The quest for the most efficient electric vehicle (EV) is a fascinating journey into the future of sustainable transportation. With the rapid advancements in technology, the automotive industry is witnessing a revolution in electric mobility. The most efficient EVs are not just about speed or range; they are a harmonious blend of cutting-edge engineering and environmental consciousness. These vehicles are designed to minimize energy waste, maximize performance, and reduce the carbon footprint, making them a key player in the global shift towards greener transportation solutions. This exploration delves into the factors that contribute to the efficiency of electric cars, from battery technology to aerodynamic design, and highlights the models that are leading the way in this exciting new era of automotive innovation.
What You'll Learn
- Battery Technology: Innovations in battery chemistry and design for higher energy density and faster charging
- Motor Efficiency: Advanced electric motors with improved power-to-weight ratios and reduced energy losses
- Aerodynamics: Streamlined body designs to minimize drag and enhance overall efficiency
- Lightweight Materials: Use of advanced materials to reduce vehicle weight without compromising strength
- Regenerative Braking: Systems that convert kinetic energy back into usable power during braking

Battery Technology: Innovations in battery chemistry and design for higher energy density and faster charging
The quest for more efficient electric vehicles (EVs) has led to significant advancements in battery technology, focusing on two critical aspects: energy density and charging speed. These innovations are crucial in addressing the range anxiety and long charging times associated with early EVs, thus making electric vehicles more practical and appealing to a broader audience.
Energy Density Innovations:
Battery chemistry plays a pivotal role in determining energy density. Researchers and engineers are exploring various avenues to increase the energy stored in a given volume or weight. One of the most promising developments is the use of lithium-ion batteries with advanced cathode materials. For instance, nickel-rich cathodes, such as NMC 811 (Niobium-Manganese-Cobalt 811), offer higher energy densities compared to traditional lithium-cobalt or lithium-manganese oxides. These materials can store more lithium ions, leading to increased capacity and, consequently, longer driving ranges. Another approach is the development of solid-state batteries, which replace the liquid electrolyte with a solid conductive material. This innovation has the potential to double the energy density of lithium-ion batteries, making it a highly attractive solution for future EVs.
Faster Charging Through Design Innovations:
Improving charging speed involves both battery design and charging infrastructure. Battery manufacturers are working on enhancing the internal structure of batteries to facilitate faster ion movement. This includes the use of nanostructured electrodes, which provide a larger surface area for electrochemical reactions, thus reducing charging times. Additionally, the development of solid-state electrolytes, as mentioned earlier, can significantly improve ion conductivity, enabling quicker charging. On the charging infrastructure side, innovations like wireless charging and high-power charging stations are being developed to support the rapid charging of EVs. Wireless charging technology, for example, eliminates the need for physical connectors, making the charging process more convenient and potentially faster.
Furthermore, the integration of advanced battery management systems (BMS) is crucial. These systems monitor and control the charging and discharging processes, ensuring optimal performance and safety. By optimizing the BMS, EVs can charge more efficiently, distribute power more effectively, and extend the lifespan of the battery.
In summary, the continuous innovation in battery chemistry and design is driving the electric vehicle industry forward. Higher energy density batteries and faster-charging technologies are making EVs more efficient, convenient, and competitive with traditional internal combustion engine vehicles. As these advancements continue, we can expect to see a more widespread adoption of electric vehicles, contributing to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly transportation future.
Is Toyota CH-R an Electric Vehicle? Unveiling the Truth
You may want to see also

Motor Efficiency: Advanced electric motors with improved power-to-weight ratios and reduced energy losses
The quest for the most efficient electric vehicle (EV) is an ongoing journey, and at the heart of this pursuit lies the electric motor, a critical component that directly influences a vehicle's performance and efficiency. Modern advancements in motor technology have led to significant improvements in power-to-weight ratios and energy efficiency, making electric vehicles more competitive and appealing to a wider audience.
One of the key focuses in motor efficiency is the development of advanced electric motors that offer higher power output while maintaining a lightweight design. This is achieved through innovative engineering techniques such as optimizing the motor's geometry, using advanced materials, and implementing sophisticated cooling systems. By reducing the weight of the motor without compromising its performance, engineers can enhance the overall power-to-weight ratio, resulting in more agile and responsive electric vehicles. This is particularly important in high-performance EVs, where acceleration and handling are crucial.
