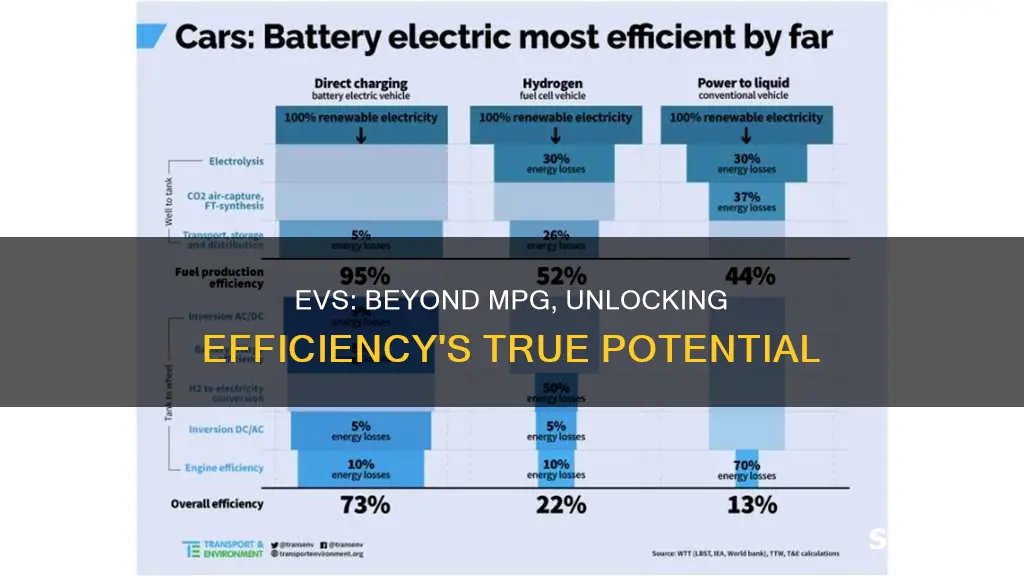
The electric vehicle (EV) market is rapidly growing, and as more drivers switch to EVs, it's important to understand the metrics used to measure their efficiency and performance. Just as traditional gasoline vehicles are often evaluated by their miles per gallon (MPG) rating, EVs have their own unique efficiency metric. This equivalent measure, often referred to as MPGe or miles per gallon equivalent, is a standardized way to compare the energy efficiency of electric cars. MPGe takes into account the energy content of electricity and provides a comparable figure to MPG, allowing drivers to easily assess the efficiency of different EV models and make informed choices about their electric vehicle purchases.
What You'll Learn
- Energy Efficiency: Measure of energy used per mile, comparing EVs to traditional cars
- Range per Charge: Miles driven on a single charge, a key EV performance metric
- Charging Time: Time required to fully charge an EV battery, similar to refueling
- Battery Capacity: Energy stored in the battery, impacting range and charging needs
- EV Efficiency Standards: Regulations setting efficiency targets for EVs, like MPG for cars

Energy Efficiency: Measure of energy used per mile, comparing EVs to traditional cars
Energy efficiency is a critical aspect when comparing electric vehicles (EVs) to traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) cars. It measures the amount of energy consumed per mile traveled, providing a clear picture of how efficiently each vehicle utilizes its energy source. This metric is essential for understanding the environmental impact and cost-effectiveness of different transportation methods.
The equivalent of miles per gallon (MPG) for electric vehicles is often referred to as 'miles per kilowatt-hour' (MPKWh). This unit of measurement indicates how many miles an EV can travel using one kilowatt-hour of electricity. For instance, if an EV has an MPKWh rating of 4, it means that for every kilowatt-hour of electricity consumed, the vehicle can travel 4 miles. This metric is particularly useful for EV owners and potential buyers as it directly relates to the real-world driving range and efficiency of the vehicle.
Calculating energy efficiency for EVs involves understanding the energy consumption of the vehicle and the distance it covers. EVs are powered by electric motors, which convert electrical energy into mechanical energy. The efficiency of this process is generally higher than that of internal combustion engines, resulting in less energy waste. When an EV travels a certain distance, it consumes a specific amount of electricity, and the MPKWh rating helps quantify this efficiency.
Comparing MPKWh ratings between different EVs allows consumers to make informed decisions. Higher MPKWh values indicate better energy efficiency, meaning the vehicle can travel more miles per unit of electricity. For example, an EV with a MPKWh rating of 5 will be more energy-efficient than one with a rating of 3, assuming all other factors are equal. This comparison is vital as it directly impacts the overall cost of ownership, with more efficient EVs potentially saving owners money on electricity bills over time.
In summary, understanding energy efficiency in the context of EVs is crucial for consumers and the automotive industry. By using MPKWh as a measurement, we can accurately assess the performance and environmental impact of electric vehicles. This metric encourages the development of more efficient EV designs, contributing to a greener and more sustainable transportation future. It also empowers individuals to make choices that align with their environmental goals and financial considerations.
Understanding DCV: Powering Electric Vehicles with Direct Current
You may want to see also

