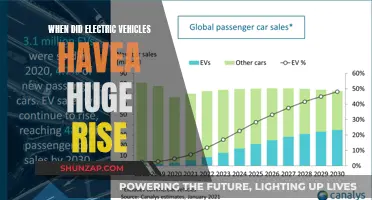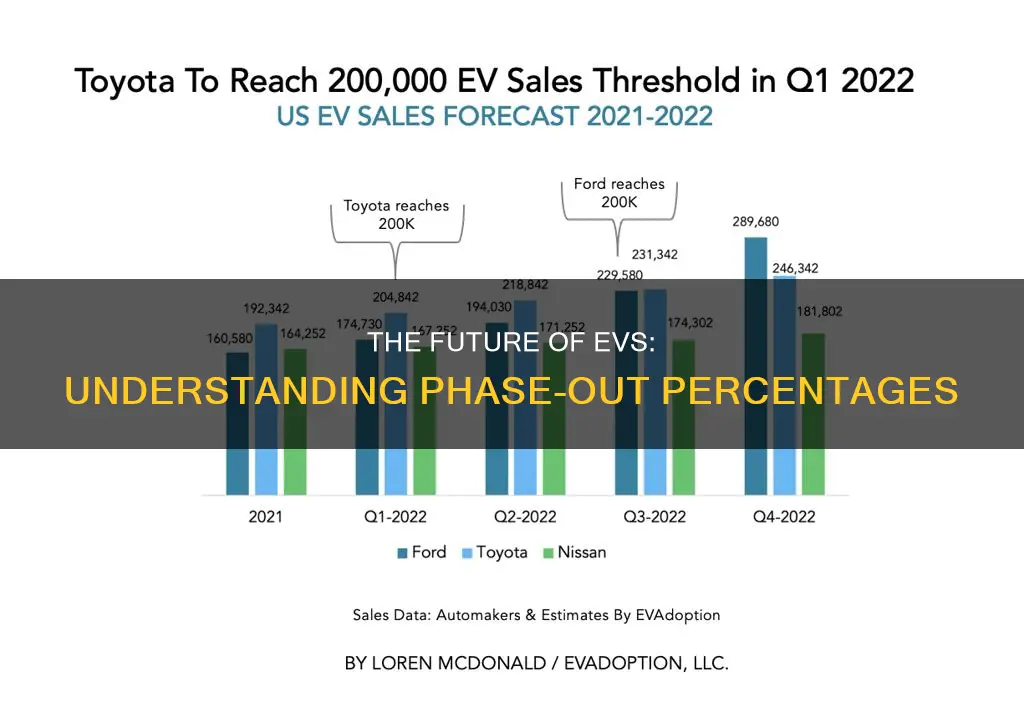
The phase-out percentage for electric vehicles (EVs) is a critical aspect of the global transition to sustainable transportation. This percentage refers to the gradual reduction in the production and sale of traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles in favor of EVs. The phase-out is designed to incentivize the adoption of cleaner, more environmentally friendly vehicles by gradually reducing the availability of older, less efficient models. This strategy aims to accelerate the shift towards a greener automotive industry, reduce greenhouse gas emissions, and promote technological advancements in the EV sector. Understanding the phase-out percentage is essential for policymakers, manufacturers, and consumers alike, as it influences the pace of the automotive industry's transformation and the future of sustainable transportation.
What You'll Learn
- Tax Incentives: Government subsidies and tax credits for EV buyers
- Battery Technology: Advancements in battery tech impact range and phase-out
- Charging Infrastructure: Availability of charging stations affects EV adoption
- Market Demand: Consumer preferences and trends influence phase-out timing
- Environmental Regulations: Stringent emissions standards may impact EV phase-out

Tax Incentives: Government subsidies and tax credits for EV buyers
The adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) has been significantly boosted by various government incentives worldwide, with tax incentives playing a pivotal role in this regard. These incentives are designed to encourage consumers to make the switch from traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles to more environmentally friendly electric alternatives. One of the most common forms of tax incentives for EV buyers is the direct subsidy provided by governments. These subsidies can take the form of cash grants or direct reductions in the purchase price of the vehicle. For instance, many countries offer a fixed amount per EV sold, which can significantly lower the upfront cost for consumers. These subsidies are often targeted at specific EV models or manufacturers, encouraging a diverse range of electric vehicles to enter the market.
