The production of batteries for electric vehicles (EVs) is a complex process that involves a network of specialized manufacturers and suppliers. These batteries are crucial components in the growing market for electric cars, trucks, and other vehicles, as they store and supply the energy needed to power the vehicle's electric motor. The production process typically includes the development and assembly of various components, such as lithium-ion cells, battery modules, and packs, which are then integrated into the vehicle's chassis. This intricate process requires a combination of advanced technology, skilled labor, and stringent quality control to ensure the reliability and performance of EV batteries.
What You'll Learn
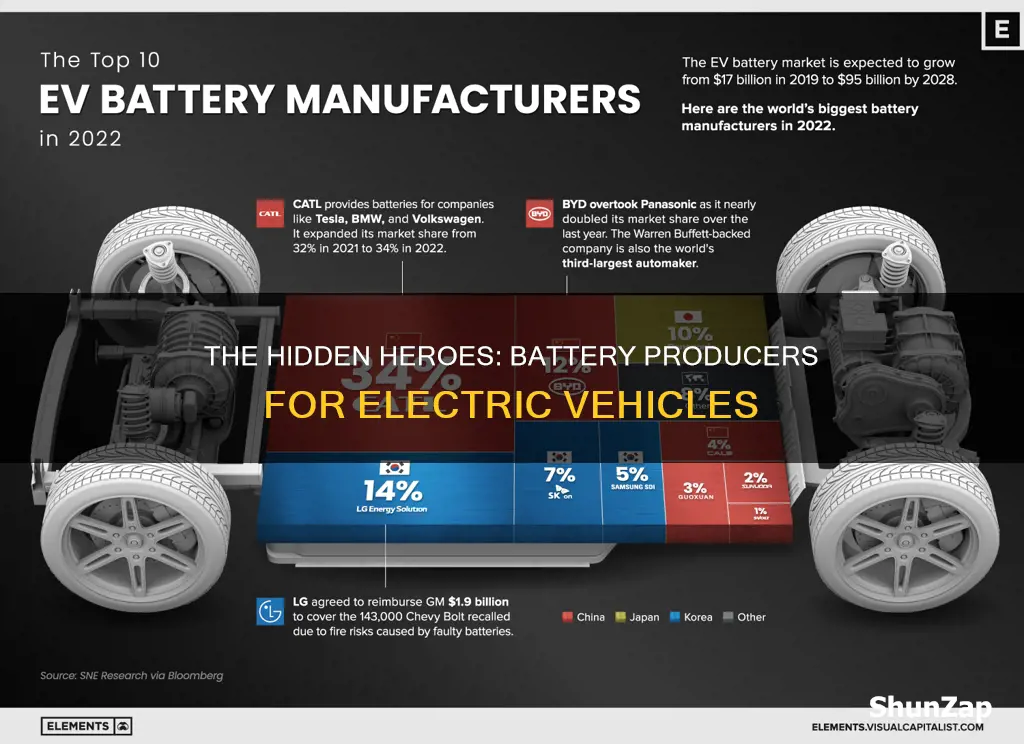
- Battery Manufacturers: Companies like CATL, LG Energy, and Panasonic dominate EV battery production
- Raw Materials: Lithium, cobalt, and nickel are key raw materials for battery production
- Recycling Processes: Recycling batteries is crucial for sustainability and resource recovery
- Supply Chains: Complex global supply chains ensure the availability of raw materials and components
- Government Incentives: Governments offer subsidies and incentives to support battery production and research

Battery Manufacturers: Companies like CATL, LG Energy, and Panasonic dominate EV battery production
The global electric vehicle (EV) market is rapidly expanding, and at the heart of this revolution are the battery manufacturers who produce the power that fuels these vehicles. Among the key players in this industry are a few giants that have established themselves as the primary suppliers of batteries for electric cars. These companies include Contemporary Amperex Technology Limited (CATL), LG Energy Solution, and Panasonic Corporation.