Range per Charge: Miles driven on a single charge, a key EV performance metric
The concept of 'Range per Charge' is akin to the miles per gallon (MPG) metric for traditional internal combustion engine vehicles. It represents a critical performance indicator for electric vehicles (EVs), providing an understanding of how far an EV can travel on a single charge. This metric is essential for EV owners and prospective buyers as it directly influences the practicality and convenience of owning an electric car.
When considering an EV, the range it offers on a full charge is a primary factor in the decision-making process. Just as MPG determines the fuel efficiency of a gasoline vehicle, 'Range per Charge' indicates the efficiency of an EV's battery. A higher range means the vehicle can cover more distance without needing to recharge, which is especially important for long-distance travel or for those with limited access to charging stations.
This metric is a measure of the vehicle's battery capacity and efficiency. It is calculated by dividing the total distance the EV can travel on a full charge by the amount of energy stored in the battery. For instance, if an EV has a battery capacity of 100 kWh and can travel 300 miles on a full charge, its 'Range per Charge' would be 300 miles per 100 kWh, or 3 miles per kWh. This calculation provides a standardized way to compare the efficiency of different EVs.
Understanding 'Range per Charge' is crucial as it directly impacts the user experience. A longer range means less frequent charging stops during a journey, reducing travel anxiety and providing a more comfortable and convenient driving experience. It also influences the overall cost of ownership, as a higher range can potentially reduce the need for frequent charging, which often comes at a higher cost compared to refueling a gasoline vehicle.
In summary, 'Range per Charge' is a vital metric for EV owners and enthusiasts, offering a clear indication of a vehicle's efficiency and practicality. It empowers buyers to make informed decisions, ensuring they choose an EV that aligns with their specific needs and driving requirements, much like how MPG guides choices in the traditional car market. This metric is a key differentiator in the EV market, allowing consumers to compare and select vehicles based on their real-world performance and usability.
Can Income Limit Your Electric Vehicle Credit?
You may want to see also

Charging Time: Time required to fully charge an EV battery, similar to refueling
The concept of 'Charging Time' is an essential aspect of electric vehicle (EV) ownership, akin to the fuel efficiency metric, miles per gallon (MPG), for conventional cars. Just as MPG indicates how far a vehicle can travel on a gallon of fuel, charging time tells us how long it takes to replenish an EV's battery. This metric is crucial for EV owners and prospective buyers, as it directly impacts convenience and the overall driving experience.
Charging time can vary significantly depending on several factors. Firstly, the type of charger used plays a vital role. There are three main charging levels: Level 1, Level 2, and DC Fast Charging. Level 1, the slowest, uses a standard 120-volt outlet and can add about 2-5 miles of range per hour. Level 2, faster, requires a 240-volt outlet and can charge an EV in 3-10 hours, depending on the battery size. DC Fast Charging, the quickest, utilizes specialized equipment and can restore a substantial portion of the battery's charge in as little as 20-30 minutes.
Secondly, the size of the EV battery is a critical factor. Larger batteries, typically found in more premium or long-range EVs, will take longer to charge fully. For instance, a compact EV with a 40 kWh battery might charge in 3-4 hours using a Level 2 charger, while a luxury sedan with a 100 kWh battery could require 8-10 hours for a full charge.
Additionally, the starting charge level of the battery is essential. If an EV is already partially charged, it will take less time to reach a full charge. Conversely, if the battery is nearly depleted, charging will take longer. This is similar to how a conventional car's fuel tank is more quickly filled when it's not already full.
Understanding charging time is vital for EV owners to plan their daily routines effectively. For example, knowing the charging time can help determine if an EV can be fully charged before a long-distance trip or if an overnight charge is sufficient for daily commuting. It also encourages the adoption of faster charging solutions, such as home Level 2 chargers or public DC Fast Charging stations, to minimize waiting times.
Uncover the Federal EV Tax Credit: A Green Car Incentive
You may want to see also

