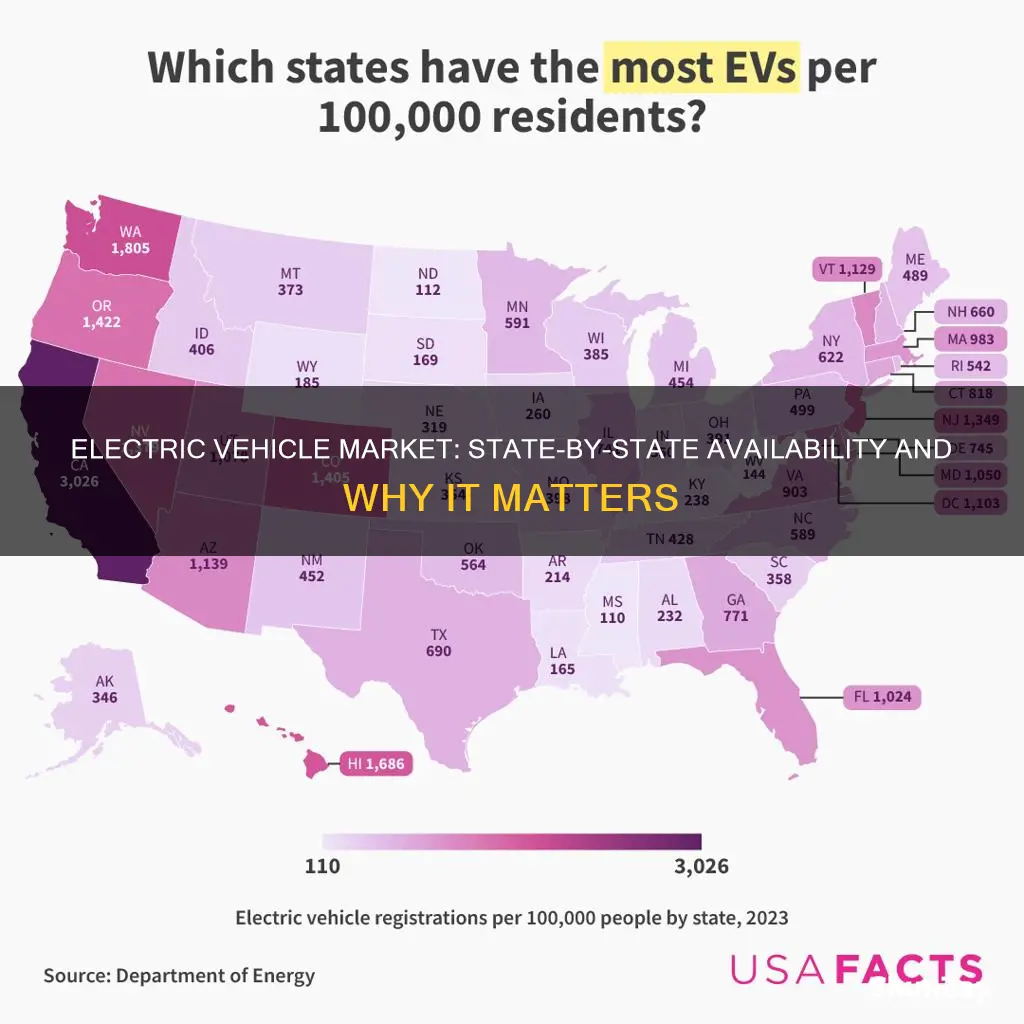
The availability of electric vehicles (EVs) varies significantly across different states, often due to a combination of factors including state-specific regulations, incentives, and market demand. Some states have implemented policies that encourage the adoption of EVs, such as tax credits, rebates, and the establishment of charging infrastructure. These incentives can make EVs more affordable and attractive to consumers, leading to higher sales and a wider range of models available in those markets. Additionally, certain states may have unique environmental regulations or goals that prioritize the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions, further driving the demand for electric vehicles. As a result, EV manufacturers often tailor their offerings to these specific markets, providing a diverse selection of models that cater to the varying needs and preferences of consumers in different states.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Market Demand and Infrastructure | States with higher demand for electric vehicles (EVs) often have more robust charging infrastructure, which encourages manufacturers to offer their models there. |
| Government Incentives and Policies | States with favorable policies, such as tax credits, rebates, and incentives for EV buyers, can attract more EV manufacturers. |
| Environmental Regulations | States with stricter emissions standards and a focus on sustainability may prioritize EV offerings to meet environmental goals. |
| Consumer Behavior | Consumer preferences and habits play a role; some states might have a higher adoption rate of EVs, leading to more availability. |
| Supply Chain Considerations | Proximity to manufacturing facilities and supply chains can influence where EVs are available, as transportation costs and logistics are considered. |
| Market Saturation | In some states, the market might be saturated with a specific EV model, leading to limited availability to avoid oversupply. |
| Brand Strategy | Some EV manufacturers may have specific market entry strategies, focusing on certain states to build brand presence and customer loyalty. |
| Economic Factors | Economic conditions, such as disposable income and the cost of living, can impact the demand for EVs and their availability. |
| Regional Preferences | Certain states might have unique preferences for specific vehicle types or brands, influencing manufacturer decisions. |
| Regulatory Barriers | States with fewer regulatory barriers or those that have streamlined processes for EV adoption may see more offerings. |
What You'll Learn
- Market Demand: Consumer preferences and local incentives drive EV availability
- Infrastructure: Charging stations and grid capacity vary by region
- Regulatory Environment: State laws and policies influence EV adoption
- Environmental Factors: Climate and pollution levels impact EV sales
- Economic Considerations: Local market and subsidies affect EV distribution

Market Demand: Consumer preferences and local incentives drive EV availability
The availability of electric vehicles (EVs) in the market is significantly influenced by consumer preferences and local incentives, which vary across different states and regions. This phenomenon is primarily driven by the unique demands and opportunities presented by each market. Consumer preferences play a pivotal role in shaping the EV market. In certain states, residents may have a higher inclination towards eco-friendly transportation options, leading to increased demand for EVs. For instance, states with a strong environmental consciousness and a well-informed population might see a surge in EV sales due to consumers actively seeking sustainable alternatives. This preference can be further influenced by factors such as the availability of charging infrastructure, which makes EVs more convenient and appealing to potential buyers.