In addition to direct subsidies, tax credits are another powerful tool in the government's arsenal to promote EV adoption. Tax credits provide a dollar-for-dollar reduction in the buyer's taxable income, effectively lowering the overall cost of the vehicle purchase. This incentive is particularly attractive as it can be combined with other purchase incentives, such as manufacturer rebates or lease offers. For example, a government might offer a tax credit of up to $7,500 for the purchase of an electric vehicle, which can be claimed in the year of purchase. This credit not only reduces the immediate financial burden but also provides a long-term benefit by lowering the vehicle's effective cost of ownership.
The phase-out percentage for these tax incentives is a critical aspect that EV buyers should be aware of. This percentage determines the rate at which the incentive value decreases over time. For instance, a government might introduce a tax credit of $10,000 for the first year of EV sales, but this amount could be reduced to $5,000 in the second year, and further phased out in subsequent years. This phase-out is often a strategic move to encourage early adoption and stimulate the market in the initial stages. As the market matures and more EVs are sold, the incentive is gradually reduced to ensure a steady and controlled growth rate.
Understanding the phase-out schedule is essential for potential EV buyers as it directly impacts the final cost-effectiveness of the purchase. Buyers should be aware that the higher the phase-out percentage, the sooner the incentive value diminishes. This knowledge can influence purchasing decisions, especially for those considering buying an EV in the near future. Moreover, it encourages buyers to act promptly to take advantage of the full incentive amount before it is phased out.
In summary, tax incentives, including government subsidies and tax credits, are powerful tools to accelerate the adoption of electric vehicles. These incentives not only make EVs more affordable but also provide long-term financial benefits to buyers. Being aware of the phase-out percentages for these incentives is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions, ensuring that consumers maximize their savings when transitioning to electric mobility.
Unlocking Savings: California's EV Tax Credit Explained
You may want to see also

Battery Technology: Advancements in battery tech impact range and phase-out
The evolution of battery technology is a critical aspect of the electric vehicle (EV) industry, significantly influencing the range and performance of these vehicles. Over the years, advancements in battery technology have played a pivotal role in addressing the primary concern of consumers: the range anxiety associated with EVs. The continuous development of battery systems has led to increased energy density, improved charging speeds, and extended vehicle ranges, making electric cars more practical and appealing to a broader audience.
One of the key advancements in battery technology is the development of lithium-ion batteries, which have become the standard for EVs due to their high energy density and relatively low cost. These batteries have enabled vehicles to travel longer distances on a single charge, addressing the range limitations of earlier electric cars. For instance, the introduction of advanced lithium-ion batteries in the Tesla Model S has allowed it to achieve impressive ranges, with some variants capable of traveling over 400 miles on a single charge. This significant improvement in range has been a major factor in the growing popularity of EVs.
In addition to increased range, advancements in battery technology have also led to faster charging times. Traditional lithium-ion batteries have been enhanced with features like improved electrolyte compositions and innovative cell designs, allowing for quicker charging without compromising battery health. This development is crucial for EV owners, as it reduces the time spent waiting for a charge, making the overall ownership experience more convenient.
The impact of these advancements is also felt in the context of government incentives and phase-out percentages for EVs. As battery technology improves, governments are becoming more inclined to provide incentives for EV adoption, knowing that the vehicles are becoming more viable and competitive with traditional gasoline cars. This, in turn, can lead to a faster phase-out of internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles, as the market gradually shifts towards electric alternatives. The phase-out percentage, which refers to the proportion of ICE vehicles being replaced by EVs, is likely to increase as battery technology continues to advance, making electric cars more efficient, affordable, and desirable.
Furthermore, the continuous improvement in battery technology is driving innovation in other areas of EV development. For example, advancements in battery management systems (BMS) are enabling more precise monitoring and control of battery performance, ensuring optimal charging and discharging cycles. This not only extends the battery's lifespan but also contributes to the overall safety and reliability of EVs. As a result, the phase-out of ICE vehicles is likely to accelerate, with governments and consumers increasingly favoring electric alternatives.
Electric Vehicles: Powering the Future, But at What Cost?
