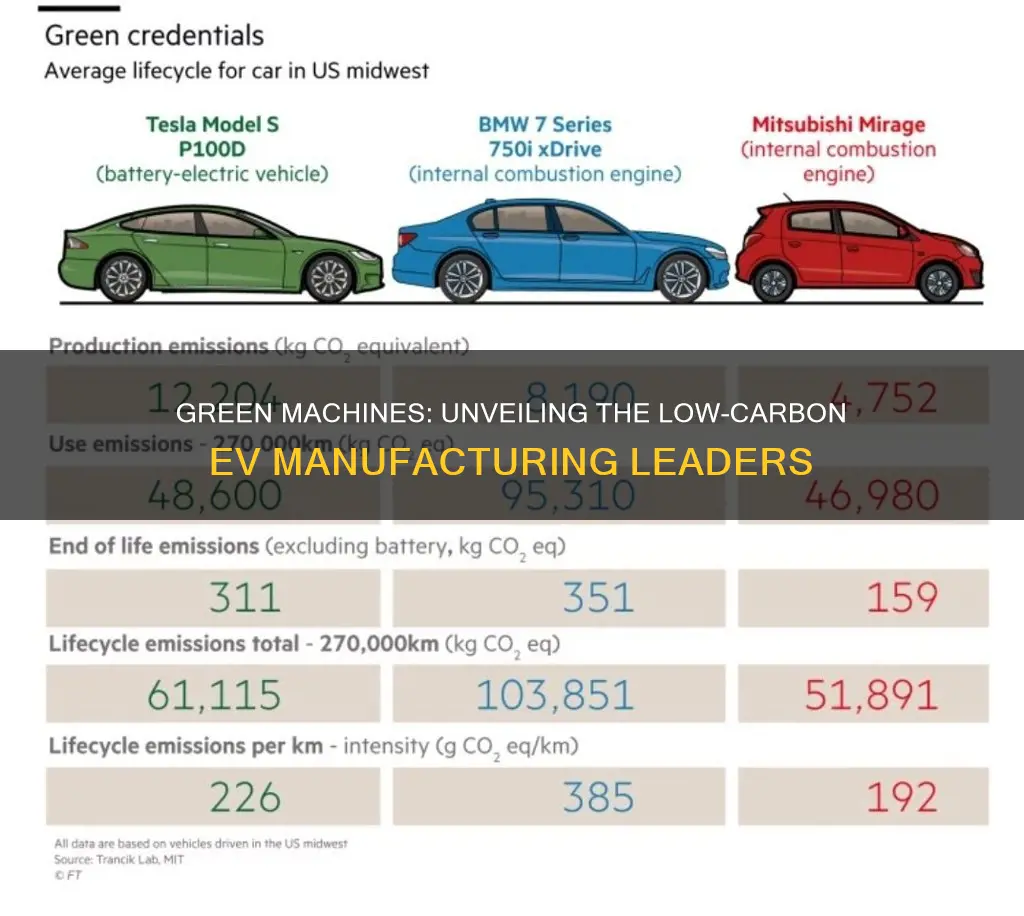
The manufacturing process of electric vehicles (EVs) has been a subject of growing interest as the world shifts towards sustainable transportation. While EVs are known for their lower carbon emissions during operation, the production of these vehicles can still contribute to significant CO2 emissions. This paragraph aims to explore the factors that influence the CO2 footprint of EV manufacturing, focusing on the materials and production methods used. By understanding these aspects, we can identify which electric vehicles require less CO2 to manufacture, contributing to a more environmentally friendly automotive industry.
What You'll Learn
- Battery Chemistry: Focus on lithium-ion batteries with recycled materials
- Recycling Processes: Efficient recycling methods for batteries and materials
- Sustainable Materials: Use of renewable resources and low-carbon materials
- Manufacturing Efficiency: Optimizing production to reduce energy consumption
- Lightweight Design: Employing lightweight materials to decrease overall weight

Battery Chemistry: Focus on lithium-ion batteries with recycled materials
The quest for more sustainable electric vehicles (EVs) has led to a growing focus on the environmental impact of their production, particularly the manufacturing of batteries. Among the various battery technologies, lithium-ion batteries dominate the market due to their high energy density and performance. However, the environmental cost of producing these batteries, especially those containing raw materials, has been a concern. This is where the concept of recycling and the use of recycled materials in lithium-ion battery chemistry comes into play, offering a more eco-friendly approach.
