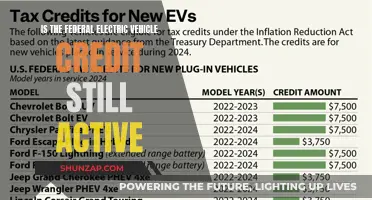
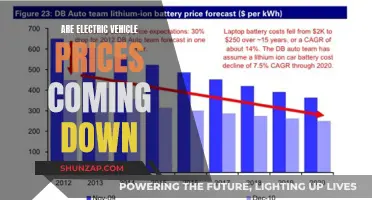
The quest for the safest electric vehicle (EV) is a critical aspect of the automotive industry's evolution towards sustainable transportation. With the rise in popularity of EVs, ensuring their safety has become a paramount concern for manufacturers and consumers alike. The safest EV is a complex topic, as it encompasses various factors such as crash safety, battery integrity, and overall reliability. This paragraph will explore the key considerations and innovations that contribute to the safety of electric vehicles, highlighting the importance of rigorous testing, advanced safety features, and the continuous efforts of manufacturers to enhance the protection of their EV models.
What You'll Learn
- Battery Safety: Advanced battery designs and cooling systems ensure thermal stability and prevent overheating
- Crash Protection: Advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) enhance safety with collision avoidance and autonomous emergency braking
- Fire Prevention: Fire-resistant materials and battery designs minimize fire risks and protect against thermal runaway
- Driver Assistance: Features like lane-keeping assist and adaptive cruise control improve overall safety and driver confidence
- Regulatory Compliance: Adherence to strict safety standards and regulations ensures vehicles meet or exceed industry safety benchmarks

Battery Safety: Advanced battery designs and cooling systems ensure thermal stability and prevent overheating
The safety of electric vehicles (EVs) is a critical aspect that has been a focus of extensive research and development in the automotive industry. One of the key areas of innovation is battery safety, which is essential to ensure the overall reliability and longevity of EVs. Modern electric vehicle batteries are designed with advanced safety features to prevent overheating, thermal runaway, and other potential hazards.
Advanced battery designs play a pivotal role in maintaining thermal stability. These designs often incorporate multiple layers of protection, such as protective casings and separators, to prevent direct contact between the battery cells and external elements. For instance, lithium-ion batteries, commonly used in EVs, are equipped with thin polymer separators that allow ions to pass through while preventing electrical contact between the anode and cathode, thus inhibiting short circuits. Additionally, battery manufacturers employ sophisticated cooling systems to regulate temperature. These cooling systems can include liquid cooling, where a coolant circulates through the battery pack to absorb heat, or advanced air-cooling mechanisms that promote efficient heat dissipation.
Overheating is a significant concern in EV batteries, as it can lead to performance degradation and, in extreme cases, thermal runaway. To mitigate this risk, engineers have developed innovative cooling techniques. One such method is the use of phase-change materials, which absorb and release heat during phase transitions, providing a stable temperature environment for the battery. Another approach involves implementing micro-channel cooling, where coolant flows through tiny channels within the battery pack, ensuring rapid and efficient heat dissipation. These cooling systems are designed to maintain optimal operating temperatures, even during high-demand driving conditions.
Furthermore, battery management systems (BMS) play a crucial role in battery safety. BMS continuously monitors the battery's temperature, voltage, and current, allowing for real-time adjustments to optimize performance and safety. If the battery temperature exceeds a certain threshold, the BMS can activate cooling mechanisms or even temporarily shut down the battery to prevent damage. This proactive approach ensures that the battery operates within safe parameters, extending its lifespan and enhancing overall safety.
In summary, the safety of electric vehicles is significantly enhanced through advanced battery designs and cooling systems. These innovations work in tandem to maintain thermal stability, prevent overheating, and mitigate the risks associated with thermal runaway. As the EV market continues to grow, ongoing research and development in battery technology will further improve safety standards, making electric vehicles an even more attractive and reliable transportation option.
Porsche's Electric Future: Rebate Eligibility Explained
You may want to see also