You may want to see also

Charging Infrastructure: Availability of charging stations affects EV adoption
The availability of charging infrastructure is a critical factor in the widespread adoption of electric vehicles (EVs). As the number of EVs on the road increases, the demand for convenient and accessible charging stations becomes more pronounced. Insufficient charging infrastructure can lead to range anxiety, a significant concern for potential EV buyers, and may hinder the growth of the EV market.
In many regions, the development of charging networks has been a gradual process, often lagging behind the sales of EVs. This disparity can create challenges for EV owners, especially those living in urban areas with limited parking options or those who frequently travel long distances. The lack of nearby charging stations can result in prolonged waiting times or the need to plan charging stops in advance, impacting the overall convenience and appeal of EV ownership.
To address this issue, governments and private entities are investing in the expansion of charging networks. This includes the installation of fast-charging stations along highways and in strategic locations, such as shopping centers and office parks. Fast-charging technology significantly reduces charging times, making it more feasible for EV owners to embark on longer journeys without the fear of running out of battery. Additionally, the integration of smart charging systems allows for more efficient energy distribution and can help manage peak demand periods.
The development of charging infrastructure also presents opportunities for innovation and entrepreneurship. Companies are developing mobile apps that provide real-time information on charging station locations, availability, and prices. These apps enable EV owners to plan their routes more efficiently and locate the nearest charging station when needed. Furthermore, the rise of home charging solutions, such as wall-mounted charging points, allows individuals to charge their vehicles overnight or during periods of low energy demand, ensuring a convenient and cost-effective charging experience.
In summary, the availability of charging stations is a key enabler for EV adoption. As the EV market continues to grow, the focus on expanding and improving charging infrastructure will be essential to address range anxiety and ensure a seamless driving experience. This includes a combination of fast-charging stations, smart grid integration, and innovative solutions that cater to the diverse needs of EV owners. By investing in comprehensive charging networks, societies can accelerate the transition to sustainable transportation and reduce the environmental impact of the transportation sector.
Electric Vehicles: Government Mandates or Consumer Choice?
You may want to see also

Market Demand: Consumer preferences and trends influence phase-out timing
The market demand for electric vehicles (EVs) is a critical factor in determining the phase-out percentage and the overall success of the EV transition. Consumer preferences and trends play a pivotal role in shaping the automotive industry's future, especially as governments and industries worldwide aim to reduce carbon emissions and promote sustainable transportation.
Consumer preferences are increasingly favoring electric and hybrid vehicles over traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) cars. This shift in preference is driven by several factors. Firstly, environmental consciousness is on the rise, with many consumers actively seeking eco-friendly alternatives to reduce their carbon footprint. EVs, being zero-emission vehicles, align with this growing trend. Secondly, technological advancements have improved the performance, range, and charging infrastructure for EVs, addressing previous concerns about limited driving range and long charging times. As a result, consumers are more confident in the practicality and reliability of electric vehicles.
Market trends indicate a rapid growth in the demand for EVs. This is evident in the increasing sales and production numbers of electric cars, which have seen a significant surge in recent years. Consumers are not only opting for EVs but also showing a willingness to invest in premium models, challenging the notion that electric vehicles are solely budget-friendly options. This trend suggests that as consumer awareness and acceptance grow, the market is moving towards a more diverse and competitive EV landscape.
The influence of consumer trends on phase-out timing is profound. As the demand for EVs rises, governments and automotive manufacturers are more inclined to accelerate the phase-out of ICE vehicles. This strategic move not only aligns with environmental goals but also captures a growing market share. For instance, many countries have set ambitious targets to phase out fossil fuel-based vehicles by a specific deadline, pushing manufacturers to invest in EV technology and infrastructure.
Additionally, consumer preferences can drive the development of innovative features and technologies in EVs. Trends such as autonomous driving, advanced infotainment systems, and improved battery efficiency are all influenced by consumer demand. This, in turn, encourages manufacturers to invest in research and development, ensuring that electric vehicles remain competitive and appealing to a wide range of consumers.
In summary, market demand, driven by consumer preferences and trends, is a powerful force shaping the phase-out percentage for electric vehicles. As consumers increasingly embrace eco-friendly and technologically advanced EVs, the automotive industry is compelled to adapt and accelerate the transition away from traditional ICE vehicles. This dynamic relationship between consumer behavior and market trends will play a crucial role in determining the success and timing of the global shift towards sustainable transportation.