Local incentives, such as subsidies, tax benefits, and grants, are powerful tools to encourage the adoption of EVs. Many states offer financial incentives to reduce the upfront cost of EVs, making them more affordable and attractive to consumers. These incentives can vary widely, with some states providing substantial rebates or tax credits, while others might offer more targeted support, such as reduced registration fees or access to carpool lanes. For example, a state with a high cost of living might introduce a comprehensive incentive program to make EVs more accessible to its residents, addressing the financial burden associated with purchasing an electric vehicle.
The impact of these incentives is twofold. Firstly, they directly influence the purchase decisions of consumers, making EVs more competitive against traditional vehicles. Secondly, they stimulate the local economy by encouraging the growth of EV-related businesses, such as charging station providers and EV service centers. As a result, states with more generous incentives often experience a faster transition to electric mobility, fostering a self-sustaining cycle of increased demand and improved infrastructure.
Moreover, the availability of EVs in a particular state can also be influenced by the presence of local EV manufacturers or the willingness of established automakers to tailor their production strategies to specific regional demands. States with a strong automotive industry presence might have more options for EV models, allowing consumers to choose vehicles that align with their preferences and local incentives. This localized approach to EV availability ensures that the market caters to the unique needs and characteristics of each state, making electric mobility more accessible and appealing to a diverse range of consumers.
In summary, the interplay between consumer preferences and local incentives is a critical factor in determining the availability of EVs in certain states. States that effectively address these factors can create a thriving EV market, fostering a sustainable future for transportation. Understanding these dynamics is essential for policymakers, automakers, and consumers alike, as it highlights the importance of localized strategies in the widespread adoption of electric vehicles.
Uncover the Top Stocks in the Electric Vehicle Revolution
You may want to see also

Infrastructure: Charging stations and grid capacity vary by region
The availability of electric vehicles (EVs) in specific states is closely tied to the underlying infrastructure, particularly the charging station network and grid capacity. These factors play a crucial role in determining the practicality and appeal of EVs in a particular region.
Charging stations are essential for EV owners to recharge their vehicles, and their distribution significantly impacts the adoption of electric cars. States with a well-developed charging infrastructure network often attract more EV manufacturers and encourage consumers to make the switch. For instance, regions with a higher density of charging stations along highways and in urban areas make long-distance travel and daily commutes more feasible for EV owners. This accessibility is a significant selling point for potential buyers, as it alleviates range anxiety and provides convenience.
The grid capacity, or the electrical grid's ability to handle the load from numerous EVs, is another critical aspect. States with older or less advanced power grids may face challenges in accommodating the increased electricity demand from a growing EV population. Insufficient grid capacity can lead to power outages, voltage fluctuations, and potential blackouts, especially during peak charging times. This issue is particularly relevant in regions with a rapid increase in EV sales, as the strain on the grid can result in unreliable charging, discouraging potential buyers.