Crash Protection: Advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) enhance safety with collision avoidance and autonomous emergency braking
The evolution of electric vehicles (EVs) has brought a revolution in the automotive industry, and with it, a heightened focus on safety. Among the myriad of features that contribute to the safety of these vehicles, Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) play a pivotal role, especially in crash protection. ADAS is a suite of technologies designed to assist and enhance the capabilities of drivers, ultimately reducing the risk of accidents and improving overall road safety.
One of the key ADAS features is collision avoidance, which employs various sensors and cameras to monitor the vehicle's surroundings. These sensors can detect obstacles, pedestrians, and other vehicles, providing the driver with valuable time to react and avoid potential collisions. For instance, when the system detects an impending collision with a vehicle in front, it can automatically apply the brakes to prevent or mitigate the impact. This technology is particularly useful in congested traffic conditions or when driving in poor weather, where human reaction time might be slower.
Autonomous emergency braking is another critical component of ADAS, designed to complement the driver's actions. This system uses sensors to detect and respond to obstacles, and if the driver doesn't take evasive action, it can apply the brakes to bring the vehicle to a stop. The effectiveness of this feature is evident in scenarios where a sudden obstacle appears in the road, and the driver might not have the reaction time to brake in time. By automatically initiating braking, the system significantly reduces the risk of rear-end collisions and potential injuries.
The combination of collision avoidance and autonomous emergency braking provides a robust safety net for drivers. These ADAS features not only help prevent accidents but also assist in reducing the severity of crashes. In the event of an unavoidable collision, the systems can automatically engage the brakes, potentially minimizing the impact speed and, consequently, the risk of serious injury to occupants.
Furthermore, the continuous development of ADAS technology ensures that electric vehicles are becoming increasingly safer over time. Manufacturers are constantly updating and improving these systems, incorporating new sensors and algorithms to enhance their performance. As a result, drivers can have increased confidence in the safety features of their electric vehicles, knowing that they are equipped with the latest advancements in crash protection.
Green Machines: Uncovering the Environmental Trade-offs of Electric Vehicles
You may want to see also

Fire Prevention: Fire-resistant materials and battery designs minimize fire risks and protect against thermal runaway
The safety of electric vehicles (EVs) is a critical aspect that has gained significant attention, especially regarding fire prevention. One of the key strategies employed by manufacturers to ensure the safety of EVs is the use of fire-resistant materials and innovative battery designs. These measures are crucial in minimizing fire risks and protecting against thermal runaway, a potentially catastrophic event where a battery overheats and releases flammable gases, leading to a fire.
Fire-resistant materials play a pivotal role in the construction of EVs. These materials are carefully selected to withstand high temperatures and prevent the spread of flames. For instance, the use of fire-resistant panels and coatings in the vehicle's interior helps create a barrier between the battery and potential ignition sources. This is particularly important in the event of a collision, where the risk of fire is higher due to the increased likelihood of damage to the battery pack. By utilizing these materials, manufacturers aim to delay the onset of a fire and provide occupants with more time to escape.
Battery design is another critical factor in fire prevention. Modern EVs employ advanced battery management systems that monitor temperature and voltage levels in real-time. These systems can detect early signs of thermal stress and initiate protective measures, such as reducing charging rates or activating cooling mechanisms. In the event of a potential thermal runaway, the battery management system can activate safety mechanisms, including the release of pressure or the injection of inert gases to suppress flames. This proactive approach significantly reduces the chances of a fire occurring.
Furthermore, advancements in battery chemistry and design have led to the development of safer, more stable battery cells. These cells are engineered to operate within a narrow temperature range, reducing the likelihood of overheating. Additionally, improved battery cooling systems, such as liquid cooling, help maintain optimal temperatures and prevent the buildup of heat. By combining these design elements, EV manufacturers aim to create a robust defense against thermal runaway and minimize the risk of fire-related incidents.
In summary, the integration of fire-resistant materials and innovative battery designs is essential for enhancing the safety of electric vehicles. These measures collectively contribute to a comprehensive fire prevention strategy, ensuring that EVs are as safe as possible on the road. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect further improvements in fire safety, solidifying the position of EVs as a reliable and secure mode of transportation.
The Dark Side of Electric Vehicles: Unveiling the Hidden Costs and Challenges
You may want to see also

Driver Assistance: Features like lane-keeping assist and adaptive cruise control improve overall safety and driver confidence
The evolution of driver assistance systems in electric vehicles (EVs) has been a game-changer, significantly enhancing safety and driving experience. These advanced features are designed to assist drivers in various driving scenarios, making the journey safer and more relaxed. One of the most notable advancements is lane-keeping assist, a feature that actively monitors and alerts the driver if the vehicle deviates from its intended lane. This system uses cameras and sensors to detect lane markings and provides gentle steering corrections to keep the car centered. For instance, the Tesla Model 3's Autopilot system includes lane-keeping assist, ensuring the vehicle stays in its lane even during sharp turns or when the road conditions are less than ideal.
Adaptive cruise control is another crucial driver assistance feature that has gained popularity. This technology allows the vehicle to automatically adjust its speed to maintain a safe distance from the car ahead. It uses radar or lidar sensors to detect nearby objects and can slow down or speed up the vehicle accordingly. For example, the Mercedes-Benz EQC's Drive Pilot system offers adaptive cruise control, ensuring a smooth and safe driving experience on highways, even in heavy traffic. This feature is particularly useful during long drives, as it reduces driver fatigue and the risk of accidents caused by sudden stops.
These driver assistance features not only improve safety but also boost driver confidence. Modern EVs are equipped with multiple sensors and cameras that provide a comprehensive view of the surroundings, allowing drivers to anticipate potential hazards and make informed decisions. For instance, the Audi e-tron's Traffic Jam Assist uses a combination of cameras and radar to navigate through slow-moving traffic, taking control of steering, acceleration, and braking as needed. This level of automation can significantly reduce driver stress, especially in challenging driving conditions.
Furthermore, the integration of these systems with the vehicle's overall safety architecture is essential. Many EVs now feature advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) that work in harmony to provide a seamless and secure driving experience. For example, the Volvo XC40 Recharge's City Safety system includes a range of ADAS features, such as emergency braking, pedestrian detection, and lane-keeping assist, all working together to prevent collisions and ensure the vehicle's stability. This holistic approach to safety is a key factor in making electric vehicles some of the safest on the road.
In summary, driver assistance features like lane-keeping assist and adaptive cruise control are pivotal in elevating the safety standards of electric vehicles. These technologies not only help drivers maintain control and awareness but also contribute to a more relaxed and confident driving experience. As EV technology continues to advance, we can expect further innovations in driver assistance, making the roads safer for all.
Ford's Future: Rumors of EV Shutdown Unraveled
You may want to see also