CATL, based in China, has emerged as the world's largest manufacturer of EV batteries. With a significant market share, CATL's technology and production capabilities are highly regarded in the industry. The company's focus on research and development has led to innovative battery designs and improved energy density, making their products highly sought-after by EV manufacturers worldwide. CATL's extensive supply chain and global presence ensure a steady supply of batteries to support the growing demand for electric vehicles.
LG Energy Solution, a South Korean multinational, is another prominent player in the EV battery market. They have a strong presence in the automotive industry, supplying batteries to major car manufacturers. LG's expertise lies in their advanced battery chemistry, particularly in the development of lithium-ion batteries with high energy density and fast charging capabilities. Their commitment to sustainability and environmental responsibility has also positioned them as a preferred choice for eco-conscious EV producers.
Panasonic, a Japanese electronics giant, has a long-standing relationship with the automotive industry, and their involvement in EV battery production is significant. With a focus on quality and reliability, Panasonic offers a range of battery solutions tailored to the unique requirements of electric vehicles. Their partnership with Tesla, one of the leading EV manufacturers, has further solidified their position as a key player in the market. Panasonic's global manufacturing network enables them to meet the increasing demand for EV batteries while maintaining strict standards of performance and safety.
These three companies, CATL, LG Energy Solution, and Panasonic, have collectively shaped the EV battery market and driven the industry forward. Their technological advancements, large-scale production capabilities, and global reach have made them indispensable partners for EV manufacturers. As the demand for electric vehicles continues to rise, these battery producers will play a crucial role in ensuring a sustainable and efficient energy supply for the future of transportation.
Is the Grid Ready for the Electric Vehicle Revolution?
You may want to see also

Raw Materials: Lithium, cobalt, and nickel are key raw materials for battery production
The production of batteries for electric vehicles relies heavily on specific raw materials, which are essential for their performance and longevity. Three key elements that play a crucial role in battery manufacturing are lithium, cobalt, and nickel. These materials are integral to the composition of lithium-ion batteries, the most common type used in electric vehicles (EVs).
Lithium is a highly sought-after element due to its ability to store and release energy efficiently. It is a critical component in the cathode, which is responsible for the battery's power output. The availability of lithium is a significant concern, as it is a finite resource, and its extraction and processing can have environmental impacts. Countries like Chile, Australia, and Argentina are major producers of lithium, with mining operations extracting this metal from brine or hard rock sources.
Cobalt, another essential raw material, is primarily used in the cathode as well. It enhances the battery's energy density and stability, making it an indispensable component. However, cobalt extraction has been associated with ethical concerns, particularly regarding child labor and human rights issues in certain mining regions. The Democratic Republic of Congo is the largest producer of cobalt, with its mines supplying a significant portion of the global market.
Nickel, while not as prominent as lithium and cobalt, still holds importance in battery production. It is used in the anode, where it facilitates the storage of energy. Nickel's role is to provide structural support and enhance the battery's performance. The extraction and processing of nickel can also have environmental consequences, including habitat destruction and water pollution. Major nickel producers include Indonesia, the Philippines, and Russia.
The demand for these raw materials has led to a global focus on sustainable mining practices and the development of recycling technologies. Recycling lithium-ion batteries is crucial to ensuring a steady supply of these materials and reducing the environmental impact of mining. As the electric vehicle market continues to grow, so does the need for responsible sourcing and efficient recycling processes to meet the increasing demand for batteries.
The Ultimate Guide to Choosing Your Perfect Electric Car
You may want to see also

Recycling Processes: Recycling batteries is crucial for sustainability and resource recovery
The process of recycling batteries is an essential practice to ensure the long-term sustainability of the electric vehicle (EV) industry and to recover valuable resources. As the demand for electric cars rises, so does the need for efficient recycling methods to handle the increasing number of batteries that will eventually need to be disposed of or recycled. This is a critical aspect of the EV ecosystem, as it addresses the environmental impact and the finite nature of certain battery materials.