To address these infrastructure challenges, governments and energy companies are investing in expanding charging station networks and upgrading power grids. This includes installing fast-charging stations along major highways and in densely populated areas, ensuring that EV owners can quickly recharge their vehicles during long journeys or daily commutes. Additionally, smart grid technologies are being implemented to optimize energy distribution and manage the increased demand efficiently.
In summary, the availability of electric vehicles in certain states is directly linked to the region's infrastructure, specifically the charging station network and grid capacity. States with robust charging infrastructure and a capable grid are more likely to attract EV manufacturers and consumers, fostering a thriving electric vehicle market. As the demand for EVs continues to grow, the focus on improving and expanding these critical infrastructure components will be essential to supporting the widespread adoption of electric transportation.
Tax Benefits for Electric Vehicles: A Green Investment
You may want to see also

Regulatory Environment: State laws and policies influence EV adoption
The regulatory environment plays a pivotal role in shaping the availability and adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) across different states. Each state in the United States has its own set of laws and policies that can either encourage or hinder the growth of the EV market. One significant factor is the implementation of zero-emission vehicle (ZEV) programs, which are designed to promote the sale and registration of EVs. These programs often set specific targets for EV sales, requiring automakers to meet these goals through a combination of traditional and electric vehicle sales. States with more aggressive ZEV programs, such as California, have been instrumental in driving EV adoption. For instance, California's ZEV program has mandated that a certain percentage of new vehicle sales be electric, leading to a more diverse range of EV models available in the state. This has not only increased consumer choice but also created a competitive market, encouraging automakers to invest in EV technology and infrastructure.
State-specific tax incentives and rebates are another critical aspect of the regulatory environment. Many states offer financial incentives to reduce the upfront cost of EVs, making them more affordable for consumers. These incentives can include tax credits, rebates, or even reduced registration fees for EV owners. For example, New York provides a significant tax credit for EV purchases, which can significantly lower the overall cost. Such financial incentives not only make EVs more accessible but also encourage consumers to make the switch from traditional gasoline vehicles. As a result, states with robust incentive programs often experience higher rates of EV adoption.
Additionally, the development of charging infrastructure is heavily influenced by state regulations. The availability of charging stations is essential for EV owners, as it addresses range anxiety and ensures convenience during long-distance travel. States with comprehensive charging networks, often supported by government grants and incentives, make EVs more attractive to potential buyers. For instance, states like Oregon have invested in public charging stations, making it easier for EV owners to travel without worrying about running out of power. This infrastructure development is a direct response to the regulatory environment, as states recognize the importance of supporting EV adoption through practical solutions.
Furthermore, state-level regulations on vehicle emissions standards have a direct impact on the types of vehicles offered in the market. States with stricter emissions standards, often aligned with federal guidelines, may require automakers to produce a higher proportion of zero-emission vehicles. This can result in a more diverse range of EVs being available in these states. On the other hand, states with less stringent standards might see a different selection of vehicles, potentially limiting the availability of certain electric models. The regulatory environment, therefore, acts as a guiding force, shaping the EV market in each state and influencing the choices available to consumers.
In summary, the regulatory environment, encompassing state laws and policies, is a critical determinant of EV availability and adoption. ZEV programs, tax incentives, charging infrastructure development, and vehicle emissions standards all contribute to the unique EV landscape in each state. As the market continues to evolve, understanding and adapting to these regulatory factors will be essential for both consumers and automakers, ensuring a sustainable and thriving EV industry across the nation.
Unveiling Electro-Hydraulic Power: The Heart of Modern Vehicle Systems
You may want to see also

Environmental Factors: Climate and pollution levels impact EV sales
The availability of electric vehicles (EVs) in specific states is influenced by various factors, and environmental considerations play a significant role in this context. One of the primary environmental factors is climate, which varies greatly across different regions. In colder climates, where temperatures drop significantly during winter, the demand for EVs with robust heating systems is higher. These vehicles are designed to provide comfortable and efficient heating, ensuring passenger comfort and safety. On the other hand, in warmer regions, the focus shifts to efficient cooling systems, as extreme heat can impact performance and passenger experience. The market demand for EVs tailored to these climate-specific needs is often higher in the respective states.
Pollution levels are another critical environmental factor affecting EV sales. States with high pollution levels, often due to industrial activities or heavy traffic, may experience increased interest in electric vehicles as a cleaner alternative. EVs produce zero tailpipe emissions, making them an attractive option for environmentally conscious consumers in these areas. Governments and local authorities in such states might also incentivize EV adoption by offering subsidies or tax benefits, further boosting sales. For instance, regions with strict emission standards and regulations might see a surge in EV sales as manufacturers cater to these markets by producing vehicles with advanced emission control systems.
