The production of batteries for electric vehicles (EVs) is a complex process that involves multiple stages and a global supply chain. These batteries, which are crucial for the performance and range of EVs, are typically manufactured in specialized facilities located in various regions around the world. The manufacturing process includes the extraction and processing of raw materials, such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel, which are then assembled into cells and modules. While the primary assembly often takes place in countries with advanced manufacturing capabilities, such as South Korea, Japan, and the United States, the sourcing of raw materials and the establishment of supply chains can span multiple continents, highlighting the global nature of EV battery production.
What You'll Learn
- Battery Cells: Manufacturing Process and Location
- Raw Materials: Extraction and Sourcing for Battery Components
- Supply Chain: Global Network for Battery Production
- Recycling and Sustainability: Environmental Impact of EV Battery Manufacturing
- Regional Specialization: Geographic Distribution of EV Battery Factories

Battery Cells: Manufacturing Process and Location
The production of battery cells for electric vehicles (EVs) is a complex process that involves multiple stages and requires specialized facilities. These cells are the heart of any EV battery pack, storing the energy needed to power the vehicle. The manufacturing process typically takes place in large, specialized factories, often located in regions with favorable economic and logistical conditions.
The journey begins with the selection of raw materials, primarily lithium, cobalt, nickel, and manganese, which are extracted and refined to create the essential components of the battery cell. These materials are then processed and combined in precise proportions to form the cathode and anode, the two key parts of the cell. The cathode is typically made from a mixture of lithium, cobalt, and nickel oxides, while the anode is often composed of graphite. This stage requires meticulous control over the composition and purity of the materials to ensure optimal performance and safety.
Once the materials are prepared, the manufacturing process continues with the formation of the battery cell. This involves several steps: first, the cathode and anode are coated onto a metal current collector, typically made of aluminum or copper. These collectors are then wound or stacked to create the cell's structure. After that, the cell is sealed, often in a cylindrical or prismatic shape, and filled with an electrolyte, a liquid or gel that facilitates the flow of ions between the electrodes. Quality control is critical at this stage to ensure the cells meet the required specifications.
The manufacturing location is a strategic decision. Many countries and regions have established themselves as hubs for EV battery production. For instance, Asia, particularly China and South Korea, has become a major player in the EV battery market due to its large-scale manufacturing capabilities and favorable government policies. These regions often offer a combination of skilled labor, advanced manufacturing infrastructure, and access to raw materials, making them attractive destinations for battery cell production.
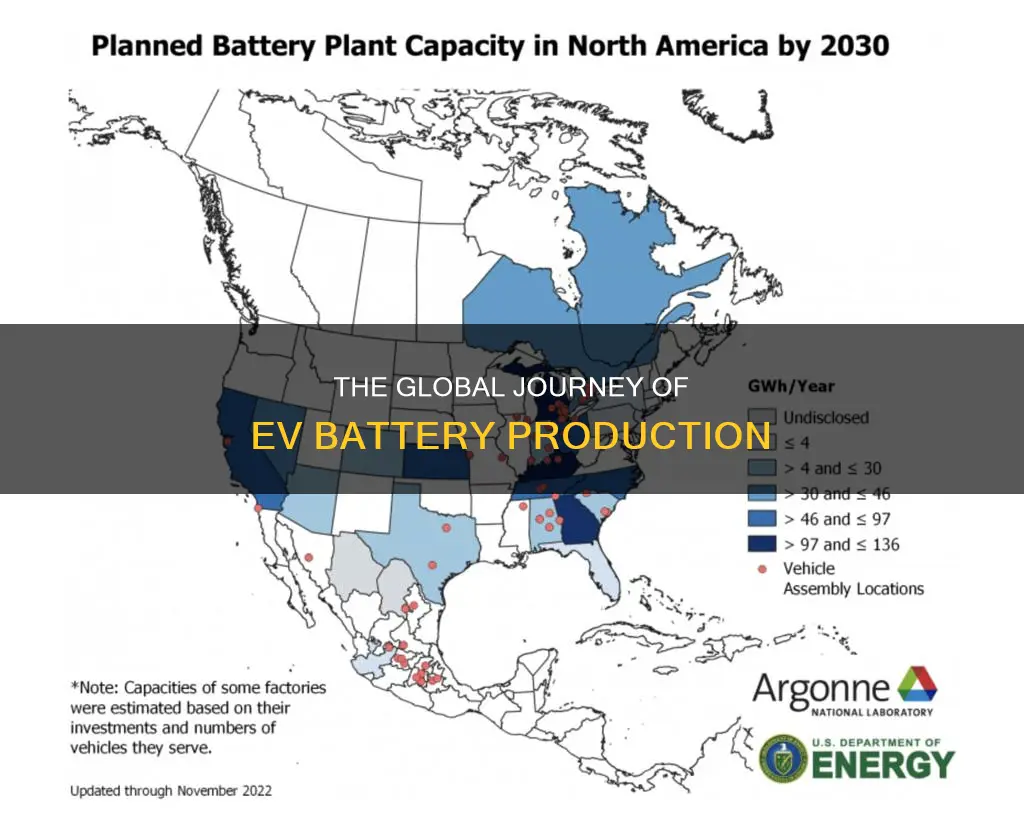
In recent years, there has been a growing trend of establishing battery cell manufacturing facilities in North America and Europe as well. This shift aims to reduce the reliance on Asian suppliers and ensure a more localized and sustainable supply chain for EVs. Governments and automotive companies are investing in building these facilities, often with incentives and subsidies, to support the development of a domestic battery industry. This expansion of manufacturing locations also contributes to the diversification of the EV battery supply chain, making it more resilient and adaptable to market demands.