Recycling batteries involves several specialized processes that aim to recover and reuse materials while minimizing the environmental footprint. One common method is called hydrometallurgy, which uses chemical processes to dissolve the battery's components and separate the metals. This technique is particularly effective for lithium-ion batteries, which are prevalent in EVs. The process begins by dismantling the battery, separating the cathode and anode materials, and then using acids or bases to dissolve and extract the metals, such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel. These metals can then be recycled and reused in new batteries.
Another recycling approach is pyrometallurgy, which involves high-temperature processes to recover metals. This method is often used for lead-acid batteries, a common type in older vehicles. The batteries are shredded, and the lead and lead oxide are recovered through melting and refining processes. Pyrometallurgy is a well-established recycling technique but is less common for newer lithium-ion batteries due to the different chemical compositions.
Advanced recycling technologies are also being developed to handle the complex chemistry of modern batteries. For instance, mechanical processes can be employed to physically separate the battery's components, such as using shredders or ball mills to break down the battery into its constituent parts. These methods can then be followed by chemical treatments to extract specific metals. Researchers are also exploring ways to directly recycle the battery's active materials, such as directly reusing the cathode and anode without extensive processing.
The recycling of batteries is a complex but necessary task to ensure a circular economy for the EV industry. It allows for the recovery of valuable metals, reduces the demand for raw materials, and minimizes the environmental impact of battery production and disposal. As the EV market grows, efficient and sustainable recycling processes will play a pivotal role in maintaining the industry's long-term viability and contributing to a greener future.
Powering the Future: Understanding Electric Vehicle Controllers
You may want to see also

Supply Chains: Complex global supply chains ensure the availability of raw materials and components
The production of batteries for electric vehicles (EVs) is a complex and global endeavor, relying on intricate supply chains to source raw materials and components from around the world. This intricate web of suppliers and manufacturers ensures the availability of essential materials, such as lithium, cobalt, nickel, and graphite, which are crucial for battery production. The process begins with the extraction of these raw materials, often involving mining operations in various countries. For instance, lithium is primarily sourced from salt flats in South America, while cobalt is mined in the Democratic Republic of Congo. These raw materials are then transported to specialized processing facilities, where they undergo refining and purification to meet the stringent requirements of battery manufacturing.
The supply chain for EV batteries is highly globalized, with companies forming strategic partnerships and collaborations to ensure a steady supply of materials and components. Battery manufacturers often have extensive networks of suppliers, each specializing in different aspects of the production process. For example, one company might source lithium-ion battery cells from a South Korean manufacturer, while another might procure the specialized separators and electrolytes required for battery assembly from different suppliers in Asia and Europe. This global reach allows for the optimization of production costs and the ability to adapt to market demands, ensuring a consistent supply of batteries for the growing EV market.
A critical aspect of this supply chain is the management of sustainability and ethical sourcing. As the demand for EVs increases, so does the pressure to ensure that the production of batteries is environmentally and socially responsible. Battery manufacturers are increasingly implementing sustainable practices, such as recycling and reusing materials, to reduce their environmental impact. Additionally, there is a growing focus on ethical sourcing, with companies working closely with suppliers to ensure fair labor practices and minimize the environmental footprint of mining operations. This includes initiatives to trace and verify the origin of raw materials, combat illegal mining, and promote local community development in areas where mining takes place.
The complexity of these supply chains is further emphasized by the need for specialized equipment and technology. Battery manufacturing requires advanced machinery and processes, such as specialized coating and assembly lines, to produce high-performance batteries. This specialized equipment is often sourced from a limited number of manufacturers, creating a concentrated market for these technologies. As a result, battery producers must carefully manage their supply chains to ensure they have access to the necessary technology and expertise to maintain their competitive edge.
