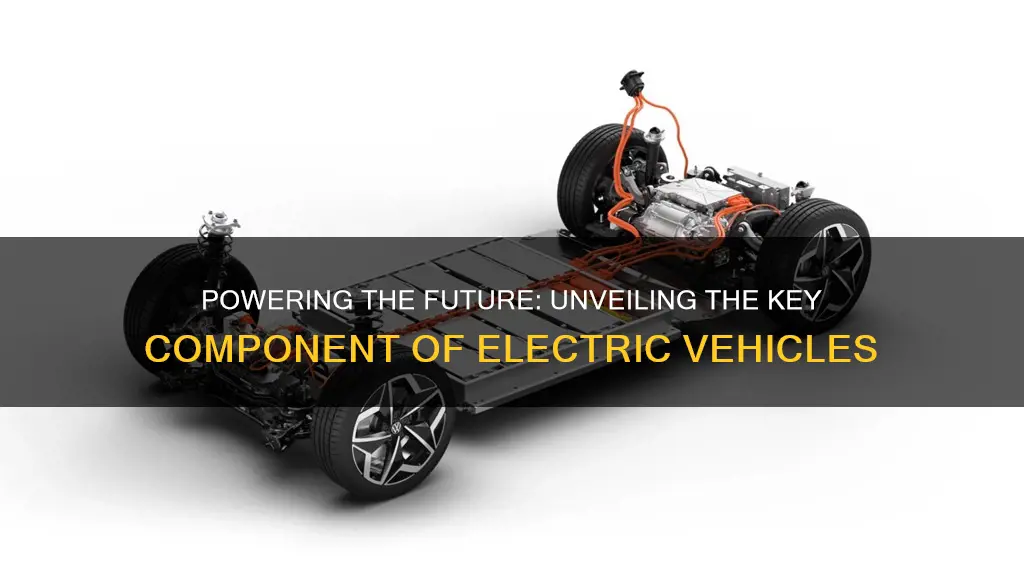
The main components of electrical vehicles (EVs) are crucial to their functionality and performance. These vehicles primarily rely on electric motors, batteries, and power electronics to operate. Electric motors convert electrical energy into mechanical energy, driving the vehicle's wheels. High-capacity batteries store the electrical energy, providing the power needed for the motor and other vehicle systems. Power electronics manage the flow of electricity between the battery, motor, and other components, ensuring efficient and safe operation. Understanding these key elements is essential for anyone interested in the technology and future of electric vehicles.
What You'll Learn
- Battery Technology: Lithium-ion batteries dominate EV power storage
- Motor Systems: Electric motors convert energy into motion
- Charging Infrastructure: Fast charging stations are essential for EV convenience
- Power Electronics: Converters manage power flow in EVs
- Energy Efficiency: Optimizing energy use extends EV range

Battery Technology: Lithium-ion batteries dominate EV power storage
The primary component that sets electric vehicles (EVs) apart from their conventional counterparts is their battery technology, specifically the use of lithium-ion batteries. These batteries have revolutionized the automotive industry and are at the heart of the EV revolution. Lithium-ion batteries have become the dominant choice for powering electric cars due to their high energy density, lightweight design, and long-lasting performance.
Lithium-ion batteries store electrical energy through a chemical reaction between lithium ions and a host material, typically a metal oxide. The key advantage of this technology is its ability to store a large amount of energy in a relatively small and lightweight package. This high energy density allows EVs to travel longer distances on a single charge compared to other battery types. The compact design of lithium-ion batteries also contributes to the overall efficiency and aesthetics of electric vehicles, making them a preferred choice for car manufacturers.
The dominance of lithium-ion batteries in EVs can be attributed to several factors. Firstly, these batteries have a low self-discharge rate, meaning they can retain their charge for extended periods when not in use. This is particularly important for EV owners who may not charge their vehicles every day. Secondly, lithium-ion batteries offer a high power-to-weight ratio, enabling rapid charging and providing the necessary power for acceleration and driving performance. The technology has also improved over the years, resulting in longer battery life, faster charging capabilities, and increased energy efficiency.
Another significant advantage of lithium-ion batteries is their ability to handle high discharge rates, which is crucial for the performance of electric vehicles. During acceleration or when driving in challenging terrain, EVs require an instant surge of power, and lithium-ion batteries can deliver this efficiently. This technology has also contributed to the development of advanced battery management systems, ensuring optimal performance, safety, and longevity of the battery pack.
Despite the dominance of lithium-ion batteries, ongoing research and development efforts are focused on improving battery technology further. Scientists and engineers are exploring ways to enhance energy density, reduce charging times, and increase the overall sustainability of battery production. The goal is to make EVs even more appealing to a wider audience by addressing range anxiety and providing a seamless charging experience. As battery technology continues to evolve, electric vehicles will become more accessible and environmentally friendly, contributing to a greener transportation future.
The EV Revolution: Federal Subsidy Expansion Act
You may want to see also

