Electric vehicle batteries have revolutionized the automotive industry, offering a sustainable and efficient alternative to traditional combustion engines. However, several valid concerns have been raised regarding their performance and longevity. One significant issue is the limited range that many electric vehicles currently offer, which can be a major drawback for long-distance travel. Additionally, the rapid depreciation of battery capacity over time, known as battery degradation, is a critical problem. This degradation can lead to reduced performance, shorter driving ranges, and even premature battery failure, causing financial strain for vehicle owners. Furthermore, the disposal and recycling of these batteries present environmental challenges, as they contain hazardous materials that require careful handling to minimize ecological impact. Addressing these issues is crucial for the widespread adoption of electric vehicles and the realization of their full potential in reducing environmental pollution.
What You'll Learn
- Limited Range: Range anxiety is a common concern for EV owners, especially for long-distance travel
- Charging Time: Long charging times can be inconvenient and impact daily use
- Battery Degradation: Over time, batteries lose capacity, affecting performance and lifespan
- Cost: High upfront costs remain a barrier to widespread adoption
- Recycling Challenges: Proper disposal and recycling of used batteries pose environmental and logistical issues

Limited Range: Range anxiety is a common concern for EV owners, especially for long-distance travel
The limited range of electric vehicle (EV) batteries is a significant concern for many potential and current EV owners, often referred to as 'range anxiety'. This anxiety is a very real issue, especially for those who frequently embark on long-distance journeys or live in regions with limited charging infrastructure. The fear of running out of power before reaching a charging station can be a deterrent for many, despite the numerous benefits of electric vehicles.
The range of EVs has traditionally been a challenge, and while advancements have been made, the current battery technology still has a way to go to match or exceed that of conventional gasoline vehicles. Modern electric cars can typically travel between 100 and 400 miles on a single charge, depending on the model and various factors such as driving conditions, temperature, and efficiency. This range is adequate for daily commutes and short trips but may not be sufficient for longer journeys, especially when considering the time required to charge the vehicle.
To address this issue, EV manufacturers are continually working on improving battery technology, aiming to increase energy density and reduce charging times. Some companies are also investing in the development of fast-charging stations, which can significantly reduce the time needed to recharge a battery. Additionally, the integration of advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) and route planning tools can help alleviate range anxiety by suggesting optimal routes and providing real-time charging station information.
For those who are still hesitant, there are strategies to manage range anxiety. Planning trips carefully, ensuring a well-maintained battery, and being aware of charging station locations along the route can help. Carpooling or using ride-sharing services for longer journeys can also be a practical solution. Furthermore, the increasing availability of public transportation and the growing network of charging stations make electric vehicles a more viable option for a wider range of consumers.
In summary, while the limited range of electric vehicle batteries is a valid concern, it is not an insurmountable one. With ongoing technological advancements and a growing infrastructure, the range of EVs is expected to improve, making long-distance travel more feasible. Until then, being informed and prepared can help alleviate range anxiety and encourage a wider adoption of electric vehicles.
Electric Vehicles: The Indian Advantage? Exploring the Benefits
You may want to see also

Charging Time: Long charging times can be inconvenient and impact daily use
Long charging times for electric vehicles (EVs) are a significant concern for many potential and current EV owners. The process of replenishing an EV's battery can take several hours, which is a stark contrast to the swift refueling of conventional gasoline or diesel vehicles. This extended charging time can have a substantial impact on daily routines and activities, presenting a valid issue that EV manufacturers and users need to address.
The inconvenience of long charging times is a critical factor in the overall user experience of owning an EV. For individuals with busy schedules, the prospect of spending several hours at a charging station can be a major deterrent. Imagine a scenario where you need to charge your EV after a long day at work, only to find that it will take over four hours to reach a full charge. This could disrupt your evening plans, especially if you rely on your vehicle for daily commutes or running errands. The time spent charging could otherwise be utilized for personal activities, work, or leisure, highlighting the need for faster and more efficient charging solutions.
The impact of long charging times on daily use is multifaceted. Firstly, it can lead to a sense of dependency on charging infrastructure. EV owners might need to plan their routes carefully, ensuring access to charging stations along the way. This planning can be time-consuming and may not always be feasible, especially for those with less predictable schedules or those traveling long distances. Secondly, the extended charging periods can cause frustration and anxiety, especially during emergencies or when unexpected delays occur. For instance, a flat battery while on a road trip could result in a significant loss of freedom and flexibility, as finding a charging station might be challenging or non-existent in remote areas.
To mitigate these issues, researchers and engineers are constantly working on improving battery technology and charging infrastructure. The development of faster charging methods, such as high-power charging stations and advanced battery chemistries, is a priority in the EV industry. These innovations aim to reduce charging times significantly, making EVs more convenient and comparable to traditional vehicles in terms of refueling speed. Additionally, the integration of smart charging systems and the utilization of renewable energy sources can further enhance the efficiency and user-friendliness of EV charging.
In conclusion, long charging times are a valid concern in the EV market, affecting the practicality and appeal of electric vehicles. The impact on daily use and convenience cannot be overlooked, as it directly influences the overall ownership experience. By addressing this issue through technological advancements and infrastructure improvements, the EV industry can work towards making electric vehicles a more attractive and accessible option for a wider range of consumers.
The Green Promise of Electric Vehicles: Unveiling the Reality
You may want to see also