The impact of climate and pollution on EV sales is further amplified by the availability of charging infrastructure. In states with harsh winters, for example, the range anxiety associated with EVs is often higher due to the limited availability of charging stations. This can influence consumer behavior, making them more inclined to purchase vehicles with extended range or faster charging capabilities. Similarly, in areas with high pollution, the presence of extensive charging networks can encourage EV adoption, as potential buyers are assured of convenient charging options.
Additionally, the environmental benefits of EVs extend beyond the vehicle itself. In regions with poor air quality, the widespread adoption of electric vehicles can significantly reduce local air pollution, improving public health and environmental conditions. This positive impact on the environment can, in turn, attract environmentally conscious consumers and businesses, fostering a culture of sustainability. As a result, states with high pollution levels may witness a virtuous cycle of increased EV sales, improved air quality, and further environmental benefits.
In summary, environmental factors, particularly climate and pollution levels, significantly influence the availability and sales of electric vehicles in certain states. Manufacturers and marketers must consider these factors to cater to the specific needs and preferences of consumers in different regions. By understanding the unique environmental challenges and opportunities of each state, the EV industry can contribute to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly future.
Unleash Savings: Tax Incentives for Your Electric Vehicle Purchase
You may want to see also

Economic Considerations: Local market and subsidies affect EV distribution
The distribution of electric vehicles (EVs) across different states is significantly influenced by economic factors, particularly local market dynamics and government subsidies. These factors play a crucial role in determining which EV models are available in a particular region and why some states have a more diverse range of options compared to others.
One of the primary economic considerations is the local market demand and consumer preferences. States with a higher demand for EVs often attract more automotive manufacturers to invest in production and distribution. This is because the market potential for electric vehicles is a significant incentive for carmakers to establish a presence in those states. For instance, regions with a strong environmental consciousness and a growing trend towards sustainable transportation may see an influx of EV models tailored to meet these specific consumer needs. In contrast, states with lower demand might not have the same incentive for manufacturers to invest, leading to a limited selection of EVs.
Government subsidies and incentives also play a pivotal role in EV distribution. Many states offer financial incentives to encourage residents to purchase electric vehicles, which can include tax credits, rebates, or reduced registration fees. These subsidies can make EVs more affordable and attractive to consumers, thereby influencing the market share of different EV models. States with more aggressive and comprehensive subsidy programs are likely to see a wider variety of electric vehicles available to residents. For example, a state offering substantial incentives for EV purchases might attract manufacturers who want to tap into this market, resulting in a broader range of models being offered.
Additionally, the economic landscape of a state, including its overall wealth and purchasing power, can impact EV distribution. Wealthier states may have a more substantial market for luxury or high-end electric vehicles, which often command higher price points. In contrast, lower-income states might prioritize more affordable EV options. This economic disparity can lead to a concentration of certain EV brands in specific regions, catering to the financial capabilities of the local population.
In summary, the economic considerations of local market demand, consumer preferences, and government subsidies are key factors that determine the availability of electric vehicles in different states. These factors create a complex interplay that influences the distribution of EVs, ensuring that the right models are offered in the right places to meet the needs and preferences of local consumers. Understanding these economic dynamics is essential for both consumers and manufacturers in navigating the EV market across various regions.
Power Down: Strategies for When Your EV's Battery Fails
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The availability of EVs can be influenced by various factors, including government incentives, infrastructure development, and market demand. Some states have implemented policies and subsidies to encourage EV adoption, making it more attractive for manufacturers to offer their models in those regions. For example, California has been a leader in EV adoption due to its strict emissions standards and incentives, leading to the availability of a wide range of EVs in the state.
Yes, legal and regulatory frameworks play a significant role. States with more favorable regulations and policies related to EV sales, tax incentives, and charging infrastructure development may attract more EV manufacturers. These incentives can include tax credits, rebates, or grants, making it financially beneficial for carmakers to focus their efforts on these markets.
Market demand and consumer preferences are crucial factors. States with a higher demand for EVs and a well-informed consumer base that understands the benefits of electric mobility may encourage manufacturers to expand their offerings. Additionally, consumer behavior and purchasing power can influence the decision of carmakers to introduce specific EV models to cater to local preferences and needs.
Absolutely. Environmental considerations and regional climate can impact the choice of EVs. For instance, states with colder climates might prioritize EVs with advanced heating systems or those that offer longer driving ranges. Similarly, regions with a strong focus on sustainability and eco-friendly transportation may drive the demand for specific EV models, leading to their availability in those areas.