Unlocking the Future: Your Guide to Electric Vehicle Investing
You may want to see also

Raw Materials: Extraction and Sourcing for Battery Components
The production of batteries for electric vehicles (EVs) relies heavily on specific raw materials, which are sourced and extracted from various regions around the world. These materials are essential for the manufacturing process and contribute to the overall performance and sustainability of EV batteries. The key components include lithium, cobalt, nickel, manganese, and graphite, each with its own unique sourcing and extraction processes.
Lithium, a crucial element in lithium-ion batteries, is primarily extracted through mining. The most common method is hard-rock mining, where lithium is found in mineral deposits, often in the form of lithium spodumene. Countries like Australia, Chile, and Argentina are significant producers of lithium, with large-scale mining operations extracting the resource from the ground. The process involves drilling and blasting to access the lithium-rich veins, followed by crushing and processing to separate the lithium minerals.
Cobalt, another critical material, is predominantly sourced through mining as well. It is often found in conjunction with nickel in the form of cobalt-nickel-manganese (CNM) ores. The Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) is the largest producer of cobalt, with a significant portion of the world's supply coming from this region. Mining operations in the DRC involve extracting the ore through open-pit mining, where large quantities of earth are removed to access the cobalt-rich layers. This process can have environmental and social impacts, emphasizing the importance of responsible sourcing and sustainable practices.
Nickel, along with cobalt, is also extracted through mining, particularly from the same CNM ores. Indonesia and the Philippines are major nickel producers, with mining operations extracting the metal from laterite deposits. These deposits are typically found in tropical regions and require specialized mining techniques due to their unique geological characteristics. The extraction process involves crushing and processing the ore to separate the nickel, often through a process called hydrometallurgy, which uses chemical solutions to extract the metal.
Manganese, an essential element for battery performance, is primarily sourced through mining as well. It is often found in association with iron ore and is extracted through open-pit or underground mining methods. South Africa and China are significant producers of manganese, with mining operations extracting the metal from various ore types. The process involves crushing and concentrating the ore to increase the manganese content, ensuring a consistent supply for battery manufacturing.
Graphite, the final key component, is sourced through mining and processing of natural graphite deposits. China is the largest producer of natural graphite, with significant reserves found in the country's northern regions. The extraction process involves crushing and grinding the ore to create a fine powder, which is then subjected to various chemical and physical processes to purify and prepare the graphite for battery use. This includes flotation, where the graphite is separated from other minerals, and roasting, which improves the material's properties.