Motor Systems: Electric motors convert energy into motion
Electric vehicles (EVs) have revolutionized the automotive industry, offering an eco-friendly and efficient mode of transportation. At the heart of these vehicles lies a complex yet fascinating system: the motor system. This system is the driving force behind the motion of electric cars, buses, and various other electric vehicles.
The primary component of the motor system is the electric motor itself. These motors are designed to convert electrical energy into mechanical motion, which is then utilized to propel the vehicle forward. Electric motors have evolved significantly over the years, with advancements in technology leading to more powerful and efficient designs. The core principle behind their operation is the interaction between magnetic fields and electric currents, a concept rooted in the fundamental laws of electromagnetism.
There are several types of electric motors used in EVs, each with its own unique characteristics and advantages. One common type is the DC (Direct Current) motor, which operates on direct current and is known for its simplicity and reliability. DC motors are often used in smaller vehicles or for specific applications where high torque is required, such as in electric bicycles or scooters. Another popular motor type is the AC (Alternating Current) motor, which is more prevalent in larger electric vehicles due to its higher efficiency and ability to generate more power. AC motors are typically found in electric cars and buses, where they provide the necessary force to accelerate and maintain speed.
The operation of an electric motor involves several key components working in harmony. Firstly, the motor's stator, which is the stationary part, creates a magnetic field when an electric current passes through it. This magnetic field interacts with the rotor, the rotating part of the motor, causing it to spin. The rotor is often connected to the vehicle's drive system, which then transfers the rotational motion to the wheels, resulting in forward movement. The efficiency and power of the motor are influenced by various factors, including the design of the stator and rotor, the type of magnetic materials used, and the control systems that regulate the flow of electricity.
Motor control is a critical aspect of electric vehicle technology. Sophisticated control units are employed to manage the motor's performance, ensuring optimal efficiency and responsiveness. These control systems adjust the voltage and current supplied to the motor, allowing for precise control over speed, torque, and overall driving experience. Modern EVs often feature regenerative braking, where the motor acts as a generator, converting kinetic energy back into electrical energy, thus improving energy efficiency.
In summary, the motor system is the linchpin of electric vehicles, enabling them to transform electrical energy into the mechanical power required for motion. The electric motor, with its various types and intricate design, plays a pivotal role in this process. As technology advances, the motor systems in EVs continue to evolve, promising even more efficient and powerful electric vehicles in the future.
Unveiling the Power of EV: Electric Vehicles Explained
You may want to see also

Charging Infrastructure: Fast charging stations are essential for EV convenience
The widespread adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) has sparked a crucial discussion about the need for robust charging infrastructure, particularly fast-charging stations. These stations play a pivotal role in ensuring that EV owners can conveniently and efficiently recharge their vehicles, addressing a significant concern associated with the range anxiety often associated with EVs. Fast-charging technology has evolved to become a cornerstone of modern EV ownership, offering a solution to the challenge of long charging times, which was once a barrier to widespread EV adoption.
Fast-charging stations are designed to significantly reduce the time required to replenish an EV's battery. Traditional charging methods, while functional, can take several hours to fully charge an EV. In contrast, fast-charging stations utilize advanced technology to rapidly replenish the battery, often reducing charging times to a fraction of the time required by standard chargers. This rapid charging capability is made possible through specialized equipment and high-voltage power supplies, ensuring that EVs can be charged quickly without compromising battery health.
The convenience of fast-charging stations is a game-changer for EV owners. These stations are strategically located along major highways and in urban areas, providing EV drivers with the flexibility to plan their journeys efficiently. With fast-charging, drivers can quickly top up their batteries during pit stops, ensuring they can continue their journeys without extended downtime. This level of convenience is particularly appealing to long-distance travelers and urban commuters, who can now rely on a reliable and efficient charging network.
The development of fast-charging infrastructure has been a collaborative effort between governments, energy companies, and automotive manufacturers. This collaboration has resulted in the establishment of extensive networks of charging stations, ensuring that EV owners have access to convenient charging options wherever they are. As the demand for EVs continues to grow, the focus on expanding and improving fast-charging infrastructure will be crucial in maintaining the momentum of the EV market and ensuring a seamless transition to sustainable transportation.
In summary, fast-charging stations are integral to the widespread adoption and convenience of electric vehicles. They address the critical issue of charging time, providing EV owners with the confidence to embark on long journeys and the convenience of rapid battery replenishment. As the EV market continues to evolve, investing in and expanding fast-charging infrastructure will be essential to support the growing demand for sustainable transportation solutions.
Disney's Electric Conveyance Vehicles: A Smooth Ride Through the Magic
You may want to see also

