typically associated with electric vehicles that support wireless charging technology. Not all EVs have this feature, as it requires specific hardware and infrastructure. However, many modern electric car models offer wireless charging as an option or standard feature, making WH MI a convenient and efficient way to charge and monitor EV performance.