Battery Capacity: Energy stored in the battery, impacting range and charging needs
Battery capacity is a critical factor in electric vehicles (EVs), analogous to miles per gallon (MPG) in traditional cars. It refers to the amount of energy that can be stored in the battery pack, which directly influences the vehicle's range and charging requirements. Understanding battery capacity is essential for EV owners and prospective buyers as it determines how far they can travel on a single charge and how long it will take to recharge.
The energy stored in an EV battery is measured in watt-hours (Wh) or kilowatt-hours (kWh). A higher kWh rating means the battery can store more energy, resulting in a longer driving range. For example, a 100 kWh battery will provide more range than a 60 kWh one, assuming all other factors are equal. This is similar to how MPG works in conventional vehicles, where a higher MPG rating indicates better fuel efficiency and, consequently, a longer distance traveled per gallon.
Battery capacity also impacts the time it takes to charge an EV. Larger batteries with higher kWh ratings generally require more time to fully charge. For instance, a 100 kWh battery might take several hours to charge from empty, while a smaller 60 kWh battery could be charged much faster. This is an important consideration for EV owners, especially those with busy schedules or limited access to charging stations. Efficient charging management can significantly improve the practicality of owning an EV.
In addition, battery capacity influences the overall cost of an EV. Higher kWh batteries tend to be more expensive due to the advanced materials and technology required. This is a trade-off between range, charging speed, and cost. Manufacturers often provide estimated driving ranges based on different battery capacities, allowing consumers to choose the option that best suits their needs and budget.
In summary, battery capacity is a key metric in the EV world, equivalent to MPG in traditional vehicles. It determines the range an EV can achieve, the time required for charging, and the overall cost. As technology advances, we can expect to see improvements in battery capacity, leading to more efficient and practical electric vehicles.
Unleash Your Wealth: Strategies for Riding the Electric Vehicle Wave
You may want to see also

EV Efficiency Standards: Regulations setting efficiency targets for EVs, like MPG for cars
The concept of EV Efficiency Standards is crucial in the automotive industry, especially as the world shifts towards more sustainable transportation. These standards aim to regulate and set efficiency targets for electric vehicles (EVs), much like how miles per gallon (MPG) is used for traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles. The goal is to encourage manufacturers to produce EVs that are not only environmentally friendly but also cost-effective and efficient in their energy usage.
In the context of EVs, efficiency is typically measured in terms of energy consumption, often expressed as kilowatt-hours (kWh) per 100 kilometers (kWh/100km) or miles per kilowatt-hour (MPKwh). This metric provides a standardized way to compare the efficiency of different EVs, allowing consumers to make informed choices. Just as MPG gives a clear indication of a car's fuel efficiency, these EV efficiency standards offer a similar measure, ensuring transparency and consistency in the market.
Regulations setting these efficiency targets are essential to drive innovation and ensure a level playing field for EV manufacturers. Governments and regulatory bodies can set mandatory or voluntary standards that EVs must meet. For instance, a regulation might require all new EVs to achieve a certain kWh/100km rating, pushing manufacturers to invest in research and development to meet or exceed these targets. This not only benefits the environment by reducing energy consumption but also encourages the creation of more efficient and cost-effective vehicles.
Implementing such standards can have a significant impact on the EV market. It can influence consumer behavior, as buyers are increasingly conscious of the environmental and economic benefits of efficient vehicles. Additionally, it can drive competition among manufacturers, leading to the development of more advanced and efficient EV technologies. Over time, these standards can contribute to a more sustainable and efficient EV ecosystem, reducing the overall environmental impact of transportation.
In summary, EV Efficiency Standards are a vital regulatory mechanism to ensure the widespread adoption of efficient electric vehicles. By setting clear efficiency targets, these standards provide a benchmark for manufacturers, consumers, and policymakers alike. As the world moves towards a greener future, such regulations will play a pivotal role in shaping the EV market and promoting sustainable transportation solutions.
India's Electric Revolution: Strategies for a Sustainable Future
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The equivalent metric for electric vehicles (EVs) is "miles per kilowatt-hour" (MPKWh). This measurement indicates the distance an EV can travel per kilowatt-hour of electricity consumed. It provides a standardized way to compare the efficiency of different electric cars, similar to how MPG is used for internal combustion engine vehicles.
MPKWh is calculated by dividing the total distance traveled by the amount of electricity used. For example, if an EV travels 300 miles on 100 kWh of electricity, its MPKWh would be 300 / 100 = 3 MPKWh. A higher MPKWh value indicates better efficiency.
MPKWh is crucial for EV owners as it helps them understand the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of their vehicle. A higher MPKWh value means the EV can travel more miles per unit of electricity, reducing charging costs and providing a better range. This metric also allows for easier comparison of different EV models and helps in making informed decisions when purchasing an electric vehicle.