Reducing energy losses is another critical aspect of motor efficiency. Traditional electric motors often suffer from energy inefficiencies due to factors like resistance in the windings, core losses, and mechanical friction. Engineers are tackling these issues by employing advanced materials such as silicon carbide (SiC) and gallium nitride (GaN) for power electronics, which offer lower resistance and higher thermal conductivity. Additionally, improved motor control algorithms and precision manufacturing techniques minimize energy wastage, ensuring that more of the electrical energy is converted into useful mechanical power.
The benefits of these advancements in motor efficiency are far-reaching. Firstly, they contribute to extended driving ranges, a critical factor for potential EV buyers. With improved power-to-weight ratios, electric vehicles can accelerate faster and maintain higher speeds without depleting their battery reserves. Secondly, reduced energy losses lead to more efficient power usage, allowing for longer periods of operation between charges. This is especially advantageous for long-distance travel and daily commutes.
Furthermore, the development of advanced electric motors with enhanced efficiency has a positive environmental impact. By optimizing power output and reducing energy losses, these motors contribute to lower electricity consumption, thereby decreasing the carbon footprint associated with EV ownership. This is a crucial aspect as the world shifts towards more sustainable transportation options. In summary, the continuous improvement of motor efficiency in electric vehicles is driving the industry forward, making EVs more powerful, responsive, and environmentally friendly.
Firefighting Tips: Battling Electric Vehicle Blazes
You may want to see also

Aerodynamics: Streamlined body designs to minimize drag and enhance overall efficiency
The pursuit of efficiency in electric vehicles (EVs) is a multifaceted endeavor, and one of the most critical aspects is aerodynamics. Aerodynamic design plays a pivotal role in reducing drag, which is the force that opposes the motion of an object as it moves through a fluid, in this case, air. For EVs, minimizing drag is essential to improving overall efficiency, range, and performance.
A streamlined body is the cornerstone of aerodynamic efficiency. The shape of the vehicle's exterior significantly influences how air flows around it. Designers aim to create a sleek, curved silhouette that smoothly deflects air, reducing turbulence and drag. This involves careful consideration of the vehicle's front end, sides, and rear, ensuring that each component contributes to a seamless airflow. For instance, the front of the vehicle should have a low, smooth hood that angles down towards the ground, reducing the pressure on the air as it moves over the surface. The sides can feature gently sloping surfaces that guide air efficiently, while the rear should have a sloping or curved design to smoothly transition the airflow over the vehicle's top and into the wake.
One of the key principles in aerodynamic design is the concept of a 'drag coefficient.' This coefficient quantifies the aerodynamic efficiency of a vehicle, with lower values indicating better performance. Designers strive to minimize this coefficient by employing various techniques. One such technique is the use of air curtains or air dams at the front of the vehicle, which help manage airflow and reduce drag. Additionally, incorporating underbody panels and diffusers at the rear can further optimize airflow, ensuring that the air exits the vehicle smoothly and efficiently.
Another critical aspect of aerodynamics is the design of the vehicle's interior. The placement of components and the overall layout can impact airflow and, consequently, efficiency. For example, positioning the battery pack in a way that minimizes air resistance and optimizes cooling is essential. Similarly, the arrangement of the interior components, such as the seats and dashboard, should be designed to allow airflow through the vehicle, reducing the overall drag.
In the quest for efficiency, EV manufacturers are pushing the boundaries of aerodynamic design. This includes the use of advanced materials and manufacturing processes to create lightweight, yet sturdy, bodies. The development of active aerodynamics, such as adjustable spoilers or air-suspended systems, further enhances the vehicle's ability to adapt to different driving conditions and optimize performance. By combining these innovative design approaches, electric vehicles can achieve remarkable efficiency, making them more environmentally friendly and economically viable for consumers.
Understanding Range: The Key to Electric Vehicle Ownership
You may want to see also

Lightweight Materials: Use of advanced materials to reduce vehicle weight without compromising strength
The pursuit of efficiency in electric vehicles (EVs) has led to a critical focus on reducing weight while maintaining structural integrity, and this is where the concept of lightweight materials comes into play. Advanced materials are being utilized across the automotive industry to achieve this delicate balance, ensuring that EVs are not only more efficient but also safer and more sustainable.
