In the rapidly evolving world of transportation, the rise of fully electric vehicles (EVs) has been transformative. These vehicles are powered entirely by electricity, eliminating the need for traditional internal combustion engines. The market now offers a diverse range of fully electric cars, trucks, buses, motorcycles, and even airplanes, each designed to reduce environmental impact and enhance performance. This paragraph aims to explore the various types of fully electric vehicles available, highlighting their benefits and contributions to a more sustainable future.
What You'll Learn
- Battery Technology: Innovations in battery chemistry and design for electric vehicles
- Charging Infrastructure: The development of charging stations and home charging solutions
- Range Anxiety: Strategies to address concerns about running out of battery power
- Vehicle Types: Electric cars, trucks, buses, and motorcycles
- Environmental Impact: The ecological benefits of fully electric transportation

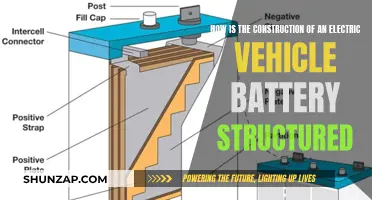
Battery Technology: Innovations in battery chemistry and design for electric vehicles
The evolution of battery technology is a pivotal aspect of the electric vehicle (EV) revolution, driving advancements in performance, efficiency, and sustainability. Innovations in battery chemistry and design have been instrumental in addressing the challenges associated with powering electric vehicles, such as range anxiety and charging infrastructure.
One of the key areas of innovation is in lithium-ion battery technology, which has become the cornerstone of modern EVs. Researchers and engineers have been working on enhancing the energy density of lithium-ion batteries, allowing for longer driving ranges. This involves the development of new cathode materials, such as nickel-rich layered compounds and solid-state electrolytes, which can store more energy per unit volume. For instance, nickel-rich cathodes offer higher energy density, while solid-state electrolytes, replacing the liquid or gel-like electrolytes in traditional lithium-ion batteries, can potentially eliminate the risk of thermal runaway and improve safety.
Another significant development is the exploration of alternative battery chemistries that can offer advantages over lithium-ion. For example, solid-state batteries, which replace the liquid electrolyte with a solid conductive material, promise higher energy density, faster charging, and improved safety. These batteries could potentially double the energy density of lithium-ion batteries, enabling EVs to travel much longer distances on a single charge. Additionally, researchers are investigating sodium-ion batteries, which are more abundant and environmentally friendly than lithium, as a potential low-cost alternative for large-scale energy storage applications.
Battery design and architecture are also being optimized to improve performance and efficiency. This includes the development of 3D battery structures, where the electrodes and electrolytes are arranged in a three-dimensional configuration, allowing for faster ion transport and improved overall efficiency. Furthermore, the integration of advanced cooling systems and smart battery management systems can enhance the performance and longevity of EV batteries by monitoring and controlling temperature, state of charge, and other critical parameters.
In the pursuit of a more sustainable future, recycling and second-life applications of EV batteries are gaining attention. Innovations in battery recycling processes aim to recover valuable materials, reduce waste, and lower the environmental impact of battery production. Additionally, researchers are exploring ways to repurpose used EV batteries for stationary energy storage, such as in homes or commercial buildings, providing a second life for these batteries and reducing the need for new ones.
The continuous advancements in battery technology are not only improving the performance and sustainability of electric vehicles but also contributing to the overall growth of the EV market. As battery chemistry and design evolve, EVs are becoming more appealing to a broader range of consumers, accelerating the transition towards a cleaner and more sustainable transportation ecosystem.
Unlocking Tax Benefits: Exploring Electric Vehicle Section 179 Eligibility
You may want to see also