Lithium-ion batteries typically consist of several key components, including the cathode, anode, electrolyte, and separator. The cathode, often made of lithium cobalt oxide (LiCoO2), has been a significant contributor to the carbon footprint of these batteries due to the energy-intensive mining and processing of cobalt. To address this, researchers and engineers are exploring alternative cathode materials that can be derived from recycled sources. For instance, lithium-ion batteries with recycled nickel-cobalt-manganese (NMC) cathodes are gaining traction. These cathodes can be produced using materials recovered from end-of-life batteries, reducing the need for virgin resources.
The process of recycling lithium-ion batteries involves several stages. Firstly, the batteries are collected, disassembled, and their components separated. The cathode material is then processed to extract lithium, cobalt, nickel, and manganese. These metals can be re-used to create new cathodes, reducing the demand for raw materials and minimizing the environmental impact associated with mining and processing. Additionally, the recycling process can help recover other valuable materials, such as copper from the anode, further contributing to a more sustainable battery manufacturing ecosystem.
Incorporating recycled materials into lithium-ion battery chemistry has multiple benefits. Firstly, it reduces the reliance on finite natural resources, ensuring a more stable supply chain for EV manufacturers. Secondly, it lowers the carbon emissions associated with mining and transportation, as the extraction and processing of raw materials often require significant energy input and contribute to greenhouse gas emissions. By utilizing recycled materials, the manufacturing process becomes more circular, minimizing waste and reducing the overall environmental footprint.
Furthermore, the development of lithium-ion batteries with recycled content encourages innovation in the recycling industry. As the demand for sustainable batteries increases, so does the need for efficient and cost-effective recycling technologies. This drives research and investment in advanced recycling methods, ensuring that the process becomes more viable and accessible on a large scale. As a result, the manufacturing of electric vehicles becomes more environmentally friendly, making them more accessible to consumers who prioritize sustainability without compromising performance.
Navigating California's EV Battery Warranty: A Step-by-Step Guide to Filing a Complaint
You may want to see also

Recycling Processes: Efficient recycling methods for batteries and materials
The focus on reducing carbon emissions in the manufacturing of electric vehicles (EVs) has led to a growing interest in sustainable practices, particularly in the recycling of batteries and materials. Efficient recycling processes are crucial to minimizing the environmental impact of EVs throughout their lifecycle. Here are some detailed insights into the recycling methods that contribute to a greener approach:
Battery Recycling:
- Hydrometallurgical Process: This method involves dissolving the battery's components in a chemical solution to separate valuable metals. For instance, lithium-ion batteries can be recycled by dissolving the cathode material in a sulfuric acid solution, allowing for the recovery of lithium, cobalt, and nickel. This process is energy-efficient and can handle large-scale recycling operations.
- Pyrometallurgy: Pyroprocessing is a high-temperature recycling technique used for batteries with metal oxides. It melts the battery's components, separating them through different melting points. This method is effective for recycling nickel-cadmium (Ni-Cd) and lead-acid batteries, ensuring the recovery of metals like nickel, cobalt, and lead.
- Mechanical Processing: A simpler approach is mechanical recycling, which involves physically breaking down batteries to recover usable materials. This can include shredding or grinding the batteries to extract individual components, such as the cathode and anode materials. Mechanical processing is cost-effective and can be combined with other recycling methods for comprehensive material recovery.
Material Recovery and Reuse:
- Cathode Material Recycling: Recycling the cathode materials is a critical aspect of EV battery recycling. Companies are developing processes to recover lithium, cobalt, and nickel from spent cathodes. These metals can then be reused in new batteries, reducing the need for primary mining and minimizing the environmental impact of extraction.
- Anode Recycling: Recycling the anode material, often graphite, is another area of focus. Graphite can be recovered from spent anodes and potentially reused in subsequent battery production. This process ensures a more circular economy for EV batteries, reducing the demand for new raw materials.
- Second-Life Applications: Instead of complete recycling, some batteries can be repurposed for other applications. For example, used EV batteries can be utilized in energy storage systems for homes or businesses, providing a second life for the battery cells while reducing the need for new manufacturing.