Regulatory Compliance: Adherence to strict safety standards and regulations ensures vehicles meet or exceed industry safety benchmarks
The quest for the safest electric vehicle involves a comprehensive understanding of the regulatory landscape governing the automotive industry. This is a critical aspect of ensuring that electric vehicles (EVs) not only perform well but also adhere to the highest safety standards. Regulatory compliance is a cornerstone of vehicle safety, as it mandates that manufacturers meet or exceed industry benchmarks, providing consumers with peace of mind.
In the context of EVs, regulatory bodies worldwide have established stringent guidelines to address the unique challenges associated with electric powertrains. These regulations cover various aspects, including battery safety, electrical systems, crash performance, and environmental impact. For instance, the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) in the United States has set forth specific standards for EV safety, focusing on crash testing and the integrity of the vehicle's electrical systems. Similarly, the European Union's New Car Assessment Programme (Euro NCAP) provides comprehensive safety ratings for EVs, evaluating their performance in various crash scenarios and overall safety features.
Adherence to these regulations is not merely a legal requirement but a fundamental principle of vehicle manufacturing. It involves a meticulous process of design, testing, and production, ensuring that every component of the EV meets or surpasses the defined safety criteria. This includes the use of advanced materials, sophisticated battery management systems, and innovative safety features. For example, many EV manufacturers employ advanced battery cooling systems to prevent overheating, a critical aspect of battery safety. They also implement robust electrical insulation and grounding techniques to minimize the risk of electrical faults and ensure the overall safety of the vehicle.
Furthermore, regulatory compliance extends beyond the vehicle's physical attributes to its software and connectivity. As EVs become increasingly connected and autonomous, regulations must keep pace to address cybersecurity and data privacy concerns. This includes implementing measures to protect against hacking and ensure the safe operation of autonomous driving features. By adhering to these regulations, EV manufacturers can provide consumers with vehicles that are not only environmentally friendly but also inherently safe and reliable.
In summary, the safest electric vehicles are those that adhere to strict regulatory compliance, ensuring they meet or exceed industry safety benchmarks. This involves a meticulous approach to design, testing, and production, incorporating advanced safety features and materials. As the EV market continues to evolve, regulatory bodies will play a pivotal role in shaping the industry, fostering a culture of safety and innovation.
Tesla's Dominance: Unveiling the Electric Vehicle Market Share
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Safety in EVs is primarily ensured by a combination of advanced technologies and design features. These include robust battery management systems that monitor and control the charging and discharging of the battery pack, preventing overheating and potential hazards. Additionally, EVs often feature advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) such as lane-keeping assist, adaptive cruise control, and automatic emergency braking, which enhance overall safety on the road.
Electric vehicles have been designed with a focus on safety, often incorporating lightweight materials and advanced crash-test simulations. While it's challenging to directly compare all models, studies suggest that EVs may have certain advantages. For instance, the absence of a traditional internal combustion engine can reduce the risk of certain types of accidents, and the lower center of gravity due to the battery pack can improve handling and stability. However, it's essential to consider that the safety of any vehicle also depends on its specific design, manufacturing quality, and post-sales support.
Battery safety is a critical aspect of EV ownership. Modern EVs use lithium-ion batteries, which are designed with multiple safety mechanisms. These include thermal management systems to prevent overheating, pressure relief valves to mitigate the risk of explosions, and sophisticated monitoring systems that can detect and respond to potential issues. Despite these measures, it's important for EV owners to follow manufacturer guidelines for charging and maintenance to ensure the longevity and safety of their batteries.
Autonomous driving features in EVs are designed to enhance safety by reducing human error, which is a leading cause of accidents. These systems use a combination of cameras, radar, lidar, and machine learning algorithms to perceive the surroundings and make driving decisions. Features like automatic emergency braking, lane-keeping assist, and adaptive cruise control can significantly reduce the risk of collisions. However, it's important to note that autonomous driving is not without its challenges, and ongoing research and development are necessary to ensure its safety and reliability.