Charging Infrastructure: The development of charging stations and home charging solutions
The widespread adoption of fully electric vehicles (EVs) relies heavily on the development of a robust charging infrastructure. As the number of EVs on the road increases, so does the demand for convenient and accessible charging solutions. This has led to significant investments and innovations in charging technology and infrastructure worldwide.
Charging stations, also known as EVSE (Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment), are a crucial component of this infrastructure. These stations are typically located in public areas, such as shopping malls, parking lots, and roadside rest stops, providing EV owners with the ability to recharge their vehicles when needed. The development of fast-charging stations has been a key focus, allowing for quicker replenishment times and reducing range anxiety among potential EV buyers. These stations often utilize advanced technologies like direct current (DC) fast charging, which can replenish a battery's charge to 80% in as little as 20-30 minutes.
In addition to public charging stations, the concept of home charging has gained traction. Many EV manufacturers now offer home charging solutions, which typically include a wall-mounted charging unit installed in the owner's residence. These units can be connected to a standard electrical outlet or, more commonly, a dedicated circuit, providing a convenient and cost-effective way to charge vehicles overnight or during periods of low energy demand. Home charging solutions often come with smart features, such as remote monitoring and control, allowing users to manage their charging sessions efficiently.
The development of charging infrastructure also involves addressing concerns related to power distribution and grid stability. As more EVs are charged simultaneously, there is a potential strain on the electrical grid. To mitigate this, smart charging systems are being implemented, which can adjust charging rates based on grid demand and supply. These systems ensure that charging sessions are optimized, reducing the impact on the power grid and promoting a more sustainable energy usage model.
Furthermore, the integration of renewable energy sources into charging infrastructure is an emerging trend. Solar-powered charging stations and wind-powered charging facilities are being explored, offering a more environmentally friendly approach to EV charging. This integration not only reduces the carbon footprint of the transportation sector but also provides a more sustainable and resilient charging network.
In summary, the development of charging infrastructure is a critical aspect of the transition to fully electric vehicles. It involves creating a network of public charging stations, offering home charging solutions, and implementing smart grid technologies to manage power distribution efficiently. As the demand for EVs continues to grow, the charging infrastructure will play a pivotal role in supporting the widespread adoption of electric mobility, ensuring convenience, and promoting a more sustainable future.
Electric Vehicles: Powering the Future, One Charge at a Time
You may want to see also

Range Anxiety: Strategies to address concerns about running out of battery power
Range anxiety is a common concern for electric vehicle (EV) drivers, especially those new to the technology. It refers to the fear of running out of battery power during a journey, potentially leaving the driver stranded. This anxiety can be a significant barrier to widespread EV adoption, as it may deter potential buyers from making the switch from traditional gasoline vehicles. However, there are several strategies that can help mitigate range anxiety and ensure a smooth and stress-free driving experience.
One effective approach is to plan your trips carefully. Before embarking on a journey, check the estimated range of your EV and plan your route accordingly. Many modern EVs come equipped with range estimators and trip planning tools that can help you identify charging stations along your route. By planning ahead, you can ensure that you have access to charging infrastructure when needed. Additionally, consider the efficiency of your vehicle; some EVs are more energy-efficient than others, allowing for longer ranges on a single charge.
Another strategy is to utilize the 'regenerative braking' feature, which is a unique advantage of electric vehicles. When you lift your foot off the accelerator, the electric motor acts as a generator, converting kinetic energy back into electrical energy and recharging the battery. This feature not only helps extend your range but also provides a more efficient driving experience. By smoothly controlling your speed and utilizing regenerative braking, you can make the most of your battery power.
Charging infrastructure plays a vital role in addressing range anxiety. Public charging stations are becoming increasingly available, allowing EV drivers to top up their batteries on the go. Many countries and cities are investing in extensive charging networks, making it convenient to find charging points during long-distance travel. Home charging is another option, providing the convenience of charging your vehicle overnight or during periods of low energy demand. Installing a home charging station can significantly reduce range anxiety, as it ensures a reliable source of power for your EV.
Lastly, consider the advancements in battery technology. Modern electric vehicles are equipped with advanced battery management systems that optimize power distribution and charging. These systems monitor the battery's health and performance, ensuring efficient energy usage. Additionally, ongoing research and development in battery technology aim to increase energy density, improve charging speeds, and extend the overall range of EVs. As technology advances, range anxiety is expected to diminish, making electric vehicles an even more attractive and reliable transportation option.
Uncover States' EV Tax Credit Secrets: Your Green Car Guide
You may want to see also

Vehicle Types: Electric cars, trucks, buses, and motorcycles
Electric cars are one of the most well-known and widely available fully electric vehicles. These cars run exclusively on electricity, typically powered by a battery pack that stores energy from a charging station or a regenerative braking system. Modern electric cars offer a range of features, from sleek designs and efficient performance to advanced driver-assistance systems and premium infotainment options. They are available in various sizes, from compact city cars to full-size luxury sedans, catering to diverse consumer preferences.
Electric trucks, often larger and more robust than their car counterparts, are designed for heavy-duty applications. These trucks utilize electric motors and battery packs to provide powerful performance and efficient operation. With a focus on sustainability, electric trucks are an eco-friendly alternative to traditional diesel-powered vehicles, reducing emissions and noise pollution. They are particularly useful for commercial applications, such as delivery services and construction, where they can offer high payload capacities and long-range capabilities.
Electric buses are a game-changer for public transportation, offering a cleaner and quieter ride for passengers. These buses are powered by electric motors and batteries, eliminating the need for diesel engines. Electric buses provide a cost-effective and environmentally friendly solution for urban transportation, with many cities adopting them for their reduced environmental impact and lower operating costs. They are available in various sizes, from small shuttles to large double-decker buses, accommodating different passenger capacities and routes.
Motorcycles, while often not the first vehicles that come to mind when thinking about electric transportation, are also making the switch to electric power. Electric motorcycles offer a thrilling and eco-conscious riding experience. These bikes are typically equipped with powerful electric motors and advanced battery technology, providing excellent acceleration and a smooth ride. With a growing market for sustainable transportation, electric motorcycles are becoming more popular, offering an alternative to traditional gasoline-powered bikes while reducing environmental impact.
The transition to fully electric vehicles across these categories is an exciting development in the automotive industry. Each type of vehicle offers unique advantages, from reduced environmental impact to improved performance and efficiency. As technology advances, we can expect to see further innovations in battery technology, charging infrastructure, and vehicle design, making electric cars, trucks, buses, and motorcycles even more accessible and appealing to a wide range of consumers.
Battling EV Fires: Rapid Response Strategies for Safety
You may want to see also