Battery Degradation: Over time, batteries lose capacity, affecting performance and lifespan
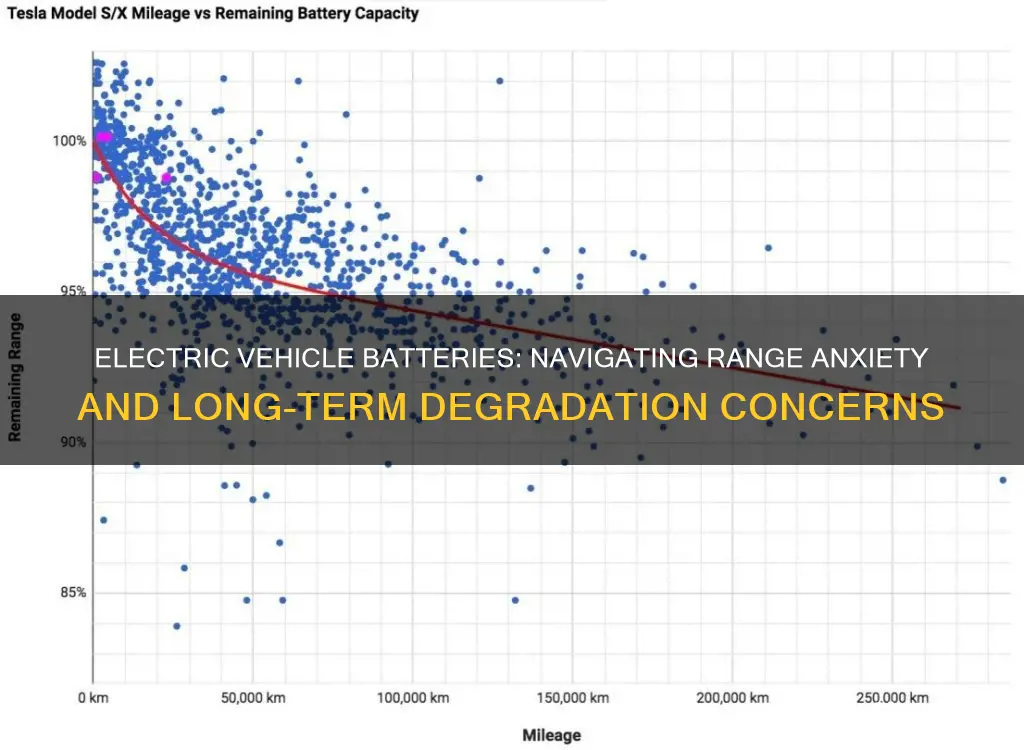
Battery degradation is a significant concern for electric vehicle (EV) owners, as it directly impacts the performance and longevity of their vehicles. Over time, the batteries in EVs undergo a natural process of capacity loss, which can lead to reduced driving range and overall efficiency. This issue is a valid and pressing challenge in the EV market, affecting both consumers and manufacturers.
The degradation process is primarily influenced by various factors, including temperature, charging habits, and the number of charge-discharge cycles the battery undergoes. High temperatures, both during operation and storage, can accelerate battery degradation. This is why EV manufacturers often provide guidelines for optimal charging and parking conditions to minimize this effect. Additionally, frequent and rapid charging, especially to very high levels, can also contribute to capacity loss. Modern EVs are designed with smart charging systems that help mitigate this, but user behavior still plays a crucial role.
Another critical factor is the number of times the battery is charged and discharged. Each cycle involves a small loss of capacity, and over time, this can add up. This is why it's essential for EV owners to understand their charging habits and try to maintain a balanced approach. For instance, avoiding complete discharges and keeping the battery at a moderate charge level can help preserve its health.
Battery degradation is an inevitable process, but its rate can be managed and minimized. Research and development in the field of EV batteries are focused on improving degradation rates and extending battery lifespan. This includes advancements in battery chemistry, thermal management systems, and smart battery management software. By optimizing these aspects, manufacturers aim to provide consumers with more reliable and long-lasting EV batteries.
In summary, battery degradation is a valid and significant issue for electric vehicle batteries, impacting their performance and lifespan. While it is a natural process, understanding the contributing factors and implementing best practices can help EV owners and manufacturers alike to mitigate its effects, ensuring a more sustainable and efficient future for electric transportation.
Powering the Future: Electric vs. Hybrid Vehicles Explained
You may want to see also