One of the key materials making a significant impact is carbon fiber. This material is renowned for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, making it an ideal choice for structural components in EVs. Carbon fiber composites can replace traditional steel or aluminum in body panels, chassis, and even in the construction of the vehicle's frame. By using carbon fiber, manufacturers can significantly reduce the overall weight of the vehicle, which directly translates to improved energy efficiency. For instance, the Tesla Model S, known for its lightweight design, utilizes carbon fiber in its body structure, contributing to its impressive acceleration and handling capabilities.
Another innovative material making waves in the EV market is high-strength steel alloys. These alloys offer a combination of lightweight properties and excellent structural integrity. Automotive engineers are increasingly using these alloys to reinforce critical areas of the vehicle, such as the chassis and underbody, without adding excessive weight. This approach ensures that the vehicle maintains its strength and safety standards while benefiting from reduced weight.
The use of lightweight materials also extends to the interior of the vehicle. Advanced polymers and composites are being employed to create lightweight seats, dashboards, and other interior components. These materials not only reduce weight but also offer improved comfort and aesthetics. For example, some EV manufacturers are using lightweight foam materials for seats, which provide better support and reduce the overall weight of the vehicle, thereby improving its efficiency.
Furthermore, the development of lightweight batteries is another crucial aspect of achieving efficiency in EVs. Researchers are exploring the use of advanced materials like silicon and graphene in battery electrodes to increase energy density while reducing weight. This innovation is vital for extending the range of electric vehicles and making them more competitive with traditional internal combustion engine cars.
In summary, the integration of lightweight materials in electric vehicles is a strategic approach to enhance efficiency. By employing advanced materials such as carbon fiber, high-strength steel alloys, and innovative polymers, manufacturers can significantly reduce vehicle weight without sacrificing safety and performance. This focus on lightweight design is a key differentiator in the EV market, contributing to the overall success and appeal of electric vehicles.
India's Electric Revolution: Is the Future Green?
You may want to see also

Regenerative Braking: Systems that convert kinetic energy back into usable power during braking
Regenerative braking is a revolutionary technology that plays a pivotal role in enhancing the efficiency of electric vehicles (EVs). This innovative system harnesses the kinetic energy that would otherwise be lost during the braking process and transforms it into usable electrical power, contributing to the overall efficiency and range of the vehicle.
When an EV's brakes are applied, the regenerative braking system springs into action. Instead of dissipating the vehicle's kinetic energy as heat, as traditional friction brakes do, this system captures and converts it. The process begins with the rotation of the wheels, which turns the electric motor in generator mode. This motor acts as a generator, converting the mechanical energy of the moving vehicle into electrical energy. The electrical energy is then directed back to the vehicle's battery pack, recharging it and extending the driving range.
The efficiency of regenerative braking is particularly notable during frequent stop-and-go driving, such as in city traffic. In these scenarios, the system can significantly reduce the energy lost during braking and provide a more seamless driving experience. By actively managing the flow of energy, regenerative braking systems can improve the overall efficiency of the vehicle, often resulting in a reduction of energy consumption and an increase in the distance the vehicle can travel on a single charge.
This technology is a key differentiator for electric vehicles, offering a practical solution to the challenge of maximizing efficiency and range. It not only contributes to the environmental benefits of EVs by reducing energy waste but also provides a more responsive and dynamic driving experience. As the demand for efficient transportation continues to grow, regenerative braking systems are becoming increasingly important, shaping the future of sustainable mobility.
In summary, regenerative braking is a sophisticated mechanism that transforms the way electric vehicles operate, making them more efficient and environmentally friendly. By capturing and reusing kinetic energy, this system contributes to the overall performance and sustainability of EVs, making them a more attractive and viable option for eco-conscious consumers.
Electric Revolution: A Global Shift Towards Sustainable Driving?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The most efficient electric vehicle as of 2023 is a subject of ongoing debate and depends on various factors such as driving conditions, battery technology, and vehicle specifications. However, the Lucid Air Dream Edition is often cited as a top contender. It boasts an EPA-estimated range of up to 520 miles on a single charge and an impressive efficiency of 0.21 kWh/mile, making it one of the most efficient EVs in terms of energy consumption.