Environmental Impact: The ecological benefits of fully electric transportation
The widespread adoption of fully electric vehicles (EVs) is a significant step towards mitigating the environmental impact of transportation. These vehicles, powered by electric motors and rechargeable batteries, offer a cleaner and more sustainable alternative to traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) cars. Here's an in-depth look at the ecological advantages of fully electric transportation:
Reduced Greenhouse Gas Emissions: One of the most critical environmental benefits of EVs is their ability to drastically reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Traditional vehicles burn fossil fuels, releasing carbon dioxide (CO2), methane, and other harmful pollutants into the atmosphere. In contrast, electric cars produce zero tailpipe emissions, meaning they don't release any pollutants during operation. This shift from fossil fuel combustion to electric power is a major contributor to lowering carbon footprints and combating climate change.
Improved Air Quality: The absence of tailpipe emissions in EVs leads to improved air quality, especially in urban areas. Cities often experience high levels of air pollution due to vehicle exhaust, which can cause respiratory issues and other health problems for residents. By encouraging the use of electric cars, buses, and trucks, we can significantly reduce the concentration of harmful pollutants like nitrogen oxides (NOx) and particulate matter, making the air cleaner and healthier for everyone.
Lower Carbon Footprint in Energy Production: The environmental benefits of EVs extend beyond the vehicle itself. When electricity is generated from renewable sources like solar, wind, or hydropower, the overall carbon footprint of the transportation sector is further reduced. Many countries are investing in renewable energy infrastructure, and as more EVs hit the roads, the demand for clean energy increases, driving the transition to a more sustainable energy system. This shift in energy production is crucial for long-term environmental sustainability.
Reduced Noise Pollution: Electric vehicles also contribute to a quieter environment. Unlike ICE vehicles, EVs operate with minimal noise, especially at lower speeds. This reduction in noise pollution can have positive effects on wildlife and urban residents, creating a more peaceful and less disruptive transportation environment.
Long-Term Sustainability and Resource Conservation: The ecological benefits of fully electric transportation are not just limited to the immediate reduction in emissions. EVs also contribute to long-term sustainability. As battery technology advances, the recycling and reuse of batteries become more feasible, ensuring that the resources used in EV production are conserved for future generations. Additionally, the shift to electric mobility can reduce the demand for finite resources like oil and gas, leading to a more sustainable and resilient energy landscape.
In summary, fully electric transportation offers a comprehensive solution to environmental challenges associated with traditional vehicles. From reducing greenhouse gas emissions and improving air quality to contributing to a more sustainable energy system, the ecological benefits are far-reaching. As the world moves towards a greener future, the widespread adoption of electric vehicles plays a pivotal role in achieving a cleaner and healthier planet.
Grid-Integrated Electric Vehicles: Powering a Sustainable Future
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
There are numerous fully electric vehicles (EVs) available today, catering to various preferences and needs. Some popular options include the Tesla Model 3 and Model Y, known for their long-range and advanced technology. Other notable EVs are the Chevrolet Bolt EV, Ford Mustang Mach-E, and the recently launched Hyundai Ioniq 5. These vehicles offer a range of features, from sleek designs to efficient performance, making them attractive choices for eco-conscious consumers.
Fully electric cars are powered by electric motors and rechargeable batteries, eliminating the need for traditional internal combustion engines. When you plug the vehicle into a charging station, the battery stores electrical energy, which then powers the motor. Advantages of electric cars include zero direct emissions, reduced noise pollution, and lower running costs compared to gasoline or diesel vehicles. They also offer instant torque, resulting in quick acceleration. Additionally, many governments provide incentives and subsidies to encourage the adoption of electric vehicles.
Charging fully electric vehicles can be done through various methods. Home charging is a convenient option, where you can install a wall-mounted charger or use a standard power outlet for slower charging. Public charging stations are also widely available, offering faster charging speeds. These stations can be found in shopping malls, parking lots, and along highways. Some EVs also support fast-charging technologies, allowing for a quicker top-up during long journeys. It's important to note that the availability of charging infrastructure varies by region, so potential buyers should research the charging network in their area.