Cost: High upfront costs remain a barrier to widespread adoption
The high upfront cost of electric vehicle (EV) batteries is a significant barrier to their widespread adoption and integration into the mainstream automotive market. This issue stems from the advanced technology and materials used in EV batteries, which are designed to provide high energy density, long-lasting performance, and fast charging capabilities. While these features are essential for the success of electric vehicles, they come at a premium.
The primary factor contributing to the high cost is the use of rare earth metals and advanced chemical compounds in the battery cells. Lithium, cobalt, and nickel are some of the key elements found in EV batteries, and their extraction and processing are energy-intensive and costly processes. Additionally, the manufacturing of these batteries requires specialized equipment and skilled labor, further increasing production expenses. As a result, the initial purchase price of electric vehicles is often significantly higher compared to their conventional gasoline or diesel counterparts.
This financial hurdle is particularly challenging for potential EV buyers who are price-sensitive or operate within limited budgets. The high upfront cost can deter individuals and businesses from making the switch to electric mobility, especially in regions where the cost of living is already high. Moreover, the lack of widespread EV adoption can hinder the development of supporting infrastructure, such as charging stations, which are crucial for the long-term success and convenience of electric vehicles.
To address this issue, governments and automotive manufacturers are exploring various strategies. One approach is to offer incentives and subsidies to consumers, reducing the effective cost of purchasing electric vehicles. Another strategy involves developing more cost-effective battery technologies, such as solid-state batteries or lithium-ion phosphate batteries, which have shown promise in reducing production costs without compromising performance.
In conclusion, the high upfront costs of electric vehicle batteries are a critical challenge that needs to be addressed to accelerate the transition to sustainable transportation. By implementing cost-saving measures and innovative battery technologies, the automotive industry can work towards making electric vehicles more accessible and affordable for a broader audience, ultimately contributing to a greener and more sustainable future.
Electric Vehicle Battery Life: Unlocking the Future of Sustainable Driving
You may want to see also

Recycling Challenges: Proper disposal and recycling of used batteries pose environmental and logistical issues
The increasing popularity of electric vehicles (EVs) has led to a surge in the demand for lithium-ion batteries, which power these vehicles. While this technology has revolutionized transportation, it also presents a significant challenge: the proper disposal and recycling of used batteries. This issue is a critical aspect of sustainable EV ownership and environmental conservation.
One of the primary concerns is the environmental impact of disposing of these batteries improperly. Lithium-ion batteries contain various hazardous materials, including lithium, cobalt, nickel, and chemicals like sulfuric acid and lithium salt. When these batteries are not recycled or disposed of correctly, these toxic substances can leach into the environment, causing soil and water pollution. For instance, cobalt, a metal used in the cathode of many lithium-ion batteries, is highly toxic and can have severe ecological consequences if released into the environment. Improper disposal can lead to the contamination of local ecosystems, affecting wildlife and potentially human health.
Additionally, the logistical challenges of recycling EV batteries are substantial. These batteries are large, heavy, and often contain multiple cells, making them difficult to transport and process. Specialized equipment and facilities are required to handle and recycle them safely. The collection and transportation of used batteries from various sources, such as dealerships, service centers, and individual vehicle owners, can be a complex and costly endeavor. Furthermore, the recycling process itself is energy-intensive and may generate additional waste, requiring careful management to minimize environmental impact.
The recycling infrastructure for EV batteries is still developing, and many regions lack the necessary facilities to handle the growing number of used batteries. This shortage of recycling centers can lead to batteries being shipped long distances, increasing transportation emissions and costs. As a result, some batteries may end up in informal recycling operations, where improper disposal methods are used, further exacerbating the environmental issues.
To address these challenges, governments, automotive manufacturers, and recycling companies must collaborate to develop comprehensive recycling programs. This includes establishing efficient collection networks, investing in advanced recycling technologies, and educating the public about the importance of proper battery disposal. By implementing these measures, we can ensure that the environmental benefits of electric vehicles are not offset by the improper handling of their batteries.
Power Down: Strategies for When Your EV's Battery Fails
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Range anxiety is a valid issue as it pertains to the fear of running out of battery power during a journey, especially for long-distance travel. While modern EVs have significantly improved their range, concerns still exist about the availability of charging stations along routes and the time required to recharge, which can be longer than refueling a conventional vehicle.
Extreme temperatures, both hot and cold, can negatively affect EV battery performance. In cold climates, batteries may experience reduced capacity and slower charging times. Conversely, high temperatures can accelerate battery degradation and potentially reduce overall lifespan. Manufacturers often provide guidelines for optimal charging and driving temperatures to mitigate these effects.
Yes, safety is a critical aspect of EV batteries. While rare, there have been incidents of battery fires and thermal events, often caused by manufacturing defects or accidents. Modern EVs are equipped with advanced safety features like cooling systems and crash-resistant designs to minimize these risks. Additionally, proper charging practices and the use of high-quality charging infrastructure can further enhance battery safety.