The Ultimate Guide to the Most Reliable Electric Vehicles
You may want to see also

Supply Chain: Global Network for Battery Production
The production of batteries for electric vehicles (EVs) has evolved into a complex global supply chain, involving a network of manufacturers, raw material suppliers, and technology providers. This intricate web of collaboration ensures the availability of high-quality batteries to power the growing EV market. The supply chain for EV batteries is a critical aspect of the green energy transition, as it directly impacts the efficiency, sustainability, and cost-effectiveness of electric mobility.
At the heart of this supply chain are the battery manufacturers, who assemble the various components to create the final product. These manufacturers are often large, well-established companies with a global footprint. For instance, companies like Contemporary Amperex Technology (CATL) in China, Panasonic in Japan, and LG Energy Solution in South Korea are among the leading battery producers for EVs. Each of these companies has a vast network of suppliers and partners, ensuring a steady supply of raw materials and components.
The raw materials for EV batteries are sourced from various regions worldwide. Lithium, a key component in lithium-ion batteries, is primarily extracted from salt flats in South America, particularly in Chile and Argentina. Other materials, such as cobalt, nickel, and manganese, are also sourced from different parts of the world, with mining operations in countries like the Democratic Republic of Congo, Australia, and Indonesia. The transportation of these raw materials involves a complex logistics network, often utilizing sea freight and specialized cargo ships to ensure the materials reach the manufacturing hubs efficiently.
Battery manufacturing facilities are strategically located near major EV markets to reduce transportation costs and ensure timely delivery. For instance, many manufacturers have set up production sites in China, Europe, and the United States to cater to the growing demand in these regions. This strategic placement also allows for better control over the supply chain, as manufacturers can closely monitor the production process and ensure quality standards. Additionally, some companies are investing in vertical integration, where they own and operate their own raw material extraction and processing facilities, further tightening the supply chain.
The global network for battery production also involves a significant amount of technology transfer and collaboration. Many battery manufacturers license or acquire technology from research institutions and other companies to enhance their production processes. This includes advancements in battery chemistry, manufacturing techniques, and recycling methods. As a result, the supply chain for EV batteries is constantly evolving, with new innovations and partnerships shaping its future. This dynamic nature of the supply chain ensures that the industry can adapt to changing market demands and environmental regulations.
The Electric Revolution: Unlocking the Percentage of New Electric Vehicles
You may want to see also

Recycling and Sustainability: Environmental Impact of EV Battery Manufacturing
The manufacturing of electric vehicle (EV) batteries has significant environmental implications, particularly in the context of recycling and sustainability. As the demand for EVs rises, so does the need for a sustainable approach to battery production and end-of-life management. The process of creating EV batteries involves the extraction of raw materials, such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel, which are then refined and assembled into battery cells. While this process has contributed to the growth of the EV market, it also raises concerns about the environmental impact of mining and processing these materials.
One of the primary environmental challenges is the energy-intensive nature of battery manufacturing. The production of lithium-ion batteries requires substantial energy, often sourced from non-renewable means. This energy consumption contributes to greenhouse gas emissions and places a strain on local power grids. Additionally, the extraction of raw materials can lead to habitat destruction and water pollution if not managed sustainably. For instance, lithium mining can result in soil erosion and the contamination of nearby water sources.
Recycling plays a crucial role in mitigating the environmental impact of EV battery manufacturing. Recycling lithium-ion batteries can recover valuable materials, reduce the demand for new raw materials, and minimize the need for energy-intensive extraction processes. The recycling process involves several steps, including collecting used batteries, disassembling them, and separating the various components. These components can then be processed to recover metals like cobalt, nickel, and lithium, which can be reused in new batteries or other industrial applications.
Sustainable practices in EV battery manufacturing also extend to the design and composition of batteries. Researchers and manufacturers are exploring ways to reduce the environmental footprint of batteries. This includes developing more efficient and sustainable battery chemistries, such as solid-state batteries, which use solid electrolytes instead of liquid ones, potentially reducing the risk of thermal events and improving recycling possibilities. Additionally, designing batteries with easily recyclable materials and modular components can simplify the recycling process and encourage the circular economy.