Efficient recycling processes are essential to the long-term sustainability of the EV industry. By implementing these methods, manufacturers can minimize the carbon footprint associated with battery production and disposal. Additionally, the development of advanced recycling technologies will further enhance the environmental benefits of EVs, making them an even more attractive and eco-friendly transportation option. This approach contributes to a more sustainable future, where the manufacturing and end-of-life management of EVs are aligned with the goal of reducing global carbon emissions.
Unraveling SOC: Powering Electric Vehicles with Smart Energy Storage
You may want to see also

Sustainable Materials: Use of renewable resources and low-carbon materials
The automotive industry is undergoing a significant transformation with the rise of electric vehicles (EVs), offering a more sustainable and environmentally friendly alternative to traditional internal combustion engine cars. One crucial aspect of making EVs more eco-friendly is the use of sustainable materials in their manufacturing process, which can significantly reduce the carbon footprint associated with vehicle production.
Renewable resources play a pivotal role in this context. For instance, the use of bio-based materials, such as plant-derived plastics, can be a game-changer. These materials are derived from renewable feedstocks, such as corn starch or cellulose, which can be grown and harvested repeatedly without depleting finite resources. By incorporating these bio-plastics into vehicle components, manufacturers can reduce the reliance on fossil fuels and decrease the overall carbon emissions during production. For example, certain EV manufacturers have started using bio-based plastics for interior trim, dashboards, and even battery casings, showcasing the potential for widespread adoption.
Low-carbon materials are another essential component of sustainable EV manufacturing. These materials have a lower embodied energy, meaning they require less energy to produce and process. For instance, aluminum, a lightweight metal, can be recycled multiple times without losing its quality, reducing the need for energy-intensive primary production. Similarly, the use of recycled steel and aluminum in vehicle manufacturing can significantly lower carbon emissions compared to producing these materials from scratch. Additionally, the adoption of lightweight composites, such as those made from natural fibers like flax or hemp, can further reduce the weight of vehicles, leading to improved energy efficiency and lower emissions.
The benefits of using sustainable materials extend beyond the manufacturing phase. EVs with a lower carbon footprint during production often have a reduced environmental impact throughout their lifecycle. This includes lower emissions during operation, as many EVs are powered by clean energy sources, and reduced waste generation at the end of their life cycle, as these materials can often be recycled or biodegraded.
In summary, the adoption of renewable resources and low-carbon materials in the manufacturing of electric vehicles is a crucial step towards a more sustainable future. By embracing these practices, the automotive industry can significantly contribute to reducing global carbon emissions and mitigating the environmental impact of vehicle production and use. As consumers become more environmentally conscious, the demand for such sustainable practices will likely drive further innovation and development in this area.
Unlocking California's Tesla Tax Credit: A Green Car Incentive Guide
You may want to see also

Manufacturing Efficiency: Optimizing production to reduce energy consumption
The manufacturing process of electric vehicles (EVs) is a critical aspect that significantly influences their overall environmental impact, particularly in terms of carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions. Optimizing production to reduce energy consumption is a key strategy to minimize the CO2 footprint of these vehicles. Here's an in-depth look at how this can be achieved:
Streamlining Production Lines: One of the primary approaches to enhancing manufacturing efficiency is by streamlining production lines. This involves reorganizing the assembly process to minimize unnecessary movements and reduce the time components spend in transit between stations. By optimizing the layout and workflow, manufacturers can decrease the overall energy required for production. For instance, implementing just-in-time inventory management ensures that parts arrive when needed, reducing storage and transportation-related emissions.
Energy-Efficient Machinery: Upgrading to energy-efficient machinery is another powerful strategy. Modern equipment often incorporates advanced technologies that minimize power consumption without compromising productivity. For example, adopting electric or hybrid-electric assembly lines can significantly reduce energy usage compared to traditional combustion-engine-powered machinery. These systems can be programmed to operate at specific times, ensuring energy is not wasted during downtime.
Renewable Energy Integration: Integrating renewable energy sources into the manufacturing process is a sustainable way to reduce CO2 emissions. Solar panels, wind turbines, or hydroelectric power can be utilized to meet the energy demands of the production facility. By generating clean energy on-site, manufacturers can decrease their reliance on fossil fuels, which are major contributors to CO2 emissions. This approach not only reduces the environmental impact but also provides long-term cost savings.