Power Electronics: Converters manage power flow in EVs
Power electronics play a crucial role in the efficient management of power flow within electric vehicles (EVs). These devices are responsible for converting and controlling the electrical energy, ensuring optimal performance and range for the vehicle. The main component that facilitates this power management is the converter, which acts as a bridge between the various electrical systems in an EV.
In an EV, power electronics converters are used to convert the direct current (DC) from the battery into alternating current (AC) required by the motor and other accessories. This process involves several stages. Initially, the DC-DC converter steps down the high voltage from the battery pack to a level suitable for the motor. This is followed by the DC-AC inverter, which converts the DC output into AC, allowing the motor to run efficiently. The inverter also controls the speed and torque of the motor, enabling the vehicle to accelerate and decelerate smoothly.
The converters' role is to ensure that the power is efficiently transferred and utilized. They manage the flow of electricity, optimizing the use of energy and minimizing losses. This is particularly important in EVs, where energy efficiency is critical to achieving longer driving ranges. By using power electronics, the converters can rapidly adjust the voltage and frequency, allowing for quick responses to the driver's commands and ensuring a seamless driving experience.
Furthermore, these converters contribute to the overall safety and reliability of the EV. They are designed to handle high-power densities and can manage the power flow during various driving conditions. In regenerative braking, for example, the inverter converts the kinetic energy back into electrical energy, which is then stored in the battery. This process not only improves energy efficiency but also helps in maintaining the battery's health.
In summary, power electronics converters are essential in electric vehicles, managing the complex task of power flow and conversion. They enable efficient energy utilization, smooth operation, and contribute to the overall performance and safety of EVs. As technology advances, these converters continue to evolve, playing a vital role in the widespread adoption of electric mobility.
Flood-Proofing Your EV: What to Do When Water Strikes
You may want to see also

Energy Efficiency: Optimizing energy use extends EV range
The primary focus of electric vehicles (EVs) is to optimize energy efficiency, which directly impacts their range and overall performance. This is achieved through various innovative techniques and technologies that minimize energy waste and maximize the distance an EV can travel on a single charge. One key aspect is the design and management of energy flow within the vehicle.
Energy efficiency in EVs starts with the battery pack, the heart of the vehicle's power system. Modern EV batteries are designed to store and deliver energy efficiently, ensuring that every unit of electricity is utilized effectively. Advanced battery management systems monitor and control the flow of energy, optimizing charging and discharging processes to extend the vehicle's range. These systems also protect the battery from overcharging and over-discharging, which can significantly impact its performance and longevity.
Another critical component is the electric motor, which converts electrical energy into mechanical energy to propel the vehicle. High-efficiency electric motors are designed to minimize energy loss during this conversion process. They are engineered to provide optimal torque and power output while consuming the least amount of energy possible. This efficiency ensures that the vehicle can accelerate and maintain speed without wasting energy, further contributing to increased range.
Regenerative braking is a unique feature that enhances energy efficiency. When the driver applies the brakes, the electric motor reverses, acting as a generator to convert kinetic energy back into electrical energy. This energy is then stored in the battery, effectively recharging it and extending the vehicle's range. Regenerative braking not only improves energy efficiency but also reduces wear and tear on traditional braking systems, making EVs more sustainable and cost-effective.
Additionally, energy efficiency in EVs is optimized through smart driving techniques and vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technologies. Smart driving involves adopting driving patterns that minimize energy consumption, such as smooth acceleration and deceleration, maintaining a steady speed, and avoiding rapid starts and stops. V2G technology allows EVs to interact with the power grid, enabling the vehicle to supply excess energy back to the grid or absorb energy when prices are low, further optimizing energy use. These strategies collectively contribute to maximizing the range of electric vehicles, making them a viable and environmentally friendly transportation option.
Maximizing Massachusetts EV Tax Benefits: A Comprehensive Guide
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The main component in electrical vehicles is the electric motor, which is powered by a battery pack.
The battery in an EV stores electrical energy and supplies it to the motor when needed. It is typically a lithium-ion battery, known for its high energy density and ability to provide rapid charging.
The electric motor is responsible for converting electrical energy from the battery into mechanical energy, which then powers the vehicle's wheels. It provides torque and enables the car to accelerate and move.
Yes, there are various types, including AC (Alternating Current) and DC (Direct Current) motors. AC motors are commonly used due to their efficiency and ability to provide smooth power delivery.
The charging system in an EV involves a charger that connects to the vehicle's battery. It converts AC power from an external source (like a wall outlet or charging station) into DC power, which is then used to recharge the battery.