The Future of Driving: Electric Revolution in the Automotive Industry
You may want to see also

Environmental Regulations: Stringent emissions standards may impact EV phase-out
The phase-out percentage for electric vehicles (EVs) is a critical aspect of environmental regulations and the broader push towards sustainable transportation. As governments worldwide strive to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and improve air quality, they are implementing stringent emissions standards that directly impact the adoption and phase-out of EVs. These regulations are designed to accelerate the transition from conventional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles to zero-emission electric powertrains.
Stringent emissions standards often set strict limits on the allowable emissions of pollutants, such as nitrogen oxides (NOx), particulate matter (PM), and volatile organic compounds (VOCs). For ICE vehicles, these standards can be challenging to meet, especially as engine technology ages and becomes less efficient. In contrast, EVs produce zero tailpipe emissions, making them an attractive solution to meet these regulations. However, the phase-out of EVs is not without its complexities.
One of the primary considerations is the impact of emissions standards on the automotive industry's production and sales strategies. Manufacturers may need to invest in new technologies and infrastructure to comply with these regulations, which can be costly and time-consuming. As a result, some companies might opt to phase out older, less efficient ICE vehicles, potentially affecting the market availability of these models. This phase-out process can influence the overall sales and adoption rates of EVs, as consumers may be hesitant to purchase vehicles that are soon to be phased out.
Environmental regulations also play a role in the development and deployment of EV charging infrastructure. Governments may incentivize the installation of charging stations in public spaces and residential areas to support the growing EV market. However, the phase-out of ICE vehicles could lead to a rapid increase in EV demand, straining the existing charging network. This situation highlights the need for strategic planning and investment in charging infrastructure to ensure a smooth transition to a fully electric transportation system.
In summary, stringent emissions standards are driving the phase-out of electric vehicles, but this process is not without challenges. Balancing the environmental benefits of EVs with the potential market disruptions caused by phasing out ICE vehicles is crucial. Effective environmental regulations should consider the entire lifecycle of vehicles, from production to end-of-life management, ensuring a sustainable and well-managed transition to a greener transportation future.
EV Battery End-of-Life: Recycling, Disposal, and Second Life Potential
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The term "phase-out percentage" is not commonly used in the context of electric vehicles (EVs). However, it could refer to the gradual reduction or elimination of incentives or subsidies for EVs as part of a government's policy to encourage the adoption of cleaner energy sources. This process is often called "phase-out" or "sunsetting" of incentives. The percentage might indicate the reduction rate of these incentives over time, typically ranging from 10% to 50% annually, depending on the region and the specific EV model.
The phase-out of incentives can impact EV buyers in several ways. Firstly, it may lead to a decrease in the overall cost of purchasing an EV, making it more affordable for consumers. Secondly, buyers might need to act quickly to take advantage of the remaining incentives before they are completely removed. This could create a sense of urgency in the market, potentially boosting sales. However, it may also result in a temporary shortage of certain EV models as manufacturers adjust their production strategies.
Yes, the criteria for phasing out EV incentives can vary widely. Governments often set sales targets or time limits for the incentives. For instance, an incentive might be available for a certain number of units sold or for a specific duration. Once these criteria are met, the incentive is phased out. Additionally, some regions may have different phase-out schedules for various EV categories, such as passenger cars, commercial vehicles, or specific battery sizes.
A phased-out incentive policy can have several advantages. It encourages consumers to make a timely purchase, which can stimulate the market and potentially reduce the waiting time for EV models. This approach also allows governments to manage the allocation of incentives effectively, ensuring that financial support is directed to those who need it most. Moreover, it may create a sense of urgency and competition among buyers, driving innovation and market growth.
Staying informed about EV incentive phase-outs is crucial for potential buyers. Consumers can monitor government websites, automotive forums, and industry news sources for official announcements and updates. Many countries have dedicated portals or databases that provide real-time information on available incentives, their eligibility criteria, and the remaining budget. Additionally, automotive manufacturers and dealers often have resources to inform customers about upcoming changes in incentives and their potential impact on vehicle pricing.