In summary, the production of batteries for electric vehicles is a highly complex and global process, with intricate supply chains that span multiple countries and industries. This complexity ensures the availability of raw materials and components, allowing for the rapid growth of the EV market. However, it also presents challenges related to sustainability, ethical sourcing, and access to specialized technology. As the industry continues to evolve, managing these supply chains effectively will be crucial to meeting the increasing demand for electric vehicles and ensuring a sustainable future for the automotive sector.
The Cost of Green: Industry Insights on EV Production
You may want to see also

Government Incentives: Governments offer subsidies and incentives to support battery production and research
In the pursuit of fostering the growth of the electric vehicle (EV) industry, governments worldwide have implemented a range of incentives and subsidies aimed at encouraging battery production and research. These initiatives are crucial in addressing the challenges associated with the high costs and technological complexities of battery manufacturing. One of the primary strategies employed by governments is the provision of financial incentives to both established battery producers and emerging startups. These incentives often take the form of grants, tax credits, or low-interest loans, which significantly reduce the financial burden on battery manufacturers. By doing so, governments aim to stimulate investment in battery production facilities, research and development (R&D), and the establishment of supply chains.
For instance, many countries have introduced tax credits for EV battery manufacturers, allowing them to claim a percentage of their investment as a tax deduction. This not only reduces the upfront costs of setting up production lines but also encourages companies to invest in cutting-edge technology and innovative processes. Additionally, governments may offer grants or subsidies to support R&D projects focused on improving battery performance, energy density, and longevity. These grants can be particularly beneficial for startups and smaller companies that might lack the financial resources to undertake extensive research independently.
Another aspect of government incentives is the establishment of favorable regulatory frameworks. Governments may introduce policies that streamline the approval process for battery production facilities, reduce import tariffs on raw materials, and provide fast-track approvals for environmental impact assessments. Such measures aim to expedite the construction and operation of battery manufacturing plants, ensuring a steady supply of batteries for the growing EV market. Furthermore, governments can offer incentives to encourage the localization of battery production, which involves attracting foreign investments and fostering partnerships between local and international battery producers.
The impact of these government incentives extends beyond individual companies. By supporting battery production and research, governments contribute to the overall development of the EV ecosystem. This includes the creation of jobs in battery manufacturing, R&D, and supporting industries, which, in turn, stimulates economic growth and reduces dependence on imported batteries. Moreover, government incentives can drive innovation, leading to the development of more efficient, sustainable, and cost-effective battery technologies.
In summary, government incentives play a pivotal role in the advancement of battery production for electric vehicles. Through financial support, favorable regulations, and the promotion of localization, governments are actively fostering an environment conducive to the growth of the EV industry. These incentives not only benefit battery manufacturers but also contribute to a more sustainable and resilient transportation sector, ultimately driving the global transition towards cleaner and more efficient mobility solutions.
Powering Electric Vehicles: Understanding Battery Voltage and Its Impact
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The market for electric vehicle (EV) battery production is dominated by a few key players. These include established automotive suppliers like LG Energy Solution, Contemporary Amperex Technology (CATL), and Panasonic, as well as specialized battery manufacturers such as Tesla's battery division and Samsung SDI.
As of 2023, there are over 20 major companies globally that produce batteries for electric vehicles, with some of the most prominent being the ones mentioned above. This number is expected to grow as the demand for EVs increases.
China is currently the largest producer of EV batteries, with a significant share of the global market. This is largely due to the presence of major battery manufacturers like CATL, which has a substantial production capacity in the country.
Yes, several new companies are entering the market, aiming to supply batteries for electric vehicles. For instance, startups like Solid Power and QuantumScape are developing solid-state battery technologies, offering potential alternatives to traditional lithium-ion batteries.
Battery production, especially for lithium-ion batteries, can have environmental implications. The process involves the extraction of raw materials, which can lead to habitat destruction and water pollution. However, efforts are being made to improve recycling technologies and adopt more sustainable practices in the industry.