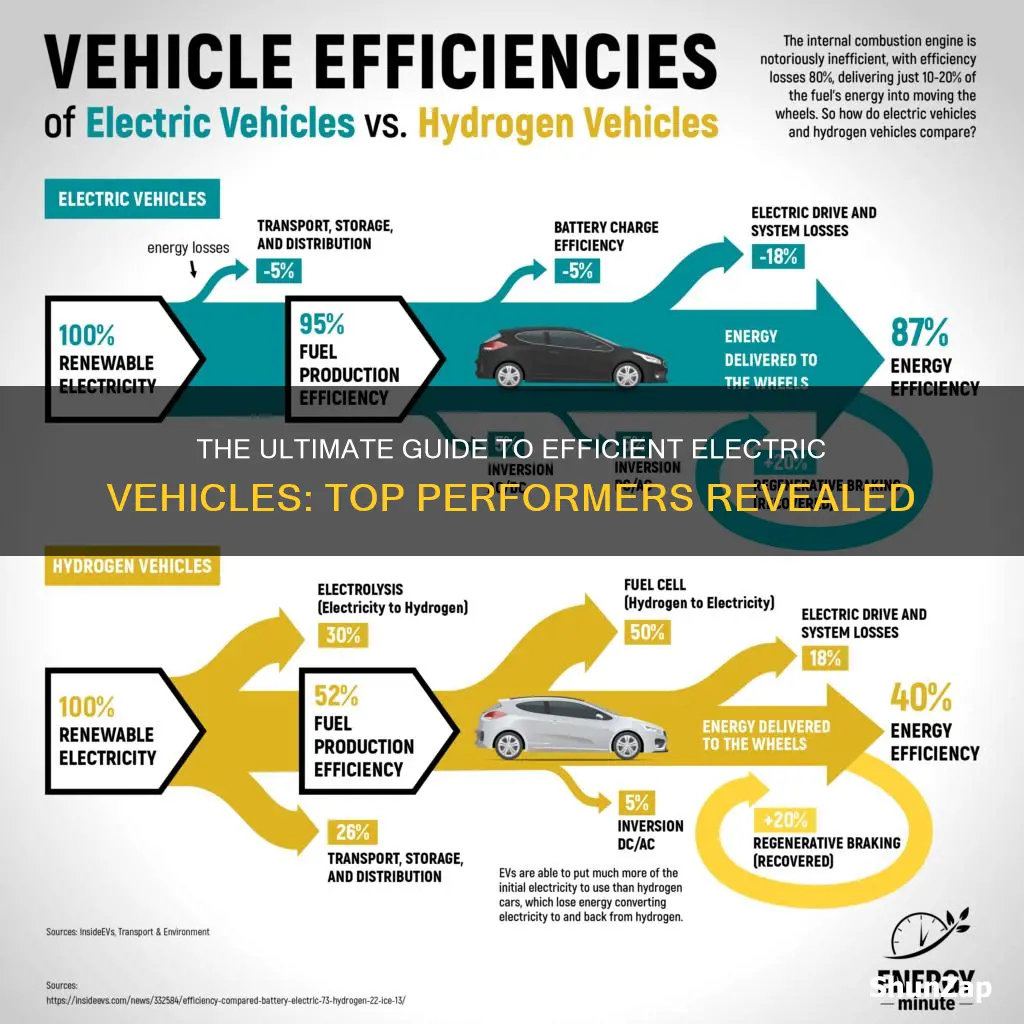
Electric vehicles achieve high efficiency due to their direct conversion of electrical energy into mechanical power. Unlike internal combustion engines, EVs have fewer moving parts, resulting in less energy loss. Additionally, advanced battery technology and efficient power electronics play a significant role. Regenerative braking, a feature common in EVs, captures and stores kinetic energy, further enhancing overall efficiency.
Yes, electric cars are generally more efficient than traditional gasoline vehicles. On average, EVs have a higher energy efficiency of around 77% compared to internal combustion engines, which typically have efficiencies between 15-30%. This means that EVs convert a larger portion of the energy stored in their batteries into actual driving power, resulting in reduced energy consumption and lower operating costs.