In summary, the environmental impact of EV battery manufacturing is a complex issue that requires a multi-faceted approach. While the production of EV batteries has contributed to the growth of sustainable transportation, it also presents challenges related to energy consumption, raw material extraction, and waste management. By implementing effective recycling processes, adopting sustainable manufacturing practices, and investing in research for greener battery technologies, the industry can work towards minimizing its environmental footprint and ensuring a more sustainable future for electric vehicles.
Arrival's Electric Vehicle Dreams: A Story of Unfulfilled Potential
You may want to see also

Regional Specialization: Geographic Distribution of EV Battery Factories
The global electric vehicle (EV) market is experiencing rapid growth, and the demand for advanced batteries is soaring. This has led to a strategic shift in the manufacturing landscape, with a growing emphasis on regional specialization and the establishment of dedicated EV battery factories worldwide. The geographic distribution of these factories is not random but rather a result of various factors, including resource availability, market proximity, and government incentives.
In North America, the United States has emerged as a key player in the EV battery manufacturing sector. States like Michigan, with its rich history in the automotive industry, have become hubs for battery production. The region's proximity to major EV manufacturers and the availability of skilled labor have contributed to the establishment of several battery factories. For instance, companies like Tesla have set up their battery production facilities in the US, ensuring a shorter supply chain and faster response to market demands. Additionally, the US government's incentives and subsidies for EV battery manufacturing have further encouraged the industry's growth in this region.
In Europe, the story is slightly different, with a more diverse distribution of EV battery factories. Countries like Germany, France, and Sweden have capitalized on their strong automotive sectors and engineering expertise. Germany, in particular, has a well-established battery cell production network, with companies like Continental and Bosch leading the way. The region's focus on sustainability and the European Union's ambitious goals for EV adoption have driven significant investments in battery technology. Countries like Norway and the Netherlands have also seen the rise of specialized battery factories, catering to the growing demand for electric mobility.
Asia, particularly China, South Korea, and Japan, has become a dominant force in the global EV battery market. China, in particular, has witnessed an unprecedented boom in battery production, with numerous local and international companies establishing their manufacturing bases. The Chinese government's support and the country's vast natural resources have made it an attractive destination for battery manufacturers. South Korea, known for its technological prowess, has also emerged as a significant player, with companies like LG Energy Solution leading the way. Japan, with its advanced automotive industry, has a strong presence in battery technology, catering to both domestic and international markets.
The strategic placement of EV battery factories is crucial for optimizing supply chains and reducing costs. Proximity to raw material sources and skilled labor pools is essential, as it minimizes transportation expenses and ensures a steady workforce. Moreover, regional specialization allows for better collaboration between battery manufacturers and EV producers, fostering innovation and rapid response to market changes. As the EV market continues to evolve, the geographic distribution of battery factories will play a pivotal role in shaping the industry's future, influencing the cost, efficiency, and sustainability of electric vehicles.
Uncover States' EV Tax Credit Secrets: Your Green Car Guide
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Battery production for electric vehicles (EVs) is a global process, with key manufacturing hubs located in various regions. The majority of EV batteries are produced in Asia, particularly in China, South Korea, and Japan. These countries have established themselves as major players in the battery supply chain due to their advanced technology, large-scale manufacturing capabilities, and significant investments in research and development.
Yes, the Asian market, especially China, has become a dominant force in the EV battery industry. Chinese companies like Contemporary Amperex Technology (CATL), BYD, and Tianjin Lishen have become leading manufacturers, supplying batteries to numerous EV brands worldwide. South Korea's LG Energy Solution and Samsung SDI are also significant players, with a strong presence in the global market. Additionally, Japan's Panasonic and Toyota Tsusho have been key suppliers for many years.
The production of EV batteries, especially lithium-ion batteries, has environmental considerations. The process involves extracting raw materials like lithium, cobalt, and nickel, which can have ecological impacts if not managed sustainably. However, many manufacturers are implementing measures to reduce their environmental footprint. These include recycling initiatives, using more sustainable materials, and adopting energy-efficient production methods. Additionally, the shift towards larger-scale manufacturing and the development of more efficient battery technologies contribute to the overall sustainability of the EV industry.