Waste Reduction and Recycling: Implementing waste reduction and recycling programs is essential for a more sustainable manufacturing process. This includes minimizing material waste during production and encouraging the use of recycled materials. For instance, EV manufacturers can utilize recycled lithium-ion batteries, which have a lower environmental impact compared to producing new ones. Additionally, proper waste management systems can capture and reuse byproducts, further reducing the overall energy consumption and CO2 emissions.
Continuous Improvement and Monitoring: Manufacturing efficiency is an ongoing process that requires continuous improvement and monitoring. Manufacturers should regularly analyze their production processes, identify areas of inefficiency, and implement corrective measures. This might involve employee training to optimize workflow, adopting new technologies, or reevaluating supply chain logistics. By treating manufacturing as a dynamic process, companies can consistently work towards reducing their CO2 footprint.
Mastering Short Electrical Wiring: Extending Vehicle Connections Efficiently
You may want to see also

Lightweight Design: Employing lightweight materials to decrease overall weight
Lightweight design is a crucial aspect of reducing the environmental impact of electric vehicles (EVs), particularly in terms of their manufacturing process and overall carbon footprint. By utilizing lightweight materials, manufacturers can significantly decrease the weight of EVs, which has a direct and positive effect on their efficiency and performance. This approach is an essential strategy to minimize the CO2 emissions associated with vehicle production.
The primary goal of lightweight design is to optimize the structural integrity of the vehicle while reducing its mass. This can be achieved by employing advanced materials that offer high strength-to-weight ratios. For instance, automotive manufacturers are increasingly turning to carbon fiber composites, which provide an exceptional strength-to-weight advantage over traditional materials like steel and aluminum. Carbon fiber composites can be used for various components, including body panels, chassis, and even battery enclosures, allowing for a substantial reduction in vehicle weight.
Another strategy is to utilize advanced alloys and high-strength steels, which offer improved strength and durability while keeping the weight low. These materials can be strategically placed in critical areas of the vehicle, such as the chassis and frame, to enhance structural rigidity without adding excessive weight. By carefully selecting and distributing materials, engineers can achieve a balance between strength and weight, ensuring the vehicle's structural integrity while reducing its overall mass.
Furthermore, lightweight design extends beyond the choice of materials. It involves innovative manufacturing processes and component design. For example, 3D printing technology allows for complex, lightweight structures to be produced with minimal waste. This additive manufacturing process enables the creation of intricate designs that would be challenging and costly to produce using traditional methods. By optimizing component shapes and structures, manufacturers can further reduce weight without compromising safety or performance.
In summary, lightweight design plays a pivotal role in minimizing the CO2 emissions associated with electric vehicle manufacturing. By adopting lightweight materials, innovative manufacturing techniques, and strategic component design, manufacturers can significantly decrease the overall weight of EVs. This approach not only improves the environmental sustainability of the production process but also contributes to enhanced vehicle performance and efficiency, making it a key focus area in the development of eco-friendly electric transportation.
Unleash the Power: Understanding the EV HomeCharge Scheme
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The electric vehicles with the lowest CO2 emissions during manufacturing are typically those with smaller battery packs and more efficient production processes. For example, the Mini Electric and the Smart ForTwo Electric Drive have relatively low emissions due to their compact designs and the use of lightweight materials.
No, the manufacturing CO2 emissions can vary significantly between different electric vehicle models. Factors such as battery chemistry, production location, and the sourcing of raw materials play a crucial role. For instance, vehicles with lithium-ion batteries may have higher emissions due to the energy-intensive extraction and processing of lithium.
The manufacturing process of electric vehicles generally has a higher upfront carbon footprint compared to ICE vehicles due to the energy-intensive production of batteries and the associated materials. However, over the vehicle's lifetime, electric cars typically offset this initial emissions through lower operational CO2 emissions.
Achieving carbon-neutral or net-zero manufacturing for electric vehicles is challenging but not impossible. Some manufacturers are working towards this goal by implementing renewable energy sources in their production facilities, recycling materials, and adopting sustainable practices. For instance, Tesla has made efforts to minimize its environmental impact by using recycled materials and powering its factories with renewable energy.
Consumers can play a role by choosing vehicles with smaller batteries and more efficient designs, supporting manufacturers with sustainable practices, and opting for second-hand electric vehicles, which have lower overall emissions. Additionally, advocating for policies that promote renewable energy and sustainable resource management can contribute to a more environmentally friendly automotive industry.







